SpringBoot的文件上传功能与下载方式
Spring对文件上传做了简单的封装,就是用MultipartFile这个对象去接收文件,当然有很多种写法,下面会一一介绍。
文件的下载很简单,给一个链接就行,而这个链接怎么生成,也有很多方式,下面也会讲解下常用的方式。
application.properties 中需要添加下面的配置:
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled=true spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=20MB spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=50MB
这里,
- spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size是对单个文件大小的限制。
- spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size是对单次请求的大小进行限制
至此,已经可以正常的进行上传下载了,就剩下写代码了。
文件上传的几种方式
在Controller的RequestMapping注解的方法参数中,直接将MultipartFile作为参数传递进来。
package com.cff.springbootwork.web.file;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import com.cff.springbootwork.dto.ResultModel;
import com.cff.springbootwork.service.UploadService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/file")
public class FileRest {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Value("${upload.static.url}")
private String uploadStaticUrl;
@Autowired
UploadService uploadService;
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public ResultModel upload(@RequestParam("files") MultipartFile file) {
try {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
return ResultModel.error("文件不能为空!");
}
String fileName = uploadService.saveUploadFile(file);
return ResultModel.ok(uploadStaticUrl + fileName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("文件上传失败!", e);
return ResultModel.error("文件上传失败!");
}
}
}
测试的时候,使用postman可以这样传参:
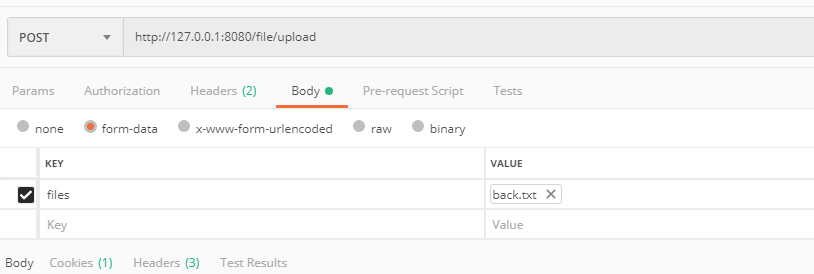
2.2 多个文件上传
在Controller的RequestMapping注解的方法参数中,直接将MultipartFile作为list传递进来。在FileRest中增加uploadList方法。
package com.cff.springbootwork.web.file;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import com.cff.springbootwork.dto.ResultModel;
import com.cff.springbootwork.service.UploadService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/file")
public class FileRest {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Value("${upload.static.url}")
private String uploadStaticUrl;
@Autowired
UploadService uploadService;
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public ResultModel upload(@RequestParam("files") MultipartFile file) {
try {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
return ResultModel.error("文件不能为空!");
}
String fileName = uploadService.saveUploadFile(file);
return ResultModel.ok(uploadStaticUrl + fileName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("文件上传失败!", e);
return ResultModel.error("文件上传失败!");
}
}
@RequestMapping("/uploadList")
public ResultModel uploadList(@RequestParam("files") List<MultipartFile> fileList) {
try {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (MultipartFile file : fileList) {
String fileName = uploadService.saveUploadFile(file);
list.add(uploadStaticUrl + fileName);
}
return ResultModel.ok(list);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("文件上传失败!", e);
return ResultModel.error("文件上传失败!");
}
}
}
测试的时候,使用postman可以这样传参:
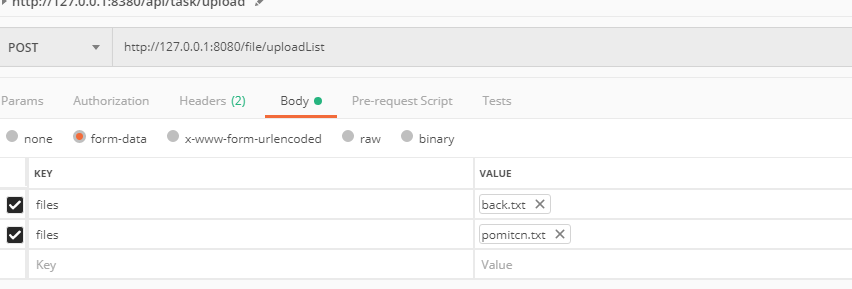
从HttpServletRequest中取文件
新建uploadByRequest方法,将HttpServletRequest作为参数,Spring自动传入。
Spring对Request做了一层封装,如果有文件,它就是MultipartHttpServletRequest。
然后我们可以从MultipartHttpServletRequest获取到MultipartFile。后面的处理方式一样了。
package com.cff.springbootwork.web.file;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartHttpServletRequest;
import com.cff.springbootwork.dto.ResultModel;
import com.cff.springbootwork.service.UploadService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/file")
public class FileRest {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Value("${upload.static.url}")
private String uploadStaticUrl;
@Autowired
UploadService uploadService;
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public ResultModel upload(@RequestParam("files") MultipartFile file) {
try {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
return ResultModel.error("文件不能为空!");
}
String fileName = uploadService.saveUploadFile(file);
