【大数据 & AI】Flink Agents 源码解读 --- (3) --- Agent
【大数据 & AI】Flink Agents 源码解读 --- (3) --- Agent
0x00 概要
Agent是 Flink Agent 框架的核心概念,它是一个可执行单元,用于处理输入事件并生成输出事件。主要功能和特色如下:
- 事件驱动处理:基于事件驱动架构,响应不同类型的事件(如 InputEvent,ChatRequestEvent等),通过定义actions来处理特定事件类型。
- 资源管理:管理各种资源,如聊天模型、工具、提示词等。支持多种资源类型(CHAT_MOEL, TOOL, PROMPT等)。
- 可扩展性:支持自定义的actions和资源,可以通过继承Agent类来创建特定功能的Agent,如ReActAgent。
- 配置支持:支持通过配置选项自定义行为,提供统一的配置管理机制。
- 模块化设计:将功能分解为独立的Actions,每个action负责处理特定类型的事件。
- 资源抽象:通过 ResourceDescriptor 抽象资源定义,支持不同类型的资源(模型,工具,提示词等)
- 状态管理:提供短期内存管理机制,支持基于key的状态隔离。
- 多环境支持:支持本地执行环境用于调试,支持远程 Flink 环境用于生产。
0x01 核心抽象
1.1 Agent抽象
Agent 作为基类提供了:
- 资源管理(resources 字典)。
- Action 注册机制(actions 字典)。
- 统一的接口供执行环境使用。
class Agent(ABC):
"""Base class for defining agent logic.
Example:
Users have two ways to create an Agent
* Declare an Agent with decorators
::
class MyAgent(Agent):
@action(InputEvent)
@staticmethod
def my_action(event: Event, ctx: RunnerContext) -> None:
action logic
@chat_model_connection
@staticmethod
def my_connection() -> ResourceDescriptor:
return ResourceDescriptor(clazz=OllamaChatModelConnection,
model="qwen2:7b",
base_url="http://localhost:11434")
@chat_model_setup
@staticmethod
def my_chat_model() -> ResourceDescriptor:
return ResourceDescriptor(clazz=OllamaChatModel,
connection="my_connection")
* Add actions and resources to an Agent instance
::
my_agent = Agent()
my_agent.add_action(name="my_action",
events=[InputEvent],
func=action_function)
.add_resource(name="my_connection",
instance=ResourceDescriptor(
clazz=OllamaChatModelConnection,
arg1=xxx
)
.add_resource(
name="my_connection",
instance=ResourceDescriptor(
clazz=OllamaChatModelConnection,
arg1=xxx
)
)
.add_resource(
name="my_chat_model",
instance=ResourceDescriptor(
clazz=OllamaChatModelSetup,
connection="my_connection"
)
)
"""
_actions: Dict[str, Tuple[List[Type[Event]], Callable, Dict[str, Any]]]
_resources: Dict[ResourceType, Dict[str, Any]]
_mcp_servers: Dict[str, MCPServer]
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""Init method."""
self._actions = {}
self._resources = {}
for type in ResourceType:
self._resources[type] = {}
@property
def actions(self) -> Dict[str, Tuple[List[Type[Event]], Callable, Dict[str, Any]]]:
"""Get added actions."""
return self._actions
@property
def resources(self) -> Dict[ResourceType, Dict[str, Any]]:
"""Get added resources."""
return self._resources
def add_action(
self, name: str, events: List[Type[Event]], func: Callable, **config: Any
) -> "Agent":
"""Add action to agent.
Parameters
----------
name : str
The name of the action, should be unique in the same Agent.
events: List[Type[Event]]
The type of events listened by this action.
func: Callable
The function to be executed when receive listened events.
**config: Any
Key named arguments can be used by this action in runtime.
Returns:
-------
Agent
The modified Agent instance.
"""
if name in self._actions:
msg = f"Action {name} already defined"
raise ValueError(msg)
self._actions[name] = (events, func, config if config else None)
return self
def add_resource(
self, name: str, instance: SerializableResource | ResourceDescriptor
) -> "Agent":
"""Add resource to agent instance.
Parameters
----------
name : str
The name of the prompt, should be unique in the same Agent.
instance: SerializableResource | ResourceDescriptor
The serializable resource instance, or the descriptor of resource.
Returns:
-------
Agent
The agent to add the resource.
"""
if isinstance(instance, SerializableResource):
resource_type = instance.resource_type()
elif isinstance(instance, ResourceDescriptor):
resource_type = instance.clazz.resource_type()
else:
err_msg = f"Unexpected resource {instance}"
raise TypeError(err_msg)
if name in self._resources[resource_type]:
msg = f"{resource_type.value} {name} already defined"
raise ValueError(msg)
self._resources[resource_type][name] = instance
return self
1.2 Action 抽象
Action 提供了:
- 事件监听机制
- 与执行上下文的交互接口
- 统一的执行接口
通过装饰器或者add_action方法定义。
@action(InputEvent)
@staticmethod
def start_action(event: InputEvent, ctx: RunnerContext) -> None:
"""Start action to format user input and send chat request event."""
usr_input = event.input
1.3 资源抽象
资源抽象包括:模型连接(CHAT_MODEL_CONNECTION),工具,提示词,MCP服务器等。
class ResourceDescriptor:
"""Descriptor of resource, includes the class and the initialize arguments."""
_clazz: Type[Resource]
_arguments: Dict[str, Any]
def __init__(self, *, clazz: Type[Resource], **arguments: Any) -> None:
"""Init method."""
self._clazz = clazz
self._arguments = arguments
@property
def clazz(self) -> Type[Resource]:
"""Get the class of the resource."""
return self._clazz
@property
def arguments(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Get the initialize arguments of the resource."""
return self._arguments
1.4 执行环境抽象
执行上下文提供:
- 事件发送机制
- 资源访问接口
- 内存管理
- 配置访问
class RunnerContext(ABC):
"""Abstract base class providing context for agent execution.
This context provides access to event handling.
1.5 事件抽象
即 Event 体系,提供了:
- 统一的事件处理机制
- 类型安全的事件分发
- 可扩展的事件类型系统
class Event(BaseModel, ABC, extra="allow"):
"""Base class for all event types in the system. Event allow extra properties, but
these properties are required isinstance of BaseModel, or json serializable.
Attributes:
----------
id : UUID
Unique identifier for the event, automatically generated using uuid4.
"""
id: UUID = Field(default_factory=uuid4)
1.6 配置抽象
AgentConfiguration 提供了:
- 类型安全的配置选项
- 默认值管理
- 从文件加载配置的能力
class AgentConfiguration(BaseModel, Configuration):
"""Base class for config objects in the system.
