更多的时候,我们得到的图像不可能是正的,多少都会有一定的倾斜,就比如下面的
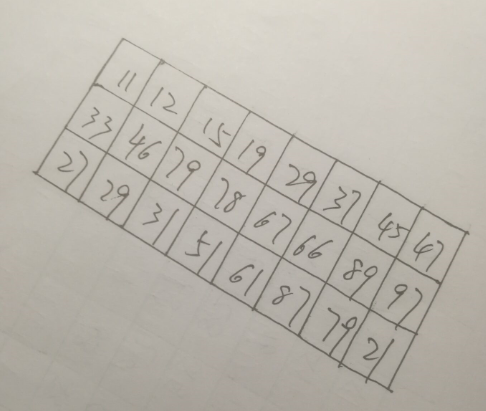
我们要做的就是把它们变成下面这样的
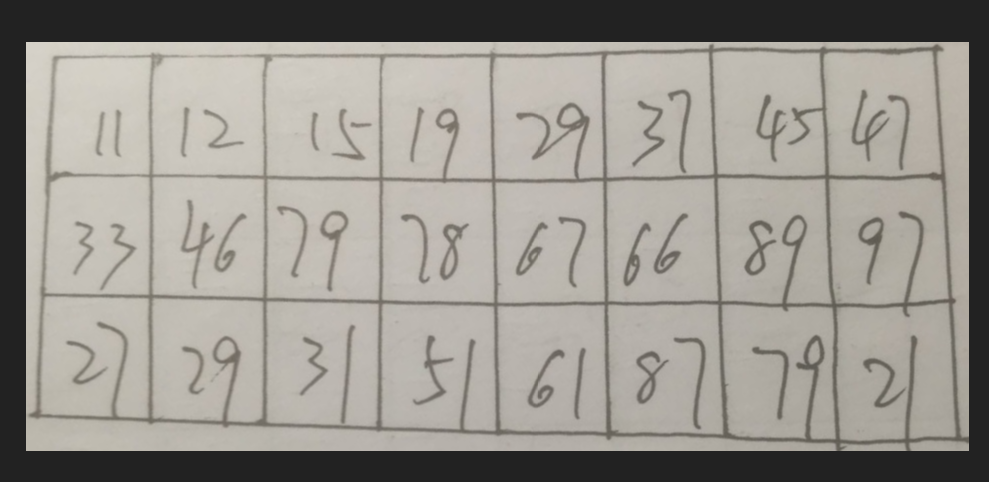
我们采用的是寻找轮廓的思路,来矫正图片;只要有明显的轮廓都可以采用这种思路
具体思路:
1、先用opencv提供的canny函数,进行一次边缘检测
2、再用opencv提供的findContours函数,寻找图像的轮廓,从中间结果种,找到最大的轮廓,就是我们图像的最外面的轮廓
3、得到最终轮廓后,计算矩形轮廓与水平的夹角,然后旋转图像
4、最后我们在从旋转后的图像中,把我们感兴趣的切割出来,就可以了
我们实际的实现一下
先用opencv提供的canny函数,进行一次边缘检测;具体的函数就不再讲解,百度上非常多
/**
* canny算法,边缘检测
*
* @param src
* @return
*/
public static Mat canny(Mat src) {
Mat mat = src.clone();
Imgproc.Canny(src, mat, 60, 200);
HandleImgUtils.saveImg(mat , "C:/Users/admin/Desktop/opencv/open/x/canny.jpg");
return mat;
}
再用opencv提供的findContours函数,寻找图像的轮廓,从中间结果种,找到最大的轮廓,就是我们图像的最外面的轮廓
/**
* 返回边缘检测之后的最大矩形,并返回
*
* @param cannyMat
* Canny之后的mat矩阵
* @return
*/
public static RotatedRect findMaxRect(Mat cannyMat) {
List<MatOfPoint> contours = new ArrayList<MatOfPoint>();
Mat hierarchy = new Mat();
// 寻找轮廓
Imgproc.findContours(cannyMat, contours, hierarchy, Imgproc.RETR_EXTERNAL, Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE,
new Point(0, 0));
// 找出匹配到的最大轮廓
double area = Imgproc.boundingRect(contours.get(0)).area();
int index = 0;
// 找出匹配到的最大轮廓
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) {
double tempArea = Imgproc.boundingRect(contours.get(i)).area();
if (tempArea > area) {
area = tempArea;
index = i;
}
}
MatOfPoint2f matOfPoint2f = new MatOfPoint2f(contours.get(index).toArray());
RotatedRect rect = Imgproc.minAreaRect(matOfPoint2f);
return rect;
}
得到最终轮廓后,计算矩形轮廓与水平的夹角,然后旋转图像
/**
* 旋转矩形
*
* @param src
* mat矩阵
* @param rect
* 矩形
* @return
*/
public static Mat rotation(Mat cannyMat, RotatedRect rect) {
// 获取矩形的四个顶点
Point[] rectPoint = new Point[4];
rect.points(rectPoint);
double angle = rect.angle + 90;
Point center = rect.center;
Mat CorrectImg = new Mat(cannyMat.size(), cannyMat.type());
cannyMat.copyTo(CorrectImg);
// 得到旋转矩阵算子
Mat matrix = Imgproc.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 0.8);
