python自动化运维之路~DAY3
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.函数
1.函数是什么?
函数一词来源于数学,但编程中的「函数」概念,与数学中的函数是有很大不同的,具体区别,我们后面会讲,编程中的函数在英文中也有很多不同的叫法。在BASIC中叫做subroutine(子过程或子程序),在Pascal中叫做procedure(过程)和function,在C中只有function,在Java里面叫做method
定义: 函数是指将一组语句的集合通过一个名字(函数名)封装起来,要想执行这个函数,只需调用其函数名即可
2.函数的特点:
- 减少重复代码
- 使程序变的可扩展
- 使程序变得易维护
3.返回值
要想获取函数的执行结果,就可以用return语句把结果返回
注意:
- 函数在执行过程中只要遇到return语句,就会停止执行并返回结果,so 也可以理解为 return 语句代表着函数的结束
- 如果未在函数中指定return,那这个函数的返回值为None
下面让我们一起看看函数吧:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:gbk _*_
#__author__ = "rianley"
import time
# #定义一个函数
# def fun():
# '''tesing'''
# print('in the func1')
# return 100
# #定义一个过程(没有返回值)
# def fun2():
# print('in the func2')
# #调用函数
# x=fun()
# y=fun2()
#
# print("from fun return is %s" % x) #如果是函数的话就会有返回值,此处会返回100
# print("from fun2 return is %s" % y) #如果是过程的话就没有返回值,python解释器会默认返回None
#
#打印日志的格式的函数
# def logger():
# time_format = '%Y-%m-%d %X' #定义时间的格式
# time_current = time.strftime(time_format) #利用time模块的strftime,将日期按照之前定义好的time_format形式打印出来!
# with open('a.txt','a+') as f:
# f.write('%s end action\n' %time_current)
# logger()
# #函数参数及调用
# def test(x,y): #x,y表示位置参数
# print(x) #此处的x表示形式参数
# print(y) #此处的y表示形式参数
# # test(100,200) #100,200这个参数表示实际参数【位置参数调用】
# # test(y=100,x=200) #【关键字调用】
# test(3,y=2) #关键字调用也可以这么写,需要一一对应的哟
# #
# def test2(x,y,z):
# print(x)
# print(y)
# print(z)
# test2(33,z=200,y=300) #位置参数和关键字调用可以这样用,但是要注意!位置参数要放在关键字参数的前面哟!换句话说就是关键字参数要放在位置参数的后面,然后后面的所有关键字参数可以无序的传参数。
#默认参数的用途:1.定义程序的安装路径;2.定义数据库连接时的端口等等。
# def test(x,y=2): #我们可以定义一个默认参数,调用这个函数的时候,默认参数非必须传递,如果传递参数就会打印传递的参数,如果不传递参数就打印默认的参数;
# print(x)
# print(y)
# test(100,3)
# test(100)
#
#以上定义的参数都存在bug,比如我们在传参的时候多传递或者少传递参数都会导致程序脚本报错!因此我们就可以定义一个参数组,用于传递参数不固定的时候!