Provides a flat dict interface to access nested config values.
"""
conf_data: Dict[str, Any]
def __init__(self, conf_data: Dict[str, Any] | None = None) -> None:
"""Initialize with optional configuration data."""
if conf_data is None:
super().__init__(conf_data = {})
else:
super().__init__(conf_data = conf_data)
0x02 Workflow Style Agent 和ReActAgent
有两种最普遍的Agents:
- Workflows 是由预定义的代码路径来编排 LLM 和工具的系统。
- Agents 则是 LLM 动态指导自身流程和工具使用的系统,它们掌控着自己完成任务的方式。
当需要处理更复杂任务时,Workflows 为定义明确的任务提供了可预测性和一致性(复现),而当需要大规模的灵活性和模型驱动的决策时,agents 则是更好的选择。
对应这两种Agent,Flink Agents 有两种不同的Agent:Workflow Style Agent 和ReActAgent。
- 在 Flink-Agents 中,工作流风格的代理(workflow-style agent)把推理与行为组织成一条由“动作(action)”构成的有向工作流,动作之间通过事件连接。这种设计借鉴了复杂多阶段任务的编排需求,希望以透明、可扩展且以数据为中心的方式利用 Apache Flink 的流式架构来完成工作。Workflow 适合任务是可以被清除的解构成固定的子任务单元。Workflow 相对于 Agent 有个天然的优势就是高效率,且效果非常稳定,执行基本都能在预期范围内,不可预知或者说未知性很低。缺点自然就是不够灵活了,面对一些开放的或者无法预定义的任务就无法处理了。
- ReAct(Reasoning and Acting)Agent 是一种通用范式,把推理与行动能力结合起来解决复杂任务。借助该范式,用户只需在提示词里指定目标并提供可用工具,大模型便会自主决定如何达成目标并执行相应动作。ReAct通过模拟人类的“Reasoning-Acting”模式,使LLM能够动态地决定数据需求 。其核心是一个循环:思考(Thought): LLM首先进行内部推理。它分析当前任务和已有信息,判断是否缺少完成任务所需的知识,并制定下一步的行动计划。在这个循环中,数据流是根据LLM的“思考”结果动态生成的。当LLM判断需要外部数据时,它会主动触发一个“行动”来获取数据,然后将获取到的“观察”数据整合进自己的上下文中,用于下一步的决策。
2.1 特性
两种Agent的详细梳理如下:
2.1.1 设计理念
Workflow Style Agent
- 可定制框架:灵活的框架,允许用户定义自己的代理逻辑
- 事件驱动架构:逻辑被组织为由事件连接的动作有向图
- 模块化设计:用户通过定义单个动作及其交互来组合代理
ReActAgent
- 预构建代理:基于 ReAct(推理+行动)范式的内置、即用型代理实现
- 以 LLM 为中心:专门为 LLM 做出采取何种行动的决策而设计
- 标准化工作流:遵循固定的“思维→行动→观察”循环模式
2.1.2 控制流
Workflow Style Agent
- 显式流程:用户明确定义事件如何触发动作
- 事件路由:动作由特定的事件类型触发
- 灵活模式:可以实现各种模式,如顺序、分支或循环工作流
ReActAgent
- 隐式流程:决策过程在内部由 LLM 处理
- 工具调用:使用 LLM 的原生函数调用功能来确定操作
- 固定模式:遵循标准的 ReAct 模式(思考→行动→观察)
2.1.3 定制级别
Workflow Style Agent
- 高度可定制:对代理逻辑、动作和事件流拥有完全控制权
- 自定义动作:用户定义所有动作及其行为
- 灵活事件:用户可以定义自定义事件类型和处理逻辑
ReActAgent
- 有限定制:定制主要通过提示词、模型和输出模式实现
- 预定义动作:使用内置动作如 start_action 和 stop_action
- 标准接口:为类似的 LLM 任务提供一致的接口
2.1.4 使用场景
Workflow Style Agent
- 具有固定序列或条件分支的多步骤流程
- 需要精确控制代理行为的场景
- 在预定顺序中与多个外部系统集成
ReActAgent
- 需要 LLM 推理使用哪些工具/操作的任务
- 带工具使用的标准问答
- LLM 应该动态决定工作流程的场景
只要“问题不可完全穷举、要跨多系统查证、并且需要在对话中澄清/协商/决策”,就更应该用ReActAgent,而不是纯 Workflow。
2.1.5 开发复杂度
Workflow Style Agent
- 更高灵活性:需要更多代码但控制力更强
- 自定义逻辑:需要实现所有动作逻辑
- 无主见:开发人员控制代理行为的所有方面
ReActAgent
- 较低门槛:更容易上手,具有预定义功能
- 代码量少:设置所需的代码最少
- 有主见:代表开发人员做出许多决策
2.1.6 总结
ReActAgent 为标准的基于 LLM 的推理任务提供了现成的解决方案,而 Workflow Style Agent 为复杂的自定义代理实现提供了最大的灵活性。
有人戏称:拉投资用 Agent 讲故事,做业务踏踏实实用 Workflow 。这句玩笑背后折射出现实的考量:Workflow 胜在确定性,而 Agent 胜在上限。
2.2 workflow
官方的快速入门(docs\content\docs\get-started\quickstart\workflow_agent.md)通过两个渐进式流式示例,展示如何用 Flink Agents 构建由大模型驱动的流水线:
- 评论分析:示例一 会持续接收商品评论流,并用单个代理从每条评论中提取评分(1-5)以及不满意原因。
- 产品改进建议:在示例一的基础上,按窗口聚合每条评论的分析结果,生成商品级别的汇总(评分分布、常见抱怨),再调用第二个代理为每件商品输出具体的改进建议。
两个示例合在一起,演示了如何用 Flink Agents 构建多代理工作流,并直接在 Flink 独立集群上运行。
2.2.1 代码导读
准备代理执行环境
创建 Agents 执行环境,注册可供代理使用的聊天模型连接。
// Set up the Flink streaming environment and the Agents execution environment.
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
AgentsExecutionEnvironment agentsEnv =
AgentsExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(env);
// Add Ollama chat model connection to be used by the ReviewAnalysisAgent.
agentsEnv.addResource(
"ollamaChatModelConnection",
ResourceType.CHAT_MODEL_CONNECTION,
CustomTypesAndResources.OLLAMA_SERVER_DESCRIPTOR);
创建代理
以 ReviewAnalysisAgent 为例,展示如何定义提示词、工具、聊天模型和动作;以及如何处理聊天响应并发送输出事件。更多细节请参考 [工作流代理] 文档。ProductSuggestionAgent 的代码与之类似。
/**
* An agent that uses a large language model (LLM) to analyze product reviews and generate a
* satisfaction score and potential reasons for dissatisfaction.
