一:用户总数的统计:
1:编辑apps/meiduo_admin/views/home_views.py
from django.utils import timezone
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.views import APIView
# 视图的目的是统计用用户的总人数,不涉及校验,也不涉及模型类,所以只需要继承APIView
from apps.users.models import User
class UserTotalCountView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
# 获取查询统计的时间和统计的人数
count = User.objects.count()
cur_time = timezone.localtime()
# cur_time: 2020-09-27 00:14:25.002694+00:00
# cur_time_date: 2020-09-27
return Response({
"count": count,
"date": cur_time.date(),
})
2:路由:
re_path(r'^statistical/total_count/$', UserTotalCountView.as_view()),
二:新增用户的统计:
1:编辑apps/meiduo_admin/views/home_views.py
# 日增用户数量的统计:
class UserDayCountView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
cur_time = timezone.localtime()
cur_time_0 = cur_time.replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
count = User.objects.filter(date_joined__gt=cur_time_0).count()
return Response({
"count": count,
"date": cur_time.date()
})
2:路由:
re_path(r'^statistical/day_increment/$', UserDayCountView.as_view()),
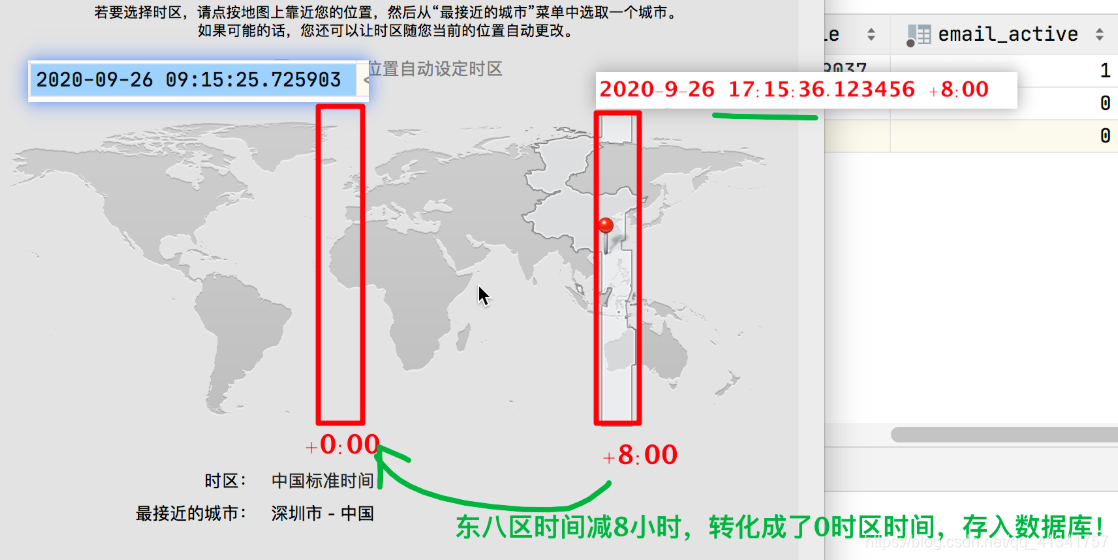
3:时间模块的分析:timezone:
3.1: timezone.localtime()返回基于配置项TIME_ZONE指定的时区的本地时间(是一个datetime对象);
from django.utils import timezone
# 2020-09-26 17:30:45.123456+08:00
cur_time = timezone.localtime()
