2.3搜索与图论

1.dfs
n皇后问题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
int n;
char g[N][N];
int col[N] , dg[N] , udg[N];//列,正对角线,斜对角线
void dfs(int u){
if(u==n){
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) puts(g[i]);
puts("");
return;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
if(!col[i] and !dg[i-u+n] and !udg[i+u]){//u是x , i是y
g[u][i] = 'Q';
col[i] = dg[i-u+n] = udg[i+u] = 1;
dfs(u+1);
col[i] = dg[i-u+n] = udg[i+u] = 0;
g[u][i] = '.';//恢复现场
}
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d" , &n);
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < n ; j++){
g[i][j] = '.';
}
}
dfs(0);
return 0;
}还有更为通用的办法,但是慢很多
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
int n;
char g[N][N];
int row[N] , col[N], dg[N] , udg[N];
void dfs(int x , int y , int k){
if(y>=n) y = 0 , x++;
if(x==n){
if(k==n){
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) puts(g[i]);
puts("");
}
return;
}//注意return顺序
//不放皇后
dfs(x,y+1,k);
//放皇后
if(!row[x] and !col[y] and !dg[n+y-x] and !udg[x+y]){
g[x][y] = 'Q';
row[x] = col[y] = dg[n+y-x] = udg[x+y] = 1;
dfs(x,y+1,k+1);
row[x] = col[y] = dg[n+y-x] = udg[x+y] = 0;
g[x][y] = '.';
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d" , &n);
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < n ; j++){
g[i][j] = '.';
}
}
dfs(0 ,0 , 0);
return 0;
}2.BFS 解所有边的权重相同的最短路问题
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
int n , m;
int g[N][N] , d[N][N];//g存原图,d存每个点至起点的距离
int bfs(){
queue<PII> q;
memset(d,-1,sizeof d);
d[0][0] = 0;
q.push({0,0});
int dx[] = {-1,0,1,0} , dy[] = {0,1,0,-1};
while(!q.empty()){
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
int x = t.first+dx[i] , y = t.second+dy[i];
if(x>=0 and x<n and y>=0 and y<m and g[x][y]==0 and d[x][y]==-1){
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second]+1;
q.push({x,y});
}
}
}
return d[n-1][m-1];
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
cin>>g[i][j];
}
}
cout<<bfs()<<endl;
return 0;
}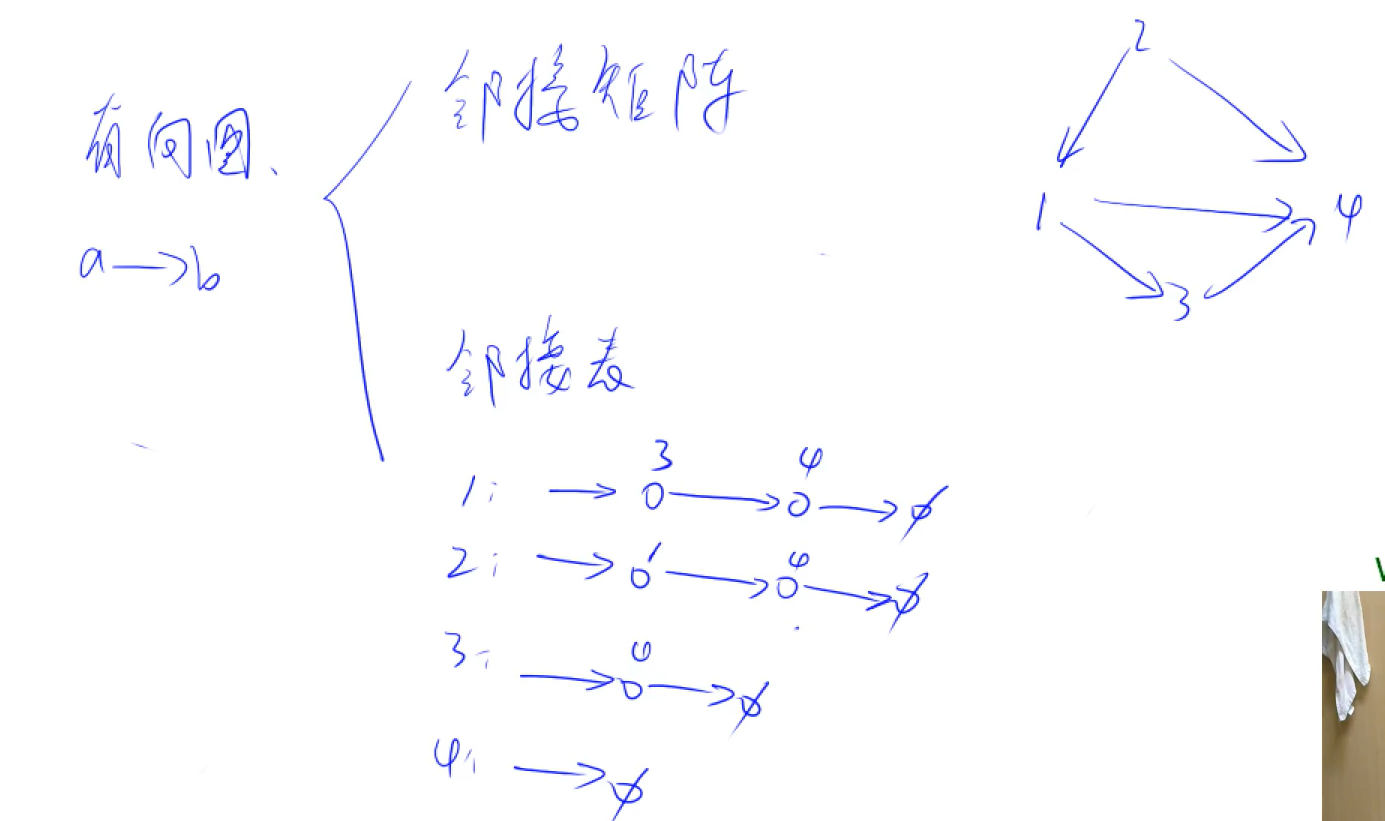
八数码问题
就是数字版华容道,先用string储存原始状态,用queue<string>创队列,用unordered_map<string,int>储存每个状态以及其用的步数,用t表示弹出的队头,用k表示队头状态中x所在的位置,用dx[]、dy[]表示上下左右移动,用swap交换x与所要移动的数字,如果unordered_map中没有新得到的这个状态,就将此状态加入队伍与哈希表
//https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/847/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int bfs(string start)
{
string end = "12345678x";
queue<string> q;
unordered_map<string , int> p;
q.push(start);
p[start] = 0;
int dx[] = {-1, 0 , 1 , 0} , dy[] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1};
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();//取出队头
q.pop();
int distance = p[t];
if(t==end) return distance;
int k = t.find('x');//找出x所在位置
int x = k/3 , y = k%3;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++)
{
int a = x + dx[i] , b = y + dy[i];
if(a >= 0 and a < 3 and b >= 0 and b < 3)
{
swap(t[k] , t[a*3+b]);
if(!p.count(t))
{
q.push(t);
p[t] = distance +1 ;
}
swap(t[k] , t[a*3+b]);//还原现场
}
}
}
return -1;//没有找到与end相同的结果,返回-1
}
int main()
{
string start;//记录初始数据
for(int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++)
{
char c;
cin>>c;
start+=c;
}
cout << bfs(start) << endl;
return 0;
}(最近听了郝斌老师的C语言教程,尝试把代码写的规范一点,虽然还是不太规范)
3.图或者表的dfs搜索

