能力全面提升综合题单-练习
Part1
语言基础题
P1089 [NOIP 2004 提高组] 津津的储蓄计划
import java.util.Scanner;
// P1089 [NOIP 2004 提高组] 津津的储蓄计划
public class P1089 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] budget = new int[12];
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
budget[i] = in.nextInt();
}
int money = 0;
int bank_money = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
money += 300;
if (money >= budget[i]) {
money -= budget[i];
int save_money = money / 100 * 100;
money -= save_money;
bank_money += save_money;
} else {
System.out.printf("-%d", i + 1);
return;
}
}
System.out.println((int) (bank_money * 1.2 + money));
}
}
关于文件读取:
使用 Reader 的子类 BufferedReader (读取大文件)
int[] budget = new int[12];
File file = new File("src/input.txt");
try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))) {
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
budget[i]= Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
};
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
System.out.println(budget[i]);
}
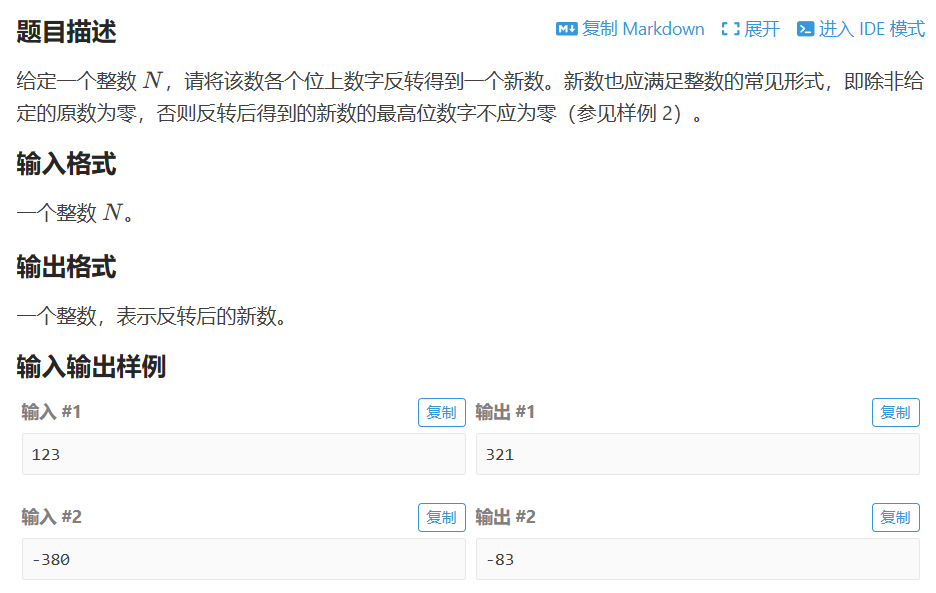
P1307 [NOIP 2011 普及组] 数字反转
使用 StringBuilder的reverse
然后
1.判断正负,负号拿掉
2.反转
3.找到 firstNonZero 第一个非负数字的索引
4.截取,只要后半段
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
// P1307 [NOIP 2011 普及组] 数字反转
public class P1307 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
boolean negative = sb.charAt(0) == '-';
if (negative) {
sb = sb.deleteCharAt(0);
}
sb = sb.reverse();
// 去除前导0
int firstNonZero = 0; // 第一个非零数字的索引
while (sb.charAt(firstNonZero) == '0' && firstNonZero < sb.length()) {
firstNonZero++;
}
String out;
if (negative) {
out = "-" + sb.substring(firstNonZero);
} else {
out = sb.substring(firstNonZero);
}
System.out.println(out);
}
}
数组
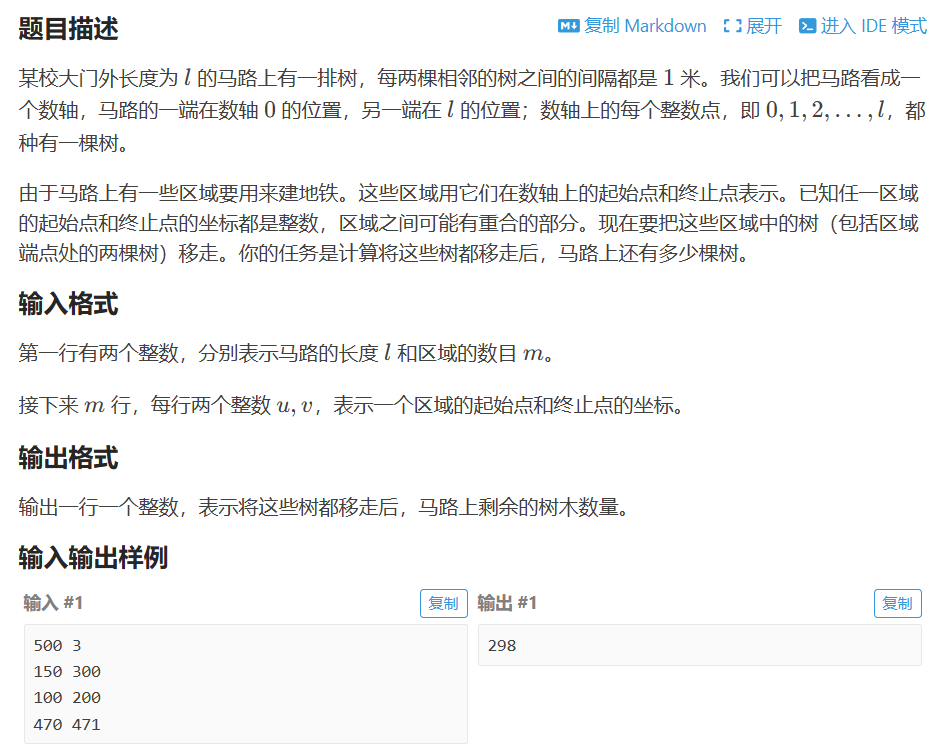
P1047 [NOIP 2005 普及组] 校门外的树
正常做法(通过70%)(注意最后结果 +1,因为 0 到 l 有 l+1 个树):
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int l = scanner.nextInt();
int[] map = new int[l];
Arrays.fill(map,1); // 1 tree; 0 not tree
int m = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int left = scanner.nextInt();
int right = scanner.nextInt();
for (int j = left; j <= right; j++) {
map[j]=0;
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
res+=map[i];
}
System.out.println(res+1);
}
优化(多个区间操作 -> 差分数组)
差分数组 和 前缀和 是一对互逆运算:
- 前缀和:用于快速 计算 某个范围
[L, R]内的和 - 差分数组:用于快速 修改 某个范围
[L, R]内的值




public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int l = scanner.nextInt();
int[] map = new int[l+1];
int[] d = new int[l+2]; // 差分数组 防止 d[right+1] 溢出
Arrays.fill(map,1); // 1 tree; 0 not tree
int m = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int left = scanner.nextInt();
int right = scanner.nextInt();
d[left]-=1;
d[right+1]+=1;
}
// 计算前缀和
map[0] = map[0] + d[0];
for (int i = 1; i <= l; i++) {
map[i]=map[i-1]+d[i];
}
// 统计
int res =0;
for (int i = 0; i <= l; i++) {
if (map[i]>0)
res++;
}
System.out.println(res);
}
P2141 [NOIP 2014 普及组] 珠心算测验
注意读题,是 有多少个数 在前
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
int[] nums = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
nums[i] = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
hashSet.add(nums[i] + nums[j]);
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (hashSet.contains(nums[i])) res++;
}
System.out.println(res);
}
字符串
P1055 [NOIP 2008 普及组] ISBN 号码

public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String string = scanner.nextLine(); // 0-670-82162-0
String[] strings = string.split("-"); // 0 670 82162 0
String concat = strings[0].concat(strings[1]).concat(strings[2]); // 0670821620
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
Integer num = concat.charAt(i) - '0'; // 字符数字转为数字