# def test3(*args): #定义一个参数组,当调用该函数的时候传入的实际参数会自动将其变成一个tuple[接受N个位置参数,转换成元组的形式]
# print(args)
# test3(1,2,3,4,5,4,5)
# test3(*[100,200,300])
#
# def test4(x,*args): # 定义一个参数组还可以这么写哟
# print(x)
# print(args)
# test4(100,2,3,4,5)
# def test5(**kwargs): #接受N个关键字参数,转换成字典的方式,
# print(kwargs)
# test5(name="程小航",age=26,set="man") #传递的参数相当于key和value哟
#
# def test6(name,age=25,*args,**kwargs): #参数组要放在位置参数合默认参数之后,不然会报错的哟!
# print(name)
# print(age)
# print(args)
# print(kwargs)
# test6("程小航",18,hobby='basketball') #用位置参数传参
# test6(name="rianley",hobby="ping-pong",age=20) #用关键字参数传参
# test6("程小航",100,800,900,1000,sex="man") #注意我再次传的第二个参数"100"是上面"age"的位置参数所对应的值哟,而后面的"800,900,1000"是给位置参数组传递的哟,最后蚕食给字典参数组传参的
#注意,在函数里面定义的变量属于局部变量,也就是仅仅在函数里面定义的函数呢(我们这里说的对象是:字符串或者是数字)
# name = "程小航" #该变量属于全局变量
# print(name)
# def names_info():
# name = "rianley" #该变量数据局部变量
# print(name)
# names_info()
# print(name) #全局和局部变量都有相同的变量的时候,是全局的变量生效的哟~
#当然如果你必须要讲局部变量在全局变量生效的话也是可以的,需要用“global”声明一下:但是这种方法知道就好!不要用!不要用!不要用!重要的事情说三遍!,不要在函数里面改全局变量!(我们这里说的对象是:字符串或者是数字)
# age = 18
# print(age)
# def age_info():
# global age #声明这个变量,让其成为全局变量!如果没有这个变量,就会新建这个变量,使其成为全局变量,这种方法千万别用,如果你的代码有几千行,你每次都这么改的话,如果你在其他的函数用到这个变量的话会让你的拍错难度加大N倍!不管全局是否有这个变量,都尽量不要这么用,我们可以看明白别人这么用是怎么回事就好,哈哈!
# age = 200
# print(age)
# age_info()
# print(age)
#上面我们说了数字或者字符串定义了全局变量,如果局部变量没有使用global声明的话就不能修改全局变量,那么像比较复杂一点的对象就可以修改,比如字典,列表,集合,类等数据结构!.
# names = ["rianley","程小航","程_小_航"]
# print(names)
# def chage_name():
# names[0] = "灵魂摆渡"
# print("inside func",names)
# chage_name()
# print(names)
#递归函数:在函数内部,可以调用其他函数,如果一个函数在内部调自身本身,这个函数就是递归函数。
#递归特性:
#1.必须有一个明确的结束条件(最大的递归次数应该是999次)
#2.每次进入更深一层递归时,问题规模相比上次递归都应有所减少
#3.递归效率不高,递归层次过多会导致栈溢出(在计算机中,函数调用是通过栈[stack]这种数据结构实现的,每次进入一个函数调用,栈就会增加一层栈帧,每当还输返回,栈就会减一层栈帧。由于栈的大小不是无限的,所以递归次数过多,会导致栈溢出的哟~)
# def calc(n):
# print(n)
# if int(n/2) > 0:
# return calc(int(n/2))
# print("--》",n)
# calc(10)
#有可能你听过函数式编程(学函数式编程建议用:lisp,hashshell,erlang),不建议用Python写函数式编程,尽管用python可以这么干,我们下面举个最简单的例子你就不想这么干了,哈哈
#比如我们先要计算:(30+40)*2-50
#传统的过程式编程,可能这样写:
# var a=30+40;
# var b=a*3;
# var c=b-4
#函数式编程要求使用函数,我们可以把运算过程定义为不同的函数,然后写成下面这样:
#var result=subtract(multiply(add1,2),3),4);
#高级函数:变量可以指向函数,函数的参数能接受变量,那么一个函数就可以接受另一个函数作为参数,这种函数称之为高阶函数
# def add(a,b,f):
# return f(a) + f(b)
# result=add(3,-7,abs)
# print(result)
#如何将字符串转换成字典"eval()"
#假设有一个字符串name_info,里面的数据格式跟字典如出一辙,如何实现转换呢?
#eval(name_info)
好了,大家学完了函数,让我们一起小试牛刀一下吧:

流程图如下:
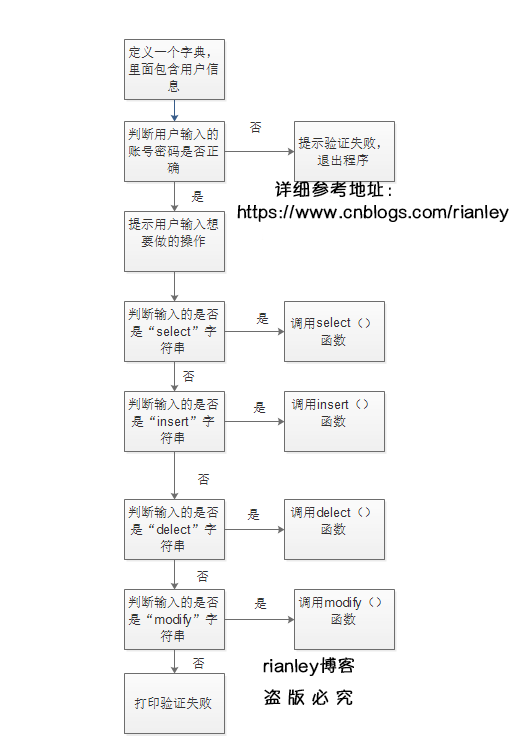
student_info表格信息如下:
staff_id name age phone dept enroll_date 1---Alex Li---22---18817778564---IT---2018-11-07 5---Rianly xxx---36---17315348564---HR---2011-02-06 3---Rianly niu---36---17312348565---HR---2011-02-06 6---'egon'---'18'---'17474747774'---'teacher'---'2018-4-8'
代码使用环境说明:
刚刚入门python,只了解简单的文件处理和字符类型,所以写出来的脚本难免会遇到bug,需要按照我给出的语法格式来进行操作哟!
