类和对象基础
1. 类和对象基础
什么是对象? 什么是类?
如何定义一个类?类中有什么 ?
对象是一个实体, 类是用来描述实体的
定义类的格式: class为定义类的关键字,ClassName为类的名字,{}中为类的主体。
// 创建类
class ClassName{
field; // 字段(属性) 或者 成员变量
method; // 行为 或者 成员方法
}类中有属性和成员方法, 属性描述对象的特性 成员方法描述对象具备哪些行为
以下面这个WashMachine类为例:
class WashMachine {
//属性 、 字段 、成员变量:这些成员变量是定义在方法外部 类的内部的
public String brand; // 品牌
public String type; // 型号
public double weight; // 重量
public double length; // 长
public double width; // 宽
public double height; // 高
public String color; // 颜色
//成员方法 -> 行为
public void washClothes(){ // 洗衣服
System.out.println("洗衣功能");
}
public void dryClothes(){ // 脱水
System.out.println("脱水功能");
}
public void setTime(){ // 定时
System.out.println("定时功能");
}
}成员变量品牌,型号,重量... 描述洗衣机实体的属性/特性
成员方法洗衣服 脱水 定时,描述洗衣机实体具备的行为
定义了一个类相当于自己定义了一种新的类型,可以用这个新的类型创建变量
class WashMachine {
//属性 、 字段 、成员变量:这些成员变量是定义在方法外部 类的内部的
public String brand; // 品牌
public String type; // 型号
public double weight; // 重量
public double length; // 长
public double width; // 宽
public double height; // 高
public String color; // 颜色
//成员方法 -> 行为
public void washClothes(){ // 洗衣服
System.out.println("洗衣功能");
}
public void dryClothes(){ // 脱水
System.out.println("脱水功能");
}
public void setTime(){ // 定时
System.out.println("定时功能");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用WashMachine类创建变量
WashMachine washMachine;
}
}
如何创建一个对象?对象中有什么 ?
使用描述该对象的类 + new关键字 创建对象:
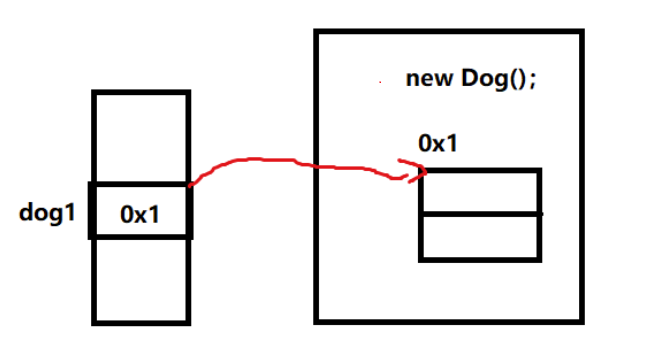
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
new Dog(); 创建(实例化) 对象
对象根据Dog类创建 ——》用Dog类定义的变量dog1存储对象地址, 此时dog1称为对象的引用 简称引用
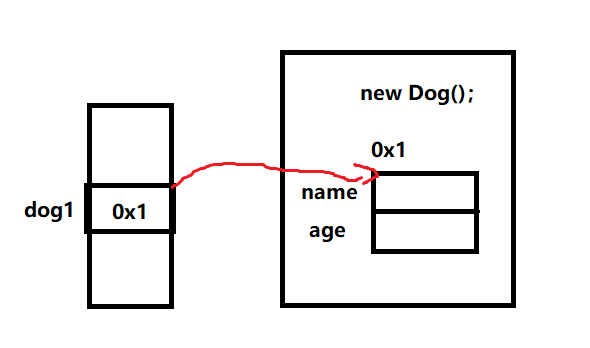
class Dog {
// 字段 / 属性 / 成员变量
public String name;
public int age;
// 行为 / 成员方法
public static void bark() {
System.out.println("汪");
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象:
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
Dog dog2 = new Dog();
}
}对象内部只存储成员变量
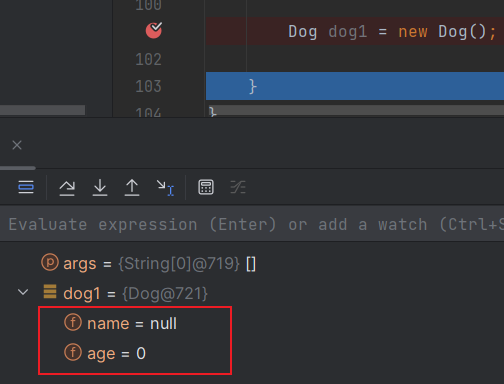
new关键字创建对象,具体执行过程是什么 ?