sum += num * (i + 1);
}
sum = sum % 11;
// 校验位 需要判断X
int check = Objects.equals(strings[3], "X") ? 10 : Integer.parseInt(strings[3]);
if (sum == check) {
System.out.println("Right");
} else {
// 拼接
String newString = null;
if (sum == 10) {
newString = strings[0] + "-" + strings[1] + "-" + strings[2] + "-X";
} else {
newString = strings[0] + "-" + strings[1] + "-" + strings[2] + "-" + sum;
}
System.out.println(newString);
}
}
基础算法
模拟
P1003 [NOIP 2011 提高组] 铺地毯
存放所有的地毯坐标 -> 内存超出
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); // key坐标 value地毯编号
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
int g = scanner.nextInt();
int k = scanner.nextInt();
hashMap = updateMap(hashMap, a, b, a + g - 1, b + k - 1, i + 1);
}
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int y = scanner.nextInt();
if (hashMap.containsKey(x + "," + y)) {
System.out.println(hashMap.get(x + "," + y));
} else {
System.out.println(-1);
}
}
private static HashMap<String, Integer> updateMap(HashMap<String, Integer> map, int x, int y, int x2, int y2, int carpet) {
for (int i = x; i <= x2; i++) {
for (int j = y; j <= y2; j++) {
map.put(i + "," + j, carpet);
}
}
return map;
}
不存坐标,而是直接存地毯对象
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static class Carpet {
int x, y, width, height, id;
Carpet(int x, int y, int width, int height, int id) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.id = id;
}
boolean covers(int px, int py) {
return px >= x && px < x + width && py >= y && py < y + height;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
List<Carpet> carpets = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
int g = scanner.nextInt();
int k = scanner.nextInt();
carpets.add(new Carpet(a, b, g, k, i + 1)); // 存储地毯的范围信息
}
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int y = scanner.nextInt();
// 从后往前遍历,找到最上面的地毯
for (int i = carpets.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (carpets.get(i).covers(x, y)) {
System.out.println(carpets.get(i).id);
return;
}
}
System.out.println(-1); // 没有地毯覆盖 (x, y)
}
}
二分答案
二分答案适用:有序 很多可行解中寻求最优解
二分查找的核心思想就是在大量可行解中,通过一个具有单调性(或单调趋势)的判断函数,快速缩小搜索范围,从而找到最优解
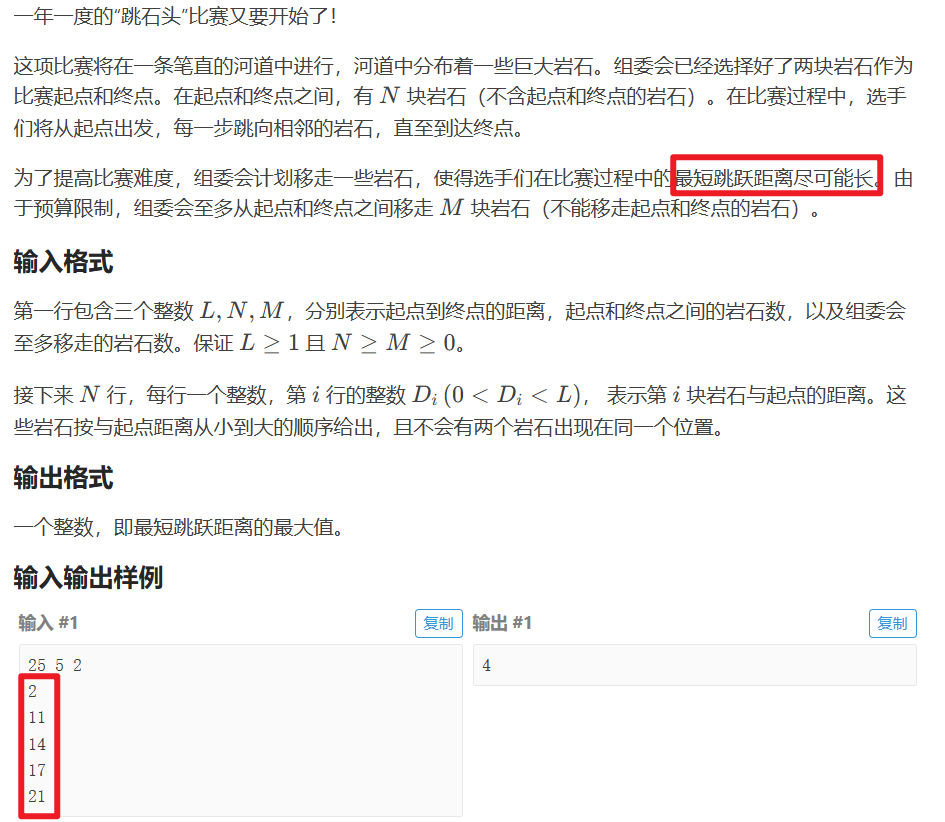
例如,在跳石头问题中,我们通过判断函数验证某个候选最小跳跃距离是否可行,再根据判断结果调整搜索区间,最终确定最大的最小跳跃距离。这种方法在很多问题中都适用,只要能证明随着候选值变化,问题的可行性也呈现出单调性趋势,就可以用二分查找来求最优解。
P2678 [NOIP 2015 提高组] 跳石头
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P2678_stoneJump {
// 全局变量:l 表示河流总长度,n 表示中间石头数量,m 表示允许移除的石头数量
static int l;
static int n;
static int m;
// 数组 map 用于存放所有石头的位置(包括起点和终点),大小足够大
static int[] map = new int[50001];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 读入河流总长度、石头数量(不含起点和终点)以及允许移除的石头数
l = scanner.nextInt();
n = scanner.nextInt();
m = scanner.nextInt();
// 读入中间石头的位置,存入 map 数组,索引从 1 开始
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
map[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// 将起点(位置0)加入数组
map[0] = 0;
// 将终点(位置 l)加入数组
map[n + 1] = l;
// 更新石头总数:原来的 n 个中间石头加上起点和终点
n += 2;
// 如果输入的石头位置没有保证有序,需要对 map 数组进行排序
// Arrays.sort(map, 0, n);
// 二分查找的初始左右边界
int left = 1; // 最小可能的跳跃距离为 1
int right = l; // 最大可能的跳跃距离为河流总长 l
int ans = -1; // 用于记录满足条件的最大最小跳跃距离
// 二分查找过程:当 left <= right 时持续查找
while (left <= right) {
// 计算当前候选的最小跳跃距离 mid,采用防止溢出的方法
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 调用 judge 函数判断当最小跳跃距离为 mid 时,能否在不超过 m 次移除石头的条件下完成跳跃
if (judge(mid)) {
// 如果可行,则记录 mid 作为当前答案,并尝试更大距离
ans = mid;
left = mid + 1;
} else {
// 如果不可行,则减小候选范围
right = mid - 1;
}
}
// 输出最终得到的最大最小跳跃距离
System.out.println(ans);
}
// judge 函数判断候选最小跳跃距离 x 是否可行
// 贪心思想:从起点开始,若相邻两个保留石头之间距离小于 x,则移除当前石头
// 最后统计需要移除的石头数是否不超过允许的 m 个
private static boolean judge(int x) {