说明几点:
1.sql语句要写完整,支持,like,大于 小于 等于 查询结果等条件的控制
2.删除的时候会新生成了一个文件”new_file“,如果不想要的话,可以用os模块将之前的这个文件os.remove掉,然后在用os,rename改名即可。
3.修改的时候我会生成一个modify.txt文件,如果想删除的话也可以用os模块来操作。
4.代码很low,大神还是不要看的好~辣眼睛 啊~
5.运行环境是python3.6
语法格式如下:
查询:
select * from staff_table where phone = "phone"
插入:
insert into staff_table values('alex','38','99999999999','teacher','2017-2-8')
删除:
delete from staff_table where id = '1'
修改:
UPDATE staff_table SET dept = "Market" where dept = "IT"
具体的实现代码
# Author:rianley
import re,os
#简单的sql操作,不支持联合查询及嵌套查询,table其实是一个文件,支持and连用 order by limit ,不支持or
# 另外 条件里的判断都是根据字符串来比对的(重要) 年龄会出现这种 9>22 字符串是成立的
class sql:
#表信息
staff_key_info={#定义字段的索引位置,等会每行数据会split成一个列表
'id':0,
'name': 1,
'age': 2,
'phone': 3,
'dept': 4,
'enroll_date':5
}
#表唯一字段
staff_unique=['id','phone']
#表名
sql_table='staff_table'
def __init__(self):
while True:
cmd=input('请输入命令:').strip()
if not cmd:continue
if cmd=='q':break
self.deal_cmd(cmd)
def deal_cmd(self,cmd):#判断命令是什么操作
operate_regex=[
'^select\s+(.*?)\s+from\s+(.*)',
'^delete\s+from\s+(.*?)\s+where\s+(.*)',#不支持删除所有行即是delete (*) from table
'^update\s+(.*?)\s+set\s+(.*)',
'^insert\s+into\s+(.*?)\s+values(.*)'
]
count=0
while count<len(operate_regex):
res = re.findall(r'%s'%operate_regex[count], cmd, re.I|re.M)
if res and len(res[0])==2 and res[0][0].strip() and res[0][1].strip():
if count==0:
return self.select_sql(res[0][0].strip(),res[0][1].strip())
elif count==1:
return self.delete_sql(res[0][0].strip(), res[0][1].strip())
elif count==2:
return self.update_sql(res[0][0].strip(), res[0][1].strip())
else:
return self.insert_sql(res[0][0].strip(), res[0][1].strip())
count+=1
print('输入有误')
return False
# 统一处理条件
def wherex(self,list_where_all,lines_list):
if not list_where_all:return True
for i in list_where_all: #其实还有大于等于,小于等于 同样道理
if len(i.strip().split('=',1))==2: #等于
key=i.strip().split('=', 1)[0].strip()
if key not in self.staff_key_info:
print('找不到%s这个字段' % key)
return None
if not lines_list[self.staff_key_info[key]]==i.strip().split('=', 1)[1].strip().replace('"','').replace("'",''):
return False
elif len(i.strip().split('>',1))==2: #大于
key = i.strip().split('>', 1)[0].strip()
if key not in self.staff_key_info:
print('找不到%s这个字段'%key)
return None
if not lines_list[self.staff_key_info[key]] > i.strip().split('>', 1)[1].strip().replace('"','').replace("'",''):
return False
elif len(i.strip().split('<',1))==2: #小于
key = i.strip().split('<', 1)[0].strip()
if key not in self.staff_key_info:
print('找不到%s这个字段' % key)
return None
if not lines_list[self.staff_key_info[key]] < i.strip().split('<', 1)[1].strip().replace('"','').replace("'",''):
return False
elif len(i.strip().split('like',1))==2: #模糊
key = i.strip().split('like', 1)[0].strip()
v=i.strip().split('like', 1)[1].strip().replace('"','').replace("'",'')
#其实这里可以用find 用in的话不在其中好像会报错
if key not in self.staff_key_info:
print('找不到%s这个字段' % key)
return None
if not re.findall(r'.*?(%s).*?' %v , lines_list[self.staff_key_info[key]], re.M):
return False
else:
pass
return True
# 表名是否正确
def table_is_exist(self,table):
if not table == self.sql_table:
print('表名不存在或条件有误!')
