计算 schemas/AMs 大小的函数及 \dn++ 和 \dA++
目录结构
注:提前言明 本文借鉴了以下博主、书籍或网站的内容,其列表如下:
1、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL数据库内核分析》
2、参考书籍:《数据库事务处理的艺术:事务管理与并发控制》
3、PostgreSQL数据库仓库链接,点击前往
4、日本著名PostgreSQL数据库专家 铃木启修 网站主页,点击前往
5、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL中文手册》
6、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL指南:内幕探索》,点击前往
7、参考书籍:《事务处理 概念与技术》
8、PgSQL · 性能优化 · PostgreSQL TPC-C极限优化玩法,点击前往
1、本文内容全部来源于开源社区 GitHub和以上博主的贡献,本文也免费开源(可能会存在问题,评论区等待大佬们的指正)
2、本文目的:开源共享 抛砖引玉 一起学习
3、本文不提供任何资源 不存在任何交易 与任何组织和机构无关
4、大家可以根据需要自行 复制粘贴以及作为其他个人用途,但是不允许转载 不允许商用 (写作不易,还请见谅 💖)
5、本文内容基于PostgreSQL master源码开发而成
@

文章快速说明索引
学习目标:
做数据库内核开发久了就会有一种 少年得志,年少轻狂 的错觉,然鹅细细一品觉得自己其实不算特别优秀 远远没有达到自己想要的。也许光鲜的表面掩盖了空洞的内在,每每想到于此,皆有夜半临渊如履薄冰之感。为了睡上几个踏实觉,即日起 暂缓其他基于PostgreSQL数据库的兼容功能开发,近段时间 将着重于学习分享Postgres的基础知识和实践内幕。
学习内容:(详见目录)
1、深入理解PostgreSQL数据库计算 schemas/AMs 大小的函数及 \dn++ 和 \dA++
学习时间:
2024-03-13 14:00:12 星期三
学习产出:
1、PostgreSQL数据库基础知识回顾 1个
2、技术博客 1篇
3、PostgreSQL数据库内核深入学习
注:下面我们所有的学习环境是Centos8+PostgreSQL master+Oracle19C+MySQL8.0
postgres=# select version();
version
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PostgreSQL 17devel on x86_64-pc-linux-gnu, compiled by gcc (GCC) 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-21), 64-bit
(1 row)
postgres=#
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------#
SQL> select * from v$version;
BANNER Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
BANNER_FULL Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 19.17.0.0.0
BANNER_LEGACY Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
CON_ID 0
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------#
mysql> select version();
+-----------+
| version() |
+-----------+
| 8.0.27 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.06 sec)
mysql>
功能使用背景说明
-
discussion:https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/flat/20210714030725.GG9600%40telsasoft.com
-
commitfest:https://commitfest.postgresql.org/47/3256/
获取最新patch,重新编译数据库 如下:
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres/patch → master]$ ls
0001-Add-pg_am_size-pg_namespace_size.patch 0002-psql-add-convenience-commands-dA-and-dn.patch 0003-f-convert-the-other-verbose-to-int-too.patch 0004-Move-the-double-plus-Size-columns-to-the-right.patch
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres/patch → master]$
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres/patch → master]$
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres/patch → master]$ ll
total 76
-rw-rw-r-- 1 postgres postgres 7768 Feb 18 18:38 0001-Add-pg_am_size-pg_namespace_size.patch
-rw-rw-r-- 1 postgres postgres 9609 Feb 18 18:38 0002-psql-add-convenience-commands-dA-and-dn.patch
-rw-rw-r-- 1 postgres postgres 41334 Feb 18 18:38 0003-f-convert-the-other-verbose-to-int-too.patch
-rw-rw-r-- 1 postgres postgres 10121 Feb 18 18:38 0004-Move-the-double-plus-Size-columns-to-the-right.patch
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres/patch → master]$
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres/patch → master]$
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres/patch → master]$ cd ..
