检查
#pytorch检验代码
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() # 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 square convolution # kernel self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5) # an affine operation: y = Wx + b self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84) self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) def forward(self, x): # Max pooling over a (2, 2) window x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2)) # If the size is a square you can only specify a single number x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2) x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x)) x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) x = self.fc3(x) return x def num_flat_features(self, x): size = x.size()[1:] # all dimensions except the batch dimension num_features = 1 for s in size: num_features *= s return num_features net = Net() print(net)
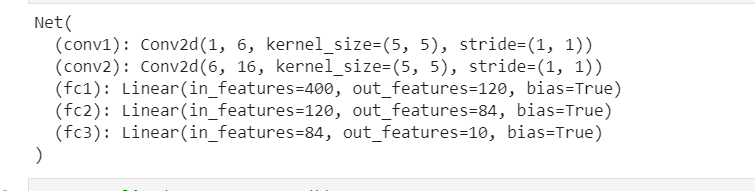
params = list(net.parameters()) print(len(params)) print(params[0].size()) # conv1's .weight input = torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 32) out = net(input) print(out) net.zero_grad() out.backward(torch.randn(1, 10)) output = net(input) target = torch.randn(10) # a dummy target, for example target = target.view(1, -1) # make it the same shape as output criterion = nn.MSELoss() loss = criterion(output, target) print(loss) print(loss.grad_fn) # MSELoss print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0]) # Linear print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0].next_functions[0][0]) # ReLU net.zero_grad() # zeroes the gradient buffers of all parameters print('conv1.bias.grad before backward') print(net.conv1.bias.grad) loss.backward() print('conv1.bias.grad after backward') print(net.conv1.bias.grad)




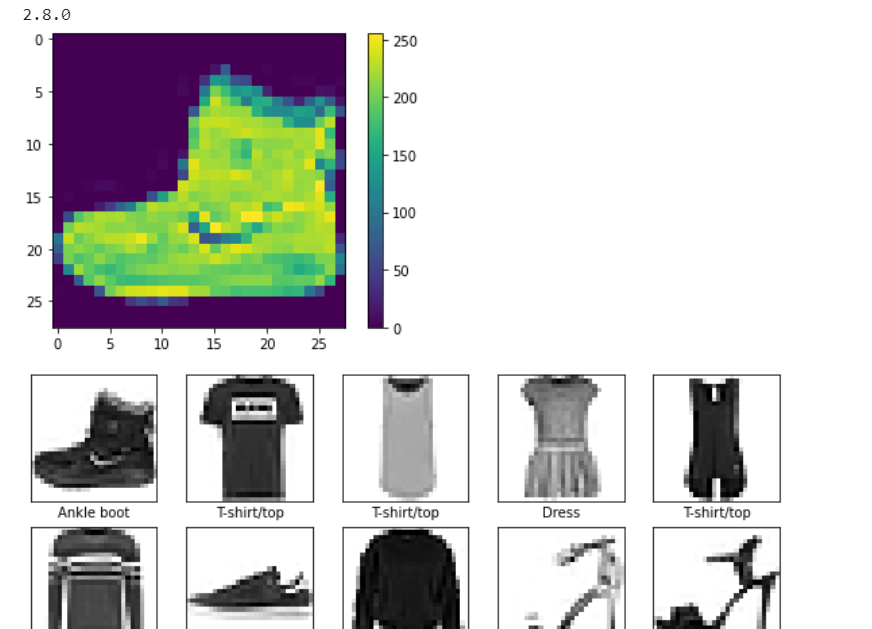
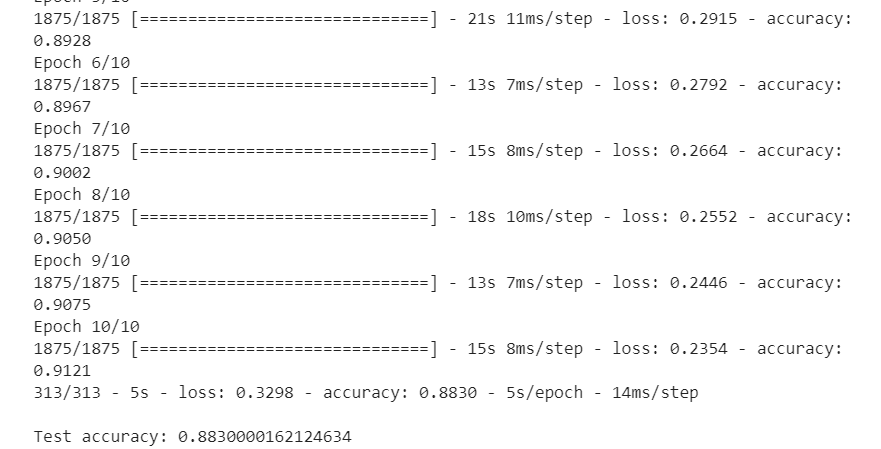
#检查TensorFlow import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow import keras # Helper libraries import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt print(tf.__version__) fashion_mnist = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data() class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'] plt.figure() plt.imshow(train_images[0]) plt.colorbar() plt.grid(False) plt.show() train_images = train_images / 255.0 test_images = test_images / 255.0 plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) for i in range(25): plt.subplot(5,5,i+1) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.grid(False) plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]]) plt.show() model = keras.Sequential([ keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)), keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'), keras.layers.Dense(10) ]) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True), metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10) test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2) print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc) probability_model = tf.keras.Sequential([model, tf.keras.layers.Softmax()]) predictions = probability_model.predict(test_images) def plot_image(i, predictions_array, true_label, img): predictions_array, true_label, img = predictions_array, true_label[i], img[i] plt.grid(False) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary) predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array) if predicted_label == true_label: color = 'blue' else: color = 'red' plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(class_names[predicted_label], 100*np.max(predictions_array), class_names[true_label]), color=color)


#猫狗识别代码
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import layers, regularizers import numpy as np import os import cv2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "1" resize = 224 path ="train/" def load_data(): imgs = os.listdir(path) num = len(imgs) train_data = np.empty((5000, resize, resize, 3), dtype="int32") train_label = np.empty((5000, ), dtype="int32") test_data = np.empty((5000, resize, resize, 3), dtype="int32") test_label = np.empty((5000, ), dtype="int32") for i in range(5000): if i % 2: train_data[i] = cv2.resize(cv2.imread(path+'/'+ 'dog.' + str(i) + '.jpg'), (resize, resize)) train_label[i] = 1 else: train_data[i] = cv2.resize(cv2.imread(path+'/' + 'cat.' + str(i) + '.jpg'), (resize, resize)) train_label[i] = 0 for i in range(5000, 10000): if i % 2: test_data[i-5000] = cv2.resize(cv2.imread(path+'/' + 'dog.' + str(i) + '.jpg'), (resize, resize)) test_label[i-5000] = 1 else: test_data[i-5000] = cv2.resize(cv2.imread(path+'/' + 'cat.' + str(i) + '.jpg'), (resize, resize)) test_label[i-5000] = 0 return train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label def vgg16(): weight_decay = 0.0005 nb_epoch = 100 batch_size = 32 # layer1 model = keras.Sequential() model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='same', input_shape=(224, 224, 3), kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.3)) # layer2 model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) # layer3 model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.4)) # layer4 model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) # layer5 model.add(layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.4)) # layer6 model.add(layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.4)) # layer7 model.add(layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) # layer8 model.add(layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.4)) # layer9 model.add(layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.4)) # layer10 