int count = 0; // 用于统计移除的石头数
int now = 0; // now 表示当前保留石头的下标(初始为起点 0)
// 遍历所有石头,从索引 1 开始判断
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// 如果当前石头与上一个保留石头之间的距离小于候选距离 x,
// 则认为当前石头无法作为跳跃点,需将其移除
if (map[i] - map[now] < x) {
count++;
// 若移除的石头数超过允许的 m,直接返回 false
if(count > m) {
return false;
}
} else {
// 否则,保留当前石头,更新 now 为当前下标
now = i;
}
}
// 判断移除的石头数是否在允许范围内
return count <= m;
}
}
分治
P1226 【模板】快速幂
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
long a = scanner.nextLong();
long b = scanner.nextLong();
long p = scanner.nextLong();
System.out.printf("%s^%s mod %s=%s", a, b, p, power(a, b, p));
//2^10 mod 9=7
}
private static long power(long a, long b, long p) {
if (b == 0)
return 1;
long temp = power(a, b / 2, p); // 只计算一次
if (b % 2 == 0)
return temp * temp % p;
else
return (temp * temp % p) * a % p; // 注意溢出,分步取余
}
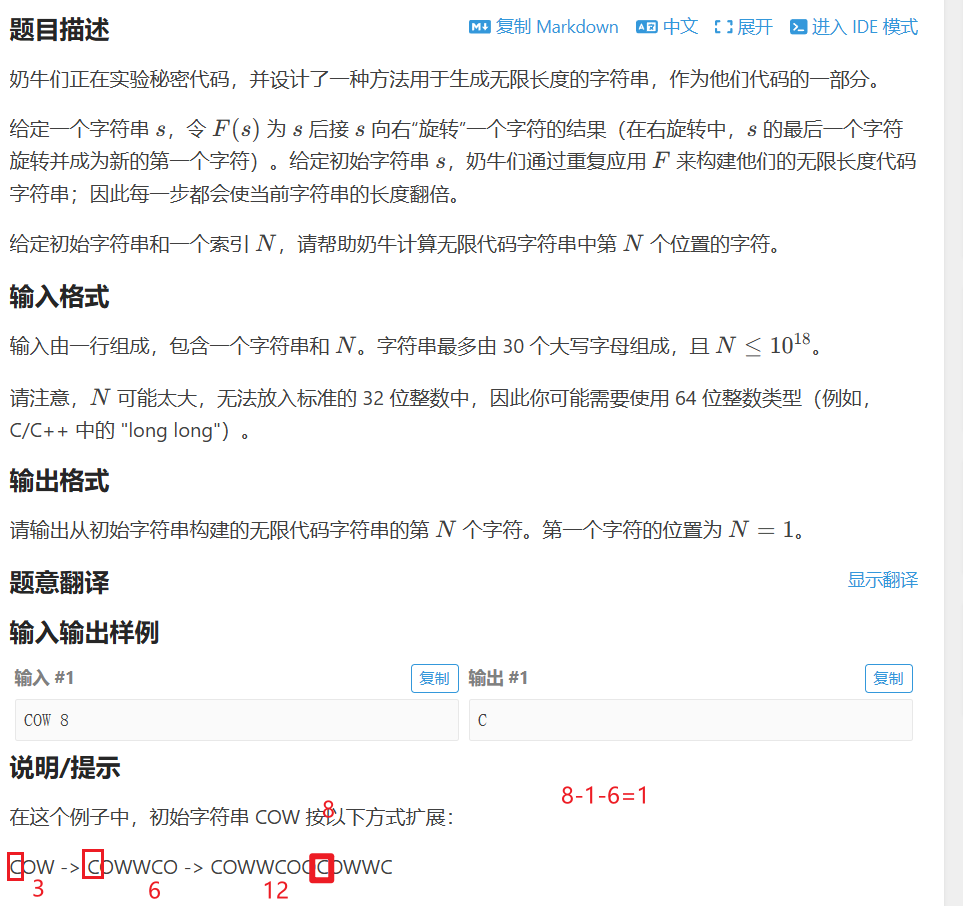
P3612 [USACO17JAN] Secret Cow Code S (二分)
找递推公式,二分(分治)
static long slen;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = scanner.next();
long n = scanner.nextLong();
slen = s.length();
long len = s.length();
while (len<=n){
len*=2;
}
System.out.println(s.charAt((int)func(len,n)-1));
}
private static long func(long length,long pos){
// 递推公式:n-1-l/2
if (slen==length)
return pos;
long half = length/2;
if (pos==half+1){
// 后半段的第 1 个字符 -> 前半段的最后 1 个字符
return func(half, half);
}else if (pos<=half){
return func(half,pos);
}else{
return func(half,pos-half-1);
}
}
前缀和 & 差分
前缀和 和 差分数组 是一对互逆运算:
- 前缀和:用于快速 计算 某个范围
[L, R]内的和 - 差分数组:用于快速 修改 某个范围
[L, R]内的值
P3612 [USACO17JAN] Secret Cow Code S【一维前缀和】
public class P3131_SubsequencesSummingtoSevensS_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int[] cows = new int[n];
int[] pre = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cows[i] = scanner.nextInt();
if (i > 0)
pre[i] = cows[i] + pre[i - 1];
else
pre[0] = cows[0];
}
// origin array [3,5,1,6,2,14,10]
// pre [3, 8, 9, 15, 17, 31, 41] -> 双循环依次减 O(n^2)
// pre mod 7 [3, 1, 2, 1, 3, 3, 6] -> 先取余再找重复值 -> 双指针 O(n^2)
// -> HashMap O(n)
// 1.先取余
pre = Arrays.stream(pre)
.map(num -> num %= 7)
.toArray();
System.out.println(findMaxDistance(pre));
}
// 2.HashMap找重复值最大距离
private static int findMaxDistance(int[] a){
int max_distance = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(0,-1); // 注意这里的赋初始值
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
if (hashMap.containsKey(a[i])){
max_distance = Math.max(max_distance,i- hashMap.get(a[i]));
}else {
hashMap.put(a[i],i);
}
}
return max_distance;
}
}
P1387 最大正方形【二维前缀和】
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1387_TheBiggestSquare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] a = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
a[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
// 1.初始化二维前缀和数组
int[][] pre = new int[n][m];
pre[0][0] = a[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
pre[i][0] = pre[i - 1][0] + a[i][0];
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++)
pre[0][j] = pre[0][j - 1] + a[0][j];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++)
pre[i][j] = a[i][j] + pre[i - 1][j] + pre[i][j - 1] - pre[i - 1][j - 1];
// origin
// 0 1 1 1
// 1 1 1 0
// 0 1 1 0
// 1 1 0 1
// pre
// 0 1 2 3
// 1 3 5 6
// 1 4 7 8
// 2 6 9 11
// 公式:int sum = pre[i][j] - pre[i-k][j] - pre[i][j-k] + pre[i-k][j-k]
// k为当前最大边长
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int k = ans + 1;
while (k <= i+1 && k <= j+1){
int sum = pre[i][j];
// 注意不能越界
if (i-k>=0) sum-=pre[i-k][j];
if (j-k>=0) sum-=pre[i][j-k];
if (i-k>=0 && j-k>=0) sum+=pre[i-k][j-k];
if (sum==k*k)
ans=Math.max(ans,k);