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$ git apply patch/0001-Add-pg_am_size-pg_namespace_size.patch
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$ git apply patch/0002-psql-add-convenience-commands-dA-and-dn.patch
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$ git apply patch/0003-f-convert-the-other-verbose-to-int-too.patch
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$ git apply patch/0004-Move-the-double-plus-Size-columns-to-the-right.patch
[postgres@localhost:~/postgres → master]$
看一下相关函数的介绍,如下:
postgres=# select version();
version
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PostgreSQL 17devel on x86_64-pc-linux-gnu, compiled by gcc (GCC) 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-21), 64-bit
(1 row)
postgres=# \df+ pg_namespace_size
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type | Volatility | Parallel | Owner | Security | Access privileges | Language | Internal name | Description
------------+-------------------+------------------+---------------------+------+------------+----------+----------+----------+-------------------+----------+------------------------+----------------------------------------------------
pg_catalog | pg_namespace_size | bigint | name | func | volatile | safe | postgres | invoker | | internal | pg_namespace_size_name | total disk space usage for the specified namespace
pg_catalog | pg_namespace_size | bigint | oid | func | volatile | safe | postgres | invoker | | internal | pg_namespace_size_oid | total disk space usage for the specified namespace
(2 rows)
postgres=#
postgres=# \duS+
List of roles
Role name | Attributes | Description
-----------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+-------------
pg_checkpoint | Cannot login |
pg_create_subscription | Cannot login |
pg_database_owner | Cannot login |
pg_execute_server_program | Cannot login |
pg_monitor | Cannot login |
pg_read_all_data | Cannot login |
pg_read_all_settings | Cannot login |
pg_read_all_stats | Cannot login |
pg_read_server_files | Cannot login |
pg_signal_backend | Cannot login |
pg_stat_scan_tables | Cannot login |
pg_use_reserved_connections | Cannot login |
pg_write_all_data | Cannot login |
pg_write_server_files | Cannot login |
postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS |
postgres=#
如上函数:计算具有指定名称或 OID 的命名空间(架构)中的表所使用的总磁盘空间。要使用此函数,您必须对指定命名空间具有 CREATE 权限或具有 pg_read_all_stats 角色的权限,除非它是当前数据库的默认命名空间。
postgres=# \df+ pg_am_size
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type | Volatility | Parallel | Owner | Security | Access privileges | Language | Internal name | Description
------------+------------+------------------+---------------------+------+------------+----------+----------+----------+-------------------+----------+-----------------+--------------------------------------------------------
pg_catalog | pg_am_size | bigint | name | func | volatile | safe | postgres | invoker | | internal | pg_am_size_name | total disk space usage for the specified access method
pg_catalog | pg_am_size | bigint | oid | func | volatile | safe | postgres | invoker | | internal | pg_am_size_oid | total disk space usage for the specified access method
(2 rows)
postgres=#
如上函数:使用具有指定名称或 OID 的访问方法计算表使用的总磁盘空间。
接下来,我们看一下schema相关的元命令,如下:
postgres=# select * from pg_namespace;
oid | nspname | nspowner | nspacl
-------+--------------------+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------
99 | pg_toast | 10 |
11 | pg_catalog | 10 | {postgres=UC/postgres,=U/postgres}
2200 | public | 6171 | {pg_database_owner=UC/pg_database_owner,=U/pg_database_owner}
13200 | information_schema | 10 | {postgres=UC/postgres,=U/postgres}
(4 rows)
postgres=# \dn *
List of schemas
Name | Owner
--------------------+-------------------
information_schema | postgres
pg_catalog | postgres
pg_toast | postgres
public | pg_database_owner
(4 rows)
postgres=#
postgres=# \dn+ *
List of schemas
Name | Owner | Access privileges | Description
--------------------+-------------------+----------------------------------------+----------------------------------
information_schema | postgres | postgres=UC/postgres +|
| | =U/postgres |
pg_catalog | postgres | postgres=UC/postgres +| system catalog schema
| | =U/postgres |
pg_toast | postgres | | reserved schema for TOAST tables
public | pg_database_owner | pg_database_owner=UC/pg_database_owner+| standard public schema
| | =U/pg_database_owner |
(4 rows)
postgres=# \dn++ *
List of schemas
Name | Owner | Access privileges | Description | Size
--------------------+-------------------+----------------------------------------+----------------------------------+---------
information_schema | postgres | postgres=UC/postgres +| | 216 kB
| | =U/postgres | |
pg_catalog | postgres | postgres=UC/postgres +| system catalog schema | 6664 kB
| | =U/postgres | |
pg_toast | postgres | | reserved schema for TOAST tables | 1000 kB
public | pg_database_owner | pg_database_owner=UC/pg_database_owner+| standard public schema | 0 bytes
| | =U/pg_database_owner | |
(4 rows)
postgres=# \dn++ pg_catalog
List of schemas
Name | Owner | Access privileges | Description | Size
------------+----------+----------------------+-----------------------+---------
pg_catalog | postgres | postgres=UC/postgres+| system catalog schema | 6664 kB
| | =U/postgres | |
(1 row)
postgres=#
如上的 + 和 ++ 也是此次patch的新特性,我们后面再详细介绍其实现原理!
