uContext(#include<ucontext.h>)
typedef struct ucontext_t
{
unsigned long __ctx(uc_flags);
struct ucontext_t *uc_link; // uc_link指向当前context 结束时待恢复的上下文
stack_t uc_stack; // context 使用的栈 初始化栈顶指针(context.uc_stack.ss_sp = stack;) 栈大小(context.uc_stack.ss_size = sizeof(stack);)
sigset_t uc_sigmask;
mcontext_t uc_mcontext;
} ucontext_t;
- int getcontext (ucontext_t *ucp); 获取当前协程的context 并保存到 ucp 指向的内存
- int setcontext (const ucontext_t *ucp); 设置ucp指向的context为运行上下文并开始执行。
- void makecontext (ucontext_t ucp, void (func) (void), int argc, ...);修改ucp指向的任务。
- int swapcontext (ucontext_t restrict oucp, const ucontext_t restrict ucp); swapcontext()实现将当前的context保存到oucp中,并切换到ucp指向context继续执行。
coroutine协程库
- coroutine在uContext的基础上,做了封装。
- coroutine采用共享栈的模式,所有的协程在运行时使用同一份栈空间。但是在切换的时候,依然会使用_save_stack来保存当前栈的内容。
- coroutine提供了如下核心部件:
- struct schedule* S; 协程调度器
- coroutine_resume(S,co1); 切入该协程
- coroutine_yield(S); 切出该协程
- 调度方式如下图:
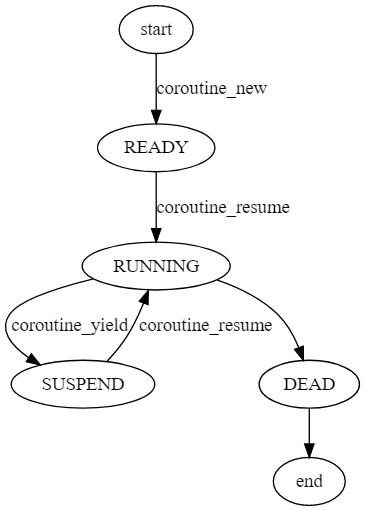
注意这里的调度方式,两个resume不能连续使用。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号