wordpress:nginx负载均衡+nignweb服务器+mysql数据库+nfs-lsync+rsync备份
所有知识结合,注意正式环境慎用:
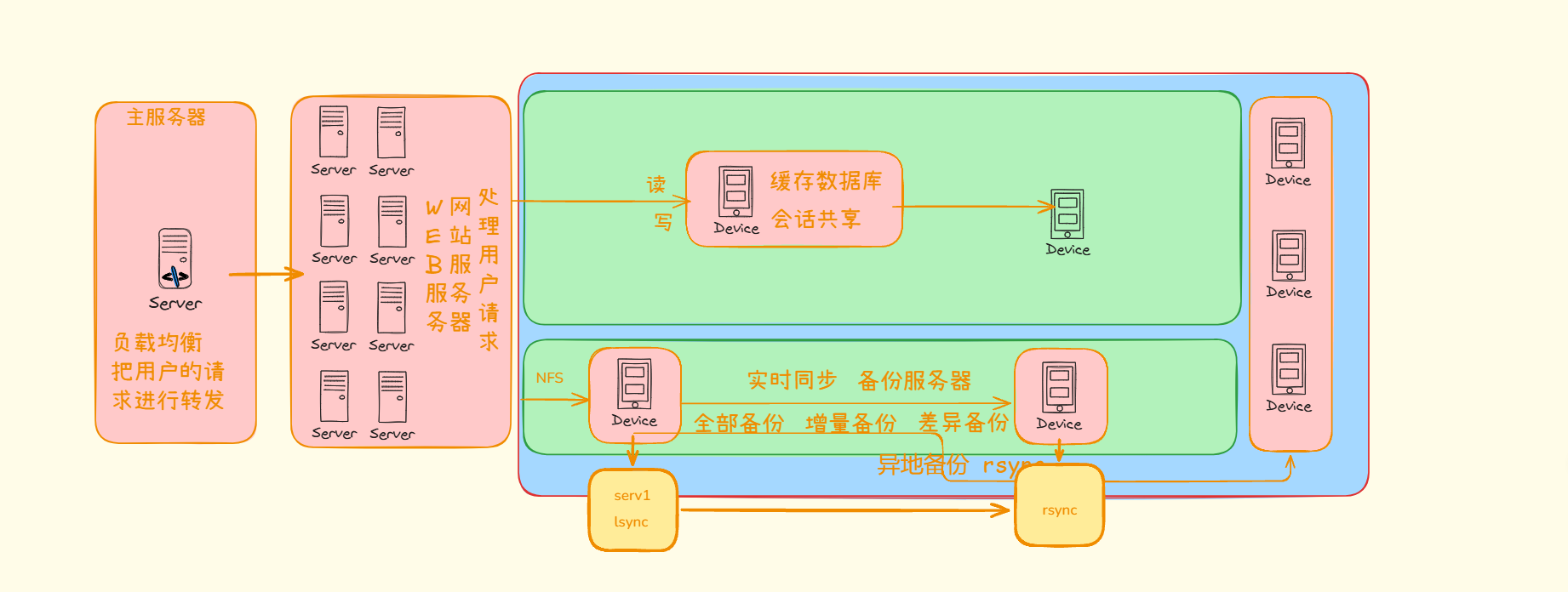
nginx负载均衡+nignweb服务器+mysql数据库+nfs-lsync+rsync备份
mariadb服务器
安装数据库
yum -y install mariadb-server启动数据库服务
systemctl enable mariadb systemctl start mariadb检查是否启动
ss -lntup | grep mysql ps -ef | grep mysql初始化数据库
mysql_secure_installation # 第一个回车,剩下的全部按Y,注意输入密码的时候不是Y,自定义登陆数据库
mysql -uroot -p[密码] # 或 mysql -rroot -p创建WordPress数据库
create database wordpress;查看是否创建成功
show databases;创建普通用户并赋予权限和密码,然后赋予本地登陆
grant all on wordpress.* to 'blog'@'localhost' identified by '1'; [数据库名] [创建的用户名] [是否本地登陆] [登陆的密码]创建普通用户并赋予权限和密码,然后赋予远程登陆,仅限远程172.16.1.0网段的用户远程登陆
grant all on wordpress.* to 'blog'@'172.16.1.%' identified by '1'; # 和上一步一样,上一步因为有了blog用户,则不再创建,所以这里生效的是有172.16.1.%这个语句本机测试是否可以本地登陆