补丁实现核心原理
计算大小
postgres=# \d
Did not find any relations.
postgres=#
postgres=# create table t1 (id int, name text);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# insert into t1 select generate_series(1,100000) as id, md5(random()::text) as name;
INSERT 0 100000
postgres=#
postgres=# select * from t1 limit 1;
id | name
----+----------------------------------
1 | cf39df21ad05c88d9a2d2264b0642a5f
(1 row)
postgres=#
计算表/schema/am的大小,如下:
postgres=# select oid from pg_class where relname like 't1';
oid
-------
16388
(1 row)
postgres=# select pg_relation_size(16388);
pg_relation_size
------------------
6832128
(1 row)
postgres=# select pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(16388));
pg_size_pretty
----------------
6672 kB
(1 row)
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------+-------+----------
public | t1 | table | postgres
(1 row)
postgres=# select pg_namespace_size('public');
pg_namespace_size
-------------------
6864896
(1 row)
postgres=# select * from pg_namespace ;
oid | nspname | nspowner | nspacl
-------+--------------------+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------
99 | pg_toast | 10 |
11 | pg_catalog | 10 | {postgres=UC/postgres,=U/postgres}
2200 | public | 6171 | {pg_database_owner=UC/pg_database_owner,=U/pg_database_owner}
13200 | information_schema | 10 | {postgres=UC/postgres,=U/postgres}
(4 rows)
postgres=# select pg_namespace_size(2200);
pg_namespace_size
-------------------
6864896
(1 row)
postgres=# select pg_size_pretty(pg_namespace_size(2200));
pg_size_pretty
----------------
6704 kB
(1 row)
postgres=#
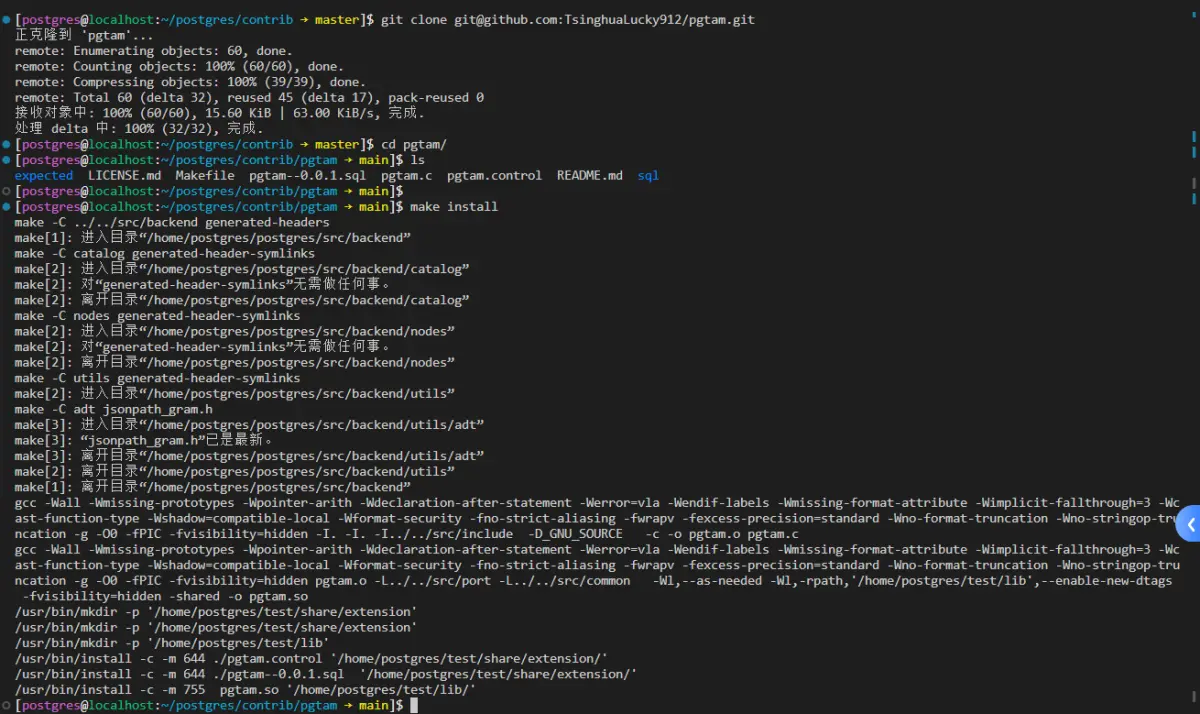
postgres=# create extension pgtam ;
CREATE EXTENSION
postgres=#
postgres=# select * from pg_am;
oid | amname | amhandler | amtype
-------+--------+----------------------+--------
2 | heap | heap_tableam_handler | t
403 | btree | bthandler | i
405 | hash | hashhandler | i
783 | gist | gisthandler | i
2742 | gin | ginhandler | i