k++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
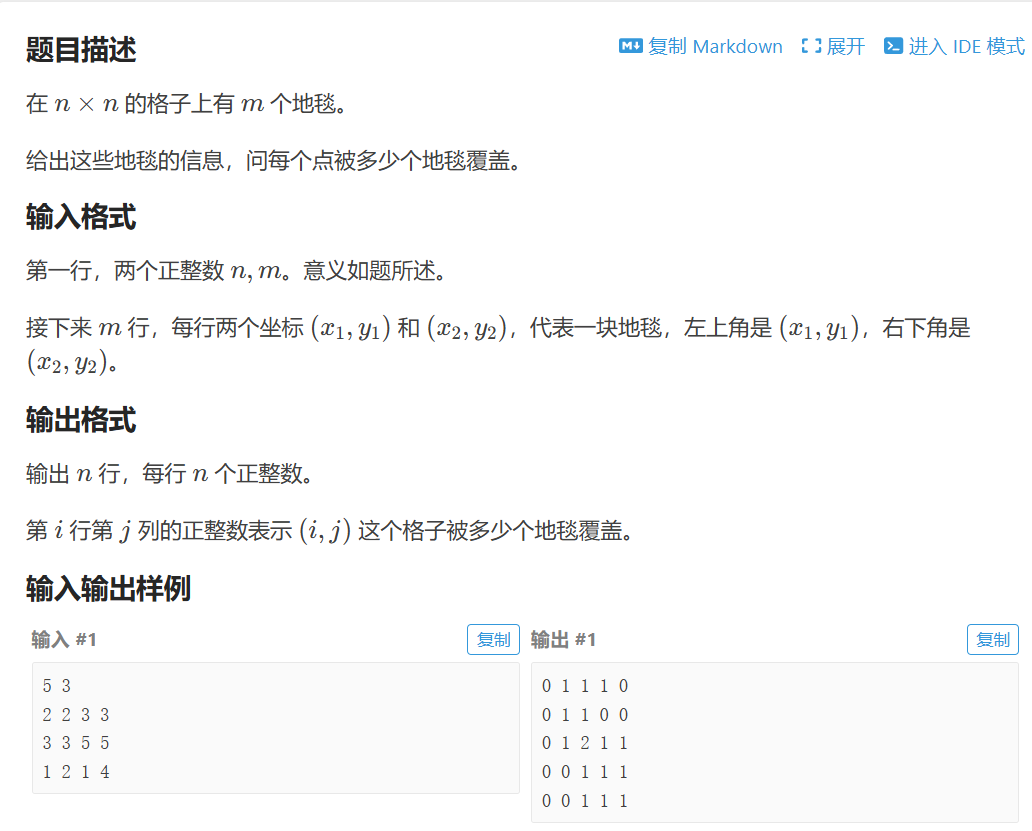
P3397 地毯【二维差分】
一维差分
用于区间操作,对于数组a,差分数组diff定义为:
diff[i] = a[i] - a[i-1], diff[0] = a[0]
对区间[l, r]加上一个v:
- 更新diff
diff[l] += v, diff[r+1] -= v - 还原a
a[i] = a[i-1] + diff[i]
二维差分

import java.io.*;
public class P3397_Carpet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));
st.nextToken();
int n = (int)st.nval; // 读取int类型数据
st.nextToken();
int m = (int)st.nval;
int[][] map = new int[n+2][n+2];
int[][] diff = new int[n+2][n+2];
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++) {
st.nextToken();
int x1 = (int)st.nval;
st.nextToken();
int y1 = (int)st.nval;
st.nextToken();
int x2 = (int)st.nval;
st.nextToken();
int y2 = (int)st.nval;
// update diff
diff[x1][y1] += 1;
diff[x2 + 1][y1] -= 1;
diff[x1][y2 + 1] -= 1;
diff[x2 + 1][y2 + 1] += 1;
}
// store map
// formula: diff[i][j] = a[i][j] - a[i-1][j] - a[i][j-1] + a[i-1][j-1]
// -> a[i][j] = diff[i][j] + a[i-1][j] + a[i][j-1] - a[i-1][j-1]
// 索引从1开始,避免边界检查
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
map[i][j] = diff[i][j] + map[i - 1][j] + map[i][j - 1] - map[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
// 输出结果
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
out.write(map[i][j]+" "); // 如果输出int型,要转为String
}
out.write("\n");
}
out.flush(); // 将输出缓冲区清空(最后如果没有这句代码,就会什么也不输出)
}
}
时间复杂度是O(nm + n^2) 不能AC,使用了快读 & 快写
快读
import java.io.*; public class test { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{ StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in))); st.nextToken(); String str = st.sval;//读取String类型数据 st.nextToken(); double num1 = st.nval;//读取double类型数据 st.nextToken(); int num2 = (int)st.nval;//读取int类型数据 st.nextToken(); long num3 = (long)st.nval;//读取long类型数据 // 读取字符串,不用每次st.nextToken() BufferedReader re = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String x = re.readLine(); System.out.println(x); } }快写
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)); out.write("hello world!") int a = 1; out.write(a.toString()); // 如果输出int型,要转为String out.flush(); // 将输出缓冲区清空(最后如果没有这句代码,就会什么也不输出)
搜索
DFS
N queens
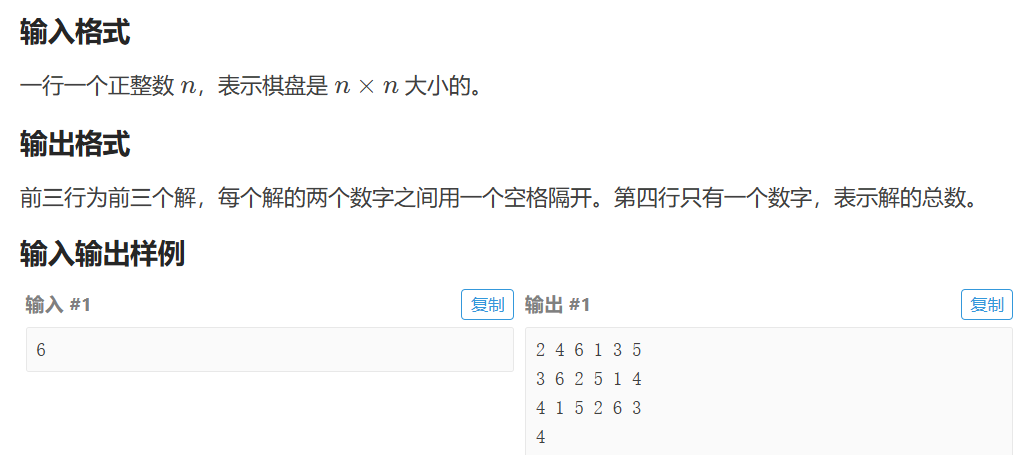
public class P1219_EightQueue {
private static List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();
private static int[] queens = new int[13]; // queens[i] = j 第i行第j列放置
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
dfs(0, n);
// 打印结果
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int[] ints = res.get(i);
for (int i1 : Arrays.stream(ints)
.limit(n)
.map(number -> number + 1)
.toArray()) {
System.out.print(i1 + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.print(res.size());
}
private static void dfs(int row, int n) {
if (row == n) {
// 但 queens 是一个引用类型的数组,因此 res 中存储的是同一个 queens 数组的引用
// 而不是其当前状态的独立副本。这样一来,dfs 继续递归并修改 queens 时
// res 中的所有解也会同步变化,导致最终 res 里所有解都相同
res.add(queens.clone());
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isValid(row, col)) {
queens[row] = col;
dfs(row + 1, n);
// backtrack 回溯
queens[row] = -1;
}
}
}
private static boolean isValid(int row, int col) {
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
// 检查列冲突
if (queens[i] == col) return false;
// 检查对角线冲突
if (Math.abs(row - i) == Math.abs(col - queens[i])) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
P5194 [USACO05DEC] Scales S
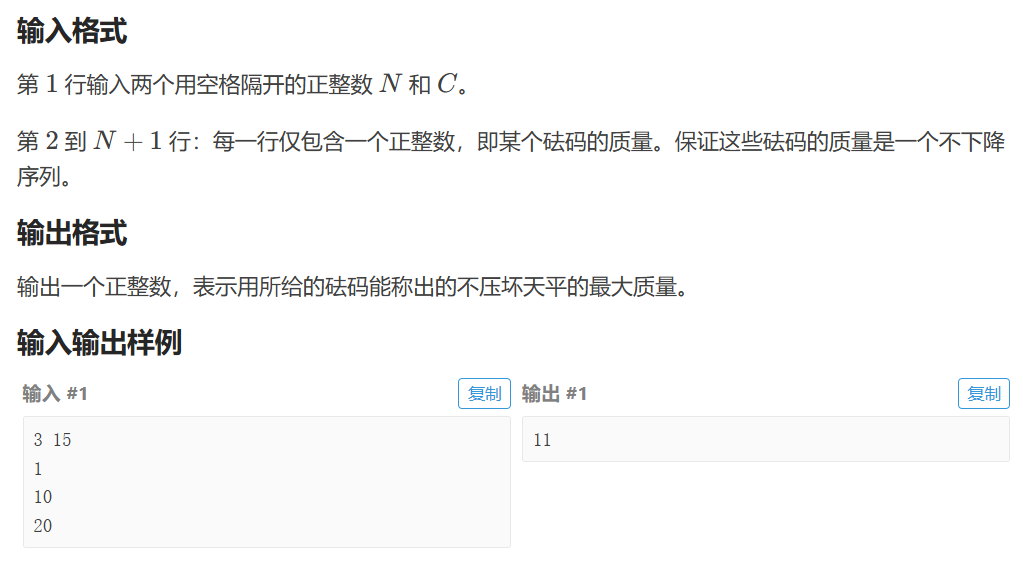
使用剪枝dfs不能AC -> 记忆化搜索
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P5194_Scales_S {
private static int C;
private static int N;
private static int res;
private static int[] weight;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
