#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<windows.h>
#define N 80
void print_text(int line,int col,char text[]);
void print_spaces(int n);
void print_blank_lines(int n);
int main(){
int line,col,i;
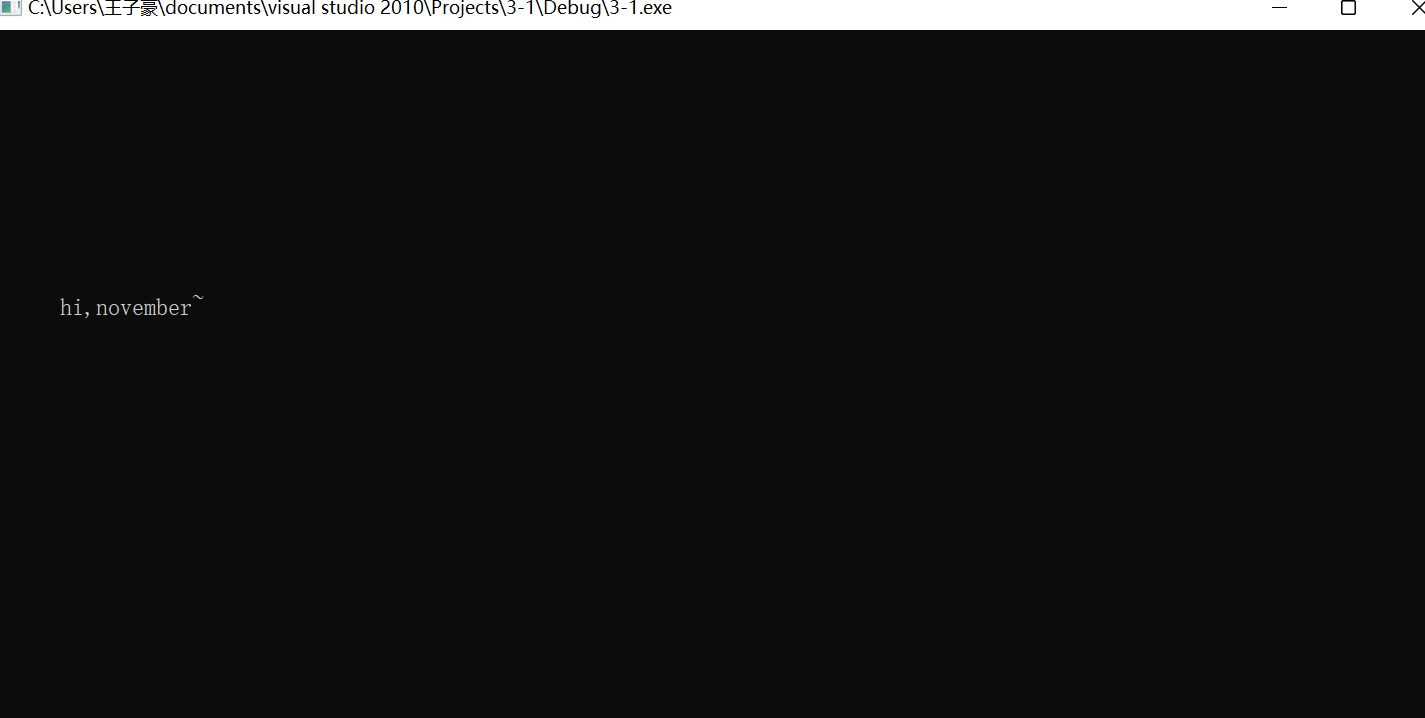
char text[N]="hi,november~";
srand(time(0));
for(i=1;i<=10;i++){
line=rand()%25;
col=rand()%80;
print_text(line,col,text);
Sleep(1000);
}return 0;
}
void print_spaces(int n)
{int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
printf(" ");
}
void print_blank_lines(int n)
{int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
printf("\n");}
void print_text(int line,int col,char text[]){
print_blank_lines(line-1);
print_spaces(col-1);
printf("%s",text);}
![]()
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
long long fac(int n);
int main(){
int i,n;
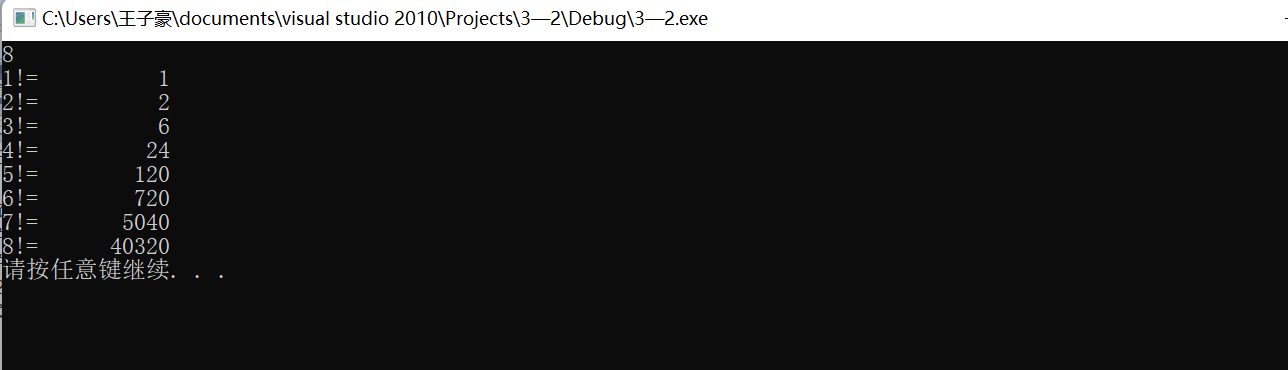
scanf_s("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d!=%11d\n",i,fac(i));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