4000 | spgist | spghandler | i
3580 | brin | brinhandler | i
16401 | mem | mem_tableam_handler | t
(8 rows)
postgres=# select pg_am_size(16401);
pg_am_size
------------
0
(1 row)
postgres=#
postgres=# create table t2 (id int, name text) using mem;
NOTICE: in mem_tableam_handler: mem_tableam handler loaded
NOTICE: Created table: [t2]
NOTICE: in memam_relation_set_new_filelocator
NOTICE: in mem_tableam_handler: mem_tableam handler loaded
NOTICE: in memam_relation_needs_toast_table
CREATE TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# insert into t2 select generate_series(1,100) as id, md5(random()::text) as name;
INSERT 0 100
postgres=#
postgres=# select pg_am_size(16401);
pg_am_size
------------
0
(1 row)
postgres=#
注:这里留上一个疑问 为什么am的size还是0?
而此时heap的size,如下:
postgres=# select pg_am_size(2);
pg_am_size
------------
11780096
(1 row)
postgres=# select pg_size_pretty(pg_am_size(2));
pg_size_pretty
----------------
11 MB
(1 row)
postgres=# drop table t1;
DROP TABLE
postgres=# vacuum;
VACUUM
postgres=# select pg_size_pretty(pg_am_size(2));
pg_size_pretty
----------------
4800 kB
(1 row)
postgres=#
注:有兴趣的小伙伴们可以自行编译安装citus,使用其列存进行实验!(目前citus上不支持最新master分支 暂不写这块)
namespace的计算逻辑,如下:
// src/backend/utils/adt/dbsize.c
Datum
pg_namespace_size_oid(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS)
{
Oid nspOid = PG_GETARG_OID(0);
int64 size;
size = calculate_namespace_size(nspOid);
if (size < 0)
PG_RETURN_NULL();
PG_RETURN_INT64(size);
}
Datum
pg_namespace_size_name(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS)
{
Name nspName = PG_GETARG_NAME(0);
Oid nspOid = get_namespace_oid(NameStr(*nspName), false);
int64 size;
size = calculate_namespace_size(nspOid);
if (size < 0)
PG_RETURN_NULL();
PG_RETURN_INT64(size);
}
/* Compute the size of relations in a schema (namespace) */
// 计算模式(命名空间)中表的大小
static int64
calculate_namespace_size(Oid nspOid)
{
/*
* User must be a member of pg_read_all_stats or have CREATE privilege for
* target namespace.