return ResultModel.ok(uploadStaticUrl + fileName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("文件上传失败!", e);
return ResultModel.error("文件上传失败!");
}
}
@RequestMapping("/uploadList")
public ResultModel uploadList(@RequestParam("files") List<MultipartFile> fileList) {
try {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (MultipartFile file : fileList) {
String fileName = uploadService.saveUploadFile(file);
list.add(uploadStaticUrl + fileName);
}
return ResultModel.ok(list);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("文件上传失败!", e);
return ResultModel.error("文件上传失败!");
}
}
@RequestMapping("/uploadByRequest")
public ResultModel uploadByRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
Map<String, MultipartFile> files = new HashMap<>();
if (request instanceof MultipartHttpServletRequest) {
MultipartHttpServletRequest req = (MultipartHttpServletRequest) request;
MultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile> multiValueMap = req.getMultiFileMap();
if (multiValueMap != null && !multiValueMap.isEmpty()) {
for (String key : multiValueMap.keySet()) {
files.put(key, multiValueMap.getFirst(key));
}
}
}
if (files.isEmpty())
return ResultModel.error("文件木有?");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (MultipartFile file : files.values()) {
String fileName = uploadService.saveUploadFile(file);
list.add(uploadStaticUrl + fileName);
}
return ResultModel.ok(list);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("文件上传失败!", e);
return ResultModel.error("文件上传失败!");
}
}
}
测试的时候,传参方式使用上面两种都可以了。
三、文件下载方式
文件上传成功后,我们同时会提供下载功能。下载功能很简单,有以下几种方式:
3.1 Spring配置映射
新建一个WebStaticConfig配置类,实现WebMvcConfigurer接口即可:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class WebStaticConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Value("${upload.static.local}")
private String uploadStaticLocal;
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("file:" + uploadStaticLocal);
}
public String getUploadStaticLocal() {
return uploadStaticLocal;
}
public void setUploadStaticLocal(String uploadStaticLocal) {
this.uploadStaticLocal = uploadStaticLocal;
}
}
这句话将当前服务器(比如是http://127.0.0.1:8080)的/static路径(http://127.0.0.1:8080/static/)下的资源,映射到uploadStaticLocal指定的本地路径下的文件。
然后我们就可以直接访问文件了。
3.2 代理(nginx)映射
代理首选nginx了。高性能快捷的代理转发工具。
比如要将http://127.0.0.1:8081/static/下的资源,映射到/static/指定的本地路径下的文件,可以这样配置
server {
listen 8081;
server_name localhost;
location /static {
alias /static/;
index index.html;
}
}
这里为什么用8081而不是上面的8080了呢?因为上面的8080端口已经被SpringBoot应用占用了。nginx要在另一个端口监听了,如果非要将SpringBoot应用和静态资源在一个端口,可以对SpringBoot应用也做代理,例如:
server { listen 8081; server_name localhost; location ^~ /api/ { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/; } location /static { alias /static/; index index.html; } }
3.3 ResponseEntity读取文件并返回
比如我们在FileRest的Controller中建立个downloadFile方法,传入文件名,将文件读取为byte,包装成ResponseEntity返回。
@RequestMapping(value = "/downloadFile", method = { RequestMethod.GET }) public ResponseEntity<byte[]> downloadFile(@RequestParam("fileName") String fileName) { try { File file = new File(fileName); byte[] body = null; InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file); body = new byte[is.available()]; is.read(body); is.close(); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.add("Content-Disposition", "attchement;filename=" + file.getName()); HttpStatus statusCode = HttpStatus.OK; ResponseEntity<byte[]> entity = new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(body, headers, statusCode); return entity; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } }
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
国之殇,未敢忘!
南京大屠杀!
731部队!
(有关书籍《恶魔的饱食》)以及核污染水排海等一系列全无人性的操作,购买他们的食品和为它们提供帮助只会更加变本加厉的害你,呼吁大家不要购买日本相关产品
昭昭前事,惕惕后人
吾辈当自强,方使国不受他人之侮!
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
作者:三号小玩家
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/q1359720840/
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。 版权信息





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号