long long fac(int n){
static long long p=1;
p=p*n;
return p;
}
![]()
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
long fanc(int n);
int main() {
int n;
long ans;
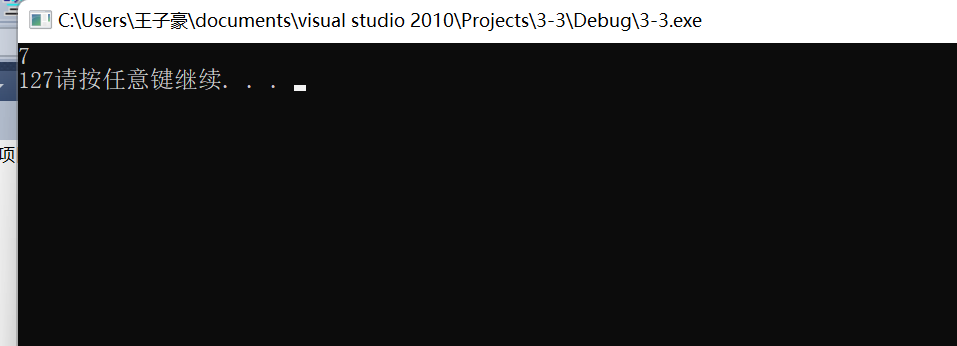
scanf_s("%d",&n);
ans = fanc(n);
printf("%d", ans);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
long fanc(int n) {
long sum = 0;
if (n == 1)
sum = 1;
else
sum = 2 * fanc(n-1)+1;
return sum;
}
![]()
#include <stdio.h>
int func(int n, int m);
int main() {
int n, m;
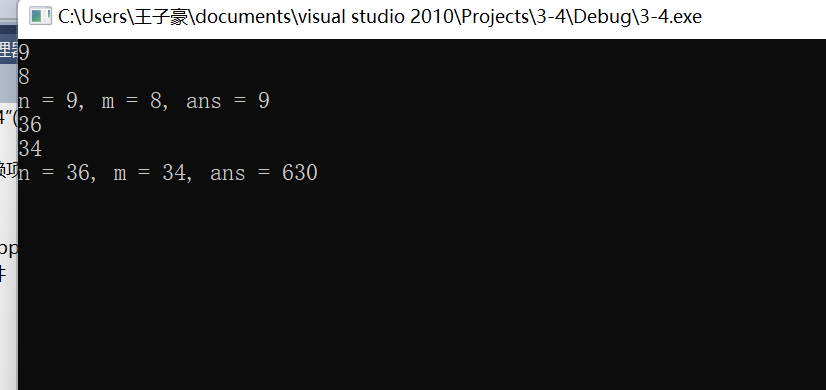
while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF)
printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n", n, m, func(n, m));
return 0;
}
int func(int n,int m){
int ans;
if(n<m)
ans=0;
else{if(n==m)
ans=1;
else
{if(m==1)
ans=n;
else
ans=func(n-1,m)+func(n-1,m-1);}}
return ans;}
![]()
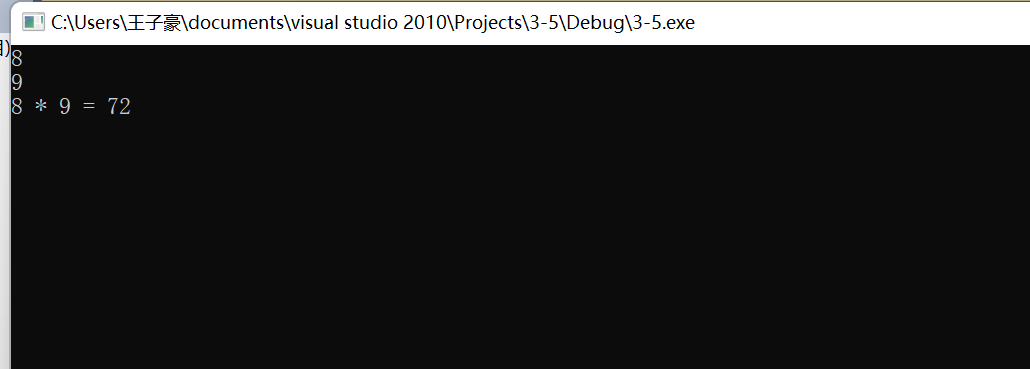
#include<stdlib.h>