*
* 用户必须是 pg_read_all_stats 的成员或具有目标命名空间的 CREATE 权限。
*/
if (!is_member_of_role(GetUserId(), ROLE_PG_READ_ALL_STATS))
{
AclResult aclresult;
aclresult = object_aclcheck(NamespaceRelationId, nspOid, GetUserId(), ACL_CREATE);
if (aclresult != ACLCHECK_OK)
aclcheck_error(aclresult, OBJECT_SCHEMA,
get_namespace_name(nspOid));
}
return calculate_size_attvalue(Anum_pg_class_relnamespace, nspOid);
}
访问方法AM的计算逻辑,如下:
// src/backend/utils/adt/dbsize.c
Datum
pg_am_size_oid(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS)
{
Oid amOid = PG_GETARG_OID(0);
int64 size;
size = calculate_am_size(amOid);
if (size < 0)
PG_RETURN_NULL();
PG_RETURN_INT64(size);
}
Datum
pg_am_size_name(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS)
{
Name amName = PG_GETARG_NAME(0);
Oid amOid = get_am_oid(NameStr(*amName), false);
int64 size;
size = calculate_am_size(amOid);
if (size < 0)
PG_RETURN_NULL();
PG_RETURN_INT64(size);
}
/* Compute the size of relations using the given access method */
// 使用给定的访问方法计算表的大小
static int64
calculate_am_size(Oid amOid)
{
/* XXX acl_check? */
return calculate_size_attvalue(Anum_pg_class_relam, amOid);
}
下面就看一下本次patch核心中的核心函数,如下:
/*
* Return the sum of size of relations for which the given attribute of
* pg_class matches the specified OID value.
*
* 返回 pg_class 的给定属性与指定 OID 值匹配的关系大小的总和
*/
static int64
calculate_size_attvalue(AttrNumber attnum, Oid attval)
{
int64 totalsize = 0;
ScanKeyData skey;
Relation pg_class;
SysScanDesc scan;
HeapTuple tuple;
ScanKeyInit(&skey, attnum,
BTEqualStrategyNumber, F_OIDEQ, attval);
pg_class = table_open(RelationRelationId, AccessShareLock);
scan = systable_beginscan(pg_class, InvalidOid, false, NULL, 1, &skey);
while (HeapTupleIsValid(tuple = systable_getnext(scan)))
{
Form_pg_class classtuple = (Form_pg_class) GETSTRUCT(tuple);
Relation rel;
rel = try_relation_open(classtuple->oid, AccessShareLock);
if (!rel)
continue;
