队列 栈
先入先出的数据结构
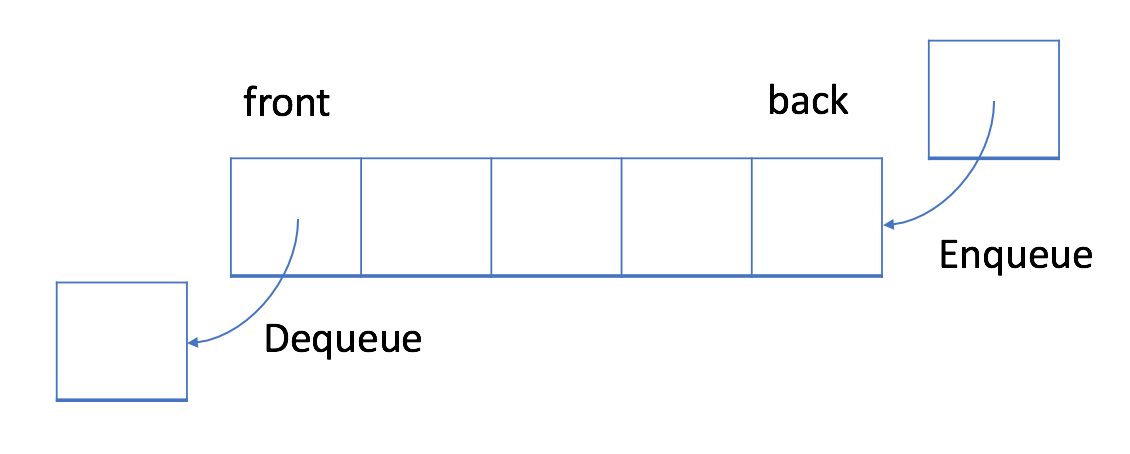
在 FIFO 数据结构中,将首先处理添加到队列中的第一个元素。
如上图所示,队列是典型的 FIFO 数据结构。插入(insert)操作也称作入队(enqueue),新元素始终被添加在队列的末尾。 删除(delete)操作也被称为出队(dequeue)。 你只能移除第一个元素。
#include <iostream> class MyQueue { private: // store elements vector<int> data; // a pointer to indicate the start position int p_start; public: MyQueue() {p_start = 0;} /** Insert an element into the queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */ bool enQueue(int x) { data.push_back(x); return true; } /** Delete an element from the queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */ bool deQueue() { if (isEmpty()) { return false; } p_start++; return true; }; /** Get the front item from the queue. */ int Front() { return data[p_start]; }; /** Checks whether the queue is empty or not. */ bool isEmpty() { return p_start >= data.size(); } }; int main() { MyQueue q; q.enQueue(5); q.enQueue(3); if (!q.isEmpty()) { cout << q.Front() << endl; } q.deQueue(); if (!q.isEmpty()) { cout << q.Front() << endl; } q.deQueue(); if (!q.isEmpty()) { cout << q.Front() << endl; } }
此前,我们提供了一种简单但低效的队列实现。
更有效的方法是使用循环队列。 具体来说,我们可以使用固定大小的数组和两个指针来指示起始位置和结束位置。 目的是重用我们之前提到的被浪费的存储。
队列的基本操作
#include <iostream> int main() { // 1. Initialize a queue. queue<int> q; // 2. Push new element. q.push(5); q.push(13); q.push(8); q.push(6); // 3. Check if queue is empty. if (q.empty()) { cout << "Queue is empty!" << endl; return 0; } // 4. Pop an element. q.pop(); // 5. Get the first element. cout << "The first element is: " << q.front() << endl; // 6. Get the last element. cout << "The last element is: " << q.back() << endl; // 7. Get the size of the queue. cout << "The size is: " << q.size() << endl; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号