int mul(int n, int m);
int main() {
int n, m;
while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF)
printf("%d * %d = %d\n", n, m, mul(n, m));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int mul(int n,int m){
int sum;
if(m>0){
if(m==1)
sum=n;
else
sum=n+mul(n,m-1);}
else
if(m==-1)
sum=-n;
else
sum=-n+mul(n,m+1);
return sum;}
![]()
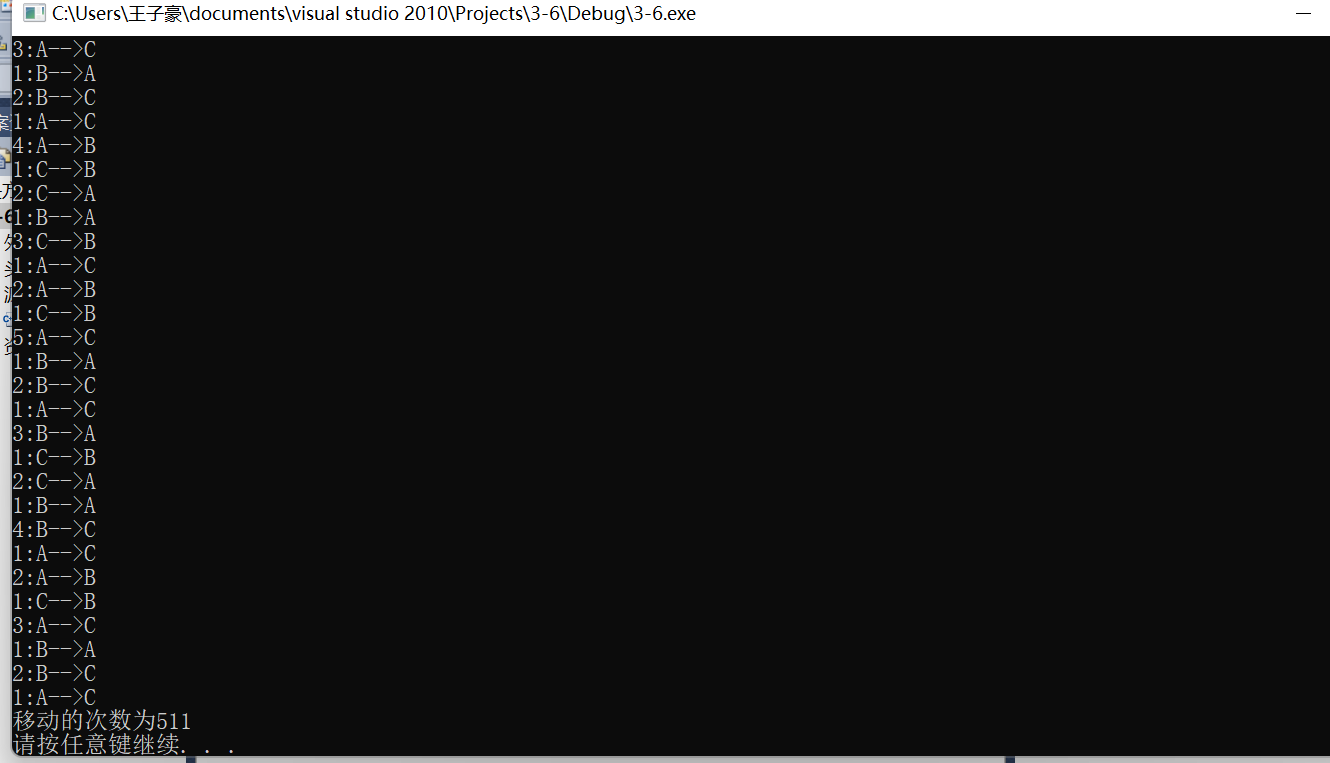
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void hanoi(unsigned int n, char from, char temp, char to);
void moveplate(unsigned int n, char from, char to);
int s;
int main()
{
unsigned int n;
scanf_s("%u", &n);
hanoi(n, 'A', 'B', 'C');
printf("移动的次数为%d\n", s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void hanoi(unsigned int n, char from, char temp, char to)
{
if (n == 1)
{
moveplate(n, from, to); s++;
}
else
{
hanoi(n - 1, from, to, temp);
moveplate(n, from, to); s++;
hanoi(n - 1, temp, from, to);
}
}
void moveplate(unsigned int n, char from, char to)