如何访问对象的属性和方法 ?
通过对象的引用加点号 访问对象的属性和方法
例子:
class Dog {
// 字段 / 属性 / 成员变量
public String name;
public int age;
// 行为 / 成员方法
public static void bark() {
System.out.println("汪");
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
// 3. 访问对象属性与方法
dog1.age = 10;
dog1.name = "大黄";
System.out.println(dog1.name);
System.out.println(dog1.age);
dog1.bark();
}
}练习: 使用类和对象知识,交换两个值
class MyValue {
int value;
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyValue num1 = new MyValue();
MyValue num2 = new MyValue();
num1.value = 1;
num2.value = 2;
System.out.printf("交换前 ---> num1 = %d num2 = %d\n",num1.value,num2.value);
Swap(num1,num2);
System.out.printf("交换后 ---> num1 = %d num2 = %d\n",num1.value,num2.value);
}
public static void Swap(MyValue num1, MyValue num2) {
int tmp = num1.value;
num1.value = num2.value;
num2.value = tmp;
}
}
2. this引用
什么是this引用 ?
谁调用成员方法 谁就是this引用
例子:
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
// this引用是隐藏参数 可以自己加
public void setDay(Date this,int y, int m, int d) {
this.year = y;
this.month = m;
this.day = d;
}
public void printDate(Date this) {
System.out.println(this.year + "/" + this.month + "/" + this.day);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date1 = new Date();
Date date2 = new Date();
// 不能自己传递当前调用方法的对象引用
// date1.setDay(date1,1,1,1);
date1.setDay(1,1,1);
date2.setDay(2,2,2);
date1.printDate();
date2.printDate();
}
}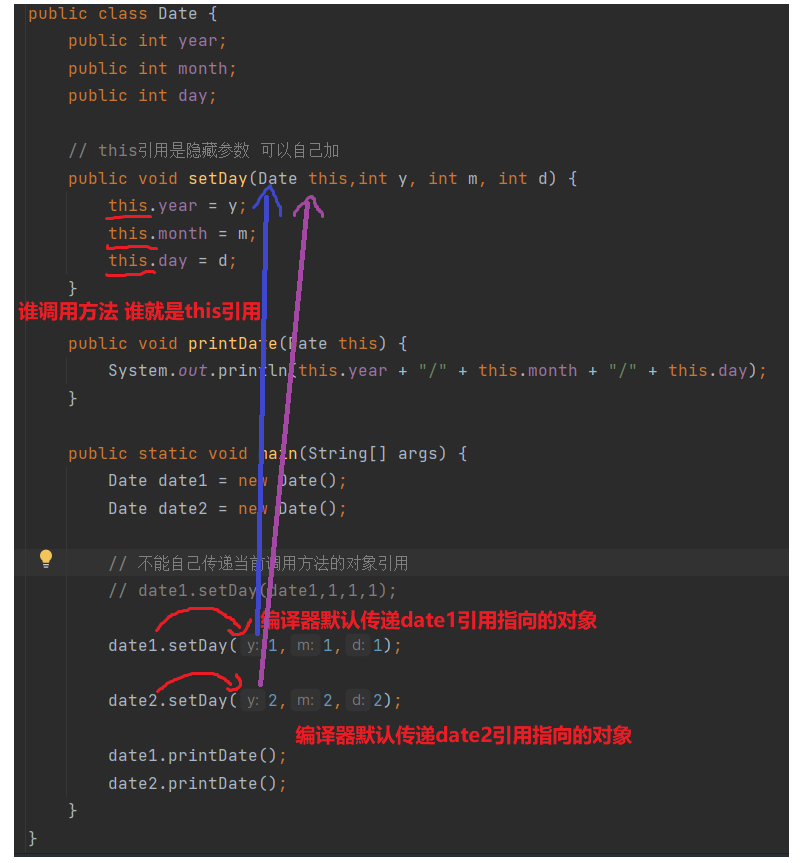
注意:
this引用是隐藏参数 可以自己加, 但是不能自己传递当前调用方法的对象引用
this引用有哪些作用 ?
