一、基本元注解:
@Retention:
说明这个注解的生命周期
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE -> 保留在原码阶段,编译时忽略
RetentionPolicy.CLASS -> 保留在编译阶段,不会被加载到jvm
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME -> 加载到jvm运行中
@Target:
指明注解运用之处
ElementType.Type -> 作用于类、接口、枚举
ElementType.FIELD -> 属性
ElementType.METHOD -> 方法
ElementType.PARAMETER -> 方法的参数
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR -> 构造方法
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE -> 局部变量
ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE -> 作用于注解
ElementType.PACKAGE -> 作用于包
ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER
ElementType.TYPE_USE
@Documented:
表示文档
@Inherited:
表示继承,作用在父类时子类可以拥有父类的注解
@Repeatable:
表明标记的注解维护一个容器,并且可以多次应用于相同的属性或声明
容器注解:

具体注解:
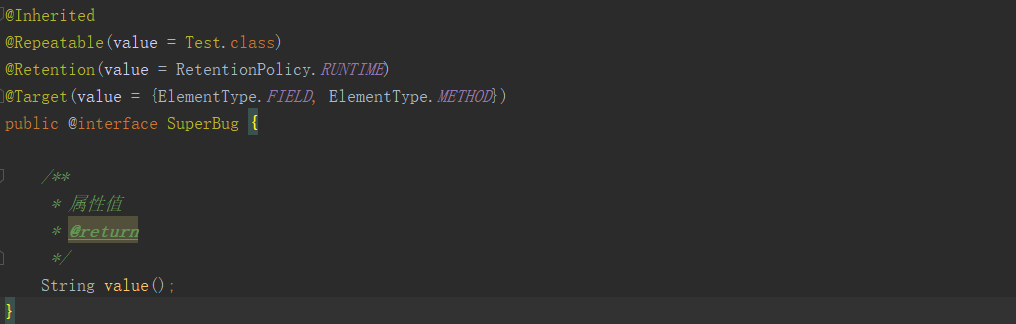
作用于方法:

二、注解的属性:
1、注解只有成员变量,没有方法。注解的成员变量在注解的定义中以“无形参的方法”形式来声明,其方法名定义了该成员变量的名字,其返回值定义了该成员变量的类型。
2、属性时它的类型必须是 8 种基本数据类型外加 类、接口、注解及它们的数组。数组属性在使用时可以加{}表示数组,也可以不加表示数组中只有一个元素。
三、注解的综合运用:
注解一般结合反射使用,通过反射模板对象获取注解的类型和属性值。
注解与反射:
1、java1.5在反射包中引入了 java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement 接口,该接口主要用于注解类型和属性的处理。
Class、Field、Method类的父类或超类都有实现AnnotatedElement 接口。

该类的子类Field、Method等关于AnnotatedElement 的方法必须被重写
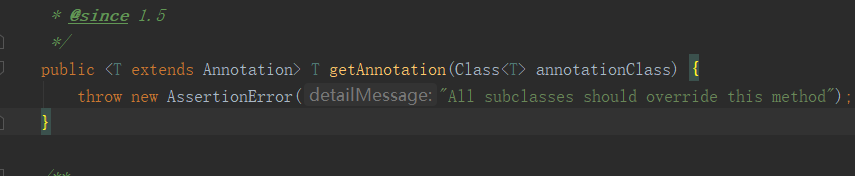
2、AnnotatedElement 接口的基本方法:
isAnnotationPresent(); 判断该元素上是否存在某个类型的注解。
getAnnotation()/getDeclaredAnnotation(); 通过注解类型获取注解对象,从而获取注解的属性值。
getAnnotations()/getDeclaredAnnotations(); 获取注解集合。
3、代码片段:
public static void main(String[] arg) throws NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException{
Class<UserController> userClass = UserController.class;
// 获取类上的注解
// 判断该对象是否有该注解
if (userClass.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = userClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
String[] value = requestMapping.value();
System.out.println("UserController类上RequestMapping注解的属性:" + Arrays.toString(value));
}else {
System.out.println("UserController类上没有RequestMapping注解!");
}
// 获取属性上的注解
Field getField = userClass.getDeclaredField("userService");
SuperBug fSuperBug = getField.getDeclaredAnnotation(SuperBug.class);
String[] fValue = fSuperBug.value();
System.out.println("userService属性上SuperBug注解的值:" + Arrays.toString(fValue));
// 获取方法上的注解
Method getMethod = userClass.getDeclaredMethod("getUserList1", String.class);
SuperBug mSuperBug = getMethod.getDeclaredAnnotation(SuperBug.class);
String[] mValue = mSuperBug.value();
System.out.println("getUserList1方法上SuperBug注解的值:" + Arrays.toString(mValue));
// 获取方法上的所有注解反射模板class
// getDeclaredAnnotations返回该元素上直接声明的注释(不包括继承)
Annotation[] annotations = getMethod.getDeclaredAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
Class<? extends Annotation> aClass = annotation.annotationType();
if ("com.superbug.word.annotation.SuperBug".equals(aClass.getTypeName())) {
SuperBug superBug1 = (SuperBug) annotation;
System.out.println(superBug1.toString());
}
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号