*
* <p>This agent receives a product review and produces a satisfaction score and a list of reasons
* for dissatisfaction. It handles prompt construction, LLM interaction, and output parsing.
*/
public class ReviewAnalysisAgent extends Agent {
private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();
@Prompt
public static org.apache.flink.agents.api.prompt.Prompt reviewAnalysisPrompt() {
return REVIEW_ANALYSIS_PROMPT;
}
@ChatModelSetup
public static ResourceDescriptor reviewAnalysisModel() {
return ResourceDescriptor.Builder.newBuilder(OllamaChatModelSetup.class.getName())
.addInitialArgument("connection", "ollamaChatModelConnection")
.addInitialArgument("model", "qwen3:8b")
.addInitialArgument("prompt", "reviewAnalysisPrompt")
.addInitialArgument("tools", Collections.singletonList("notifyShippingManager"))
.addInitialArgument("extract_reasoning", "true")
.build();
}
/**
* Tool for notifying the shipping manager when product received a negative review due to
* shipping damage.
*
* @param id The id of the product that received a negative review due to shipping damage
* @param review The negative review content
*/
@Tool(
description =
"Notify the shipping manager when product received a negative review due to shipping damage.")
public static void notifyShippingManager(
@ToolParam(name = "id") String id, @ToolParam(name = "review") String review) {
CustomTypesAndResources.notifyShippingManager(id, review);
}
/** Process input event and send chat request for review analysis. */
@Action(listenEvents = {InputEvent.class})
public static void processInput(InputEvent event, RunnerContext ctx) throws Exception {
String input = (String) event.getInput();
MAPPER.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
CustomTypesAndResources.ProductReview inputObj =
MAPPER.readValue(input, CustomTypesAndResources.ProductReview.class);
ctx.getShortTermMemory().set("id", inputObj.getId());
String content =
String.format(
"{\n" + "\"id\": %s,\n" + "\"review\": \"%s\"\n" + "}",
inputObj.getId(), inputObj.getReview());
ChatMessage msg = new ChatMessage(MessageRole.USER, "", Map.of("input", content));
ctx.sendEvent(new ChatRequestEvent("reviewAnalysisModel", List.of(msg)));
}
@Action(listenEvents = ChatResponseEvent.class)
public static void processChatResponse(ChatResponseEvent event, RunnerContext ctx)
throws Exception {
JsonNode jsonNode = MAPPER.readTree(event.getResponse().getContent());
JsonNode scoreNode = jsonNode.findValue("score");
JsonNode reasonsNode = jsonNode.findValue("reasons");
if (scoreNode == null || reasonsNode == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Invalid response from LLM: missing 'score' or 'reasons' field.");
}
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (reasonsNode.isArray()) {
for (JsonNode node : reasonsNode) {
result.add(node.asText());
}
}
ctx.sendEvent(
new OutputEvent(
new CustomTypesAndResources.ProductReviewAnalysisRes(
ctx.getShortTermMemory().get("id").getValue().toString(),
scoreNode.asInt(),
result)));
}
}
与 Flink 集成
读取文本文件中的商品评论流作为输入 DataStream,用 ReviewAnalysisAgent 分析并生成结果 DataStream,最后打印输出。
// Read product reviews from input_data.txt file as a streaming source.
// Each element represents a ProductReview.
DataStream<String> productReviewStream =
env.fromSource(
FileSource.forRecordStreamFormat(
new TextLineInputFormat(),
new Path(inputDataFile.getAbsolutePath()))
.build(),
WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(),
"streaming-agent-example");
// Use the ReviewAnalysisAgent to analyze each product review.
DataStream<Object> reviewAnalysisResStream =
agentsEnv
.fromDataStream(productReviewStream)
.apply(new ReviewAnalysisAgent())
.toDataStream();
// Print the analysis results to stdout.
reviewAnalysisResStream.print();
// Execute the Flink pipeline.
agentsEnv.execute();
2.3 ReAct Agent
本快速入门用一个迷你示例演示如何用 Flink Agents 构建流式 ReAct Agent:
评论分析 代理持续消费商品评论流,用单个代理提取评分(1-5)以及不满意原因;若评论涉及物流不满,则自动通知物流经理。
2.3.1 代码导读
准备代理执行环境
创建 Agents 执行环境,注册可用的聊天模型连接与工具。
# Set up the Flink streaming environment and the Agents execution environment.
env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment()
agents_env = AgentsExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment(env)
# Add Ollama chat model connection and notify shipping manager tool to be used
# by the Agent.
agents_env.add_resource(
"ollama_server",
ResourceDescriptor(clazz=OllamaChatModelConnection, request_timeout=120),
).add_resource(
"notify_shipping_manager", Tool.from_callable(notify_shipping_manager)
)
创建 ReAct Agent
实例化 ReAct Agent,配置聊天模型、提示词以及结果的输出模式。
review_analysis_react_agent = ReActAgent(
chat_model=ResourceDescriptor(
clazz=OllamaChatModelSetup,
connection="ollama_server",
model="qwen3:8b",
tools=["notify_shipping_manager"],
),
prompt=review_analysis_react_prompt,
output_schema=ProductReviewAnalysisRes,
)
与 Flink 集成
读取商品评论文本文件生成 Source DataStream,用 ReAct Agent 分析并生成结果 DataStream,最后打印输出。
# Read product reviews from a text file as a streaming source.
# Each line in the file should be a JSON string representing a ProductReview.
product_review_stream = env.from_source(
source=FileSource.for_record_stream_format(
StreamFormat.text_line_format(),
f"file:///{current_dir}/resources/",
)
.monitor_continuously(Duration.of_minutes(1))
.build(),
watermark_strategy=WatermarkStrategy.no_watermarks(),
source_name="streaming_agent_example",
).map(
lambda x: ProductReview.model_validate_json(
x
) # Deserialize JSON to ProductReview.
