Spring AOP面向切面
简介
面向切面编程(Aspect Oriented Programming):一种编程思想,是面向对象编程(OOP)的一种补充。面向对象编程将程序抽象成各个层次的对象,而面向切面编程是将程序抽象成各个切面
为什么要使用AOP
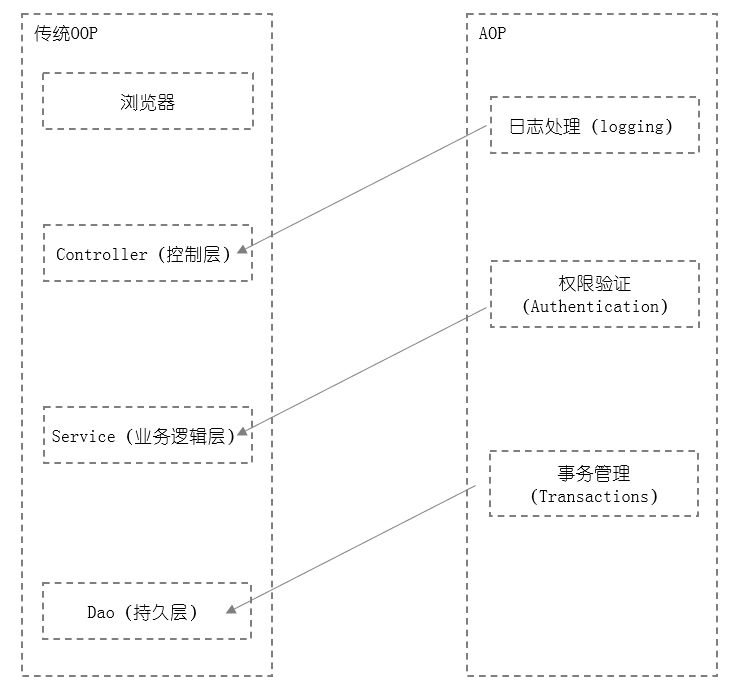
从图上就可以看得出来,在传统的OOP开发过程中,避免不了一些日志处理、事务管理等代码的融入。如果每个业务逻辑都加上相同的代码,就会导致严重的代码冗余问题。使用AOP就可以对这些次要问题进行解耦、统一管理权限,统一管理异常抛出、统一日志处理。宝宝们,看图是不是一目了然,特别简单。
使用场景
- 权限(Authentication)
- 缓存(Caching)
- 内容传递(Context passing)
- 错误处理(Error handling)
- 懒加载(Lazy loading)
- 调试(Debugging)
- 日志(logging)
- 性能优化(Performance optimization)
- 持久化(Persistence)
- 同步(Synchronization)
- 事务(Transactions)
专业术语
-
切面(Aspect):一个关注点的模块化,这个关注点可能会横切多个对象。事务管理是J2EE应用中一个关于横切关注点的很好的例子。在Spring AOP中,切面可以使用基于模式)或者基于@Aspect注解的方式来实现。 -
连接点(Joinpoint):在程序执行过程中某个特定的点,比如某方法调用的时候或者处理异常的时候。在Spring AOP中,一个连接点总是表示一个方法的执行。 -
通知(Advice):在切面的某个特定的连接点上执行的动作。其中包括了“around”、“before”和“after”等不同类型的通知(通知的类型将在后面部分进行讨论)。许多AOP框架(包括Spring)都是以拦截器做通知模型,并维护一个以连接点为中心的拦截器链。 -
切入点(Pointcut):匹配连接点的断言。通知和一个切入点表达式关联,并在满足这个切入点的连接点上运行(例如,当执行某个特定名称的方法时)。切入点表达式如何和连接点匹配是AOP的核心:Spring缺省使用AspectJ切入点语法。 -
引入(Introduction):用来给一个类型声明额外的方法或属性(也被称为连接类型声明(inter-type declaration))。Spring允许引入新的接口(以及一个对应的实现)到任何被代理的对象。例如,你可以使用引入来使一个bean实现IsModified接口,以便简化缓存机制。 -
目标对象(Target Object): 被一个或者多个切面所通知的对象。也被称做被通知(advised)对象。 既然Spring AOP是通过运行时代理实现的,这个对象永远是一个被代理(proxied)对象。 -
AOP代理(AOP Proxy):AOP框架创建的对象,用来实现切面契约(例如通知方法执行等等)。在Spring中,AOP代理可以是JDK动态代理或者CGLIB代理。
织入(Weaving):把切面连接到其它的应用程序类型或者对象上,并创建一个被通知的对象。这些可以在编译时(例如使用AspectJ编译器),类加载时和运行时完成。Spring和其他纯Java AOP框架一样,在运行时完成织入。
Advice通知类型
-
前置通知(Before advice):在某连接点之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点之前的执行流程(除非它抛出一个异常)。 -
后置通知(After returning advice):在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知:例如,一个方法没有抛出任何异常,正常返回。 -
异常通知(After throwing advice):在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。 -
最终通知(After (finally) advice):当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。 -
环绕通知(Around Advice):包围一个连接点的通知,如方法调用。这是最强大的一种通知类型。环绕通知可以在方法调用前后完成自定义的行为。它也会选择是否继续执行连接点或直接返回它自己的返回值或抛出异常来结束执行
注意点:日常开发过程中,环绕通知是最常用的通知类型。和AspectJ一样,Spring提供所有类型的通知,为了避免很多潜在的错误,尽可能使用最简单的通知类型来实现需要的功能。
Spring Aop / Aspectj 的区别
- Spring aop属于运行时增强,而AspectJ是编译时增强
- Spring aop基于代理,而AspectJ基于字节码操作
- AspectJ相比于Spring Aop功能更加强大,但是Spring Aop相对来说更简单。如果切面比较少,那么两者性能差异不大。但是,当切面太多的话,最好选择AspectJ,它比SpringAop快很多
AOP实现分类
-
静态 AOP 实现, AOP 框架在编译阶段对程序源代码进行修改,生成了静态的 AOP 代理类(生成的 *.class 文件已经被改掉了,需要使用特定的编译器),比如 AspectJ。
-
动态 AOP 实现, AOP 框架在运行阶段对动态生成代理对象(在内存中以 JDK 动态代理,或 CGlib 动态地生成 AOP 代理类),如 SpringAOP。
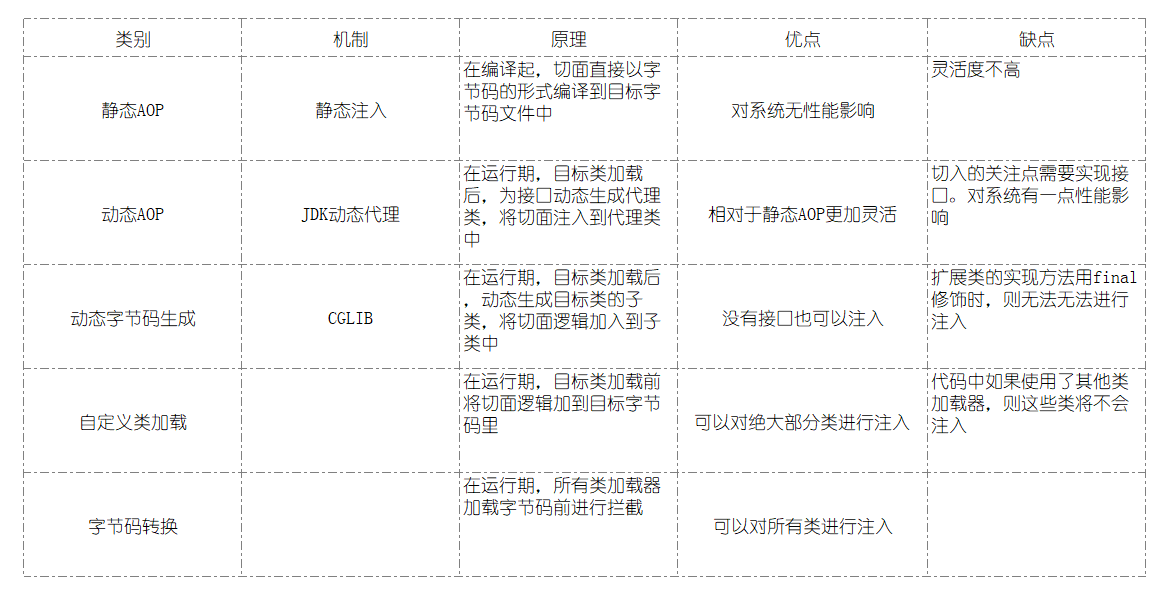
常用AOP实现比较
初步认识AOP
