第四章 微服务架构分层设计
字数 2573,阅读大约需 13 分钟
第四章 微服务架构分层设计
在实际项目中,很多团队对微服务的理解停留在"把单体应用拆小"的层面。但真正的微服务架构需要精心设计的分层结构,就像建造一座大厦,需要清晰的蓝图和稳固的地基。
4.1 整体架构设计
4.1.1 微服务架构的核心组件
经过多个项目的实践,我发现一个健壮的微服务架构通常包含以下核心组件。让我用一张图来展示这些组件的关系:
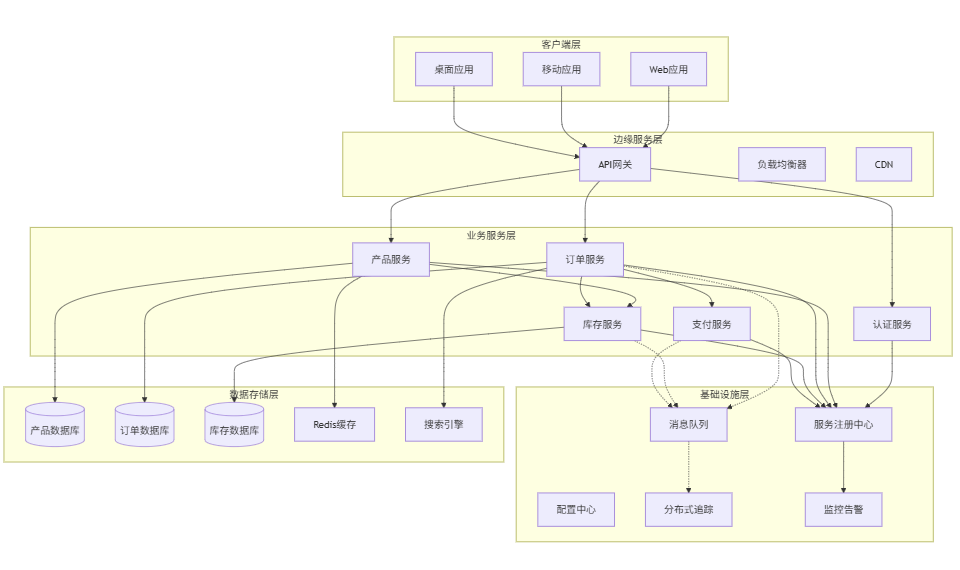
让我详细解释每个组件的作用和实践经验:
1. API网关:系统的门面
API网关不仅仅是路由转发,它是整个系统的战略要地。在实际项目中,我通常使用Ocelot(.NET生态)或Kong作为网关。
- • 描述: 微服务架构的单一入口点。它负责将客户端请求路由到相应的微服务,并处理一些横切关注点(如认证、授权、限流、缓存、日志、监控)。
- • 重要性: 简化客户端与微服务之间的交互,提供统一的 API 接口,并增强安全性。
// Ocelot配置示例
{
"Routes": [
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/api/products/{everything}",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "product-service",
"Port": 80
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/products/{everything}",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Post", "Put", "Delete" ],
"AuthenticationOptions": {
"AuthenticationProviderKey": "Bearer",
"AllowedScopes": [ "product_api" ]
},
"RateLimitOptions": {
"ClientWhitelist": [],
"EnableRateLimiting": true,
"Period": "1s",
"PeriodTimespan": 1,
"Limit": 10
}
}
],
"GlobalConfiguration": {
"BaseUrl": "https://api.yourdomain.com"
}
}2. 服务注册与发现
在Docker和Kubernetes环境中,服务实例的IP是动态变化的,服务发现变得至关重要。
// 使用Consul作为服务注册中心
public class ConsulServiceRegistry : IServiceRegistry
{
private readonly ConsulClient _consulClient;
private readonly ILogger<ConsulServiceRegistry> _logger;
public ConsulServiceRegistry(IConfiguration configuration, ILogger<ConsulServiceRegistry> logger)
{
_consulClient = new ConsulClient(config =>
{
config.Address = new Uri(configuration["Consul:Address"]);
});
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task RegisterServiceAsync(string serviceName, string serviceId, string serviceAddress, int servicePort)
{
var registration = new AgentServiceRegistration()
{
ID = serviceId,
Name = serviceName,
Address = serviceAddress,
Port = servicePort,
Check = new AgentServiceCheck()
{
HTTP = $"http://{serviceAddress}:{servicePort}/health",
Interval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10),
Timeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5),
DeregisterCriticalServiceAfter = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1)
}
};
await _consulClient.Agent.ServiceRegister(registration);
_logger.LogInformation($"Service {serviceName} registered with Consul");
}
public async Task UnregisterServiceAsync(string serviceId)
{
await _consulClient.Agent.ServiceDeregister(serviceId);
_logger.LogInformation($"Service {serviceId} unregistered from Consul");
}
}
// 在Program.cs中注册服务
var app = builder.Build();
var consulRegistry = app.Services.GetRequiredService<ConsulServiceRegistry>();
var lifetime = app.Services.GetRequiredService<IHostApplicationLifetime>();
var config = app.Configuration;
var serviceId = $"{config["Service:Name"]}-{Guid.NewGuid()}";
var serviceAddress = config["Service:Address"] ?? "localhost";
var servicePort = int.Parse(config["Service:Port"] ?? "5000");
lifetime.ApplicationStarted.Register(async () =>
{
await consulRegistry.RegisterServiceAsync(
config["Service:Name"],
serviceId,
serviceAddress,
servicePort);
});
lifetime.ApplicationStopping.Register(async () =>
{
await consulRegistry.UnregisterServiceAsync(serviceId);
});3. 配置中心
集中管理配置是微服务运维的关键。
// 使用Apollo配置中心
public class ApolloConfigurationProvider : ConfigurationProvider
{
private readonly ApolloClient _apolloClient;
private readonly ILogger<ApolloConfigurationProvider> _logger;
public ApolloConfigurationProvider(ApolloOptions options, ILogger<ApolloConfigurationProvider> logger)
{
_apolloClient = new ApolloClient(options);
_logger = logger;
}
public override void Load()
{
try
{
var configurations = _apolloClient.GetConfigurationsAsync().Result;
foreach (var config in configurations)
{
Data[config.Key] = config.Value;
}
// 监听配置变更
_apolloClient.OnConfigChanged += (sender, args) =>
{