)
# Use the ReAct agent to analyze each product review and notify the shipping manager
# when needed.
review_analysis_res_stream = (
agents_env.from_datastream(
input=product_review_stream, key_selector=lambda x: x.id
)
.apply(review_analysis_react_agent)
.to_datastream()
)
# Print the analysis results to stdout.
review_analysis_res_stream.print()
0x03 ReActAgent
ReActAgent 是 Agent 抽象的一个具体实现,展示了这些抽象如何协同工作。
- 资源管理:管理聊天模型和提示词资源
- Action定义:定义 start_action 和 stop_action 处理输入和输出
- 事件处理:响应 InputEvent 和 ChatResponseEvent
- 配置管理:支持错误处理策略配置
- 输出格式化:支持基于 schema 的输出验证和格式化
这种抽象设计使得 Agent 系统具有高度的灵活性和可扩展性,开发者可以通过组合不同的资源、actions和配置来构建满足特定需求的Agent。
3.1 定义
ReActAgent 的定义如下。
class ReActAgent(Agent):
"""Built-in implementation of ReAct agent which is based on the function
call ability of llm.
This implementation is not based on the foundational ReAct paper which uses
prompt to force llm output contain <Thought>, <Action> and <Observation> and
extract tool calls by text parsing. For a more robust and feature-rich
implementation we use the tool/function call ability of current llm, and get
the tool calls from response directly.
Example:
::
class OutputData(BaseModel):
result: int
env = AgentsExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment()
# register resource to execution environment
(
env.add_resource(
"ollama",
ResourceDescriptor(clazz=OllamaChatModelConnection, model=model),
)
.add_resource("add", add)
.add_resource("multiply", multiply)
)
# prepare prompt
prompt = Prompt.from_messages(
messages=[
ChatMessage(
role=MessageRole.SYSTEM,
content='An example of output is {"result": 30.32}.',
),
ChatMessage(
role=MessageRole.USER, content="What is ({a} + {b}) * {c}"
),
],
)
# create ReAct agent.
agent = ReActAgent(
chat_model=ResourceDescriptor(
clazz=OllamaChatModelSetup,
connection="ollama_server",
tools=["notify_shipping_manager"],
),
prompt=prompt,
output_schema=OutputData,
)
"""
def __init__(
self,
*,
chat_model: ResourceDescriptor,
prompt: Prompt | None = None,
output_schema: type[BaseModel] | RowTypeInfo | None = None,
) -> None:
"""Init method of ReActAgent.
Parameters
----------
chat_model : ResourceDescriptor
The descriptor of the chat model used in this ReAct agent.
prompt : Optional[Prompt] = None
Prompt to instruct the llm, could include input and output example,
task and so on.
output_schema : Optional[Union[type[BaseModel], RowTypeInfo]] = None
The schema should be RowTypeInfo or subclass of BaseModel. When user
provide output schema, ReAct agent will add system prompt to instruct
response format of llm, and add output parser according to the schema.
"""
super().__init__()
self.add_resource(_DEFAULT_CHAT_MODEL, chat_model)
if output_schema:
if isinstance(output_schema, type) and issubclass(output_schema, BaseModel):
json_schema = output_schema.model_json_schema()
elif isinstance(output_schema, RowTypeInfo):
json_schema = str(output_schema)
else:
err_msg = f"Output schema {output_schema.__class__} is not supported."
raise TypeError(err_msg)
schema_prompt = f"The final response should be json format, and match the schema {json_schema}."
self._resources[ResourceType.PROMPT][_DEFAULT_SCHEMA_PROMPT] = (
Prompt.from_text(text=schema_prompt)
)
if prompt:
self._resources[ResourceType.PROMPT][_DEFAULT_USER_PROMPT] = prompt
self.add_action(
name="stop_action",
events=[ChatResponseEvent],
func=self.stop_action,
output_schema=OutputSchema(output_schema=output_schema),
)
3.2 深度定制
Flink 对 ReActAgent 做了深度定制,使其能在分布式流处理环境中高效执行,并提供了丰富的功能来简化 LLM 应用开发。
3.2.1 ReActAgent 特色
流式处理适配
Flink 将传统的 ReAct 模式适配到了流处理环境中:
- 通过 InputEvent 和 OutputEvent 包装输入输出数据
- 利用 Flink 的事件驱动架构实现异步处理
- 通过 RunnerContext 管理状态和资源
agents_env = AgentsExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment(env)
agents_env.fromDataStream(dataStream) # 从DataStream输入
agents_env.fromTable(table) # 从Table输入
agents_env.fromList(list) # 从List输入
review_analysis_res_stream = (
agents_env.from_datastream( # 从DataSteam创建Agent流程
input=product_review_stream, key_selector=lambda x: x.id
)
.apply(review_analysis_react_agent) # 应用Agent
.to_datastream() # 转换回Stream
)
特定的行为模式
ReActAgent 实现了特定的 ReAct(Reasoning + Action)范式,这是一种结合推理和行动的 AI Agent 模式。它内置了两个核心动作:start_action()和 stop_action()。使用预定义的流程来处理输入并生成输出,而非让用户完全自定义行为逻辑。
- start_action 接收输入并发送 ChatRequestEvent
- stop_action 处理 ChatResponseEvent 并产生最终输出
键控状态支持
支持Flink的键控状态特性
review_analysis_res_stream = (
agents_env.from_datastream(
input=product_review_stream, key_selector=lambda x: x.id
)
.apply(review_analysis_react_agent)
.to_datastream()
)
LLM 集成优化
ReActAgent 专门为 LLM 交互进行优化:内置了提示词管理和格式化功能;支持结构化输出模式,可以指定输出的数据schema;集成了错误处理策略,当LLM输出不符合预期格式时可以选择失败或者忽略。
资源管理方式
ReActAgent 中自动添加默认资源,相比普通的Agent,ReActAgent 会自动为用户设置好必要的资源,简化使用流程。通过统一的资源管理系统与Flink集成。ReActAgent 通过 _DEFAULT_CHAT_MODEL 等常量引用在 AgentsExecutionEnvironment 中注册的资源。
agents_env.add_resource(_DEFAULT_CHAT_MODEL, chat_model)
agents_env.addResource("ollama_server", ResourceDescriptor(...))
agents_env.addResource("notify_shipping_manager", Tool.from_callable(...))
类型信息处理
Flink Agent能够处理Flink的类型系统
if (outputSchema != null) {
String jsonSchema;
// 支持RowTypeInfo和POJO类型
if (outputSchema instanceof RowTypeInfo) {
// 处理Row类型
jsonSchema = outputSchema.toString();
outputSchema = new OutputSchema((RowTypeInfo) outputSchema);
} else if (outputSchema instanceof Class) {
// 处理POJO类型
try {
jsonSchema = mapper.generateJsonSchema((Class<?>) outputSchema).toString();
} catch (JsonMappingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
错误处理机制
Flink 为 ReActAgent 实现了灵活的处理处理策略,运行用户选择在解析失败时抛出异常还是忽略错误。
except Exception:
if error_handling_strategy == ErrorHandlingStrategy.IGNORE:
logging.warning(
f"The response of llm {output} doesn't match schema constraint, ignoring."