return False
return True
#处理查询语句 分割order limit
def limit_and_order(self,where):
where_select_all={
'limit':'',
'order': '',
'where': ''
}
re_limit='.*?limit(.*)'
res1 = re.findall(r'%s' % re_limit, where, re.I | re.M)
order=where
if res1:
where_select_all['limit']=res1[0].strip(''' '"''')
order=where.split('limit')[0].strip(''' '"''')
re_order='.*?order\s+by\s+(.*)'
res2 = re.findall(r'%s' % re_order, order, re.I | re.M)
where=order
if res2:
where_select_all['order'] = res2[0].strip(''' '"''')
where=order.split('order')[0].strip(''' '"''')
where_select_all['where']=where.strip(''' '"''')
return where_select_all
def select_sql(self,select_content,where):
#查询
where_select_all=self.limit_and_order(where)
where=where_select_all['where']
if select_content=='*':
list_select_conten=list(self.staff_key_info)
else:
list_select_conten=select_content.split(',')
list_where_all=[] #没有where条件
if where.find('where')>-1 :
list_where=where.split('where',1)
#只检测and的 小写的
list_where_all=list_where[1].strip().split('and')
if not self.table_is_exist(list_where[0].strip()):return False
else:
if not self.table_is_exist(where.strip()): return False
select_result_list=[]
with open('%s.txt'%self.sql_table,'r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line_list=line.strip(' \n').split('---')
tag=self.wherex(list_where_all,line_list)
if tag == None: return False
if tag:
select_result_list.append([])
for i in list_select_conten:
if i not in self.staff_key_info:
if i.isdigit():
select_result_list[-1].append(i)
else:
print('查询内容出错!')
return False
else:
select_result_list[-1].append(line_list[self.staff_key_info[i]])
#输出
for i in list_select_conten:
print(i,end=' ')
print()
# 处理order
if where_select_all['order']:
if where_select_all['order'].find('desc')>-1:#是否倒序
order_list=where_select_all['order'].split('desc')[0].strip().split(',')
for i in order_list:
key=i.strip()
if key not in self.staff_key_info:
print('order by 字段错误:%s'%key)
return False
select_result_list=self.asc_or_desc(select_result_list,key,1)
else:
order_list = where_select_all['order'].strip().split(',')
for i in order_list:
key=i.strip()
if key not in self.staff_key_info:
print('order by 字段错误:%s'%key)
return False
select_result_list=self.asc_or_desc(select_result_list,key,0)
#处理limit
start_list=0
end_list=len(select_result_list)
if where_select_all['limit']:
limit_list=where_select_all['limit'].split(',')
if len(limit_list)==2:
if not limit_list[0].isdigit() and not limit_list[1].isdigit():
print('limit错误!')
return False
start_list=int(limit_list[0])
end_list=int(limit_list[0])+int(limit_list[1])
else:
if not limit_list[0].isdigit():
print('limit错误!')
return False
end_list = int(limit_list[0])
for j in select_result_list[start_list:end_list]:
for k in j:
print(k,end=" ")
print()
print('当前查询结果为%s行'%len(select_result_list[start_list:end_list]))
def asc_or_desc(self,select_result_list,field,a=0):#0:正序,1:倒序,冒泡
if not select_result_list:return select_result_list
key=self.staff_key_info[field]
for i in range(len(select_result_list) - 1):
for j in range(len(select_result_list) - 1 - i):
if a==0:
if select_result_list[j][key] > select_result_list[j + 1][key]:
select_result_list[j], select_result_list[j + 1] = select_result_list[j + 1], select_result_list[j]
else:
if select_result_list[j][key] < select_result_list[j + 1][key]:
select_result_list[j], select_result_list[j + 1] = select_result_list[j + 1], select_result_list[j]
return select_result_list
def delete_sql(self,delete_table,where):
if not self.table_is_exist(delete_table): return False
if where :
list_where_all=where.split('and')
else:
print('条件有误!')