_logger.LogInformation($"Configuration changed: {args.Namespace}");
OnReload();
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Failed to load configuration from Apollo");
}
}
}4.2 微服务内部分层设计
每个微服务内部也需要清晰的分层结构。我通常采用这样的分层:
ProductService/
├── src/
│ ├── ProductService.Api/ # API层(控制器)
│ ├── ProductService.Application/ # 应用层(用例、CQRS)
│ ├── ProductService.Domain/ # 领域层(实体、值对象)
│ ├── ProductService.Infrastructure/# 基础设施层(数据访问、外部服务)
│ └── ProductService.Shared/ # 共享组件4.2.1 API层(Presentation Layer)
负责处理HTTP请求,验证输入,返回响应。
[ApiController]
[Route("api/v1/[controller]")]
[Authorize]
public class ProductsController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IMediator _mediator;
private readonly ILogger<ProductsController> _logger;
public ProductsController(IMediator mediator, ILogger<ProductsController> logger)
{
_mediator = mediator;
_logger = logger;
}
[HttpGet("{id}")]
[ProducesResponseType(typeof(ProductDto), StatusCodes.Status200OK)]
[ProducesResponseType(StatusCodes.Status404NotFound)]
public async Task<ActionResult<ProductDto>> GetById(Guid id)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Getting product {ProductId}", id);
var query = new GetProductByIdQuery(id);
var result = await _mediator.Send(query);
return result.Match<ActionResult<ProductDto>>(
product => Ok(product),
notFound => NotFound());
}
[HttpPost]
[ProducesResponseType(typeof(ProductDto), StatusCodes.Status201Created)]
[ProducesResponseType(typeof(ValidationProblemDetails), StatusCodes.Status400BadRequest)]
public async Task<ActionResult<ProductDto>> Create([FromBody] CreateProductCommand command)
{
var result = await _mediator.Send(command);
return result.Match<ActionResult<ProductDto>>(
product => CreatedAtAction(
nameof(GetById),
new { id = product.Id },
product),
validationError => BadRequest(validationError));
}
}4.2.2 应用层(Application Layer)
协调领域对象完成业务用例,不包含业务规则。
// CQRS命令处理器
public class CreateProductCommandHandler : IRequestHandler<CreateProductCommand, Result<ProductDto>>
{
private readonly IProductRepository _repository;
private readonly IUnitOfWork _unitOfWork;
private readonly IMapper _mapper;
private readonly ILogger<CreateProductCommandHandler> _logger;
public CreateProductCommandHandler(
IProductRepository repository,
IUnitOfWork unitOfWork,
IMapper mapper,
ILogger<CreateProductCommandHandler> logger)
{
_repository = repository;
_unitOfWork = unitOfWork;
_mapper = mapper;
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task<Result<ProductDto>> Handle(CreateProductCommand request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Creating product {ProductName}", request.Name);
// 验证产品名称唯一性
var existingProduct = await _repository.GetByNameAsync(request.Name);
if (existingProduct != null)
{
return Result.Failure<ProductDto>("Product name already exists");
}
// 创建领域实体
var product = Product.Create(
request.Name,
request.Description,
Money.Create(request.Price, request.Currency),
request.CategoryId);
// 保存到数据库
await _repository.AddAsync(product);
await _unitOfWork.SaveChangesAsync();
// 发布领域事件
await _unitOfWork.PublishDomainEventsAsync();
_logger.LogInformation("Product created {ProductId}", product.Id);
return Result.Success(_mapper.Map<ProductDto>(product));
}
}4.2.3 领域层(Domain Layer)
包含业务逻辑的核心,是系统的灵魂。
// 聚合根
public class Product : AggregateRoot
{
private Product() { } // EF Core需要
private Product(string name, string description, Money price, Guid categoryId)
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid();
Name = name;
Description = description;
Price = price;
CategoryId = categoryId;
CreatedAt = DateTime.UtcNow;
Status = ProductStatus.Draft;
}
public string Name { get; private set; }
public string Description { get; private set; }
public Money Price { get; private set; }
public Guid CategoryId { get; private set; }
public ProductStatus Status { get; private set; }