)
return
elif error_handling_strategy == ErrorHandlingStrategy.FAIL:
raise
结构化输出支持
Flink 为 ReActAgent 添加了结构化输出的能力,这样可以让 LLM 的输出符合预定义的数据结构,便于后续管理。
if output_schema:
if isinstance(output_schema, type) and issubclass(output_schema, BaseModel):
json_schema = output_schema.model_json_schema()
elif isinstance(output_schema, RowTypeInfo):
json_schema = str(output_schema)
else:
err_msg = f"Output schema {output_schema.__class__} is not supported."
raise TypeError(err_msg)
schema_prompt = f"The final response should be json format, and match the schema {json_schema}."
self._resources[ResourceType.PROMPT][_DEFAULT_SCHEMA_PROMPT] = (
Prompt.from_text(text=schema_prompt)
)
提示词模板系统
Flink 实现了一个完整的提示词模板管理系统:
- 支持字符串模板和消息列表模型
- 提供格式化功能,可以动态替换模板中的占位符
- 自动处理不同类型输入的转换
工具调用集成
Flink 将工具调用集成到 ReActAgent中。
# 注册工具资源
# Add Ollama chat model connection and notify shipping manager tool to be used
# by the Agent.
agents_env.add_resource(
"ollama_server",
ResourceDescriptor(clazz=OllamaChatModelConnection, request_timeout=120),
).add_resource(
"notify_shipping_manager", Tool.from_callable(notify_shipping_manager)
)
# 在Agent 中使用工具
# Create react agent
review_analysis_react_agent = ReActAgent(
chat_model=ResourceDescriptor(
clazz=OllamaChatModelSetup,
connection="ollama_server",
model="qwen3:8b",
tools=["notify_shipping_manager"],
),
prompt=review_analysis_react_prompt,
output_schema=ProductReviewAnalysisRes,
)
运行时协作
- 执行环境负责调度和运行Agent中的各个组件
- Agent通过RunnerContext 访问在环境中注册的资源
- 整个过程采用事件驱动的方式,通过发送和接收事件来推进执行流程
3.3 典型执行流程
对于 ReActAgent 来说,具体适配流程如下:
- 环境初始化:通过 AgentsExecutionEnvironment.get_execution_environment(env) 获取适当的执行环境
- 资源配置:使用 addResource() 添加模型、工具等资源
- 输入设置:通过fromDataStream()、 fromTable()等设置输入源
- Agent应用:使用 apply()方法应用Agent 逻辑
- 输出获取:通过 toDataStream() 获取处理后的 DataStream
- 执行:通过execute() 触发Flink作业执行
典型的执行流程如下:
- run 函数接收到输入数据
- 创建InputEvent 并发送到事件队列
- start_action处理InputEvent,格式化输入并发送 ChatRequestEvent
- LLM处理后产生 ChatResponseEvent
- stop_action 处理 ChatResponseEvent,解析结果并发送 OutputEvent
- run 函数收集 OutputEvent 并返回结果
关键特点是:
- 事件驱动:使用事件队列驱动整个执行流程
- 上下文隔离:每个键值对应独立的执行上下文
- 异步支持:虽然本地执行环境回退到同步执行,但仍然支持异步接口
- 状态管理:通过 LocalRunnerContext 管理短期记忆和资源配置
3.4 start_action 与 stop_action
整体流程特色
这两个 action 构成完整的 ReAct 模式:
- 开始-结束模式:start_action 作为入口,将原始输入转化为适合 LLM 处理的格式;stop_action 作为出口,将 LLM 响应转换为结构化输出。
- 中间处理透明化:用户无需关心中间步骤(如工具调用、上下文检索等),这些由内置的 CHAT_MODEL_ACTION、TOOL_CALL_ACTION 等自动处理。
- 可配置性:支持自定义 Prompt、输出 schema 定义及错误处理策略。
功能
ReActAgent 的 start_action 与 stop_action 各具特征,二者分别承担对话的发起与终结职责。
- start_action 负责输入事件的处理。它首先接收 InputEvent,作为整个 Agent 流程的起点,可接受原始类型、复杂对象或 Row 等多种数据。若提供 Prompt,则以此格式化用户输入,将简单字符串或复杂对象(如 Row 或 POJO)的属性自动提取并填入模板。随后,系统自动追加 schema prompt,约束大模型输出结构,再将整理后的内容封装为 ChatRequestEvent,触发后续处理,默认调用 _DEFAULT_CHAT_MODEL 完成首次生成。
- stop_action 则处理输出事件。它以 ChatResponseEvent 为输入,标志大模型生成完毕,是整个流程的终点。该动作支持按 schema 解析与验证返回结果,可将 JSON 文本转换为 Pydantic 模型或 RowTypeInfo 指定结构,并提供错误处理策略(忽略或抛出异常),保证输出类型安全与业务一致性。
与其他组件的协作
在 ReActAgent 初始化时注册这两个 action:
self.add_action(
name="stop_action",
events=[ChatResponseEvent],
func=self.stop_action,
output_schema=OutputSchema(output_schema=output_schema),
)
这两个 action 与 Agent 内置的其他 action(如工具调用、上下文检索)配合工作,在 ActionExecutionOperator 中形成一个完整的事件驱动处理链。
3.5 输入输出
Flink Agent 的输入输出具有以下几个显著特点,并通过特定机制与Flink进行适配。
3.5.1 事件驱动架构
Flink Agent 基于事件驱动模型,输入和输出都是通过事件对象进行传递:
- 输入:通过InputEvent 封装原始数据
- 输出:通过OutputEvent封装处理结果
- 中间事件:包括 ChatRequestEvent、ChatResponseEvent、ToolRequestEvent、ToolResponseEvent等
3.5.2 统一的数据封装
所有数据都被封装成事件对象,便于Agent内部流转和处理。
3.5.3 支持多种数据类型
输入支持多种数据类型:
- 基本数据类型
- Flink Row对象
- POJO对象
- 复杂嵌套结果
输出同样支持灵活的数据结构,可以通过schema进行约束
3.5.4 内置模板支持
通过Prompt类支持模板化输入处理,可以定义复杂的提示词模板
3.6 模板系统
模板可以用在提示词和Schema。Flink Agent 中的模板系统主要在 Prompt 类中实现,支持两种类型的模板:
3.6.1 字符串模板
最基本的模板形式,就是一个包含占位符的字符串:
String specialTemplate = "Handle special chars: {text} with symbols like @#$%^&*()";
Prompt specialPrompt = new Prompt(specialTemplate);
Map<String, String> specialVars = new HashMap<>();
specialVars.put("text", "Hello & Welcome!");
String result = specialPrompt.formatString(specialVars);
3.6.2 消息模板
更复杂的模板形式,包含多个 ChatMessage 对象,可以指定不同的角色。
List<ChatMessage> multipleMessages =
Arrays.asList(
new ChatMessage(MessageRole.SYSTEM, "You are a helpful assistant."),
new ChatMessage(MessageRole.USER, "First message"),
new ChatMessage(MessageRole.ASSISTANT, "I understand"),
new ChatMessage(
MessageRole.USER, "Second message - this should be the response"));
Prompt multiPrompt = new Prompt(multipleMessages);
模板的管理流程如下:
- 模板创建:用户创建 Prompt 对象,可以是字符串或消息列表。
- 变量替换:使用 formatString() 或者 formatMessages() 方法对传入变量映射进行替换
- LLM 调用:格式化的消息被发送给LLM进行处理。
class Prompt(SerializableResource, ABC):
"""Base prompt abstract."""
