Codeforces Round #149 (Div. 2) E. XOR on Segment
http://codeforces.com/contest/242/problem/E
You've got an array a, consisting of n integers a1, a2, ..., an. You are allowed to perform two operations on this array:
- Calculate the sum of current array elements on the segment [l, r], that is, count value al + al + 1 + ... + ar.
- Apply the xor operation with a given number x to each array element on the segment [l, r], that is, execute
![]() . This operation changes exactly r - l + 1 array elements.
. This operation changes exactly r - l + 1 array elements.
Expression 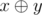 means applying bitwise xor operation to numbers x and y. The given operation exists in all modern programming languages, for example in language C++ and Java it is marked as "^", in Pascal — as "xor".
means applying bitwise xor operation to numbers x and y. The given operation exists in all modern programming languages, for example in language C++ and Java it is marked as "^", in Pascal — as "xor".
You've got a list of m operations of the indicated type. Your task is to perform all given operations, for each sum query you should print the result you get.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the size of the array. The second line contains space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an(0 ≤ ai ≤ 106) — the original array.
The third line contains integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 5·104) — the number of operations with the array. The i-th of the following m lines first contains an integer ti (1 ≤ ti ≤ 2) — the type of the i-th query. If ti = 1, then this is the query of the sum, if ti = 2, then this is the query to change array elements. If the i-th operation is of type 1, then next follow two integers li, ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ n). If the i-th operation is of type 2, then next follow three integers li, ri, xi (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ n, 1 ≤ xi ≤ 106). The numbers on the lines are separated by single spaces.
For each query of type 1 print in a single line the sum of numbers on the given segment. Print the answers to the queries in the order in which the queries go in the input.
Please, do not use the %lld specifier to read or write 64-bit integers in С++. It is preferred to use the cin, cout streams, or the%I64d specifier.
5
4 10 3 13 7
8
1 2 4
2 1 3 3
1 2 4
1 3 3
2 2 5 5
1 1 5
2 1 2 10
1 2 3
26
22
0
34
11
6
4 7 4 0 7 3
5
2 2 3 8
1 1 5
2 3 5 1
2 4 5 6
1 2 3
38
28
线段树. 网上都说是建20棵线段树, 没看他们的代码还不知道20棵树的该怎么写. 直接放在了一棵树里, 每个节点k维护三个值: x,v,num[len]. 4s时限跑了530ms.
x有三种情况: 大于0表示以k为根的子树所覆盖的区间统一需要异或x; 0表示以k为根的子树上所有节点x都是0,即都不需要异或; -1表示以k为根的子树下还有节点x不为0
v表示以k为根的子树所覆盖的区间的和; (仅当x==0时值是有效的,其他情况还需要维护)
num[len]表示当前以k为根的子树所覆盖的区间按位加和, num[i]即从小到大第i个二进制位为1的数的个数. 这样计算区间和可以在O(len)时间内算出.
.. 这居然是第一次纯手打线段树= =,感觉线段树的思想就是能不计算就不计算, 能以后算就以后算, 能不往下维护就不往下维护 这么一种"惰性"思想. 工作你就输了?
这里是通过每个节点的x值来维护这种"惰性",修改时仅作标记而不计算, 只有在查询时才将需要的子树计算出来, 而且只在子树的根处更新并计算出值, 然后将需要更新的x抛给儿子, 留待以后需要访问到儿子的时候再用.
开始写挫了, 将x劈成了两个, willx和didx, 一个是还没给当前节点更新的x,一个是当前节点更新过但孩子还没有更新的x (这个其实直接抛给儿子的x就行...) 代码巨挫无比,挂了三次各种debug后发现是len开小了,需要20只开了10. 最后用那烂代码过了.
后来想想不对, 合成一个x之后写得就很愉快了.