public DateTime CreatedAt { get; private set; }
// 值对象集合
private readonly List<ProductImage> _images = new();
public IReadOnlyCollection<ProductImage> Images => _images.AsReadOnly();
// 工厂方法
public static Product Create(string name, string description, Money price, Guid categoryId)
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(name))
throw new BusinessRuleException("Product name cannot be empty");
if (price.Amount <= 0)
throw new BusinessRuleException("Product price must be greater than zero");
var product = new Product(name, description, price, categoryId);
// 添加领域事件
product.AddDomainEvent(new ProductCreatedEvent(product.Id, product.Name));
return product;
}
// 领域行为
public void UpdatePrice(Money newPrice)
{
if (newPrice.Amount <= 0)
throw new BusinessRuleException("Price must be greater than zero");
var oldPrice = Price;
Price = newPrice;
// 发布价格变更事件
AddDomainEvent(new ProductPriceChangedEvent(Id, oldPrice, newPrice));
}
public void AddImage(string url, string altText)
{
if (_images.Count >= 10)
throw new BusinessRuleException("Product cannot have more than 10 images");
var image = new ProductImage(url, altText);
_images.Add(image);
}
public void Publish()
{
if (Status != ProductStatus.Draft)
throw new BusinessRuleException("Only draft products can be published");
if (_images.Count == 0)
throw new BusinessRuleException("Product must have at least one image to be published");
Status = ProductStatus.Published;
AddDomainEvent(new ProductPublishedEvent(Id));
}
}
// 值对象
public record Money
{
public decimal Amount { get; }
public string Currency { get; }
private Money(decimal amount, string currency)
{
Amount = amount;
Currency = currency;
}
public static Money Create(decimal amount, string currency)
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(currency))
throw new BusinessRuleException("Currency is required");
if (currency.Length != 3)
throw new BusinessRuleException("Currency must be 3 characters");
return new Money(amount, currency.ToUpper());
}
// 值对象相等性
protected override IEnumerable<object> GetEqualityComponents()
{
yield return Amount;
yield return Currency;
}
}4.2.4 基础设施层(Infrastructure Layer)
提供技术实现,如数据持久化、外部服务调用等。
// Entity Framework Core仓储实现
public class ProductRepository : IProductRepository
{
private readonly ProductDbContext _context;
public ProductRepository(ProductDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public async Task<Product> GetByIdAsync(Guid id)
{
return await _context.Products
.Include(p => p.Images)
.FirstOrDefaultAsync(p => p.Id == id);
}
public async Task<Product> GetByNameAsync(string name)
{
return await _context.Products
.FirstOrDefaultAsync(p => p.Name == name);
}
public async Task AddAsync(Product product)
{
await _context.Products.AddAsync(product);
}
public void Update(Product product)
{
_context.Products.Update(product);
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<Product>> GetPublishedProductsAsync(int page, int pageSize)
{
return await _context.Products
.Where(p => p.Status == ProductStatus.Published)
.OrderByDescending(p => p.CreatedAt)
.Skip((page - 1) * pageSize)
.Take(pageSize)
.ToListAsync();
}
}
// DbContext配置
public class ProductDbContext : DbContext
{
public ProductDbContext(DbContextOptions<ProductDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
// 配置聚合根
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>(entity =>
{
entity.HasKey(e => e.Id);
entity.Property(e => e.Id).ValueGeneratedNever();
// 配置值对象
entity.OwnsOne(e => e.Price, price =>
{
price.Property(p => p.Amount).HasColumnName("Price_Amount");
price.Property(p => p.Currency).HasColumnName("Price_Currency").HasMaxLength(3);
});
// 配置枚举
entity.Property(e => e.Status)
.HasConversion<string>()
.HasMaxLength(20);
// 配置集合
entity.HasMany(e => e.Images)
.WithOne()
.HasForeignKey("ProductId");