# 如何获取当日的零时刻?!
# datetime对象的replace函数作业是替换日期属性返回一个新的datetime对象
# 2020-09-26 0:0:0.000000 +08:00
cur_0_time = cur_time.replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
3.2: USE_TZ配置参数
# 启动Django时区功能:1、所有存储到mysql中的时间,统一按照零时区存储;2、在按照时间过滤的时候,统一把时间转化成0时区进行比较;
USE_TZ = True
三:日活跃用户:
注意这里只统计前台页面进入的,不统计后台进入到,为了方便也统计上,需要先更改自定义认证后端:在检验完成后,手动更新最后登录时间。
if user.check_password(password):
user.last_login = timezone.localtime()
user.save()
return user
class UserActiveCountView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
cur_time = timezone.localtime()
cur_time_0 = cur_time.replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
count = User.objects.filter(last_login__gt=cur_time_0).count()
return Response({
"count": count,
"date": cur_time.date()
})
re_path(r'^statistical/day_active/$', UserActiveCountView.as_view()),
四:日下单用户统计:
<一>: 从表入手:
# 日下单用户统计
class UserOrderCountView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
cur_time = timezone.localtime()
cur_time_0 = cur_time.replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
# 方案一:从表入手
orders = OrderInfo.objects.filter(
create_time__gt=cur_time_0
)
count = len(set(order.user for order in orders))
return Response({
"count": count,
"date": cur_time.date()
})
路由:
re_path(r'^statistical/day_orders/$', UserOrderCountView.as_view()),
<二>: 从主表入手:
class UserOrderCountView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
cur_time = timezone.localtime()
cur_time_0 = cur_time.replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
# 方案二: 从主表入手:
count = len(set(User.objects.filter(orders__create_time__gt=cur_time_0)))
return Response({
"count": count,
"date": cur_time.date()
})
五:月增用户统计:
描述:返回最近30天商品的访问统计:
1: 编辑apps/meiduo_admin/views/home_views.py
# 月新增用户统计
class UserMonthCountView(APIView):
def get(self, request):
end_time = timezone.localtime()
end_time_0 = end_time.replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
start_time = end_time - timedelta(days=29)
ret_list = list()
for index in range(30):
# 获取某天的0时刻时间
day_time_0 = start_time + timedelta(days=index)
# 获取某天的第二天0时刻时间
day_time_next_0 = day_time_0 + timedelta(days=1)
count = User.objects.filter(date_joined__gte=day_time_0, date_joined__lt=day_time_next_0).count()
ret_list.append({"count": count, "date": day_time_0.date()})
return Response(ret_list)
2:路由:
urlpatterns = [
# 5、月增用户统计
re_path(r'^statistical/month_increment/$', UserMonthCountView.as_view()),
]
六:日分类商品统计量:
1:定义模型类,迁移建表。
编辑apps/goods/models.py新增模型类记录分类商品访问量:
GoodsVisitCount : 分类商品的外键 + 分类商品的访问量
class GoodsVisitCount(BaseModel):
"""统计分类商品访问量模型类"""
category = models.ForeignKey(GoodsCategory, on_delete=models.CASCADE, verbose_name='商品分类')
count = models.IntegerField(verbose_name='访问量', default=0)
date = models.DateField(auto_now_add=True, verbose_name='统计日期')
class Meta:
db_table = 'tb_goods_visit'
verbose_name = '统计分类商品访问量'
verbose_name_plural = verbose_name
以上模型类,我们只需要定义在modes.py文件中就可以了,数据库表在goods.sql脚本中已经新建;所以我们无需重新迁移建表;
2:在浏览历史记录接口中补充代码实现记录分类商品访问量
也就是当前台用户浏览完一个商品后,后台需要统计sku商品分类的访问量。
编辑apps/users/views.py补充视图UserBrowseHistory中" 添加历史"视图函数代码
思路:如果当日的这个商品分类存在则使count 增加1 , 如果商品的分类不存在,新建商品分类,并初始化数量为 1。
# TODO:商品访问量的记录
cur_0_time = timezone.localtime().replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0)
try:
visit_obj = GoodsVisitCount.objects.get(
category_id=sku.category_id,
create_time__gte=cur_0_time
)
except GoodsVisitCount.DoesNotExist as e:
GoodsVisitCount.objects.create(
category_id=sku.category_id,
count=1
)
else:
visit_obj.count += 1
visit_obj.save()
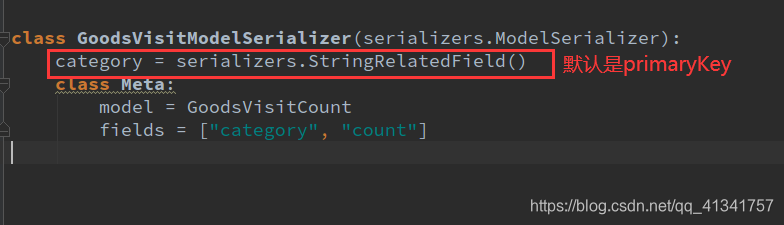
3:通过分析,将GoodsVisitCount里面的两个字段进行序列化,所以,还需要定义一个序列化器。
编辑apps/meiduo_admin/serializers/home_serializers.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from apps.goods.models import GoodsVisitCount
class GoodsVisitModelSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = GoodsVisitCount
fields = ["category", "count"]
4:编辑apps/meiduo_admin/serializers/home_serializers.py
# 获取访问量数据列表:
class GoodsDayView(ListAPIView):
# 能不能在视图中直接查找呢?不能,因为此时的cur_0_time是类属性,他是在程序执行的时候执行,所以
# 获取到的时间是服务器启动时的时间,而不是管理员用户查询的时间。
# cur_0_time = timezone.localtime().replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0)
# queryset = GoodsVisitCount.objects.filter(
# create_time__gte=cur_0_time
# )
# 如何解决? ---> 每次请求都需要执行get_queryset方法,所以只需要重写get_queryset方法就可以了。
queryset = GoodsVisitCount.objects.all()
serializer_class = GoodsVisitModelSerializer
def get_queryset(self):
cur_time = timezone.localtime()
cur_time_0 = cur_time.replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
return self.queryset.filter(
create_time__gte=cur_time_0
)
路由:
urlpatterns = [
# ......
# 6、日分类商品访问量统计
re_path(r'^statistical/goods_day_views/$', GoodsDayView.as_view()),
]
此时存在一个问题:
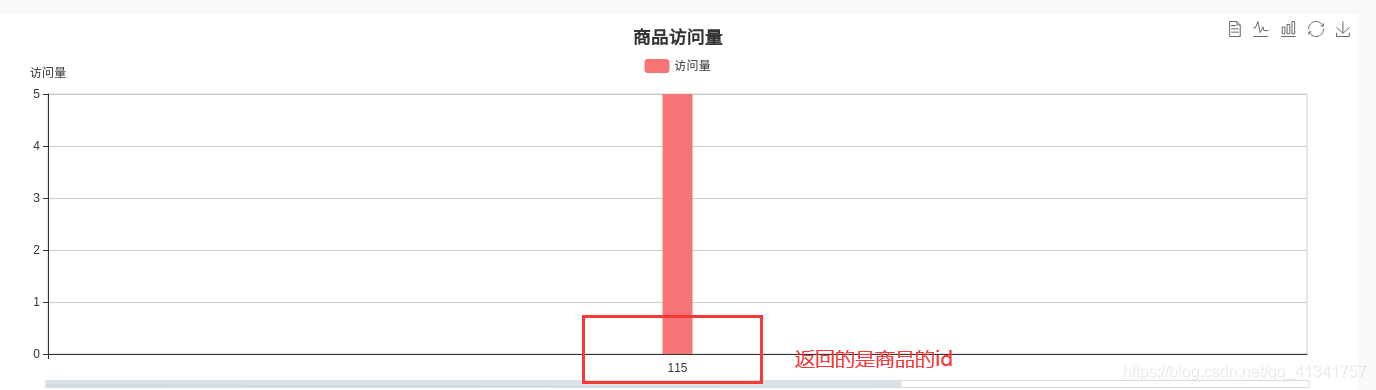
前端返回的是商品的id:返回id的原因是什么?如何修改???
原因:因为在序列化器中,对于外键我们默认使用的是PrimaryKeyRelatedField()。
解决方案:在序列化器中重写这个同名类属性,覆盖之前的PrimaryKeyRelatedField。
修改后:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号