N = scanner.nextInt();
C = scanner.nextInt();
weight = new int[N]; // 砝码
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
weight[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
dfs(0, 0, weight);
System.out.println(res);
}
/**
* @param id 砝码序号
* @param sum 总重
*/
private static void dfs(int id, int sum, int[] weight) {
if (sum <= C) {
res = Math.max(res, sum);
} else {
return; // 剪枝
}
if (id == N) {
return;
}
// N皇后问题中,有多个情况,用for依次遍历,这里只有两种情况,一种选,一种不选
// for (int i = id; i < N; i++) {
// sum+=weight[i];
// dfs(i,sum,weight); // 选择当前砝码
// sum-=weight[i];
// dfs(i+1,sum,weight); // 不选择当前砝码
// }
/* 在 N 皇后 问题中,queens[row] 是全局状态,需要回溯 */
/* 这里不需要回溯:sum 在 dfs 每一层调用时是独立的,不会影响其他递归分支 */
// 1.选当前砝码
dfs(id + 1, sum + weight[id], weight);
// 2.不选当前砝码
dfs(id + 1, sum, weight);
}
}
两种选项 -> 时间复杂度O(n^2)
改进:使用 记忆化搜索
- 使用
boolean[][] memo记录dfs(id, sum)是否已经计算过 - 如果已经计算过,直接返回
cantorHash:
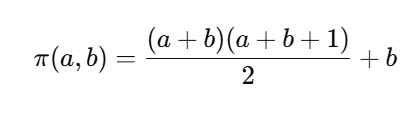
BFS
P1162 填涂颜色
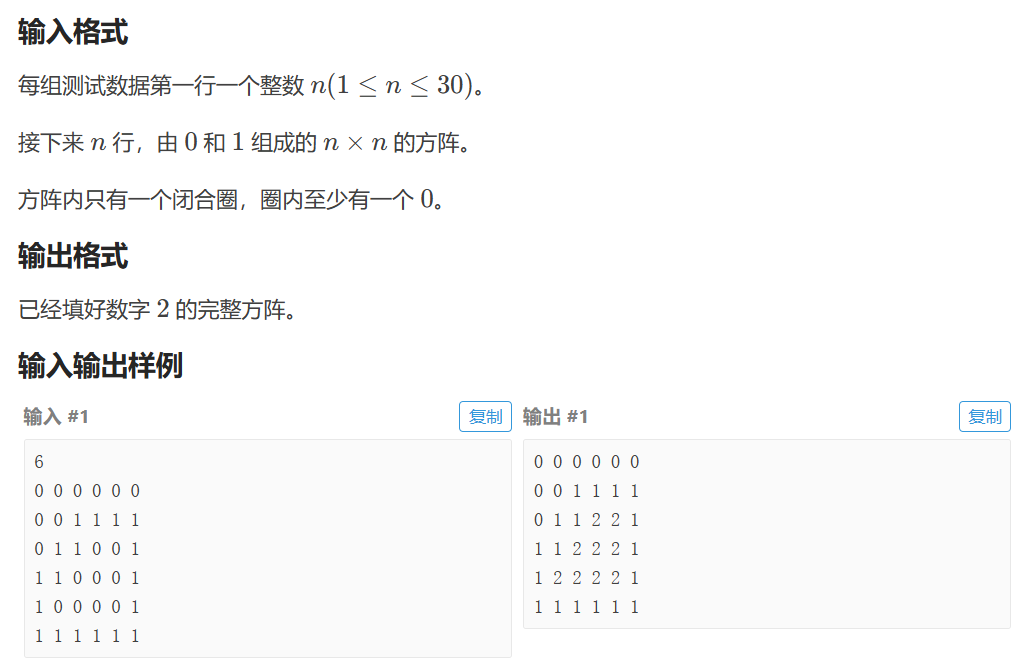
import java.util.*;
public class P1162_FillColor {
private static int N;
private static int[][] map;
private static boolean[][] visited;
private static int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
private static boolean isClose = true;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
map = new int[N + 1][N + 1];
visited = new boolean[N + 1][N + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
map[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 0 && !visited[i][j])
bfs(i, j);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
private static void bfs(int x, int y) {
isClose = true;
if (map[x][y] == 1 || visited[x][y]) return;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // BFS 需要用 队列(FIFO 先进先出) 来保证层次遍历
queue.offer(new int[]{x, y}); // 表示这个位置要进行扩展搜索
List<int[]> region = new LinkedList<>();
region.add(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = true;
map[x][y] = 2;
// -----BFS 流程------
// while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // 当队列不为空时,继续搜索
// int[] curr = queue.poll(); // 取出队首的坐标 (x, y)
// int cx = curr[0], cy = curr[1]; // 当前处理的坐标
//
// for (int[] dir : direction) { // 遍历上下左右四个方向
// int newX = cx + dir[0], newY = cy + dir[1];
//
// if (边界合法(newX, newY) && 未访问(newX, newY)) {
// queue.offer(new int[]{newX, newY}); // 将新坐标加入队列
// visited[newX][newY] = true; // 标记已访问
// }
// }
//}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = queue.poll();
int cx = curr[0], cy = curr[1];
for (int[] dir : direction) {
int newX = cx + dir[0], newY = cy + dir[1];
// 判断逻辑:1.不越界 2.未访问过 3.不是墙
if (newX >= 1 && newX <= N && newY >= 1 && newY <= N && !visited[newX][newY] && map[newX][newY] == 0) {
if (newX == 1 || newY == 1 || newX == N || newY == N) isClose = false;
queue.offer(new int[]{newX, newY});
visited[newX][newY] = true;
map[newX][newY] = 2;
region.add(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
}
// 会把别的 BFS 处理过的 2 也改回 0,因为前面是把所有的0依次bfs,这里是把所有的2都换成0
// if (!isClose)
// for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
// for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
// if (map[i][j] == 2) map[i][j] = 0;
if (!isClose)
for (int[] re : region)
map[re[0]][re[1]] = 0;
}
}
P1443 马的遍历
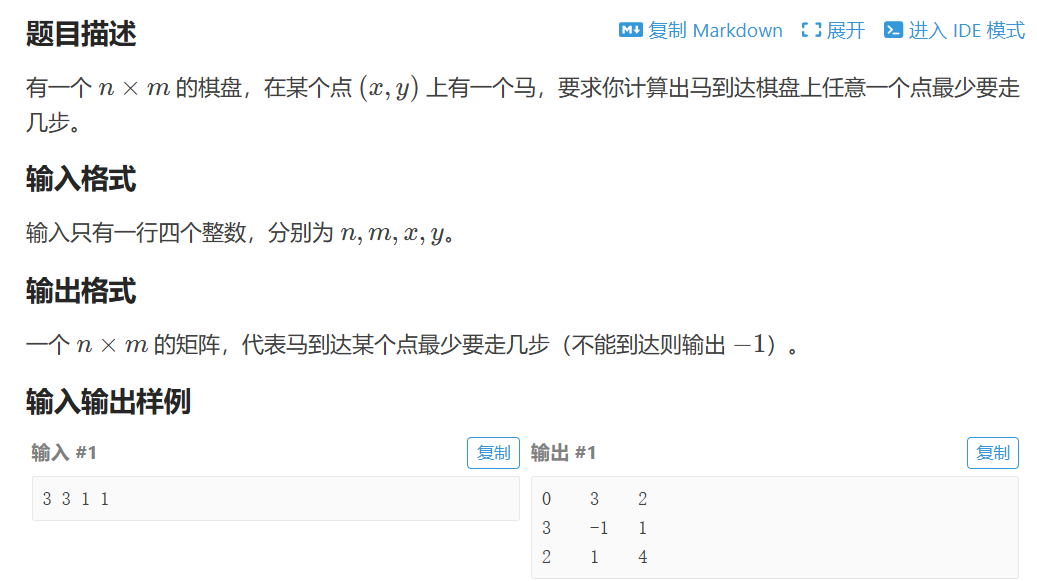
import java.util.*;
public class P1443_HorseTraversal {
private static int[][] map;
private static boolean[][] visited;
private static int[][] res;
private static int[][] direction =
{{1, 2}, {1, -2}, {-1, 2}, {-1, -2},
{2, 1}, {2, -1}, {-2, 1}, {-2, -1}};
private static int N;
private static int M;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
M = sc.nextInt();
map = new int[N + 1][M + 1];