});
// 配置领域事件
modelBuilder.Ignore<ProductCreatedEvent>();
modelBuilder.Ignore<ProductPriceChangedEvent>();
}
}4.3 跨服务通信设计
微服务之间的通信是架构设计的重点。我通常采用混合通信模式:
4.3.1 同步通信(REST/gRPC)
适用于实时性要求高的场景:
// gRPC服务定义
service InventoryService {
rpc CheckStock (CheckStockRequest) returns (CheckStockResponse);
rpc ReserveStock (ReserveStockRequest) returns (ReserveStockResponse);
rpc ReleaseStock (ReleaseStockRequest) returns (ReleaseStockResponse);
}
// .NET gRPC客户端
public class InventoryServiceClient : IInventoryService
{
private readonly InventoryService.InventoryServiceClient _client;
private readonly ILogger<InventoryServiceClient> _logger;
public InventoryServiceClient(GrpcChannel channel, ILogger<InventoryServiceClient> logger)
{
_client = new InventoryService.InventoryServiceClient(channel);
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task<bool> CheckStockAsync(Guid productId, int quantity)
{
try
{
var request = new CheckStockRequest
{
ProductId = productId.ToString(),
Quantity = quantity
};
var response = await _client.CheckStockAsync(request);
return response.Available;
}
catch (RpcException ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error checking stock for product {ProductId}", productId);
throw new ServiceUnavailableException("Inventory service is unavailable");
}
}
}4.3.2 异步通信(消息队列)
适用于解耦服务和处理长时间运行的业务:
// 定义集成事件
public record OrderCreatedEvent : IntegrationEvent
{
public Guid OrderId { get; init; }
public Guid CustomerId { get; init; }
public List<OrderItem> Items { get; init; }
public DateTime CreatedAt { get; init; }
}
// 事件发布者
public class EventPublisher : IEventPublisher
{
private readonly IPublishEndpoint _publishEndpoint;
private readonly ILogger<EventPublisher> _logger;
public EventPublisher(IPublishEndpoint publishEndpoint, ILogger<EventPublisher> logger)
{
_publishEndpoint = publishEndpoint;
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task PublishAsync<T>(T integrationEvent) where T : IntegrationEvent
{
try
{
await _publishEndpoint.Publish(integrationEvent);
_logger.LogInformation("Published event {EventType}", typeof(T).Name);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error publishing event {EventType}", typeof(T).Name);
throw;
}
}
}
// 事件消费者
public class OrderCreatedEventConsumer : IConsumer<OrderCreatedEvent>
{
private readonly IInventoryService _inventoryService;
private readonly ILogger<OrderCreatedEventConsumer> _logger;
public OrderCreatedEventConsumer(IInventoryService inventoryService, ILogger<OrderCreatedEventConsumer> logger)
{
_inventoryService = inventoryService;
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task Consume(ConsumeContext<OrderCreatedEvent> context)
{
var orderCreatedEvent = context.Message;
try
{
_logger.LogInformation("Processing order created event for order {OrderId}", orderCreatedEvent.OrderId);
// 预留库存
foreach (var item in orderCreatedEvent.Items)
{
var reserved = await _inventoryService.ReserveStockAsync(
item.ProductId,
item.Quantity);
if (!reserved)
{
_logger.LogWarning("Failed to reserve stock for product {ProductId}", item.ProductId);
// 发布库存不足事件
await context.Publish(new StockInsufficientEvent
{
OrderId = orderCreatedEvent.OrderId,
ProductId = item.ProductId,
RequestedQuantity = item.Quantity
});
return;
}
}
_logger.LogInformation("Successfully reserved stock for order {OrderId}", orderCreatedEvent.OrderId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error processing order created event for order {OrderId}", orderCreatedEvent.OrderId);
throw;
}
}
}4.4 小结
微服务架构的分层设计不是一蹴而就的,它需要根据业务需求、团队规模和技术栈来不断演进。记住几个关键原则:
- 1. 清晰的层次边界:每一层都有明确的职责
- 2. 依赖倒置:领域层不依赖其他层
- 3. 技术异构:不同服务可以选择最合适的技术栈
- 4. 渐进式演进:从单体到微服务是一个渐进的过程
最重要的是,不要为了微服务而微服务。我见过很多项目盲目追求微服务,结果导致系统复杂度急剧上升,维护成本暴增。微服务架构是为了解决特定问题而存在的,只有当单体架构真正成为瓶颈时,才需要考虑微服务化。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号