1. this.成员变量
2. this.成员方法
3. this() 调用构造函数
1 2 很好理解 this是对象的引用 通过点号访问对象的属性和方法,3 在构造方法中介绍
3. 构造方法
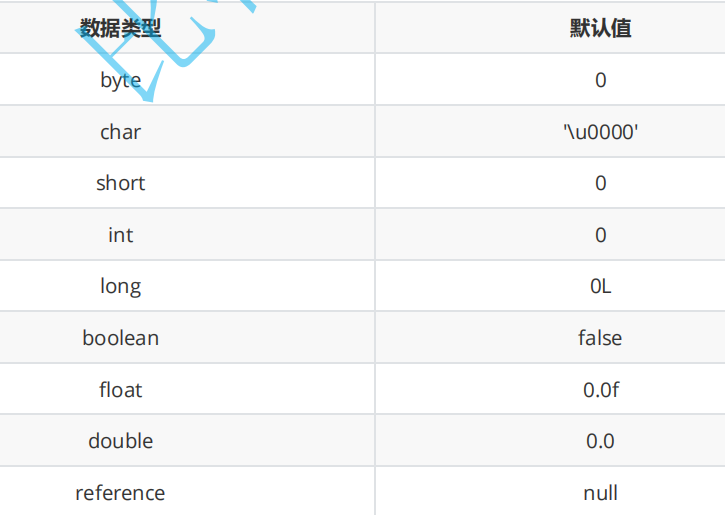
一共有几种初始化对象属性的方法 ?
1. 默认初始化
使用new关键字创建对象 开辟空间后 会根据数据类型分配一个默认的值
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
// this引用是隐藏参数 可以自己加
public void setDay(Date this,int y, int m, int d) {
this.year = y;
this.month = m;
this.day = d;
}
public void printDate(Date this) {
System.out.println(this.year + "/" + this.month + "/" + this.day);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date1 = new Date();
date1.printDate(); // 0 0 0
}
}2. 就地初始化
public class Date {
// 就地初始化
// 声明成员变量时赋值
public int year = 1;
public int month = 1;
public int day = 1;
// this引用是隐藏参数 可以自己加
public void setDay(Date this,int y, int m, int d) {
this.year = y;
this.month = m;
this.day = d;
}
public void printDate(Date this) {
System.out.println(this.year + "/" + this.month + "/" + this.day);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date1 = new Date();
date1.printDate();
}
}3. 使用构造方法进行初始化
什么是构造方法 ? 构造方法有什么用 ?
构造方法是类中特殊成员方法 用来对对象的成员变量进行初始化
如何定义构造方法 ?
写法: 方法名与类名相同没有返回值
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
// 构造方法:
public Date() {
this.year = 1;
this.month = 1;
this.day = 1;
}
public void setDay(Date this,int y, int m, int d) {
this.year = y;
this.month = m;
this.day = d;
}
public void printDate(Date this) {
System.out.println(this.year + "/" + this.month + "/" + this.day);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date1 = new Date();
date1.printDate();
}
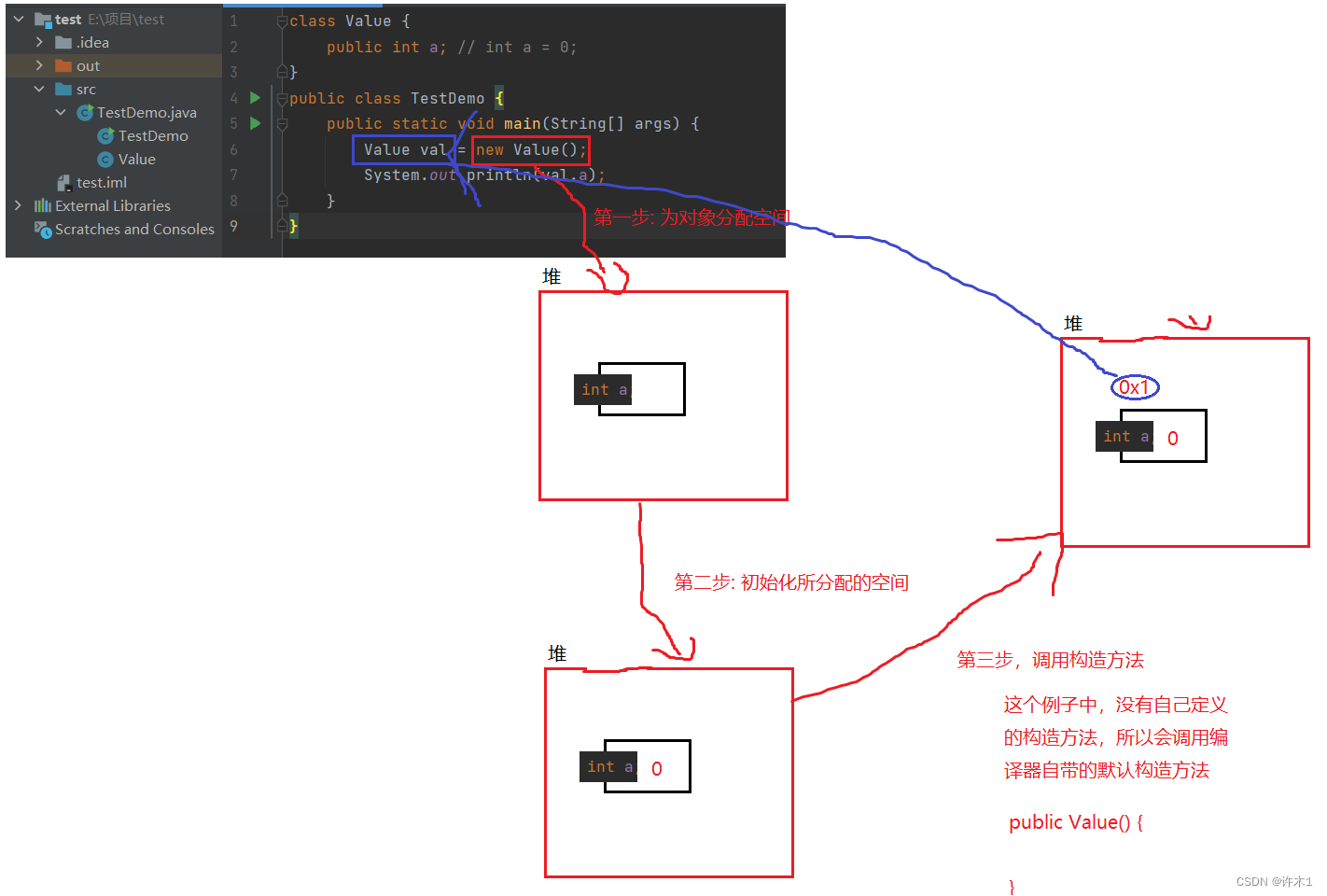
}构造方法什么时候调用的 ?
new创建对象时调用构造方法 且只调用一次
new对象大致过程:
首先给对象分配内存,然后编译器自动调用合适的构造方法(构造方法可以重载)给对象进行初始化,这里的合适指,编译器会根据参数选取构造方法进行初始化
查看代码
class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
