异常的产生过程解析以及throw关键字
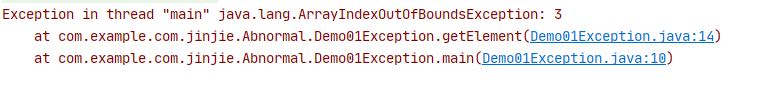
异常的产生过程解析
public static void main(String[] args){ int[] arr = {1,2,3}; int e = getElement(arr, 3); System.out.println(e); } public static int getElement(int[] arr,int index){ int i = arr[index]; return i; }

throw关键字
作用:
可以使用thorw关键字在指定的方法中抛出指定的异常
使用格式:
thorw new xxxException(“异常产生原因”);
注意事项:
1.throw关键字必须写在方法内部
2.throw关键字后边new的对象必须是Exception或者Exception的子类对象
3.throw关键字抛出指定的异常对象,我们就必须处理这个异常对象
throw关键字后边创建的是RuntimeException或者是RuntimeException的子类对象,我们可以不处理,默认交给JVM处理(打印异常对象,中断程序)
throw关键字后边创建的是编译异常(写代码的时候报错),我们就必须处理这个异常,要么throw,要么try....cathc
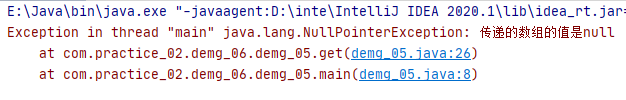
public class demg_05 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = null; int e = get(arr,0); System.out.println(e); } /** *1.定义一个方法,获取数组指定索引处的元素 *参数: * int[] arr * int index * 以后我们首先必须对方法传递过来的梦数进行合法性校验 * 如果参数不合法,那么我们就必须使用抛出异常的万式,告知方法的调用者,传递的参数有问题 */ public static int get(int[] arr,int index){ /* 我们可以对传递过来的参数数组,进行合法性校验 如果数组arr的值是null 那么我们就抛出空指针异常,告知方法的调用者“传递的数组的值是null” */ if (arr == null){ throw new NullPointerException("传递的数组的值是null"); } int i = arr[index]; return i; } }
运行结果:
我们可以对传递过来的参数index进行合法性校验如果index的范围不在数组的索引范国内那么我们就抛出数组索引越界异常,告知方法的调用者传递的索引超出了数组的使用范围
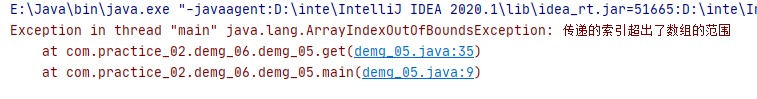
public static void main(String[] args) { // int[] arr = null; int[] arr = {1,2,3}; int e = get(arr,3); System.out.println(e); } /** *1.定义一个方法,获取数组指定索引处的元素 *参数: * int[] arr * int index * 以后我们首先必须对方法传递过来的梦数进行合法性校验 * 如果参数不合法,那么我们就必须使用抛出异常的万式,告知方法的调用者,传递的参数有问题 */ public static int get(int[] arr,int index){ /* 我们可以对传递过来的参数数组,进行合法性校验 如果数组arr的值是null 那么我们就抛出空指针异常,告知方法的调用者“传递的数组的值是null” */ if (arr == null){ throw new NullPointerException("传递的数组的值是null"); } /* 我们可以对传递过来的参数index进行合法性校验 如果index的范围不在数组的索引范围内 那么我们就抛出数组索引越界的异常,告知方法的调用者“传递的索引超出了数组的范围” */ if (index<0 || index>arr.length-1){ throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("传递的索引超出了数组的范围");//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException():数组索引越界 } int i = arr[index]; return i; } }
运行结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号