//https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/848/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10 , M = 2*N;
int n;
int h[N] , e[M] , ne[M] , idx;
bool st[N];
int ans = N;//最终答案,即去掉重心剩下的最少的点数
void add(int a , int b){
e[idx] = b , ne[idx] = h[a] , h[a] = idx++;
}
int dfs(int u){
int sum = 1 , res = 0;//sum是以u点为根节点的点数和,res是删掉u后最大的可以连接的节点数
st[u] = true;//标记一下u点已经搜过了
for(int i = h[u] ; i!=-1 ; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j]){//如果没有被搜过
int s = dfs(j);
res = max(res , s);//删掉某个点A后最大的可以连接的点数就是以该A点直接连接的某点B为根的点数和(1)
sum+=s;
}
}
res = max(res , n - sum);//(1)或者n-该点数和
ans = min(ans , res);
return sum;
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
memset(h , -1 , sizeof h);//让表头指向-1
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
int a , b;
cin>>a>>b;
add(a,b);
add(b,a);//没有箭头,所以加双向箭头
}
dfs(1);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}4.图的宽搜最经典的应用就是拓扑序列
拓扑序列针对的是有向图,对于拓扑序列当我们把其中的点排列好后,其所有边都是从前指到后的(拓扑序列不会有环,有向无环图也被称为拓扑图,如果一个图存在环,则环上的所有点都进不了拓扑序列)。
拓扑图每个点都有入度及出度,就是指向该点的点的数量、该点指向的点的数量

#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n , m;
int h[N] , e[N] , ne[N] , idx;
int q[N] , d[N];
void add(int a , int b){
e[idx] = b , ne[idx] = h[a] , h[a] = idx++;
}
bool topsort(){
int hh = 0 , tt = -1;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++){
if(d[i]==0) q[++tt] = i;
}
while(hh<=tt){
int t = q[hh++];//取出队头
for(int i = h[t] ; i!=-1 ; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
d[j]--;
if(d[j]==0) q[++tt] = j;
}
}
return tt+1==n;//判断是否所有元素入队
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
memset(h , -1 , sizeof h);
while(m--){
int a, b;
cin>>a>>b;
add(a,b);
d[b]++;
}
if(topsort()){
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) printf("%d " , q[i]);
}
else puts("-1");
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号