mysql -ublog -p远程测试是都可以远程登陆,打开另一台在172.16.1.0网段的服务器,并安装数据库进行测试
# 这条语句在另外一台同网段的服务器测试,不是本机,注意!!! mysql -ublog -p -h 172.16.1.51本地测试和远程测试都成功则完成!
NFS服务器配置
NFS服务器配置
在 NFS 服务器上安装所需的 NFS 服务
yum install nfs-utils -y编辑
/etc/exports文件:/etc/exports文件用于指定哪些目录共享给哪些客户端以及如何共享vim /etc/exports # 写入以下内容 # [NFS本机共享的目录] [仅限远程服务器web01访问] /wordpress 172.16.1.7/24(rw,sync,no_root_squash) /wordpress 172.16.1.8/24(rw,sync,no_root_squash)启动NFS服务
systemctl start rpcbind systemctl enable rpcbind systemctl status rpcbind systemctl start nfs systemctl enable nfs systemctl reload nfs刷新共享目录,并查看
exportfs -ra exportfs -v rpcinfo -p showmount -e # 全部输入然后查看内容是否符合你的配置,查看是否成功web01服务器配置
安装NFS客户端服务工具
yum install nfs-utils -y挂载远程共享目录
mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/wordpress /mnt/wordpress永久挂载
vim /etc/fstab 172.16.1.31:/wordpress /mnt/wordpress nfs defaults 0 0检查是否挂载成功
df -h # 或者 mount | grep nfsweb02服务器配置
安装NFS客户端服务工具
yum install nfs-utils -y挂载远程共享目录
mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/wordpress /mnt/wordpress永久挂载
vim /etc/fstab 172.16.1.31:/wordpress /mnt/wordpress nfs defaults 0 0检查是否挂载成功
df -h # 或者 mount | grep nfs上传wordpress文件并解压到NFS服务器的/wordpress中
[root@web01-kylin ~]$ wget https://cn.wordpress.org/latest-zh_CN.zip [root@web01-kylin ~]$ mkdir ~/wordpress [root@web01-kylin ~]$ unzip latest-zh_CN.zip -d /~ # 因为解压是解压到wordpress文件夹中,所以“/”后不加内容即可 [root@web01-kylin ~]$ mv ~/wordpress/* /wordpress chown -R nobody.nobody /wordpress #[本机共享的目录]
web服务器配置
web01配置
安装nginx
yum install nginx写入配置文件
[root@web01-kylin ~]$ vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/blog.ren.wordpress.cn.conf server { listen 80; server_name blog.ren.wordpress.cn; root /mnt/wordpress; error_log /var/log/nginx/blog-error.log notice; access_log /var/log/nginx/blog-access.log main; location / { index index.php; } location ~ \.php$ { fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; } }检查语法是否正确
nginx -t启动服务以及开机自启
systemctl enable nginx systemctl start nginx systemctl status nginx检查是否安装了PHP
systemctl stop php-fpm yum -y remove php* # 没有输出或者是没有服务是对的安装PHP
yum -y install php php-bcmath php-cli php-common php-devel php-embedded php-fpm php-gd php-intl php-mbstring php-mysqlnd php-opcache php-pdo php-process php-xml php-json设置开机自启和开启服务
systemctl enable --now php-fpm systemctl start php-fpm ps -ef | grep php ss -lntup | grep php检查服务进程是否开启
ps -ef | grep php ss -lntup | grep php修改配置文件进程用户,apache ---> nginx
vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf 24:user = apache 26:group = apache 38:listen = /run/php-fpm/www.sock # 改为 user = nginx group = nginx listen = 127.0.0.1:9000检查语法
php-fpm -t重启服务,重新读取配置文件
systemctl reload php-fpm ps -ef | grep php ss -lntup | grep php # 检查进程服务是否更改web02服务器配置
和web01一模一样,什么都不变,一模一样来一遍!!!