{
printf("%u:%c-->%c\n", n, from, to);
}
![]()
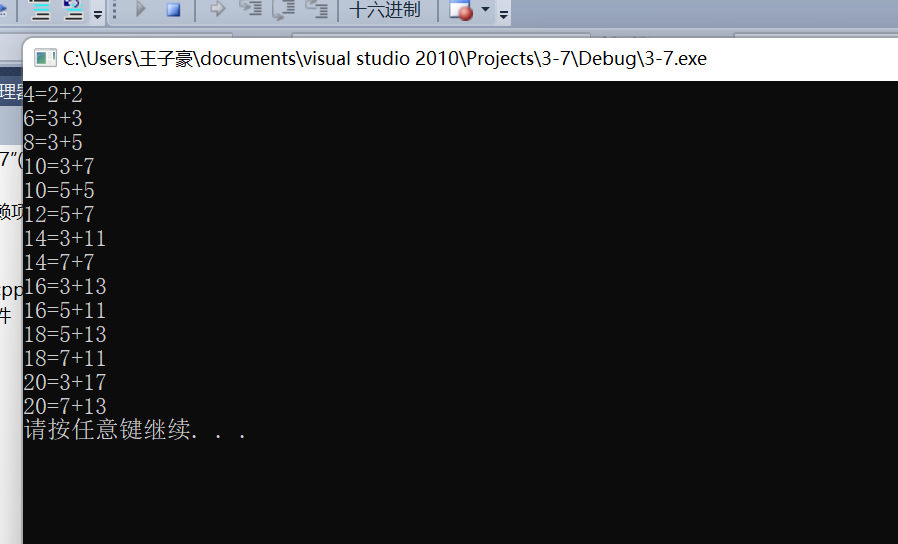
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int prime(int n){
int i,f=1;
for(i=2;i<n;i++)
if(n%i==0)
f=0;
return f;}
int main(){
int a[19];
int i,co=0,m,n;
for(i=2;i<=20;i++)
if(prime(i))
{a[co]=i;
co++;}
for(i=2;i<=10;i++)
for(m=0;m<=co/2;m++)
for(n=m;n<=co;n++)
if(2*i==a[m]+a[n]){
printf("%d=%d+%d\n",2*i,a[m],a[n]);
break;}
system("pause");
return 0;}
![]()
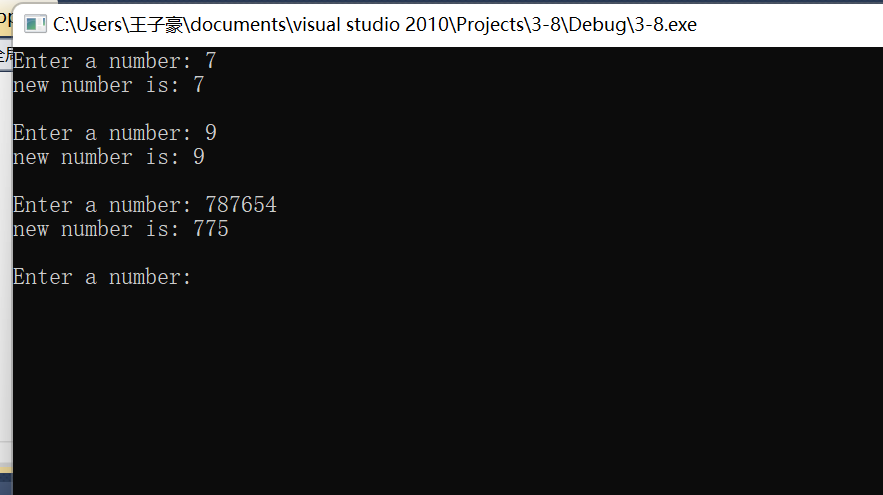
#include <stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
long fun(long s); // 函数声明
int main() {
long s, t;
printf("Enter a number: ");
while (scanf("%ld", &s) != EOF) {
t = fun(s); // 函数调用
printf("new number is: %ld\n\n", t);
printf("Enter a number: ");
}
return 0;
}
long fun(long s){
int t=0,co=0,x;
while(s){
if(s%2)
{t=t+pow(10.0,co)*(s-s/10*10);
co++;}
s=s/10;
}
return t;}
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号