SpringBoot-01-启动第一个项目
通过官网quickstart快速生成一个项目
https://start.spring.io/
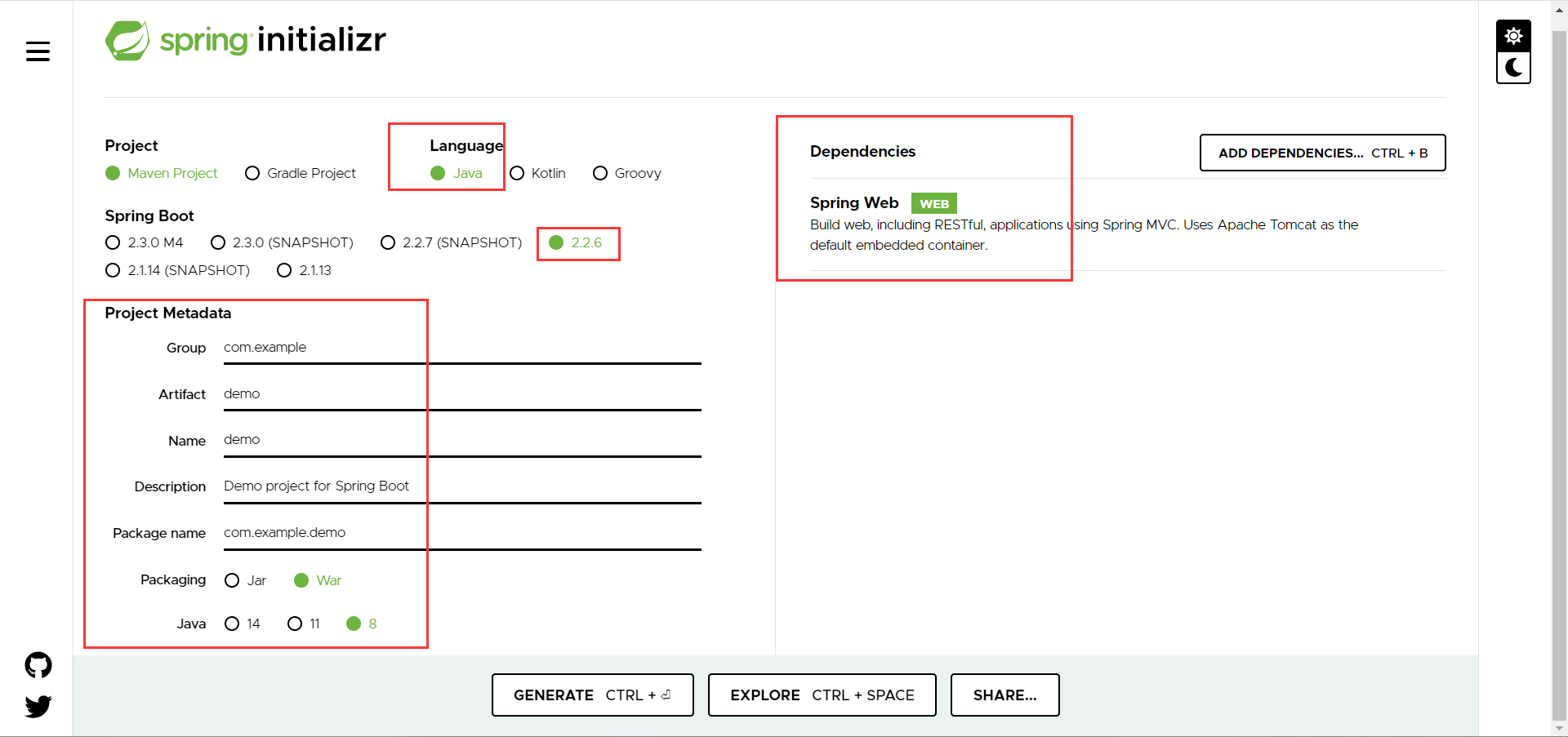
即可generate(生成)项目并下载到本地
idea移除一个现有项目
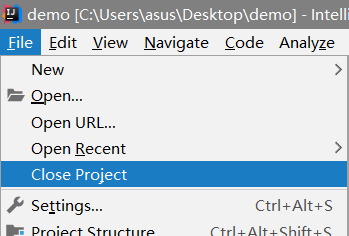

导入刚刚生成的项目
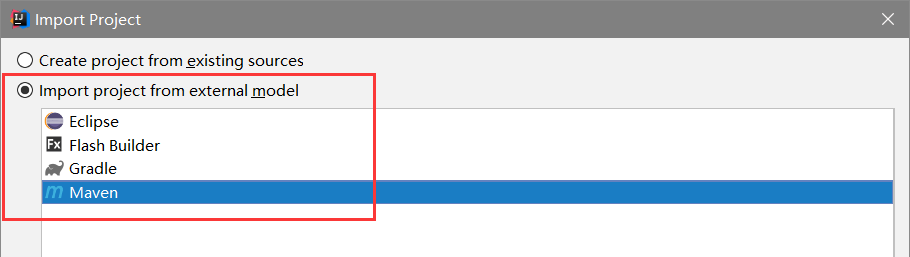
此时idea会去中央仓库下载jar包
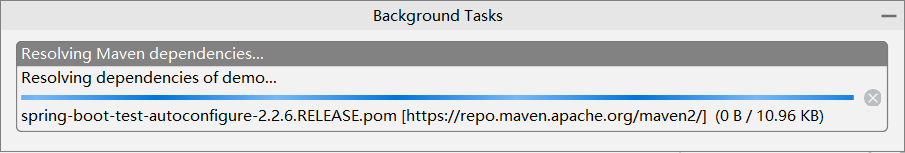
(上面的操作是原始的做法,idea集成了这个网站)
在Idea中新建一个项目
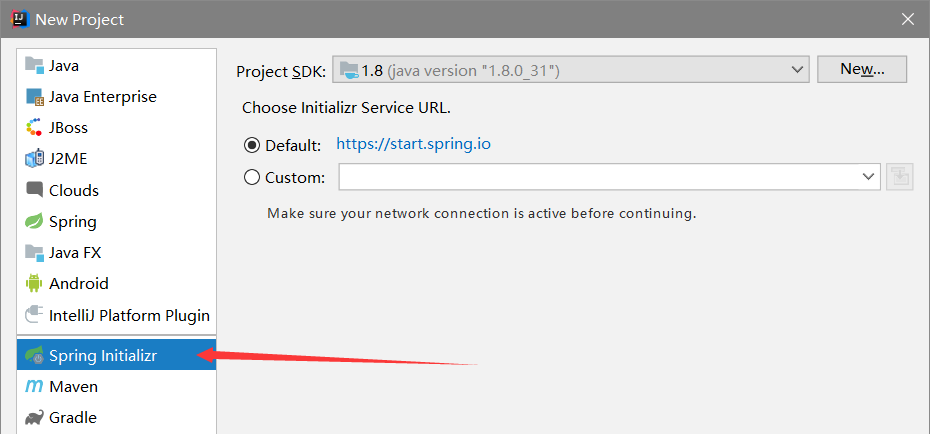
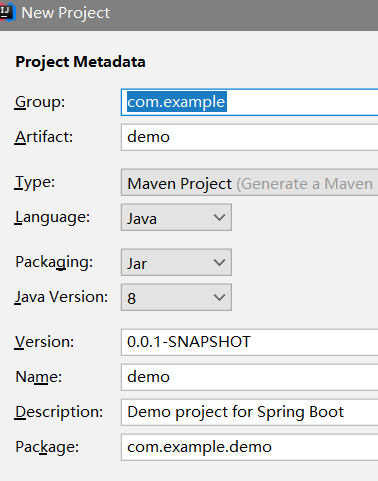
这种方式和官网上下载的方式配置是一样的
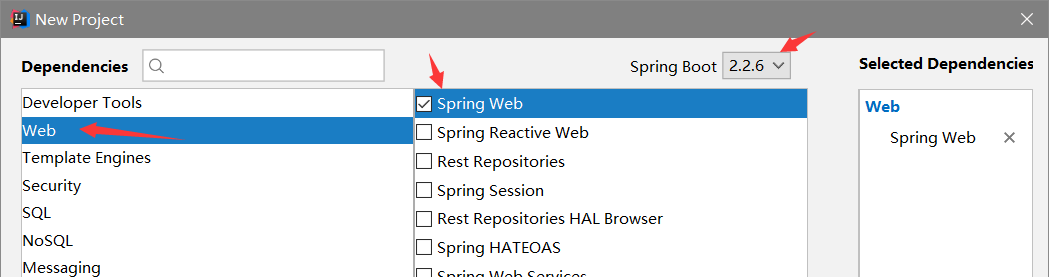
结果这种方式同样要去中央库下载jar包
去setting里边(检查maven配置)
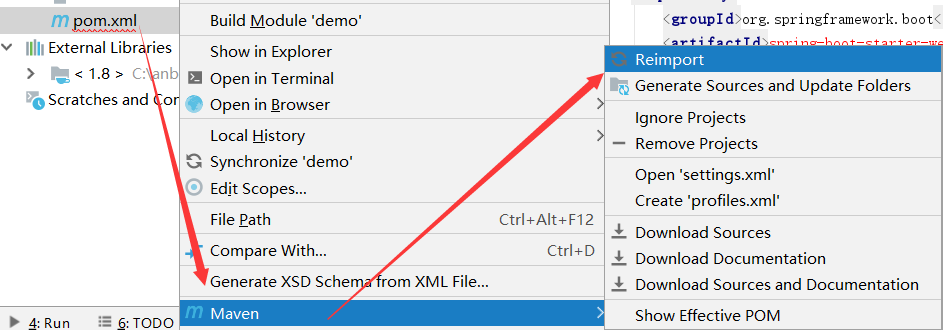
Reimport和Generate Sources and Update Folders
<!-- 连接阿里云中央仓库 --> <mirror> <id>aliyun</id> <name>aliyun Maven</name> <mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf> <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url> </mirror>
此时,N多的依赖jar包就开始下载了
完了执行contextLoads()空测试方法或者DemoSpplication的main方法,耐心等待几分钟