public Date(int y,int m,int d) {
this.year = y;
this.month = m;
this.day = d;
}
public Date() {
this.year = 1;
this.month = 1;
this.day = 1;
}
public void print(Date this) {
System.out.print(this.year + " " + this.month + " " + this.day);
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 调用带有3个参数的构造方法
Date date1 = new Date(2,2,2);
date1.print();
// 调用带有无参构造
Date date2 = new Date();
date2.print();
}
}
如何在类中调用其他构造 ?
构造方法中,可以通过this调用其他构造方法
注意: 使用this调用必须放在当前构造方法的第一行,this调用也是根据参数选取构造方法进行调用
查看代码
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
// 默认生成的构造方法
public Date(){
// 调用三个参数的构造方法
this(2024,1,24);
}
public Date(int year,int month,int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public void printDate(Date this) {
System.out.println(this.year + "/" + this.month + "/" + this.day);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date1 = new Date();
date1.printDate();
}
}
构造方法是new对象时调用的 所以一定会被调用 那么为什么不写构造方法并没有报错 ?
如果没有自己定义构造方法,编译器会生成一份默认的构造方法,生成的默认构造方法一定是无参且没有具体的实现
如果自己定义了构造方法,编译器将不再生成
查看代码
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
// 默认生成的构造方法
public Date(){
}
public void setDay(Date this,int y, int m, int d) {
this.year = y;
this.month = m;
this.day = d;
}
public void printDate(Date this) {
System.out.println(this.year + "/" + this.month + "/" + this.day);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date1 = new Date();
date1.printDate();
}
}
4. 封装
什么是封装 ?在java中如何实现封装 ?
封装就是隐藏类内部实现的细节, 只对外提供一些开发的接口
在java中使用 private关键字实现
class Student {
// private修饰的成员变量和方法 只能在当前类中使用
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 只对外提供一些开发的接口
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("小白",19);
System.out.println(student1.getName());
}
}
5. static 关键字
static关键字的作用是什么 ?