for (ForkNumber forkNum = 0; forkNum <= MAX_FORKNUM; forkNum++)
totalsize += calculate_relation_size(&(rel->rd_locator), rel->rd_backend, forkNum);
relation_close(rel, AccessShareLock);
}
systable_endscan(scan);
table_close(pg_class, AccessShareLock);
return totalsize;
}
postgres=# select count(*) from pg_class where relam = 2;
count
-------
108
(1 row)
postgres=# select count(*) from pg_class where relnamespace = 2200;
count
-------
0
(1 row)
postgres=# create table t1 (id int, name text);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# insert into t1 select generate_series(1,100000) as id, md5(random()::text) as name;
INSERT 0 100000
postgres=#
## 多出来的2个 分别是 pg_toast_16410 t1
postgres=# select count(*) from pg_class where relam = 2;
count
-------
110
(1 row)
postgres=# select count(*) from pg_class where relnamespace = 2200;
count
-------
1
(1 row)
postgres=#
如上的代码逻辑,开表pg_class 然后索引循环遍历,然后就可以使用函数 calculate_relation_size
这里调用如下片段的函数,还有(蓝色框的):
for (ForkNumber forkNum = 0; forkNum <= MAX_FORKNUM; forkNum++)
totalsize += calculate_relation_size(&(rel->rd_locator), rel->rd_backend, forkNum);
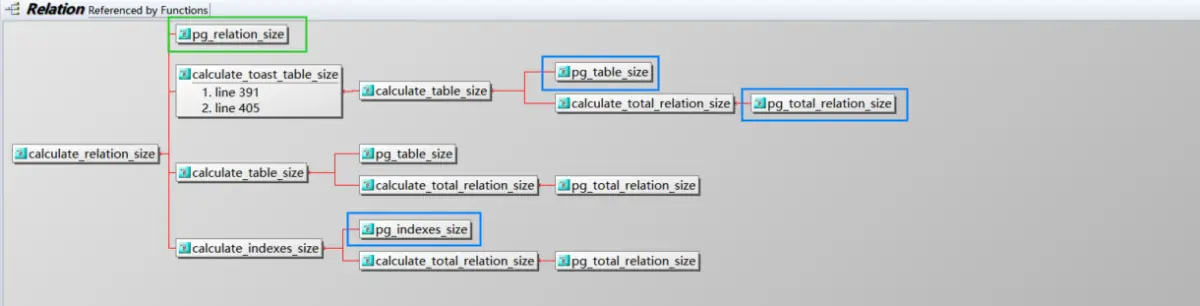
注:从上面图就可以知道 pg_relation_size和 pg_table_size 的差别在哪里了!
list ++
首先我们先看一下,上面两个元命令的内部转换情况,如下:
postgres=# create table t1 (id int, name text);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# insert into t1 select generate_series(1,100000) as id, md5(random()::text) as name;
INSERT 0 100000
postgres=# \dn public
List of schemas
Name | Owner
--------+-------------------
public | pg_database_owner
(1 row)
postgres=# \dn+ public
List of schemas
Name | Owner | Access privileges | Description
--------+-------------------+----------------------------------------+------------------------
public | pg_database_owner | pg_database_owner=UC/pg_database_owner+| standard public schema
| | =U/pg_database_owner |
(1 row)
postgres=# \dn++ public