return False
list_delete_other=[]
delete_count_line=0
with open('%s.txt' % self.sql_table, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line_list = line.strip(' \n').split('---')
tag = self.wherex(list_where_all, line_list)
if tag == None: return False
if tag:
delete_count_line+=1
else:
list_delete_other.append(line)
if list_delete_other:
list_delete_other[-1]=list_delete_other[-1].replace('\n','')
os.remove('%s.txt' % self.sql_table)
with open('test_tabel_delete.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f1:
f1.writelines(list_delete_other)
os.rename('test_tabel_delete.txt', '%s.txt' % self.sql_table)
print('当前受影响行数为:%s'%delete_count_line)
def deal_update_set(self,set_state):
#处理修改的语句,,
list_setx={}
for i in set_state:
key=i.split('=')[0].strip()
v=i.split('=')[1].strip().replace('"','').replace("'",'')
list_setx[key]=v
return list_setx
def update_sql(self,update_table,where):
if not self.table_is_exist(update_table): return False
if where.find('where') > -1:
list_where = where.split('where', 1)
list_where0 = self.deal_update_set(list_where[0].split(','))
# 只检测and的 小写的
list_where_all = list_where[1].strip().split('and')
else:
print('条件有误!')
return False
update_count_line=0
update_line_list=[]
lists=[]
for j in range(0, len(self.staff_key_info)):#检测是否有重复
lists.append('0')
with open('%s.txt' % self.sql_table, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line_list = line.strip(' \n').split('---')
tag = self.wherex(list_where_all, line_list)
if tag == None: return False
if tag:
for i in list_where0:
if i not in self.staff_key_info or i=='id':
print('修改字段出错或是id不可改')
return False
else:
line_list[self.staff_key_info[i]]=list_where0[i]
lists[self.staff_key_info[i]]=list_where0[i]
update_line_list.append('%s\n'%'---'.join(line_list))
update_count_line += 1
else:
update_line_list.append(line)
if self.is_unique(self.staff_unique,line_list,lists):return False
os.remove('%s.txt' % self.sql_table)
with open('test_tabel_delete.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f1:
f1.writelines(update_line_list)
os.rename('test_tabel_delete.txt', '%s.txt' % self.sql_table)
print('当前受影响行数为:%s' % update_count_line)
def insert_sql(self,insert_field,insert_conten):
res_table=insert_field.split('(')[0].strip()
if not self.table_is_exist(res_table): return False
regex=re.findall(r'^.*\((.*?)\)' , insert_field, re.I | re.M)
if regex:
res1 = regex[0].split(',')
else:
res1=[]
res2 = re.findall(r'^\((.*?)\)', insert_conten, re.I | re.M)[0].split(',')
if res1:
if len(res1)==len(res2) and len(res1)==len(self.staff_key_info):
pass
elif len(res1)==len(res2) and len(res1)==(len(self.staff_key_info)-1) and self.staff_key_info.get('id',None)==0:#有主键
res1.append('id')
if set(res1)==set(self.staff_key_info):
append_list = []
for j in range(0, len(self.staff_key_info)):
append_list.append('0')
for i in res1:
if i == 'id': continue
keyx = self.staff_key_info.get(i)
append_list[keyx] = res2[res1.index(i)]
return self.insert_all(append_list)
else:
print('字段不对等!')