visited = new boolean[N + 1][M + 1];
// 初始化
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
Arrays.fill(map[i], -1);
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
bfs(x, y);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++)
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
private static void bfs(int x, int y) {
map[x][y] = 0;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
int cx = cur[0];
int cy = cur[1];
for (int[] dir : direction) {
int newX = cur[0] + dir[0];
int newY = cur[1] + dir[1];
if (newX >= 1 && newY >= 1 && newX <= N && newY <= M && !visited[newX][newY]) {
queue.offer(new int[]{newX, newY});
map[newX][newY] = map[cx][cy] + 1; // 新的坐标步是上次的加1
visited[newX][newY] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
动态规划
能用动态规划解决的问题,需要满足三个条件:
- 最优子结构
- 无后效性
- 子问题重叠
线性动态规划
例题1 最大子数组和
问题描述:给定一个整数数组,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组
// f(i) 前i个数字的最大和
// f(i) = max(f(i+1),f(i))
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int ans = nums[0];
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1]+nums[i],nums[i]);
ans = Math.max(ans,dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
例题2 最长递增子序列(LIS)
问题描述:给定一个整数数组,找到其中最长的严格递增子序列的长度
状态转移方程
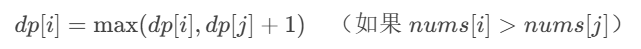
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
int ans = 1;
// 初始化最大长度都是1
Arrays.fill(dp,1);
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length ; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <i ; j++)
if (nums[i]>nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
ans = Math.max(ans,dp[i]);
}
return ans ;
}
例题3 最长公共子序列(LCS)
问题描述:给定两个字符串,找到它们的最长公共子序列
// 状态定义
// dp[i][j] -> text1 的前 i 个字符、text2的前 j 个字符的最长长度
// 状态转移方程
// dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1, c1 == c2
// dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j]), c1 != c2
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int l1 = text1.length();
int l2 = text2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[l1 + 1][l2 + 1];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= l1; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= l2; j++) {
char c1 = text1.charAt(i - 1);
char c2 = text2.charAt(j - 1);
if (c1 == c2)
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]);
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][j]);
}
return ans;
}
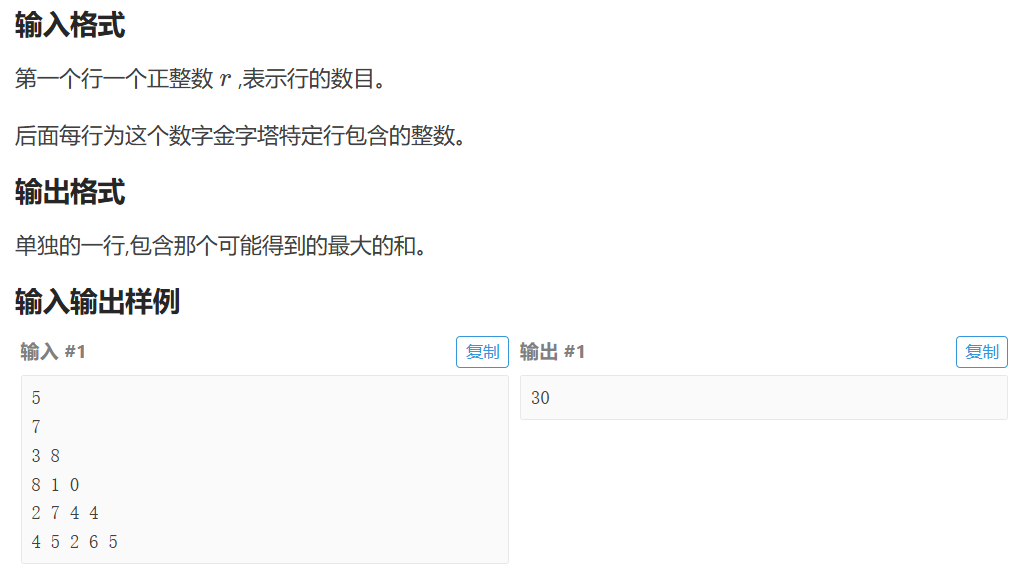
P1216 [IOI 1994] 数字三角形 Number Triangles
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1216_NumberTriangles {
private static int[][] map;
private static int n;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
map = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
map[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(f());
}
// 转移方程 f(i,j) 其中 i是第i行,j是第j列,f是最大价值
// f(i,j) = 当前数字的价值 + max(f(i+1, j), f(i+1, j+1))
// 1. 递归dfs,时间复杂度 O(2^n)
private static int f(int i, int j) {
if (i == n)
return map[i][j];
int value = map[i][j];
int max = value + Math.max(f(i + 1, j), f(i + 1, j + 1));
return max;
}
// 2. 动态规划,时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度 O(n^2)
// private static int f() {
// int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
//
// // 初始化dp最后一层
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// dp[n][i] = map[n][i];
//
// // 从倒数第二行开始 【自底向上】
// for (int k = n - 1; k >= 1; k--)
// for (int l = 1; l <= k; l++)
// dp[k][l] = map[k][l] + Math.max(dp[k + 1][l], dp[k + 1][l + 1]);
//
// return dp[1][1];
// }
// 3. 动态规划 + 滚动数组,时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度 O(n)
private static int f() {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
