一组 李剑辰 7/20
.String
1.类中可以包含的结构:
- 属性 eg:String name;int num等等
- 方法:权限修饰符+返回值类型+方法名(参数类型+参数)
- 构造器:权限修饰符+类名(有参/无参){}
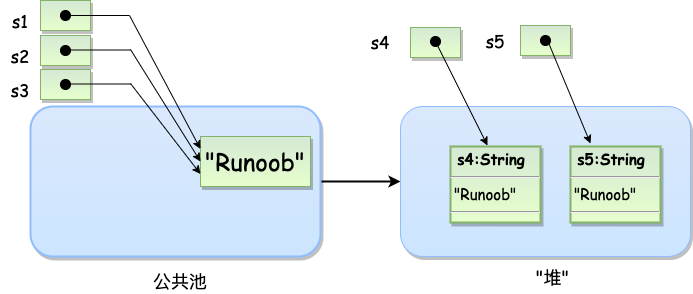
2.String类是不可改变的,一旦创建了String对象,那它的值就无法改变了 - 浅析String在创建字符串和new字符串的区别:
String s1 = "Runoob"; // String 直接创建
String s2 = "Runoob"; // String 直接创建
String s3 = s1; // 相同引用
String s4 = new String("Runoob"); // String 对象创建
String s5 = new String("Runoob"); // String 对象创建
它们主要的区别在于存储的位置不同,如下图![]()
直接由String创建的字符串是存储在公共池中,而由new创建的是存储在堆中
3.比较字符串的内容: - equals方法:需要传参(传String类型的参数);有返回值(为Boolean类型);访问权限为public
- length方法:不需要传参;有返回值(返回值类型为int);访问权限为public
注:字符串获取长度的方法和数组获取长度的方法的区别:
- 字符串的length()是方法
- 数组的length是属性
4.String方法: - charAt():取出指定位置的字符
点击查看代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s = "abcderg";
char result = s.charAt(6);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
点击查看代码
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String string = "aaa456ac";
//查找指定字符是在字符串中的下标。在则返回所在字符串下标;不在则返回-1.
System.out.println(string.indexOf("b")); // indexOf(String str); 返回结果:-1,"b"不存在
// 从第四个字符位置开始往后继续查找,包含当前位置
System.out.println(string.indexOf("a",3));//indexOf(String str, int fromIndex); 返回结果:6
//(与之前的差别:上面的参数是 String 类型,下面的参数是 int 类型)参考数据:a-97,b-98,c-99
// 从头开始查找是否存在指定的字符
System.out.println(string.indexOf(99));//indexOf(int ch);返回结果:7
System.out.println(string.indexOf('c'));//indexOf(int ch);返回结果:7
//从fromIndex查找ch,这个是字符型变量,不是字符串。字符a对应的数字就是97。
System.out.println(string.indexOf(97,3));//indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex); 返回结果:6
System.out.println(string.indexOf('a',3));//indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex); 返回结果:6
}
}
点击查看代码
public class RunoobTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String Str = new String("This is text");
System.out.print("返回值 :" );
System.out.println(Str.substring(4) );
System.out.print("返回值 :" );
System.out.println(Str.substring(4, 10) );
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号