List of schemas
Name | Owner | Access privileges | Description | Size
--------+-------------------+----------------------------------------+------------------------+---------
public | pg_database_owner | pg_database_owner=UC/pg_database_owner+| standard public schema | 6696 kB
| | =U/pg_database_owner | |
(1 row)
postgres=#
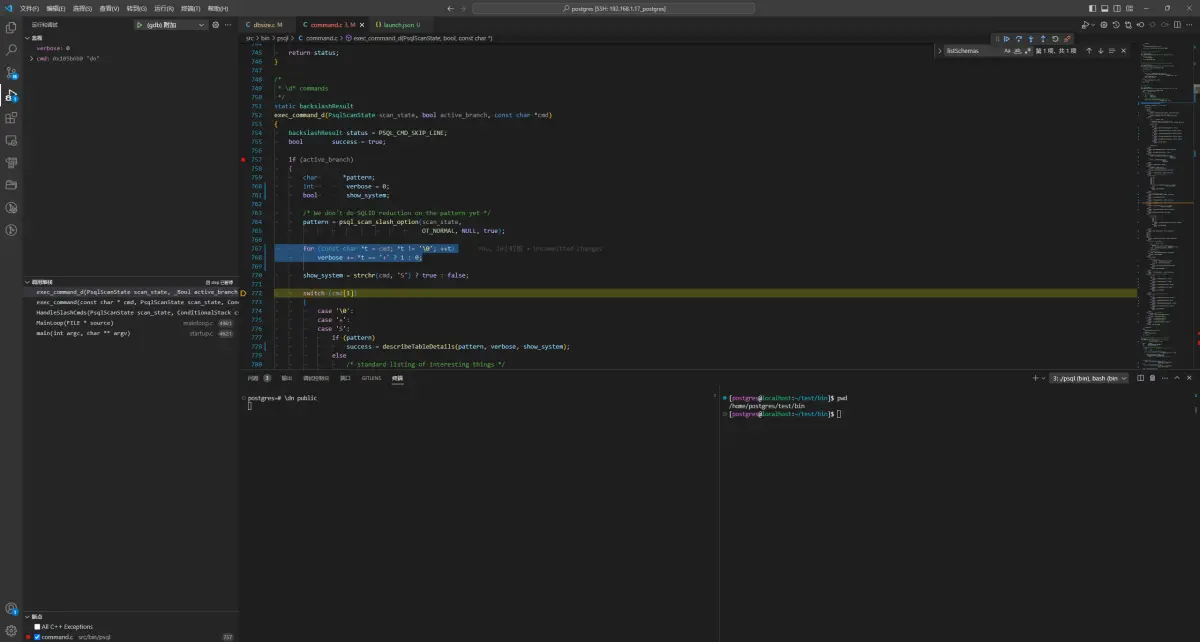
如上便是计算 + 的个数,对于 \dn \dn+ \dn++ 它们分别对应的SQL自然就是不同的,如下:
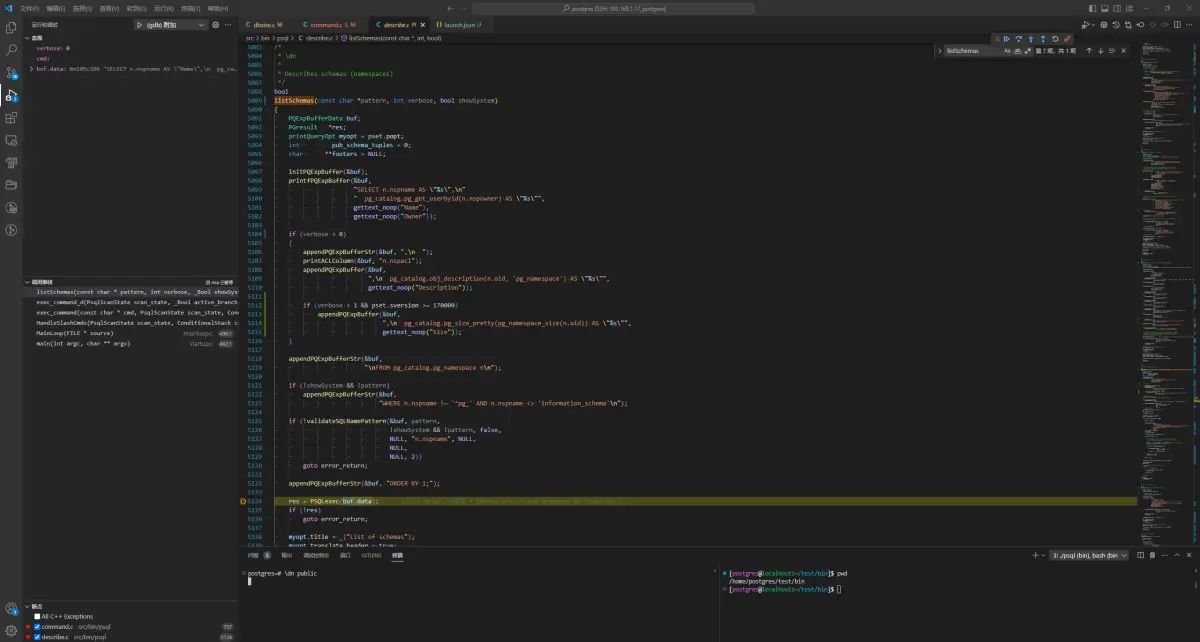
// 这里 buf.data 的值为:
\dn public
0x105c280 "SELECT n.nspname AS \"Name\",\n pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(n.nspowner) AS \"Owner\"\nFROM pg_catalog.pg_namespace n\nWHERE n.nspname OPERATOR(pg_catalog.~) '^(public)$' COLLATE pg_catalog.default\nORDER BY 1;"
\dn+ public
0x106d600 "SELECT n.nspname AS \"Name\",\n pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(n.nspowner) AS \"Owner\",\n CASE WHEN pg_catalog.cardinality(n.nspacl) = 0 THEN '(none)' ELSE pg_catalog.array_to_string(n.nspacl, E'\\n') END AS \"Access privileges\",\n pg_catalog.obj_description(n.oid, 'pg_namespace') AS \"Description\"\nFROM pg_catalog.pg_namespace n\nWHERE n.nspname OPERATOR(pg_catalog.~) '^(public)$' COLLATE pg_catalog.default\nORDER BY 1;"
\dn++ public
0x106d810 "SELECT n.nspname AS \"Name\",\n pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(n.nspowner) AS \"Owner\",\n CASE WHEN pg_catalog.cardinality(n.nspacl) = 0 THEN '(none)' ELSE pg_catalog.array_to_string(n.nspacl, E'\\n') END AS \"Access privileges\",\n pg_catalog.obj_description(n.oid, 'pg_namespace') AS \"Description\",\n pg_catalog.pg_size_pretty(pg_namespace_size(n.oid)) AS \"Size\"\nFROM pg_catalog.pg_namespace n\nWHERE n.nspname OPERATOR(pg_catalog.~) '^(public)$' COLLATE pg_catalog.default\nORDER BY 1;"
\dA的函数堆栈,如下:
describeAccessMethods(const char * pattern, int verbose) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\bin\psql\describe.c:148)