@staticmethod
def from_messages(messages: Sequence[ChatMessage]) -> "Prompt":
"""Create prompt from sequence of ChatMessage."""
return LocalPrompt(template=messages)
@staticmethod
def from_text(text: str) -> "Prompt":
"""Create prompt from text string."""
return LocalPrompt(template=text)
@abstractmethod
def format_string(self, **kwargs: str) -> str:
"""Generate text string from template with additional arguments."""
@abstractmethod
def format_messages(
self, role: MessageRole = MessageRole.SYSTEM, **kwargs: str
) -> List[ChatMessage]:
"""Generate list of ChatMessage from template with additional arguments."""
@classmethod
@override
def resource_type(cls) -> ResourceType:
"""Get the resource type."""
return ResourceType.PROMPT
class LocalPrompt(Prompt):
"""Prompt for a language model.
Attributes:
----------
template : Union[Sequence[ChatMessage], str]
The prompt template.
"""
template: Sequence[ChatMessage] | str
def format_string(self, **kwargs: str) -> str:
"""Generate text string from template with input arguments."""
if isinstance(self.template, str):
return format_string(self.template, **kwargs)
else:
msgs = []
for m in self.template:
msg = f"{m.role.value}: {format_string(m.content, **kwargs)}"
if m.extra_args is not None and len(m.extra_args) > 0:
msg += f"{m.extra_args}"
msgs.append(msg)
return "\n".join(msgs)
def format_messages(
self, role: MessageRole = MessageRole.SYSTEM, **kwargs: str
) -> List[ChatMessage]:
"""Generate list of ChatMessage from template with input arguments."""
if isinstance(self.template, str):
return [
ChatMessage(role=role, content=format_string(self.template, **kwargs))
]
else:
msgs = []
for m in self.template:
msg = ChatMessage(
role=m.role, content=format_string(m.content, **kwargs)
)
msgs.append(msg)
return msgs
3.7 FunctionTool 与 Action 的关联及注册机制
在 Flink Agents 框架中,function tool 与 action 的联系和注册涉及多个组件和步骤。
3.7.1 实际转换流程
具体的工具到 prompt 的转换过程如下:
- 工具通过 @Tool 或 @tool 注册到执行环境中
- 在创建 ResourceDescriptor 时,通过 tools 参数引用这些已注册的工具
- 当聊天模型 setup 类(如 OllamaChatModelSetup)初始化时,它会获取这些工具的元数据(包括名称和描述)
- 这些工具信息会被自动整合到发送给 LLM 的系统 prompt 中,告知 LLM 有哪些可用工具及其用途
这种方式使得开发者只需关注工具的定义和注册,而无需手动编写工具描述到 prompt 中,提高了开发效率并减少了出错可能性。
Function Tool 注册到 Agent
Function tool 首先通过以下几种方式注册到执行环境中:
方式一:使用装饰器
@tool
@staticmethod
def notify_shipping_manager(id: str, review: str) -> None:
"""Notify the shipping manager when product received a negative review due to
shipping damage.
Parameters
----------
id : str
The id of the product that received a negative review due to shipping damage
review: str
The negative review content
"""
# reuse the declared function, but for parsing the tool metadata, we write doc
# string here again.
notify_shipping_manager(id=id, review=review)
方式二:使用 add_resource 方法
即,在执行环境注册工具资源。
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Calculate the sum of a and b.
Parameters
----------
a : int
The first operand
b : int
The second operand
Returns:
-------
int:
The sum of a and b
"""
return a + b
env.add_resource("add", ResourceType.TOOL, add)
方式三:在 Agent 构造函数中添加
class MyAgent(Agent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.add_resource("add", add) # 添加到 TOOL 类型资源中
方式四:在 ReActAgent 构建时候传入
即,通过 tools 参数指定。
// Create ReAct agent.