至此,这个spring boot程序就搭建完成了,现在开始解剖这家伙
认识springboot工程
(首先从直观上看到这家伙依赖的jar包真不少,应该很健壮)
程序的入口,启动之后该web工程发布到tomcat8080端口(http://localhost:8080/error)
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; //本身就是spring的一个组件 //程序入口 @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
核心配置文件application.properties
Java代码必须要放到与Application类同级的包的下面
Controller类
package com.example.demo.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; //spring boot 自动装配 @RestController public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello")//这个接口的名字就叫做http://localhost:8080/hello //// 它就单纯的成了一个接口 不用再去管web.xml 前端 等等一系列东西了 它就和vue完全前后端分离了 public String hello(){ //接收前端的参数,调用业务 return "hello world"; } }
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <!-- 有一个父项目 --> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <name>demo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- web依赖:tomcat,dispatcherServlet,xml等--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!--所有spring boot依赖都是使用spring-boot-starter开头的--> <!--单元测试--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId> <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <!--打jar包插件--> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
这里可以下载依赖包的源码(方便在pom中直接ctrl点进去)

对该spring boot程序进行打包
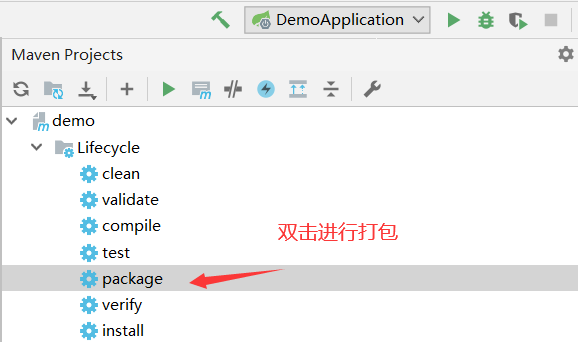
(打包成功之后target目录下生成jar包;install安装到本地仓库)
java -jar demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
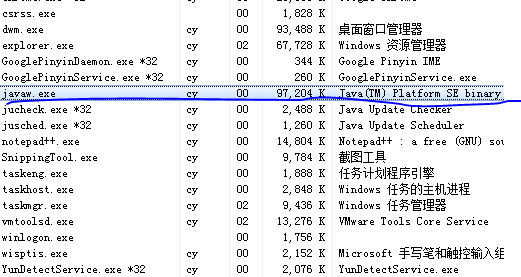
(内置tomcat,可直接在浏览器访问)
修改端口号
application.properties中配置
#更改项目的端口号 server.port=8081
修改springboot banner
https://www.bootschool.net/ascii-art
resource目录下新建文件banner.txt
主程序丶注解
pom.xml中有它的parent,其parent中还有parent(祖父母),其祖父母管理了各依赖版本号……约定大于配置(以往那种jar包冲突的问题就没了)
pom.xml中有很多启动器,各种场景的启动器,自动装配;要使用什么功能,只需要开启对应的启动器!