Imgproc.warpAffine(CorrectImg, CorrectImg, matrix, CorrectImg.size(), 1, 0, new Scalar(0, 0, 0));
return CorrectImg;
}
最后我们在从旋转后的图像中,把我们感兴趣的切割出来,就可以了
/**
* 把矫正后的图像切割出来
*
* @param correctMat
* 图像矫正后的Mat矩阵
*/
public static void cutRect(Mat correctMat , Mat nativeCorrectMat) {
// 获取最大矩形
RotatedRect rect = findMaxRect(correctMat);
Point[] rectPoint = new Point[4];
rect.points(rectPoint);
int startLeft = (int)Math.abs(rectPoint[0].x);
int startUp = (int)Math.abs(rectPoint[0].y < rectPoint[1].y ? rectPoint[0].y : rectPoint[1].y);
int width = (int)Math.abs(rectPoint[2].x - rectPoint[0].x);
int height = (int)Math.abs(rectPoint[1].y - rectPoint[0].y);
System.out.println("startLeft = " + startLeft);
System.out.println("startUp = " + startUp);
System.out.println("width = " + width);
System.out.println("height = " + height);
for(Point p : rectPoint) {
System.out.println(p.x + " , " + p.y);
}
Mat temp = new Mat(nativeCorrectMat , new Rect(startLeft , startUp , width , height ));
Mat t = new Mat();
temp.copyTo(t);
HandleImgUtils.saveImg(t , "C:/Users/admin/Desktop/opencv/open/x/cutRect.jpg");
}
整合整个过程
/**
* 矫正图像
*
* @param src
* @return
*/
public static void correct(Mat src) {
// Canny
Mat cannyMat = canny(src);
// 获取最大矩形
RotatedRect rect = findMaxRect(cannyMat);
// 旋转矩形
Mat CorrectImg = rotation(cannyMat , rect);
Mat NativeCorrectImg = rotation(src , rect);
//裁剪矩形
cutRect(CorrectImg , NativeCorrectImg);
HandleImgUtils.saveImg(src, "C:/Users/admin/Desktop/opencv/open/x/srcImg.jpg");
HandleImgUtils.saveImg(CorrectImg, "C:/Users/admin/Desktop/opencv/open/x/correct.jpg");
}
测试代码
/**
* 测试矫正图像
*/
public void testCorrect() {
System.loadLibrary(Core.NATIVE_LIBRARY_NAME);
Mat src = HandleImgUtils.matFactory("C:/Users/admin/Desktop/opencv/open/x/x7.jpg");
HandleImgUtils.correct(src);
}
Java方面opencv的例子还是蛮少的,代码都是自己参考博客写的,照顾不周的地方,请见谅
本项目的所有代码地址:https://github.com/YLDarren/opencvHandleImg



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号