// 初始化dp最后一层
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = map[n][i];
// 从倒数第二行开始 【自底向上】
for (int k = n - 1; k >= 1; k--)
for (int l = 1; l <= k; l++)
dp[l] = map[k][l] + Math.max(dp[l], dp[l + 1]);
return dp[1];
}
}
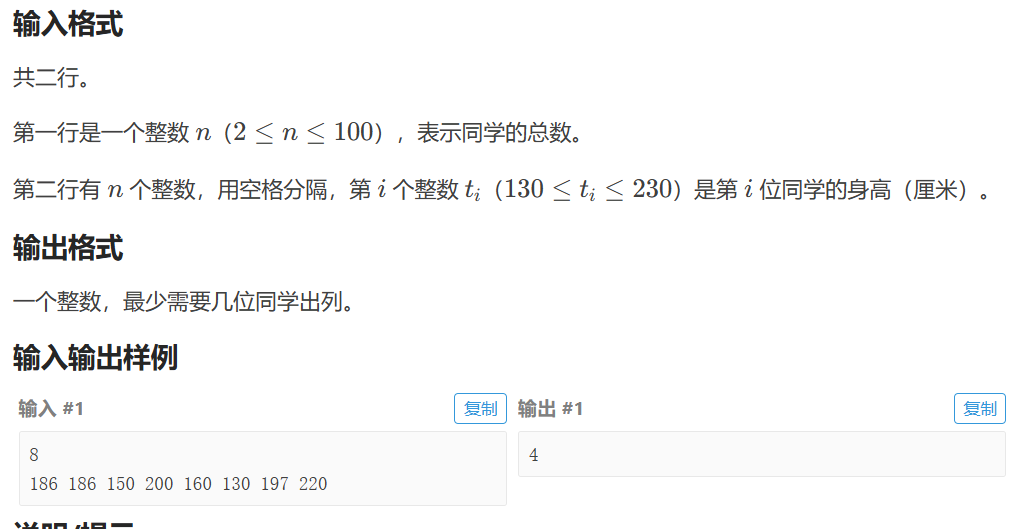
P1091 [NOIP 2004 提高组] 合唱队形
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1091_ChorusFormation {
private static int[] a;
private static int n;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
a = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(f());
}
private static int f() {
int[] dp1 = new int[a.length];
int[] dp2 = new int[a.length];
// 最长递增子序列
Arrays.fill(dp1, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (a[i] > a[j])
dp1[i] = Math.max(dp1[i], dp1[j] + 1);
// 最长递减子序列
Arrays.fill(dp2, 1);
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
for (int j = n - 1; j > i; j--)
if (a[i] > a[j])
dp2[i] = Math.max(dp2[i], dp2[j] + 1);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// i多加了一次
ans = Math.max(ans,dp1[i]+dp2[i]-1);
}
return n-ans;
}
}
P1095 [NOIP 2007 普及组] 守望者的逃离
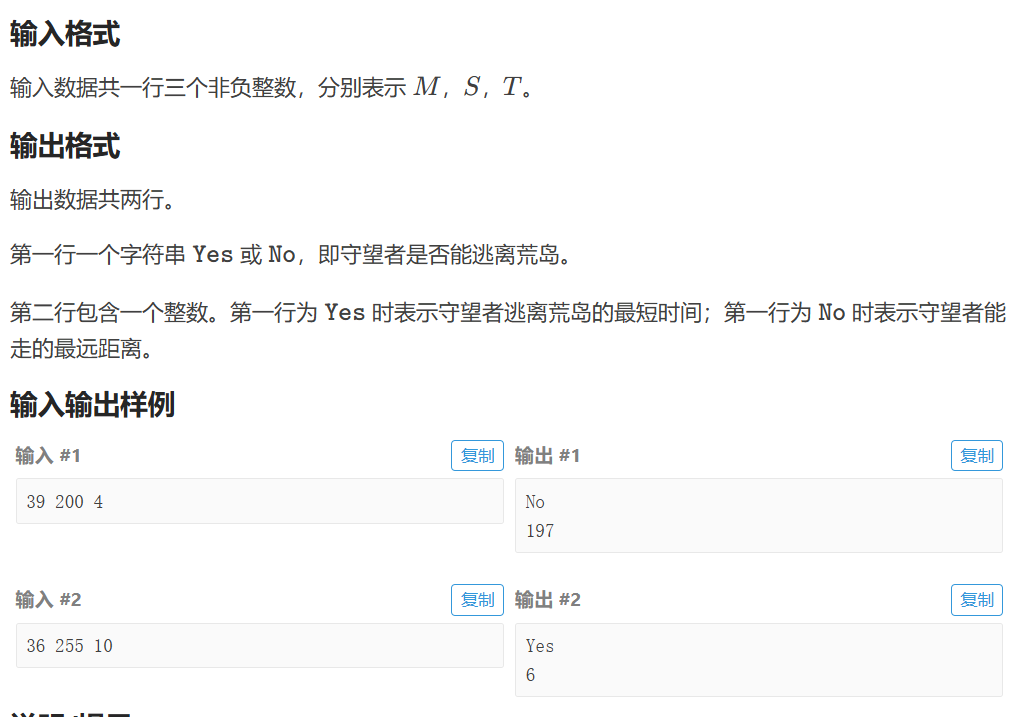
有点问题
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1095_EscapeOfTheWatchman {
private static int M;
private static int S;
private static int T;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
M = sc.nextInt();
S = sc.nextInt();
T = sc.nextInt();
int second = 0;
int magic = M;
int[] dp = new int[T + 1]; // dp[i] 表示i时间内的最远距离
// for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
// if (dp[i] >= S) {
// second = i;
// break;
// }
// if (magic>=10){
// magic-=10;
// dp[i]=dp[i-1]+60;
// }else{
// int restore =(10-magic)%4==0?(10-magic)/4:(10-magic)/4+1;
// if (restore*17>60 || i+restore>T){
// // run
// dp[i] = dp[i-1]+17;
// }else {
// // wait
// int save_i = i;
// i+=restore;
// magic+=4*restore;
// magic-=10;
// dp[i]=dp[save_i-1]+60;
// }
// }
// }
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
// 默认先跑步
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 17;
// 如果magic足够,优先闪烁
if (magic >= 10) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[i - 1] + 60);
magic -= 10;
}
if (magic < 10) {
magic += 4; // 只有魔法值不足 10 时,每秒恢复 4 点
}
if (dp[i] >= S) {
System.out.println("Yes");
System.out.println(i);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("No");
System.out.println(dp[T]);
}
}
P1541 [NOIP 2010 提高组] 乌龟棋


P1868 饥饿的奶牛【区间DP】
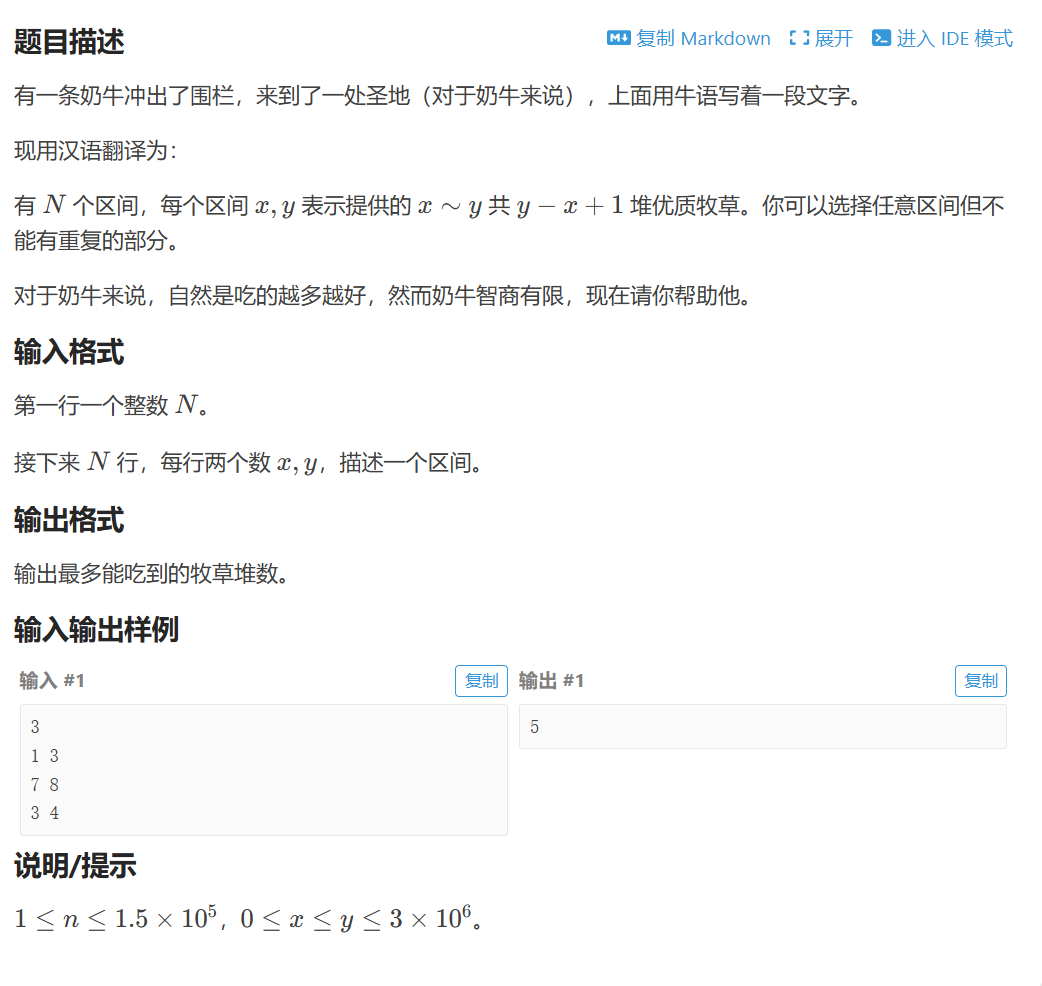
错误总结
排序顺序错误
初始代码中曾使用结束时间降序排序。
正确做法是按结束时间升序排序,以保证在计算 dp 时,前面的区间状态已经确定。
内外循环顺序不对
状态转移应只依赖于已计算好的状态,因此在外层循环遍历到区间 i 时,只能使用 j < i 的 dp 值进行更新。
遍历整个数组(包括 j ≥ i)会导致使用未来未计算状态,逻辑上不正确。
区间不重叠判断条件错误
代码中使用了条件 if (x2 >= y1 || y2 <= x1) 判断两个区间是否不重叠。
在排序后,只需判断“前一个区间 j 的结束时间是否小于当前区间 i 的起始时间”,即 if (maps[j].end < maps[i].start)。
累加区间权重错误
当两个区间不重叠时,应该累加的是当前区间 i 的长度,而非区间 j 的长度。
错误地使用 int score = y1-x1+1; 或 int score = y2-x2+1; 作为累加项都会导致错误。
dp[i] 初始化位置不正确
dp[i] 应在外层循环开始时初始化为当前区间 i 的长度。
内层循环中重复赋值会覆盖已经累积的结果,导致最终结果错误。

import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1868_HungryCow {
private static class Map {
int start;
int end;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Map[] maps = new Map[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
maps[i] = new Map();
maps[i].start = sc.nextInt();
maps[i].end = sc.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(maps, (a, b) -> a.end - b.end);
int[] dp = new int[n];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 先选自己
dp[i] = maps[i].end - maps[i].start + 1;
// 在动态规划中,我们要求状态转移只依赖于已经计算好的状态
// 所以从0到i
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
// 区间不重叠
// 如果 j 的结束时间 < i 的开始时间,说明 j 和 i 不重叠(因为前面进行了排序,不需要更复杂的判断)