@SpringBootApplication表示这是一个springboot应用
@SpringBootConfiguration具备springboot配置
@Configuration具备spring配置
@Component表示其本质还是一个spring组件
@EnableAutoConfiguration自动配置
@AutoConfigurationPackage自动配置包
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)自动配置“包注册”
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)自动配置导入选择
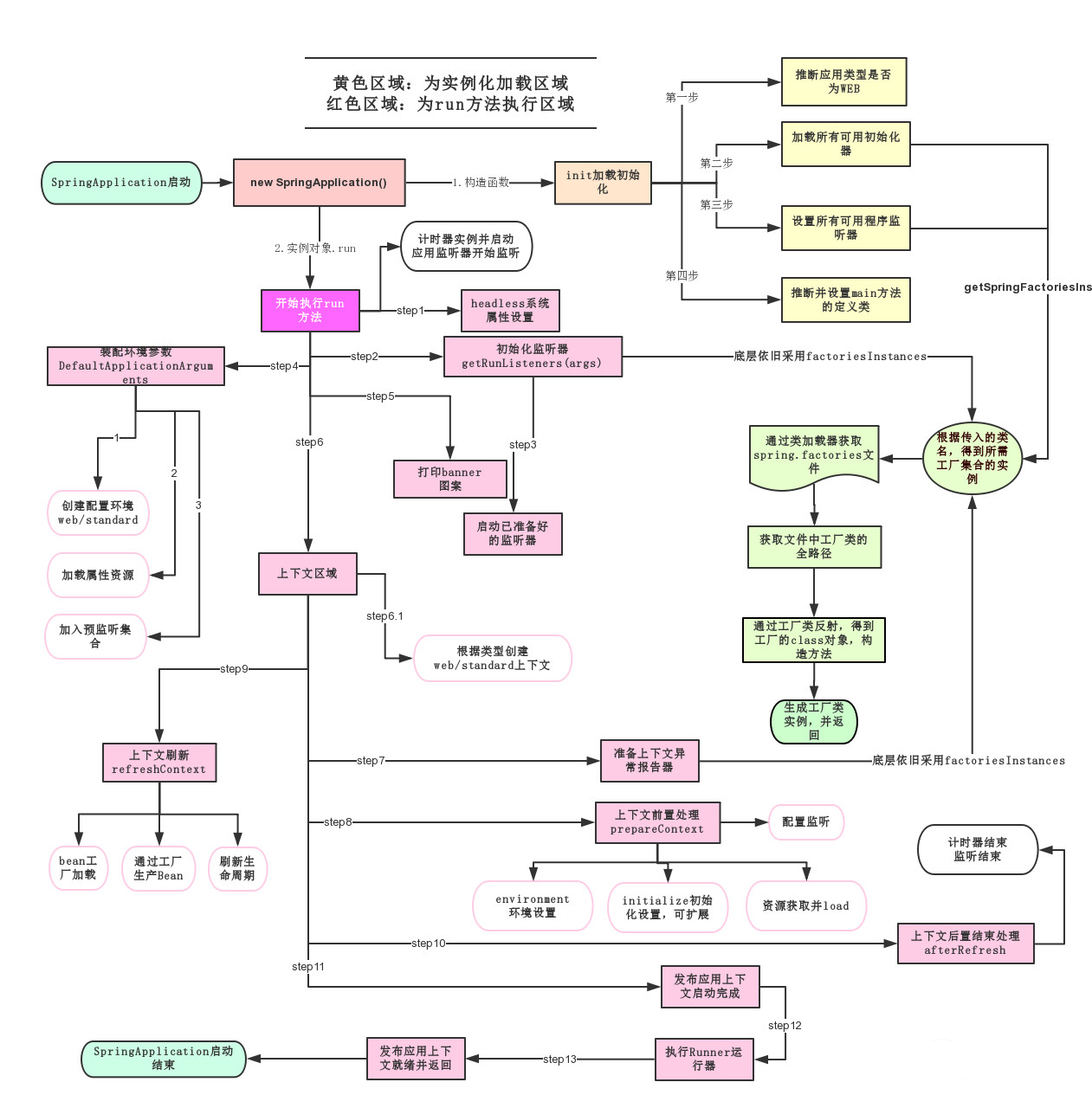
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
//META-INF/spring.factories(autoconfigure下的)
//List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),getBeanClassLoader());
//private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader)
//classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION)
//Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);//所有资源加载到配置类中
另:自动配置一核心注解@ConditionalOnXxx这里边的条件都满足才会生效!
结论
springboot的所有自动配置都在启动的时候被扫描并加载的;
spring.factories所有的自动配置都在这里边,但是不一定生效,要判断条件是否成立;
只要导入了对应的start,就有对应的启动器了,有了启动器,我们自动装配就会生效。
{从/META-INF/spring.factories获取指定的值,将这些自动配置类导入容器;
自动配置的东西都在spring-boot-autoconfigure-包下;
容器中存在非常多的xxxAutoConfigure类,给容器导入这个场景中的所有组件。}
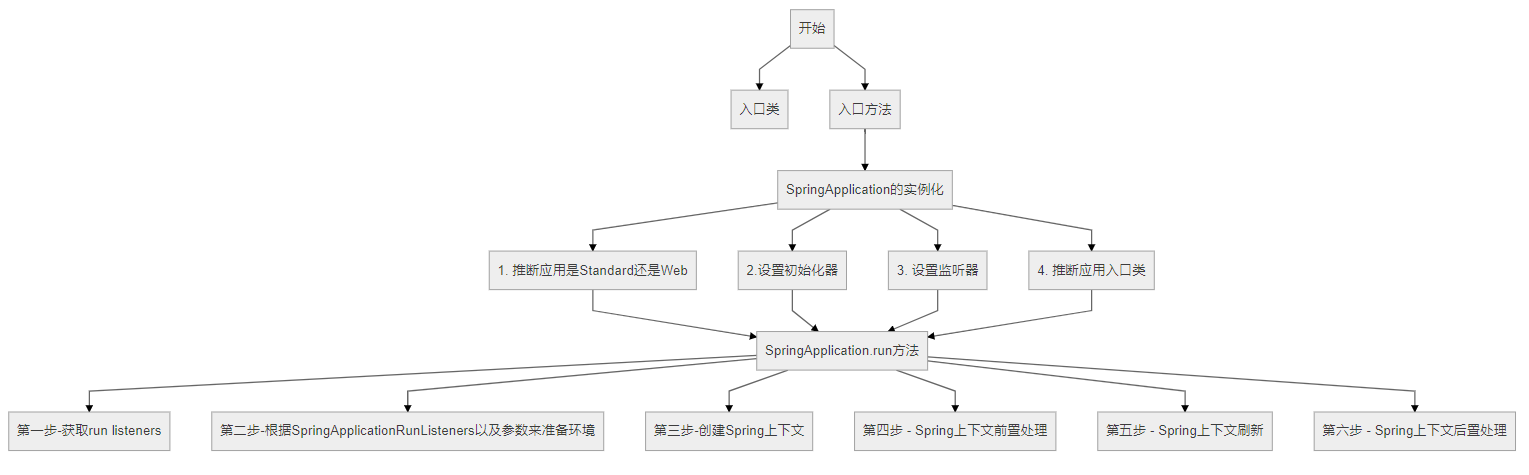
主程序丶启动
run();
配置文件
可以配置哪些东西?很多,官网上有。怎么记忆?一会说
application*.properties 语法结构 :key=value application*.yml 语法结构 :key:空格 value
yaml用法(可以注入到配置类中)
对象
student:
name: xiaoming
age: 3
行内写法
student: {name: xiaoming,age: 3}
数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
给某一些配置类赋值(@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person"))

package com.example.demo.pojo; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component //注册bean到容器中 public class Dog { private String name; private Integer age; public Dog() { } public Dog(String name, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }

package com.example.demo.pojo; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; /* @ConfigurationProperties作用: 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中; 告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定 参数 prefix = “person” : 将配置文件中的person下面的所有属性一一对应 */ @Component //注册bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; private Boolean happy; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog; public Person() { } public Person(String name, Integer age, Boolean happy, Date birth , Map<String, Object> maps, List<Object> lists, Dog dog) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.happy = happy; this.birth = birth; this.maps = maps; this.lists = lists; this.dog = dog; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Boolean getHappy() { return happy; } public void setHappy(Boolean happy) { this.happy = happy; } public Date getBirth() { return birth; } public void setBirth(Date birth) { this.birth = birth; } public Map<String, Object> getMaps() { return maps; } public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) { this.maps = maps; } public List<Object> getLists() { return lists; } public void setLists(List<Object> lists) { this.lists = lists; } public Dog getDog() { return dog; } public void setDog(Dog dog) { this.dog = dog; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", happy=" + happy + ", birth=" + birth + ", maps=" + maps + ", lists=" + lists + ", dog=" + dog + '}'; } }

person:
name: xiaoming
age: 3
happy: false
birth: 2000/01/01
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- code
- girl
- music
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 1

package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.pojo.Person; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest class DemoApplicationTests { @Autowired //将狗狗自动注入进来 Person p; @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(p); //打印看下狗狗对象 } }

<!-- 导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示,需要重启 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
选择@ConfigurationProperties还是@Value
1、@ConfigurationProperties只需要写一次即可,@Value则需要每个字段都添加
2、松散绑定:yml中写的last-name,这个和lastName是一样的
3、JSR303数据校验,这个就是我们可以在字段是增加一层过滤器验证,可以保证数据的合法性
4、复杂类型封装,yml中可以封装对象,使用value就不支持
配置文件放置的位置
-file:./config/ (项目根目录的config下)优先级最高 -file:./ (项目根目录) -classpath:/config/ (类路径resource的config下) -classpath:/ (类路径resource下)优先级最低
多环境配置
application.yml中配置如下 spring: profiles: active: test application-test.yml中配置如下 server: port: 8082 application-dev.yml中配置如下 server: port: 8081
yml的多文档块还可以对上面的动作进一步简化
spring:
profiles:
active: test
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: test
自动配置

得到如下spring.factories(里边包含很多自动配置类)
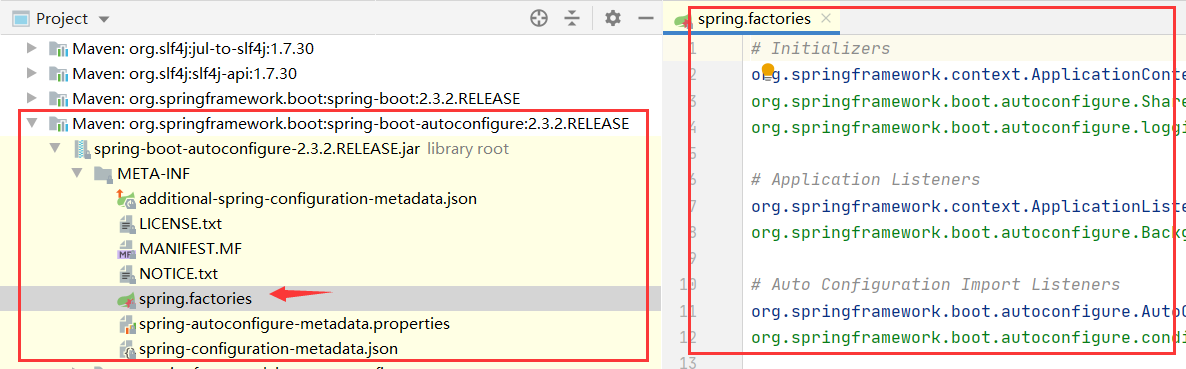
现在找application.yml中配置的内容与spring.factories的联系(spring.factories就像springboot的一个工具箱)
以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例学习自动配置原理
//表示这个是一个配置类,被spring接管 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //ServerProperties中的内容和yml中提示的内容,显然配置文件中的配置项和该配置类
//进行了绑定(@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true))