return False
else:
print('插入有误!1')
return False
else:
if len(res2)==len(self.staff_key_info):
append_list=[]
for j in range(0, len(self.staff_key_info)):
append_list.append('0')
for i in self.staff_key_info:
keyx=self.staff_key_info[i]
append_list[keyx]=res2[keyx]
return self.insert_all(append_list,1)
elif len(res2)==len(self.staff_key_info)-1:
append_list=[]
res2.insert(0,0)
for j in range(0, len(self.staff_key_info)):
append_list.append('0')
for i in self.staff_key_info:
keyx=self.staff_key_info[i]
append_list[keyx]=res2[keyx]
return self.insert_all(append_list,0)
else:
print('插入有误!2')
return False
def insert_all(self,append_list,is_id=0):#is_id 是否给id赋值
with open('%s.txt' % self.sql_table, 'r+', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
if is_id==0:append_list[0] = self.max_id(lines)
for i in lines:#检测是否重复
if self.is_unique(self.staff_unique,i.strip(' \n').split('---'),append_list):
return False
ns='\n' if len(lines)>0 else ''
f.write('%s%s' %(ns,'---'.join(append_list)))
print('当前受影响行数为:1')
#检测是否有重复
def is_unique(self,unique_content,lines,lists):
for i in unique_content:
key=self.staff_key_info[i]
if lines[key].strip(''' '"''')==lists[key].strip(''' '"'''):#去空格及引号
print('字段%s不能重复'%i)
return True
return False
def max_id(self,lines):#取最大ID
max_c=0
for i in lines:
lines_list=i.strip(' \n').split('---')
num=int(lines_list[self.staff_key_info['id']])
if num>max_c:
max_c=num
return str(max_c+1)
sql()
测试结果如下:
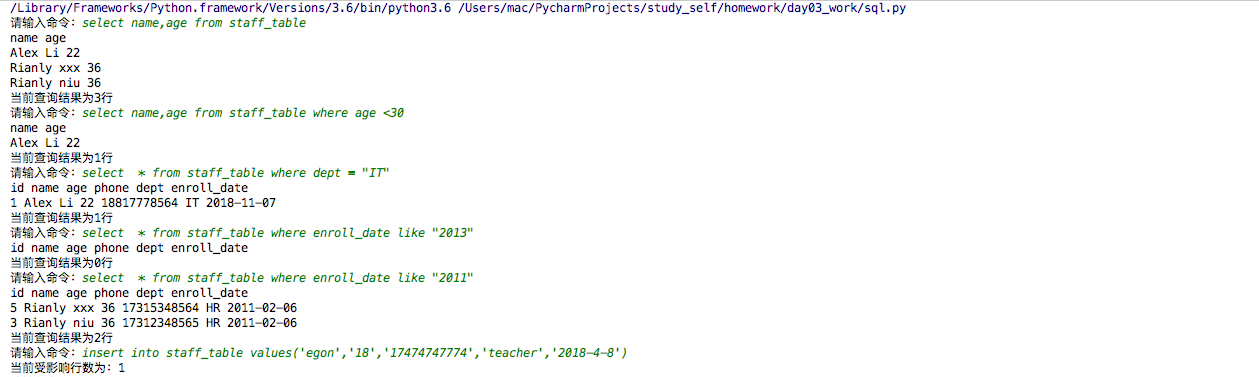
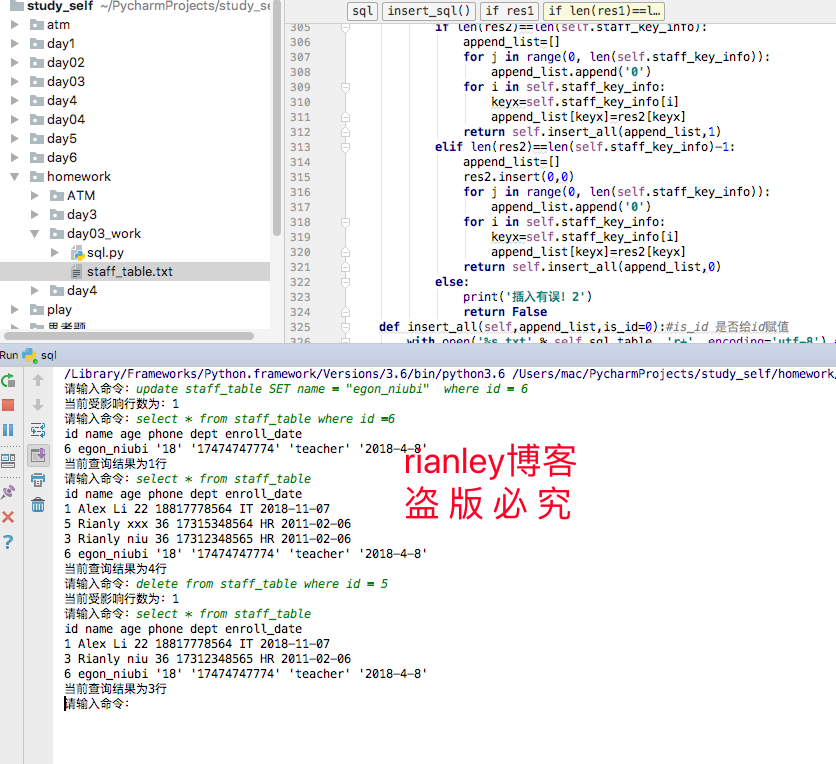
@rianley博客 莫让惰性,成为惯性


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号