#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <cassert> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cmath> #include <numeric> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> using namespace std; #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0, _n = (int)(n); i < _n; i++) #define fer(i, x, n) for (int i = (int)(x), _n = (int)(n); i < _n; i++) #define rof(i, n, x) for (int i = (int)(n), _x = (int)(x); i-- > _x; ) #define fch(i, x) for (__typeof(x.begin()) i = x.begin(); i != x.end(); i++) #define sz(x) (int((x).size())) #define pb push_back #define mkp make_pair #define all(X) (X).begin(),(X).end() #define X first #define Y second template<class T> inline void smin(T &a, T b){if(b<a)a=b;} template<class T> inline void smax(T &a, T b){if(a<b)a=b;} typedef long long ll; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<int, int> pii; typedef pair<ll,ll> pll; typedef vector<pii> vii; typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<vi> vvi; typedef vector<vii> vvii; typedef vector<char> VC; typedef vector<string> VS; typedef vector<ll> VL; typedef vector<double> VD; typedef set<int> SI; typedef set<string> SS; typedef map<int, int> MII; typedef map<string, int> MSI; template<class T> inline void RST(T &A){memset(A, 0, sizeof(A));} template<class T> inline void FLC(T &A, int x){memset(A, x, sizeof(A));} template<class T> inline void CLR(T &A){A.clear();} /** Constant List .. **/ //{ const int dx4[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; const int dy4[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; const int dx8[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0 , -1 , -1 , 1 , 1}; const int dy8[] = {0, 1, 0, -1 , -1 , 1 , -1 , 1}; const int mod = 1000000007; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; //} template<class T> inline T min(T a, T b, T c){return min(min(a, b), c);} template<class T> inline T max(T a, T b, T c){return max(max(a, b), c);} template<class T> inline T min(T a, T b, T c, T d){return min(min(a, b), min(c, d));} template<class T> inline T max(T a, T b, T c, T d){return max(max(a, b), max(c, d));} template<class T> inline T sqr(T a){return a*a;} template<class T> inline T cub(T a){return a*a*a;} //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// const int len = 20; const int N = 100000; int n,m,l,r,type,x; struct node { ll v; int nums,x; int num[len]; }t[6*N]; int a[N*3]; // 原数组需要开大一些, 因为建树的时候会超范围访问 void build(int k,int l,int r){//建树,在叶节点将初始值转换为二进制位, 并向上转移 if(l==r){ t[k].v = a[k-n]; t[k].nums = 1; t[k].x=0; int tmp = a[k-n],i=0; while(tmp) t[k].num[i++]=tmp&1,tmp>>=1; return; } int mid = (l+r)>>1,lc=k<<1,rc=k<<1|1; build(lc,l,mid); build(rc,mid+1,r); t[k].v = t[lc].v+t[rc].v; t[k].nums = r-l+1; t[k].x=0; rep(i,len) t[k].num[i]=t[lc].num[i]+t[rc].num[i]; } void pushdown(int k,int l,int r,int x){// 将当前节点处的x值向两儿子转移,转移后当前节点x值还需要自行判断赋值 if(x<=0 || l==r) return; int mid = (l+r)>>1,lc=k<<1,rc=k<<1|1; if(t[lc].x>=0) t[lc].x^=x; else pushdown(lc,l,mid,x); if(t[rc].x>=0) t[rc].x^=x; else pushdown(rc,mid+1,r,x); } void update(int k,int l,int r,int L,int R,int x){// 0 : 子树下无x; -1 : 有x; x+ : 子树整个需要异或x int mid = (l+r)>>1,lc=k<<1,rc=k<<1|1; if(L>r || R<l) return; else if(L<=l && r<=R){ if(t[k].x>=0) t[k].x ^= x; else{ update(lc,l,mid,L,R,x); update(rc,mid+1,r,L,R,x); t[k].x=-1; } }else{ pushdown(k,l,r,t[k].x); t[k].x=-1; update(lc,l,mid,L,R,x); update(rc,mid+1,r,L,R,x); } } ll query(int k,int l,int r,int L,int R){ int mid = (l+r)>>1,lc=k<<1,rc=k<<1|1; if(L>r || R<l) return 0; else if(L<=l && r<=R){ if(t[k].x>0){ pushdown(k,l,r,t[k].x); //开始忘了这里.. 当前节点更新前需要将x值抛给儿子,因为之后仅仅更新这个节点, //儿子上的数据不会异或x,而是留待以后需要时才维护 int tmp = t[k].x,i=0; t[k].v= t[k].x = 0; while(tmp){ if(tmp&1) t[k].num[i]=t[k].nums-t[k].num[i]; i++,tmp>>=1; } rof(i,len,0) t[k].v = (t[k].v<<1)+t[k].num[i]; }else if(t[k].x<0){ t[k].v = query(lc,l,mid,L,R)+query(rc,mid+1,r,L,R); t[k].x = 0; rep(i,len) t[k].num[i] = t[lc].num[i]+t[rc].num[i]; } return t[k].v; }else{ if(t[k].x>0){pushdown(k,l,r,t[k].x); t[k].x=-1;} return query(lc,l,mid,L,R)+query(rc,mid+1,r,L,R); } } int main() { //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); scanf("%d",&n); rep(i,n) scanf("%d",a+i); int tmp = 1; while(tmp<n) tmp<<=1; n = tmp; build(1,1,n); scanf("%d",&m); while(m--){ scanf("%d%d%d",&type,&l,&r); if(type==2){ scanf("%d",&x); update(1,1,n,l,r,x); }else{ printf("%I64d\n",query(1,1,n,l,r) ); } } return 0; }


 . This operation changes exactly
. This operation changes exactly 
 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号