//从另一个角度说,yml中的每一个配置项,都有一个XxxProperties类与之对应 @EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class) //(ConditionalOnXxx)spring底层注解:根据条件判断当前配置类是否生效。更多同类注解见下图 @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "server.servlet.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { private final Encoding properties; public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(ServerProperties properties) { this.properties = properties.getServlet().getEncoding(); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Encoding.Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Encoding.Type.RESPONSE)); return filter; } @Bean public LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer localeCharsetMappingsCustomizer() { return new LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer(this.properties); } static class LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>, Ordered { private final Encoding properties; LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer(Encoding properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Override public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) { if (this.properties.getMapping() != null) { factory.setLocaleCharsetMappings(this.properties.getMapping()); } } @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } } }
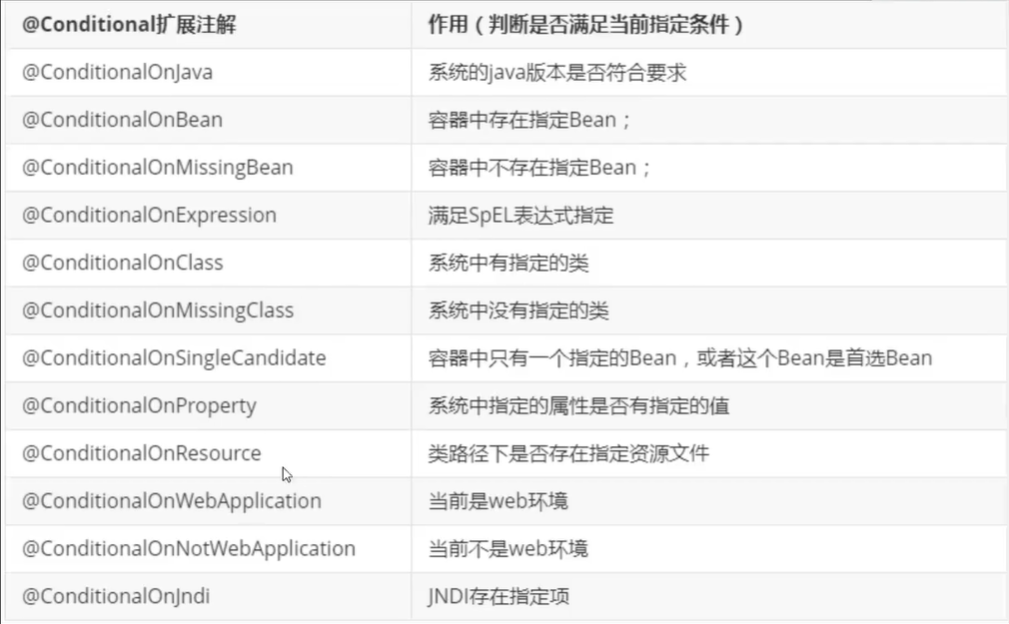
springboot装配各种XxxAutoConfiguration配置类,(配置类决定该类型工具是否加载, 工具类用自己的特长帮sping干事情)。工具加不加载,用不用yml配置,都在XxxAutoConfiguration中确定。
- 一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加组件;
- 这些组件的属性是从对应的XxxProperties类中获取的,XxxProperties类里面的每一个属性又是和yml配置文件绑定的;
- 配置文件能配置什么自然就可以参照某个功能对应的这个XxxProperties属性类
- 而至于加不加载这个工具,就看你的pom.xml里边有没有添加响应依赖丶
debug: true可查看哪些配置类生效了





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号