private static ReActAgent getReActAgent() {
return new ReActAgent(
ResourceDescriptor.Builder.newBuilder(OllamaChatModelSetup.class.getName())
.addInitialArgument("connection", "ollamaChatModelConnection")
.addInitialArgument("model", "qwen3:8b")
.addInitialArgument(
"tools", Collections.singletonList("notifyShippingManager"))
.build(),
reviewAnalysisReactPrompt(),
CustomTypesAndResources.ProductReviewAnalysisRes.class);
}
与模型交互
Chat Model Setup 中引用工具
在创建 Chat Model Setup 时,通过 tools 参数指定要使用的工具列表:
chat_model_descriptor = ResourceDescriptor(
clazz=OllamaChatModelSetup,
connection="my_ollama_connection",
model="qwen3:8b",
tools=["notify_shipping_manager"] # 引用已注册的工具
)
3.7.2 AgentPlan 编译过程中工具的处理
Flink Agents 内置了一个 TOOL_CALL_ACTION,,专门用于调用工具。TOOL_CALL_ACTION 与用户定义工具函数的联系主要依赖于:
- 统一的命名系统:工具函数的名称作为唯一标识符
- 资源管理机制:通过 RunnerContext.get_resource() 方法按名称检索工具
- 标准化接口:所有工具都实现相同的 call() 接口
- 事件驱动架构:通过 ToolRequestEvent 和 ToolResponseEvent 传递调用信息
这种设计使得系统可以在运行时动态地将 LLM 的工具调用请求路由到正确的用户定义函数,而无需硬编码具体的函数引用。
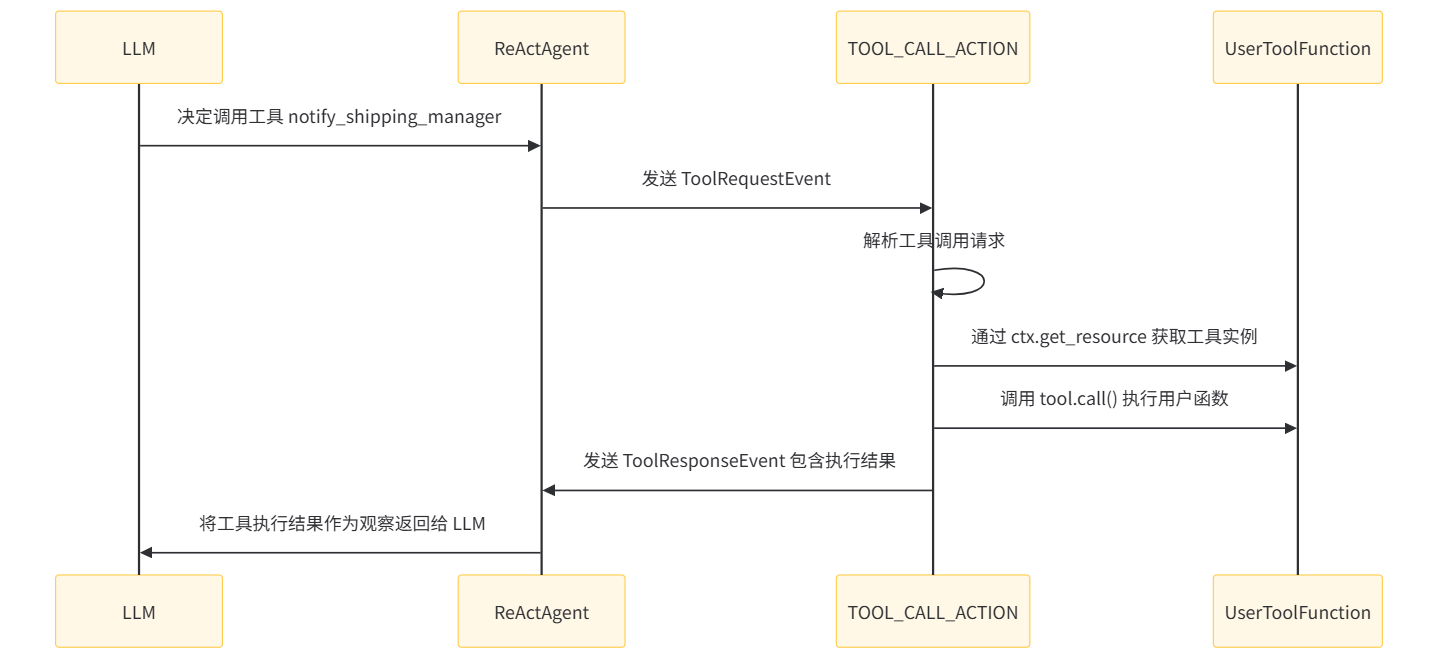
用户定义的 Function Tool 转换为 Action
当 Agent 被编译成 AgentPlan 时,系统会收集所有资源(包括工具) ,这些工具会被转换为可执行的 Action:
- 在 _get_resource_providers 函数中,识别带有 _is_tool 属性的资源
- 使用 from_callable 将函数转换为工具对象
- 工具被包装为 ResourceProvider 并存储在 AgentPlan 中,即通过 PythonSerializableResourceProvider 包装工具资源
内置 Tool Call Action
框架提供了一个内置的 TOOL_CALL_ACTION,专门用于调用工具:
TOOL_CALL_ACTION = Action(
name="tool_call_action",
exec=PythonFunction.from_callable(process_tool_request),
listen_event_types=[f"{ToolRequestEvent.__module__}.{ToolRequestEvent.__name__}"],
)
对应Action 为ToolCallAction,其中 processToolRequest 函数会与用户自定义的工具函数相互关联。具体联系机制如下:
- 命名匹配:当 LLM 决定调用某个工具时,它会在 tool_call 中指定工具名称(如 "notify_shipping_manager")
- 资源查找:TOOL_CALL_ACTION 使用这个名称通过 ctx.get_resource(name, ResourceType.TOOL) 查找已注册的工具
- 动态调用:找到工具后,通过 tool.call(**kwargs) 调用用户定义的实际函数
public class ToolCallAction {
public static Action getToolCallAction() throws Exception {
return new Action(
"tool_call_action",
new JavaFunction(
ToolCallAction.class,
"processToolRequest",
new Class[] {ToolRequestEvent.class, RunnerContext.class}),
List.of(ToolRequestEvent.class.getName()));
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void processToolRequest(ToolRequestEvent event, RunnerContext ctx) {
Map<String, Boolean> success = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, String> error = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, ToolResponse> responses = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, String> externalIds = new HashMap<>();
for (Map<String, Object> toolCall : event.getToolCalls()) {
String id = String.valueOf(toolCall.get("id"));
Map<String, Object> function = (Map<String, Object>) toolCall.get("function");
String name = (String) function.get("name");// 获取工具名称
Map<String, Object> arguments = (Map<String, Object>) function.get("arguments"); // 获取工具参数
if (toolCall.containsKey("original_id")) {
externalIds.put(id, (String) toolCall.get("original_id"));