为了不创建对象去访问成员变量和方法,static修饰的静态成员变量和方法使用类名+点号访问
public class Test {
public int a = 1;
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1: 非静态方法");
}
public static int b = 2;
public static void test2() {
System.out.println("test2: 静态方法");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 非静态成员方法和变量 需要对象去访问成员变量和方法
Test obj = new Test();
obj.test1();
System.out.println(obj.a);
// static修饰的静态成员变量和方法 不需要对象 使用类名 + 点号访问
Test.test2();
System.out.println(Test.b);
}
}注意:
1. 虽然使用类实例化对象的引用也可以访问静态成员变量,但是不合适不建议
2. 静态成员属于类的属性,存储在方法区 且只存储一份
3. 静态的成员变量 随着类被加载而创建 类被销毁而销毁
4. static 只能修饰成员变量和方法,不能修饰局部变量
静态方法中是否可以使用非静态成员变量和方法 ?
不可以,static修饰的成员属于类 使用类名访问,而不是用对象的引用
所以不会传递this引用, 没有this引用 就不能调用普通成员 因为普通成员调用需要对象,参考例4
但是 非静态方法中可以使用静态成员,参考例3
public class Test {
public int a = 1;
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1: 非静态方法");
}
public static int b = 2;
public static void test2() {
System.out.println("test2: 静态方法");
}
// 3. 非静态方法中可以使用静态成员
public void test3() {
test2();
System.out.println(b);
}
// 4. 但是 静态方法中不能使用非静态成员变量和方法
public static void test4() {
// 报错 !
/*System.out.println(this.a);
this.test1();*/
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 非静态成员方法和变量 需要对象去访问成员变量和方法
/*Test obj = new Test();
obj.test1();
System.out.println(obj.a);*/
// 2. static修饰的静态成员变量和方法 不需要对象 使用类名 + 点号访问
/*Test.test2();
System.out.println(Test.b);*/
// 3.
/*Test obj = new Test();
obj.test3();*/
// 4.
//Test.test4();
}
}
6. 代码块和内部类
class TestStatic {
public static int staticNum = 100;
public int data1 = 10;
{
// 构造代码块 || 实例代码块
// 创建对象时才会执行
System.out.println("实例代码块被执行了....");
data1 = 1000;// 1. 构造代码块一般情况下 用来初始化 非静态的数据成员
//staticNum = 1000000; 2. 构造代码块 也可以初始化静态的数据成员
}
// 3. 静态代码块 只能初始化静态成员
// JVM 加载类时执行
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块被执行了....");
staticNum = 9999;
// data1 = 20;
}
static {
staticNum = 20;
}
public TestStatic() {
System.out.println("执行构造方法.....");
}
// 4. 执行顺序: 静态 -> 实例 -> 构造方法
public static void main1(String[] args) {
TestStatic testStatic = new TestStatic();
}
// 5. 如果一个类中包含多个静态代码块,在编译代码时,编译器会按照定义的先后次序依次执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(TestStatic.staticNum);
}
}
// 静态内部类
/*
class Outer {
public int a = 1;
public static int b = 2;
// 1. 把静态内部类当作类的成员
static class innerClass {
// 3. 内部类中无法直接访问 外部类非静态的成员变量
public void get() {
// 因为需要对象的引用
Outer outer = new Outer();
System.out.println(outer.a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println("innerClass::func");
}
}
// 2. 方法2: 实例化静态内部类对象
public void test() {
innerClass innerClass = new innerClass();
innerClass.get();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2. 方法1: 实例化静态内部类对象
*/
/*
Outer.innerClass innerClass = new Outer.innerClass();
innerClass.get();
Outer outer = new Outer();
outer.test();
*//*
}
}*/
// 实例内部类
/*class Outer {
public int a = 1;
public static int b = 2;
// 1. 实例内部类定义
class innerClass {
// 2. 实例内部类中不能定义 静态成员变量
// 因为实例内部类 看作是类的成员 会被对象引用进行调用
//public static int a = 1;
// 3. 如果一定要定义 必须加final修饰
public static final int b = 3;
public void get() {
// 5. 指定访问外部类成员
// 方法1: 外部类对象引用
Outer outer = new Outer();
System.out.println(outer.a);
// 方法2: 外部类.this
System.out.println(Outer.this.a);
System.out.println("innerClass::func");
}
}
public void test() {
innerClass innerClass = new innerClass();
innerClass.get();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
*//*Outer outer = new Outer();
outer.test();*//*
// 4. 实例内部类 实例化对象
Outer.innerClass innerClass = new Outer().new innerClass();
innerClass.get();
}
}*/
// 匿名内部类
/*
interface InterfaceA {
void fun();
}
class Test implements InterfaceA {
@Override
public void fun() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InterfaceA interfaceA = new InterfaceA() {
@Override
public void fun() {
System.out.println("test2");
}
};
interfaceA.fun();
}
}
*/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号