exec_command_d(PsqlScanState scan_state, _Bool active_branch, const char * cmd) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\bin\psql\command.c:794)
exec_command(const char * cmd, PsqlScanState scan_state, ConditionalStack cstack, PQExpBuffer query_buf, PQExpBuffer previous_buf) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\bin\psql\command.c:329)
HandleSlashCmds(PsqlScanState scan_state, ConditionalStack cstack, PQExpBuffer query_buf, PQExpBuffer previous_buf) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\bin\psql\command.c:230)
MainLoop(FILE * source) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\bin\psql\mainloop.c:496)
main(int argc, char ** argv) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\bin\psql\startup.c:462)
// 这里 buf.data 的值为:
\dA heap
0x105c5b0 "SELECT amname AS \"Name\",\n CASE amtype WHEN 'i' THEN 'Index' WHEN 't' THEN 'Table' END AS \"Type\"\nFROM pg_catalog.pg_am\nWHERE amname OPERATOR(pg_catalog.~) '^(heap)$' COLLATE pg_catalog.default\nORDER BY 1;"
\dA+ heap
0x106db30 "SELECT amname AS \"Name\",\n CASE amtype WHEN 'i' THEN 'Index' WHEN 't' THEN 'Table' END AS \"Type\",\n amhandler AS \"Handler\",\n pg_catalog.obj_description(oid, 'pg_am') AS \"Description\"\nFROM pg_catalog.pg_am\nWHERE amname OPERATOR(pg_catalog.~) '^(heap)$' COLLATE pg_catalog.default\nORDER BY 1;"
\dA++ heap
0x106de70 "SELECT amname AS \"Name\",\n CASE amtype WHEN 'i' THEN 'Index' WHEN 't' THEN 'Table' END AS \"Type\",\n amhandler AS \"Handler\",\n pg_catalog.obj_description(oid, 'pg_am') AS \"Description\",\n pg_catalog.pg_size_pretty(pg_catalog.pg_am_size(oid)) AS \"Size\"\nFROM pg_catalog.pg_am\nWHERE amname OPERATOR(pg_catalog.~) '^(heap)$' COLLATE pg_catalog.default\nORDER BY 1;"
小结一下:
- 元命令中根据+的个数,以转换出不同的SQL
- 对于获取size,元命令(不只是上面这两个)都是调用具体的pg_proc函数 例如:pg_am_size等



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号