引入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-aspects -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
配置版
常用 AOP 标签
| 标签 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| <aop:config /> | 顶层AOP配置标签,大多数的 <aop:* > 系列的标签都在它里面 |
| <aop:advisor /> | 定义AOP通知器 |
| <aop:pointcut /> | 定义一个切点 |
| <aop:aspect /> | 定义一个切面 |
| <aop:before /> | 定义AOP前置通知 |
| <aop:around /> | 定义环绕通知 |
| <aop:after /> | 定义AOP后置通知 |
| <aop:after-returning /> | 定义AOP返回通知 |
| <aop:after-throwing /> | 定义AOP异常通知 |
| <aop:declare-parents /> | 以透明的方式引入外部接口 |
| <aop:declare-parents /> | 以透明的方式引入外部接口 |
| <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> | 启动AOP代理 |
xml 文件配置注入的方式
CGlib 代理方式:
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true"> </aop:config>
JDK 代理方式:
<aop:config proxy-target-class="false"> </aop:config>
用例
编写 HelloService.java 类
public interface HelloService {
/**
* 打印
*/
void show();
}
编写 HelloServiceImpl.java 类
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
编写 HelloAspectJ.java 类
public class HelloAspectJ {
public void before(){
System.out.println("before............");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("after............");
}
public void afterReturn(){
System.out.println("afterReturn............");
}
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint point){
try {
System.out.println("around 1...");
point.proceed();
System.out.println("around 2...");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在 resources 的 applicationContext.xml 编写配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="helloService" class="com.helloworld.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl" />
<bean id="helloAspectJ" class="com.helloworld.aop.HelloAspectJ" />
<!-- proxy-target-class="true":启动aop代理 -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:pointcut id="apoint" expression="execution(* com.helloworld.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl.show(..))"/>
<aop:aspect id="hello" ref="helloAspectJ">
<aop:before pointcut-ref="apoint" method="before"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref="apoint" method="after"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="apoint" method="afterReturn"/>
<aop:around pointcut-ref="apoint" method="around"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
编写测试用例
public class HelloTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloService helloService = context.getBean(HelloServiceImpl.class);
helloService.show();
}
结果打印
before............
