Spark(七)Dataset与DataFrame的类型安全性
原文链接:
https://blog.knoldus.com/spark-type-safety-in-dataset-vs-dataframe/
基于类型安全特性,编程语言可以避免类型错误,或者说编译器会在编译时检查类型安全然后在遇到错误的类型赋值时会抛出错误。Spark,一个为大数据处理为生的统一的分析引擎提供了两个有用且易用的API,它们是DataFrame和Dataset,它们直观地并且有表达力以提高了开发者的效率。这两个API最主要的区别就是Dataset是类型安全的而DataFrame不是类型安全的。
在这篇博文里,我们会看到为什么DataFrame不是类型安全的而Dataset API是类型安全的。我们将会看到这个区别在三个上下文中是如何影响spark应用开发者的:
- 当在filter和map函数中使用lambda表达式;
- 查询不存在的列;
- DataFrames and Datasets在转化回RDD后是否保留schema。
为什么Dataframe不是类型安全的, 而Dataset确实类型安全的
从Apache Spark 2.0开始,这两组API已经被统一然后Dataframe被称为Dataset
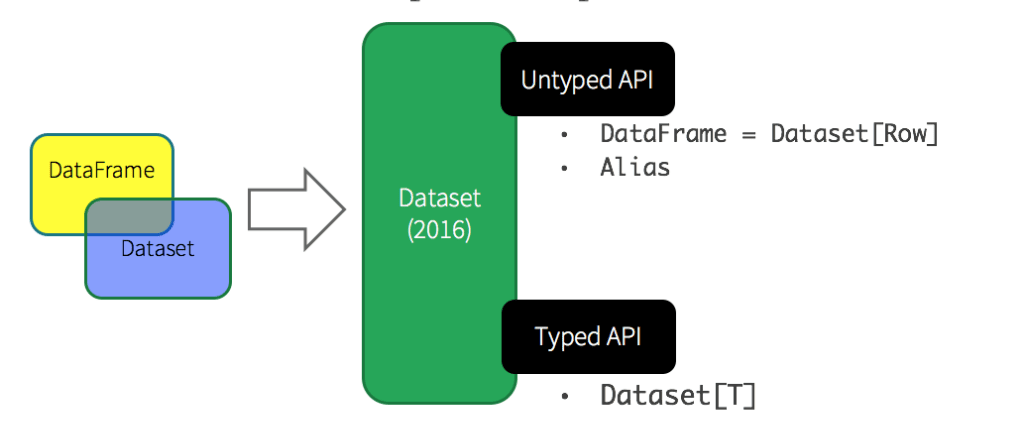
Spark是在运行时检查DataFrame的类型的,比如这篇文章。因为DataFrame是Row的集合,Row是一个通用的类型,编译无法将它理解成一个我们想要的强类型。
相反,Dataset是强类型的集合,它能在编译时就能检查出类型是否出错。
现在,让我们看看类型安全性是如何影响spark应用开发者,当他们应用lambda表达式于filter和map函数,查询不存在的列以及两组API转换回RDD后是否会保留schema。
case class Employ(name: String, age: Int, id: Int, department: String)
Created a case class Employ with attributes name, age, id, and department. Now create sample employ data.
val empData = Seq(Employ("A", 24, 132, "HR"), Employ("B", 26, 131, "Engineering"), Employ("C", 25, 135, "Data Science"))
Let’s create a RDD from empData.
val empRDD = spark.sparkContext.makeRDD(empData)
Now, Let’s create DataFrame and Dataset from the RDD.
val empDataFrame = empRDD.toDf()
empDataFrame: org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame = [name: string, age: int ... 2 more fields]
val empDataset = empRDD.toDS()
empDataset: org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset[Employ] = [name: string, age: int ... 2 more fields]
we are now ready with DataFrame and Dataset so, let’s see the different scenario’s a spark developer faces while using these two API’s.