if (maps[j].end < maps[i].start)
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + (maps[i].end - maps[i].start + 1));
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i]);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
P1048 采药【01背包dp】

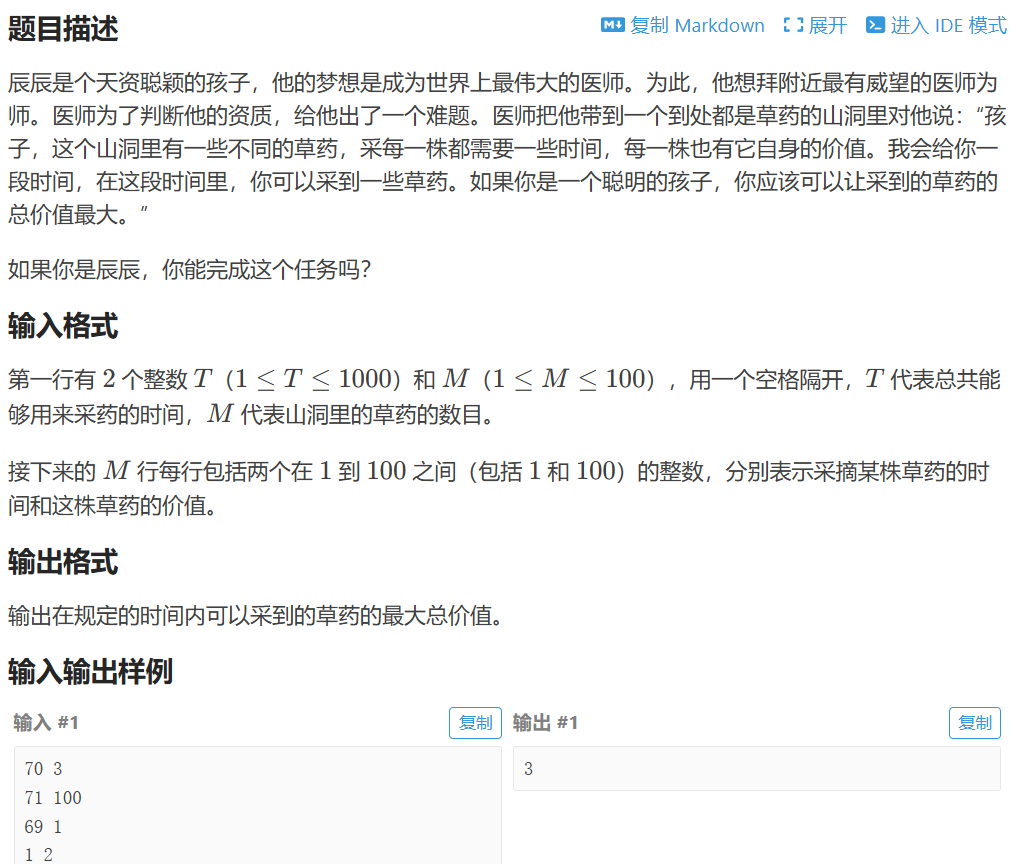
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1048_PickMedicine {
static int W;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
W = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] w = new int[n + 1];
int[] v = new int[n + 1];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
w[i] = sc.nextInt();
v[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
// 1.二维数组 -> 空间复杂度O((W+1)^2)
// f(i,j) 前i个物品,容量为j的最大价值
// int[][] f = new int[100][100];
// for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// for (int j = W; j >=w[i] ; j--) {
// f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i-1][j],f[i-1][j-w[i]]+v[i]);
// ans = Math.max(ans,f[i][j]);
// }
// }
// System.out.println(ans);
// 2.滚动数组
// f(i) 容量为i的最大价值
int[] f = new int[W + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = W; j >= w[i]; j--) {
// 0-1背包问题,内层从大到小
f[j] = Math.max(f[j], f[j - w[i]] + v[i]);
ans = Math.max(ans, f[j]);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
P1616 疯狂的采药【完全背包dp】
注意使用long
public class P1048_PickMedicine {
static int W;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
W = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] w = new int[n + 1];
int[] v = new int[n + 1];
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
w[i] = sc.nextInt();
v[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
long[] f = new long[W + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = w[i]; j <= W; j++) {
// 完全背包问题,内层从小到大
f[j] = Math.max(f[j], f[j - w[i]] + v[i]);
ans = Math.max(ans, f[j]);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
P1855 榨取kkksc03 【二维01背包dp】
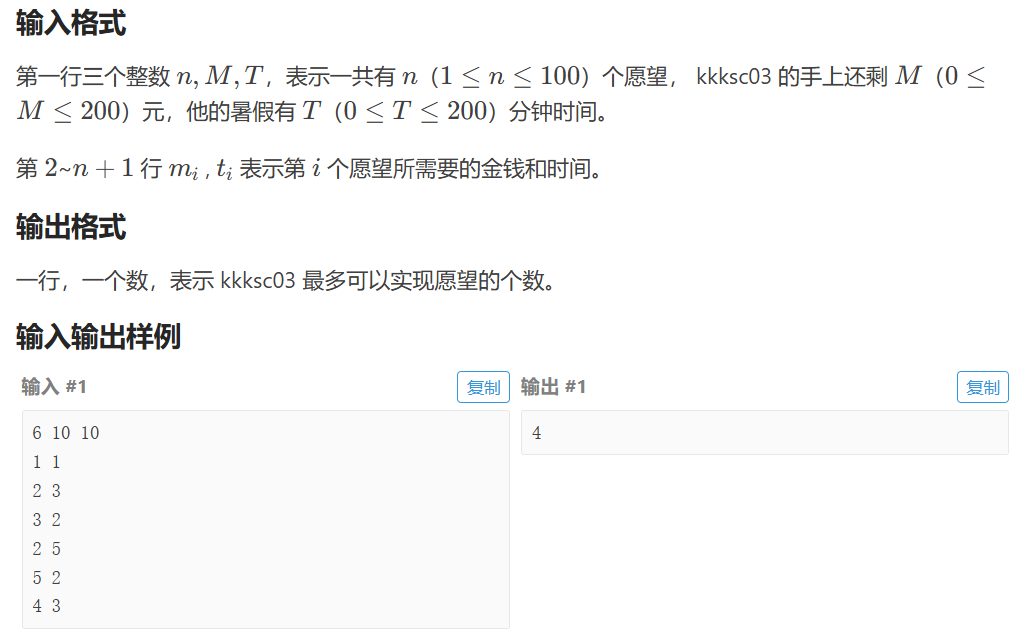
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1855_kkksc03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int T = sc.nextInt();
int[] money = new int[n + 1];
int[] time = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
money[i] = sc.nextInt();
time[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int ans = 0;
int[][] f = new int[201][201]; // f(i, j)花了i钱j时间得到的最多愿望数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = M; j >= money[i]; j--)
for (int k = T; k >= time[i]; k--) {
f[j][k] = Math.max(f[j][k], f[j - money[i]][k - time[i]] + 1);
ans = Math.max(ans, f[j][k]);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
P1757 通天之分组背包【分组背包dp】
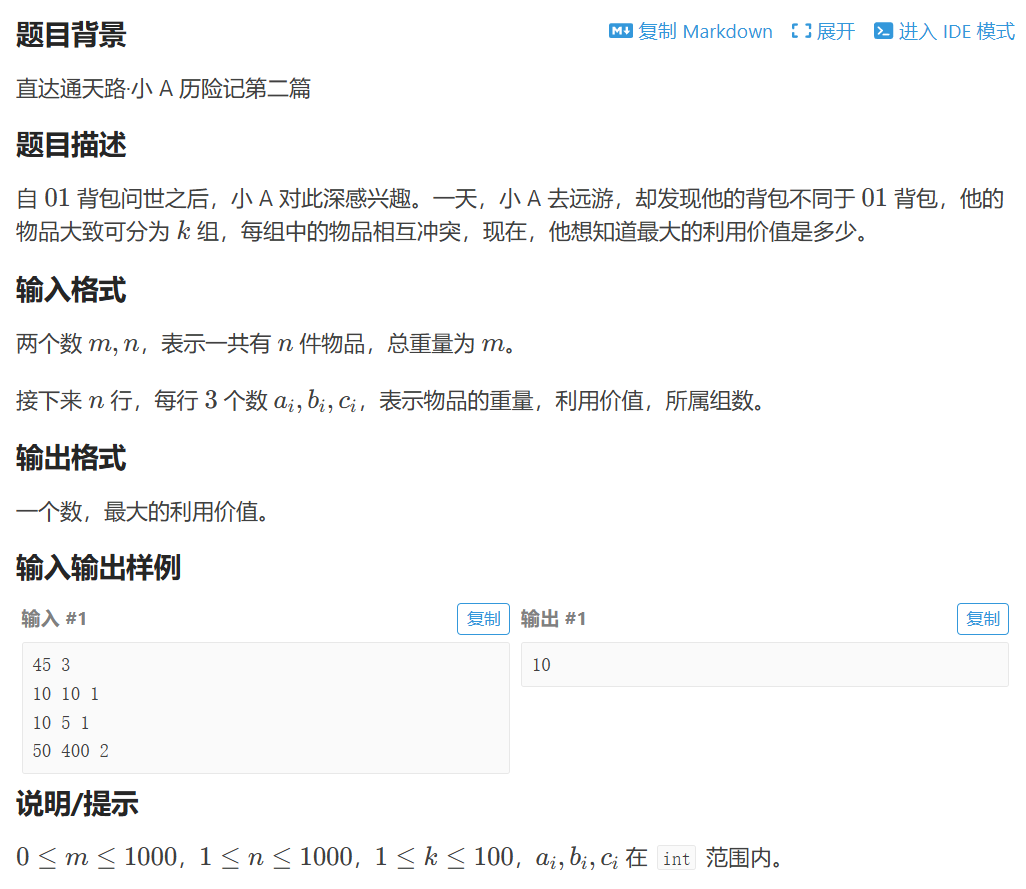
import java.util.*;
public class P1757_GroupBcakpack {
static class Item {
int w;
int v;
int group;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
Item[] items = new Item[n + 1];
// 分组
List<Item>[] groups = new ArrayList[100 + 1];
items[0] = new Item();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int w = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
int g = sc.nextInt();
Item item = new Item();
item.w = w;
item.v = v;
if (groups[g] == null) groups[g] = new ArrayList<>();
groups[g].add(item);
}
int ans = 0;
int[] f = new int[10001];
// 遍历分组而不是i从[1,n]
for (int g = 1; g <= 100; g++) {
if (groups[g] == null) continue; // 跳过没有的组
for (int j = m; j>=0; j--) {
for (Item item : groups[g]){
if (j - item.w>=0)
f[j] = Math.max(f[j], f[j - item.w] + item.v);
}
ans = Math.max(ans, f[j]);
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}


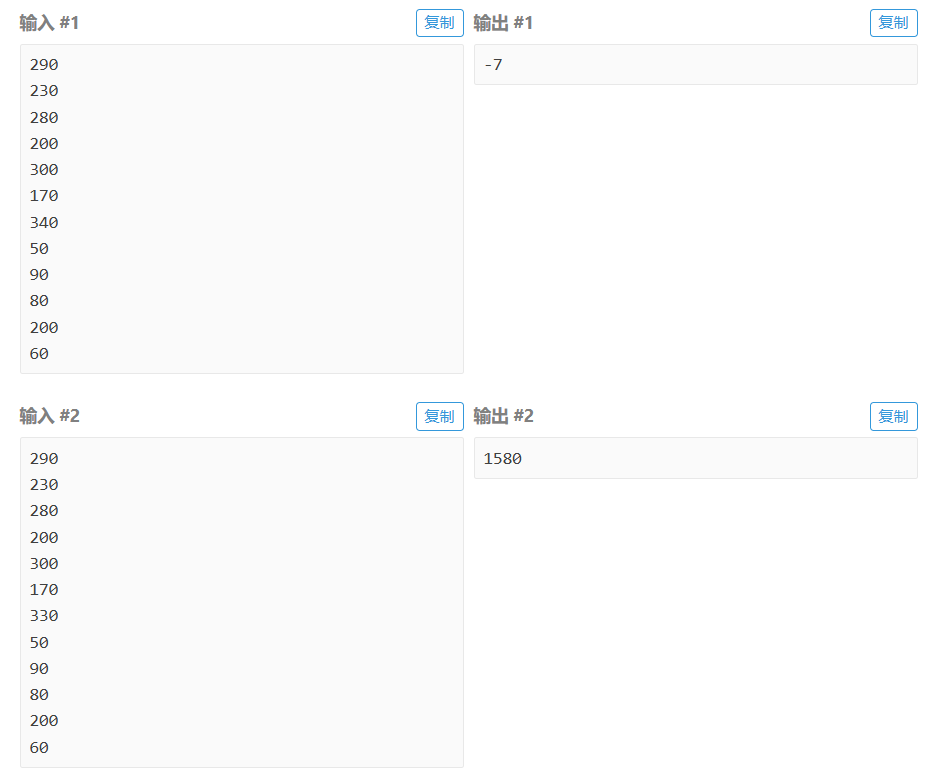

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号