最后在Windows中,修改hosts文件,然后登陆一下,是否能进入wordpress,如果进入什么都不要做,关掉继续下一步
Nginx负载均衡
目前就一天负载均衡,所以这里就配一台
安装nginx
yum install nginx写入配置文件
[root@lb01-kylin ~]$ vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/blog.ren.wordpress.cn.conf upstream lb_pools { server 10.0.0.7:80; server 10.0.0.8:80; } server { listen 80; server_name blog.ren.wordpress.cn; location / { proxy_pass http://lb_pools; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Real-Ip $remote_addr; } }检查语法错误
nginx -t重启服务以及开机自启
systemctl enable nginx systemctl start nginx systemctl reload nginx systemctl status nginx在Windows上测试能否登陆,注意在hosts文件中写入域名,进入浏览器进行测试,如果测试成功推出进行下一步
10.0.0.5 blog.ren.wordpress.cn
backup备份服务器配置rsync
先配置rsync
检查安装rsync
# 检查是否有rsync rpm -qa |grep rsync # 安装rsync yum install rsync # 查看版本 rsync -V编辑配置文件
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf uid=root gid=root max connections=10 log file=/var/log/rsyncd.log pid file=/var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file=/var/run/rsyncd.lock hosts allow = 172.16.1.31 #---> 这里写的是NFS服务器的IP地址 [syncdata] comment=backup data path=/s1/bak read only=no ignore errors auth users=wordpress secrets file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd配置密码文件
vim /etc/rsyncd.passwd wordpress:1 [暗号] [密码]赋予密码文件600权限
chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.passwd启动rsync
systemctl start rsyncd # 或者使用 rsync --daemon --config=/etc/rsyncd.conf检查是否启动
systemctl status rsync # 注意这里容易failed,只要不是dead就行,先别管,如果是running更好检查服务进程是否启动
ps -ef |grep rsync
NFS服务器安装lsync进行实时同步
NFS服务器目前已经安装了NFS共享目录服务,检查对应的/wordpress是否存在,检查web01和web02上的磁盘是否挂载正确,是否三端能够同步进行读写文件,使用touch命令进行尝试
安装lsyncd软件
yum install -y lsyncd检查安装的版本
lsyncd -version配置同步策略
vim /etc/lsyncd.conf --全局部分主要配置lsyncd服务,日志,pid文件. settings { --日志文件,主要查看日志文件. logfile = "/var/log/lsyncd.log", --这是pid文件 pidfile = "/var/run/lsyncd.pid", --服务状态文件 statusFile = "/var/log/lsyncd.status", --改为非守护进程模式,默认.rsync命令,lsyncd nodaemon = true, --控制最多用于传输数据的进程数量 rsync进程数(最大) --根据cpu核心数来 一致或2倍 maxProcesses = 2 } --配置rsync命令,rsync服务端与客户端模式 --sync部分可以有多个. sync { --指定rsync工作模式 default.rsync, --指定lsyncd监控目录,源目录 source = "/wordpress", -------------------------> 注意这里需要监控的目录是哪个 --指定目标 rsync服务端 用户名@ip地址::模块名字 target = "wordpress@172.16.1.41::wordpress", ----> 注意这里的写法 [暗号]@[backupIP][模块] --每隔5秒同步一次. delay = 5, --这是rsync命令的 --delete 选项 delete = true, -- 配置rsync命令位置,rsync命令选项, rsync = { -- 命令位置 binary = "/usr/bin/rsync", ------------> 使用which rsync查看一下命令是否是这个位置 -- rsync命令的 -a选项 archive = true, -- rsync命令的 -z选项 压缩 compress = true, -- 配置rsync--password-file密码文件 password_file = "/etc/rsync.client" -------------------> 密码文件路径要记住!!! } }写入密码
vim /etc/rsync.client 1给予密码文件600的权限
chmod 600 /etc/rsync.client启动服务
systemctl enable lsyncd systemctl start lsyncd systemctl status lsyncd
有错误麻烦评论,看到立马更改
注意正式环境慎用



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号