Applying lambda function on DataFrame and Dataset
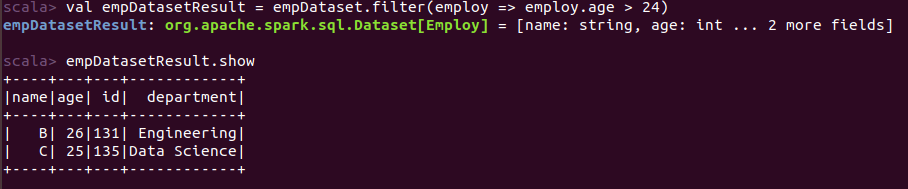
val empDatasetResult = empDataset.filter(employ => employ.age > 24)
Above, we have just filter employ Dataset with age greater than 24. See the output, it work fine.
Let’s see how DataFrame reacts when applying lambda function on it.
val empDataFrameResult = empDataFrame.filter(employ => employ.age > 24)
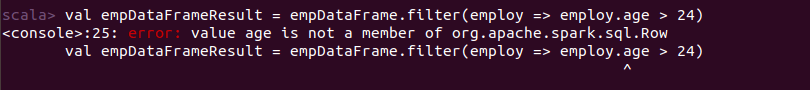
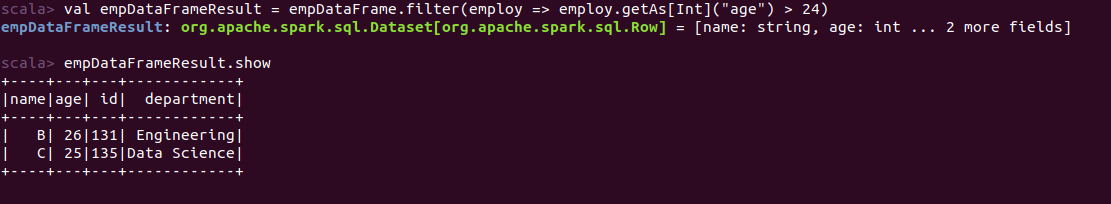
Oops! we get an error, value is not a member of Row object. In the case of DataFrame when we apply lambda function it returns a Row object and to access column value from Row object we need to typecast out there, simply giving column name won’t allow us to access column value out there. But we can access column value by lambda function and in the case of DataFrame need a change in code something like:
val empDataFrameResult = empDataFrame.filter(employ => employ.getAs[Int]("age") > 24)
Querying on non existing column
Now, let’s see how DataFrame and Dataset behave differently when querying on non-existing column.
Let’s query on a salary column which is not present in DataFrame.
val empDataFrameResult1 = empDataFrame.select("salary")
org.apache.spark.sql.AnalysisException: cannot resolve '`salary`' given input columns: [age, department, id, name];;
'Project ['salary]
And we will get a Runtime error, salary cannot be resolve in given input columns: [age, department, id, name] and thrown AnalysisException.
In the case of Dataset we have the opportunity to get that error in compile time itself.
val empDatasetResult1 = empDataset.map(employ => employ.salary)
<console>:25: error: value salary is not a member of Employ
val empDatasetResult1 = empDataset.map(employ => employ.salary)
^
It throws a compile time error, value salary is not a member of Employ.
Preserving schema or not when converted back to RDD
Now let’s have a look whether DataFrame and Dataset Preserve schema when converted back to RDD.
Let’s Create RDD from the DataFrame
val rddFromDataFrame = empDataFrame.rdd
rddFromDataFrame: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[org.apache.spark.sql.Row] = MapPartitionsRDD[11] at rdd at <console>:25
It returns a Row of RDD and if we try to do any normal operation on RDD we should not be able to do it in a normal way for instance,
rddFromDataFrame.map(employ => employ.name).foreach(println)
<console>:26: error: value name is not a member of org.apache.spark.sql.Row
It gives an error, value name is not a member of Row object. So, in this case DataFrame couldn’t preserve schema.
Now let’s see what happen when we do same thing with Dataset.
val rddFromDataset = empDataset.rdd
rddFromDataset: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Employ] = MapPartitionsRDD[14] at rdd at <console>:25
It returns RDD of Employ so, in this case we should be able to do normal RDD operations on that RDD.
rddFromDataset.map(employ => employ.name).foreach(println)
We will get output:
A
B
C
So, Dataset will preserve schema when converting back to RDD.
Happy Reading !!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号