around 1...
hello world
around 2...
afterReturn............
after............
注解版
声明切点指示器
| 指示器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| arg() | 限制连接点匹配参数为指定类型的执行方法 |
| @args() | 限制连接点匹配参数由指定注解标注的执行方法 |
| execution() | 用于匹配是连接点的执行方法 |
| this() | 限制连接点匹配 AOP 代理和Bean引用为指定类型的类 |
| target() | 限制连接点匹配目标对象为指定类型的类 |
| @target() | 限制连接点匹配特定的执行方法 |
| within() | 限制连接点匹配指定的类型 |
| @within() | 限制连接点匹配指定注解所标注的类型 |
| @annotation | 限制匹配带有指定注解连接点 |
补充:在使用 execution() 多个匹配之间我们可以使用链接符 &&、||、!来表示 “且”、“或”、“非”的关系。但是在使用 XML 文件配置时,这些符号有特殊的含义,所以我们使用 “and”、“or”、“not”来表示
用例
FruitsService.java
/**
* @author q-linyu
* @className FruitsService
* @description 水果接口
* @date 2021/03/25 22:46
*/
public interface FruitsService {
/**
* 水果方法
* @param price 水果的价钱
*/
void fruits(double price);
}
AppleServiceImpl.java
/**
* @author q-linyu
* @className Apple
* @description 苹果
* @date 2021/03/25 22:47
*/
@Service
public class AppleServiceImpl implements FruitsService {
@Override
public void fruits(double price) {
System.out.println("这个是一个苹果,价格为:" + price);
}
}
BananaServiceImpl.java
/**
* @author q-linyu
* @className BananaServiceImpl
* @description 香蕉
* @date 2021/03/25 22:49
*/
@Service
public class BananaServiceImpl implements FruitsService {
@Override
public void fruits(double price) {
System.out.println("这个是一条香蕉,价格为:" + price);
}
}
AppConfig.java
/**
* @author q-linyu
* @className AppConfig
* @description 系统配置类
* @date 2021/03/25 22:58
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = {FruitsService.class})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class AppConfig {
}
FruitsAspectJ.java
/**
* @author q-linyu
* @className FruitsAspectJ
* @description 水果切面类
* @date 2021/03/25 22:33
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class FruitsAspectJ {
/*
@Pointcut("execution(* com.helloworld.service.FruitsService.fruits(..))")
public void point(){}
@Before("point()")
public void hehe() {
System.out.println("before......");
}
@After("point()")
public void haha() {
System.out.println("After......");
}
@AfterReturning("point()")
public void xixi() {
System.out.println("AfterReturning......");
}
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.helloworld.service.FruitsService.fruits(double)) && args(price) && bean(appleServiceImpl) && bean(bananaServiceImpl)")
public void gif(double price) {
}
// @Around("point()")
@Around("gif(price)")
public void show(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,double price) {
try {
joinPoint.proceed();
if (price > 100){
System.out.println("如果这种水果这么贵, 我的考虑考虑");
}
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
编写测试用例
/**
* @author q-linyu
* @className FruitsTest
* @description
* @date 2021/03/25 23:06
*/
public class FruitsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
AppleServiceImpl appleService = context.getBean(AppleServiceImpl.class);
BananaServiceImpl bananaService = context.getBean(BananaServiceImpl.class);
appleService.fruits(25);
bananaService.fruits(26);
}
}
结果
这个是一个苹果,价格为:25.0
这个是一条香蕉,价格为:26.0


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号