}
Tool tool = null;
try {
// 从上下文获取对应名称的工具资源
tool = (Tool) ctx.getResource(name, ResourceType.TOOL);
} catch (Exception e) {
success.put(id, false);
responses.put(
id, ToolResponse.error(String.format("Tool %s does not exist.", name)));
error.put(id, e.getMessage());
}
if (tool != null) {
try {
// 调用用户实际工具
ToolResponse response = tool.call(new ToolParameters(arguments));
success.put(id, true);
responses.put(id, response);
} catch (Exception e) {
success.put(id, false);
responses.put(
id, ToolResponse.error(String.format("Tool %s execute failed.", name)));
error.put(id, e.getMessage());
}
}
}
// 返回工具响应事件
ctx.sendEvent(new ToolResponseEvent(event.getId(), responses, success, error, externalIds));
}
}
这个 action 监听 ToolRequestEvent 事件,并执行工具调用。调用完成后,将结果通过 ToolReponseEvent 返回。
"tool_call_action": {
"name": "tool_call_action",
"exec": {
"func_type": "PythonFunction",
"module": "flink_agents.plan.actions.tool_call_action",
"qualname": "process_tool_request"
},
"listen_event_types": [
"flink_agents.api.events.tool_event.ToolRequestEvent"
]
}
TOOL_CALL_ACTION 如何编译到AgentPlan
-
在 AgentPlan.from_agent 方法中:
- 当创建 AgentPlan 时,会收集所有动作,包括用户定义的动作和内置动作
- 代码中明确包含了内置动作:
BUILT_IN_ACTIONS = [CHAT_MODEL_ACTION, TOOL_CALL_ACTION, CONTEXT_RETRIEVAL_ACTION] - 在 _get_actions(agent) 函数中,这些内置动作会被添加到动作列表中
-
具体编译过程:
- AgentPlan.from_agent() 方法调用 _get_actions(agent) 获取所有动作
- _get_actions() 函数不仅提取用户定义的动作,还会包含 BUILT_IN_ACTIONS
- 这些动作随后被编译进 AgentPlan 的 actions 和 actions_by_event 字段中
-
在最终的 AgentPlan 中:
- TOOL_CALL_ACTION 会作为一个普通的动作存在于 actions 映射中
- 它会监听 ToolRequestEvent 事件类型,并在该事件发生时被触发执行
因此,TOOL_CALL_ACTION 确实会被编译到 AgentPlan 中,作为处理工具调用的标准机制。当 LLM 决定调用工具时,会发出 ToolRequestEvent,然后 TOOL_CALL_ACTION 就会被触发来实际执行相应的工具调用。
3.7.3 工具调用流程
整个流程中,工具不是直接绑定到 ActionExecutionOperator,而是通过 AgentPlan 中的资源提供者机制,在需要时动态获取和实例化。这种设计实现了工具与操作符的松耦合,同时支持多种类型的工具(Java、Python 等)。
- LLM 决定调用某个工具
- TOOL_CALL_ACTION 内置动作被触发
- 通过 RunnerContext 获取对应工具资源
- RunnerContextImpl.get_resource() 方法根据名称和类型查找工具资源
- 工具实际在需要时才通过 ResourceProvider 实例化
- 通过 ToolCallFunction 查找并执行相应的工具函数
- 结果作为新事件发送到事件队列
3.7.4 完整流程图
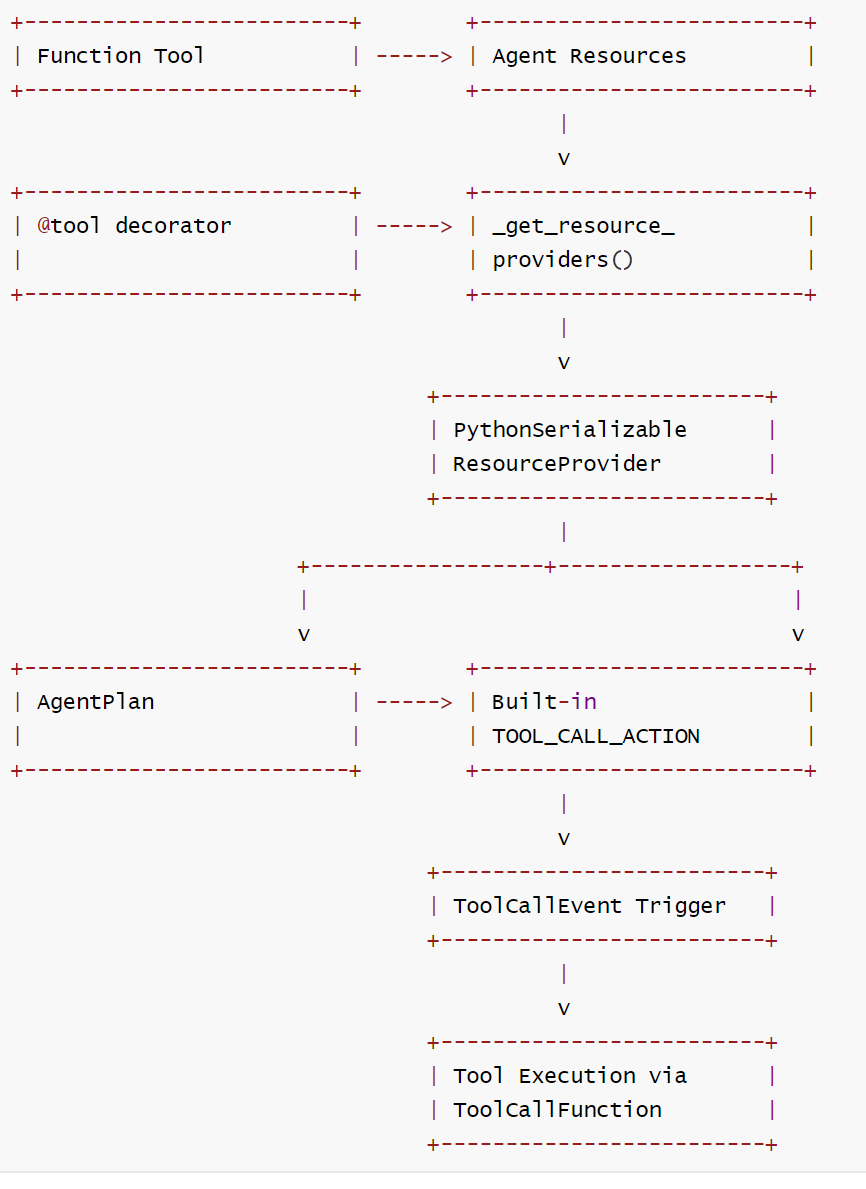
3.7.5 代码
在 agent_plan.py中处理工具资源的代码如下:
# 识别工具资源并创建提供者
elif hasattr(value, "_is_tool"):
if isinstance(value, staticmethod):
value = value.__func__
if callable(value):
# TODO: support other tool type.
tool = from_callable(func=value)
resource_providers.append(
PythonSerializableResourceProvider.from_resource(
name=name, resource=tool
)
)
# 或者通过add_resource 添加的工具
for name, tool in agent.resources[ResourceType.TOOL].items():
resource_providers.append(
PythonSerializableResourceProvider.from_resource(
name=name, resource=from_callable(tool.func)
)
)
总结来说,function_tool 通过资源注册机制与Agent关联,然后在编译阶段被转换为可序列化的资源提供者,最终通过内置的工具调用Action来执行。这种设计使得工具可以在分布式环境种正确传输和执行。
0xFF 参考
https://ce101.mintlify.app/core-tech/agent#7-2-5-multi-agent
https://www.zhihu.com/question/1959742114519844109/answer/1983526566437880277

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号