model.add(layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) # layer11 model.add(layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.4)) # layer12 model.add(layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.4)) # layer13 model.add(layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5)) # layer14 model.add(layers.Flatten()) model.add(layers.Dense(512, kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) # layer15 model.add(layers.Dense(512, kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(weight_decay))) model.add(layers.Activation('relu')) model.add(layers.BatchNormalization()) # layer16 model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5)) model.add(layers.Dense(2)) model.add(layers.Activation('softmax')) return model #if __name__ == '__main__': train_data, train_label, test_data, test_label = load_data() train_data = train_data.astype('float32') test_data = test_data.astype('float32') train_label = keras.utils.to_categorical(train_label, 2) test_label = keras.utils.to_categorical(test_label, 2) #定义训练方法,超参数设置 model = vgg16() sgd = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True) #设置优化器为SGD model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=sgd, metrics=['accuracy']) history = model.fit(train_data, train_label, batch_size=20, epochs=10, validation_split=0.2, #把训练集中的五分之一作为验证集 shuffle=True) scores = model.evaluate(test_data,test_label,verbose=1) print(scores) model.save('model/vgg16dogcat.h5')
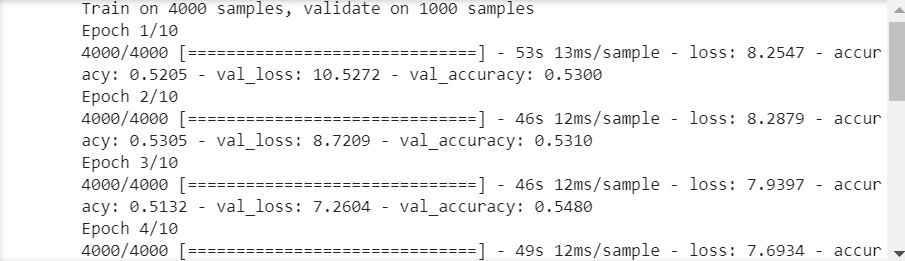

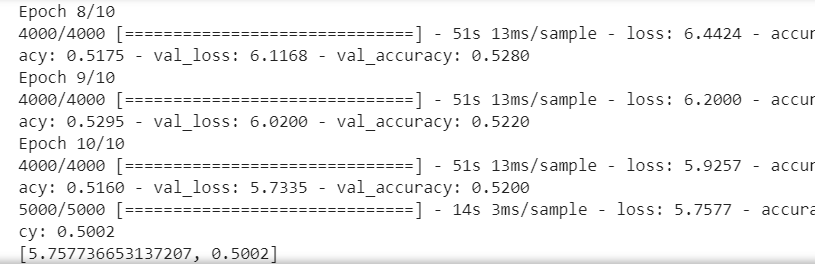
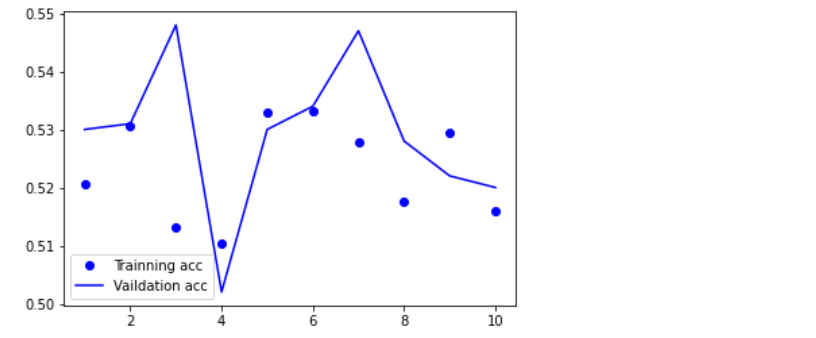
acc = history.history['accuracy'] # 获取训练集准确性数据
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy'] # 获取验证集准确性数据
loss = history.history['loss'] # 获取训练集错误值数据
val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] # 获取验证集错误值数据
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Trainning acc') # 以epochs为横坐标,以训练集准确性为纵坐标
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Vaildation acc') # 以epochs为横坐标,以验证集准确性为纵坐标
plt.legend() # 绘制图例,即标明图中的线段代表何种含义
plt.show()
#BP神经网络检验代码
#2022-03-22
#导入相应的库
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import os
from scipy import stats
import pandas as pd
#数据的导入
titanic_data = pd.read_csv(r"C:\Users\86133\Desktop\titanic3.csv")
print(titanic_data.columns )#打印列名
#用哑变量将指定字段转成one-hot
titanic_data = pd.concat([titanic_data,
pd.get_dummies(titanic_data['sex']),
pd.get_dummies(titanic_data['embarked'],prefix="embark"),
pd.get_dummies(titanic_data['pclass'],prefix="class")], axis=1)
#处理None值
titanic_data["age"] = titanic_data["age"].fillna(titanic_data["age"].mean())
titanic_data["fare"] = titanic_data["fare"].fillna(titanic_data["fare"].mean())#乘客票价
#删去无用的列
titanic_data = titanic_data.drop(['name','ticket','cabin','boat','body','home.dest','sex','embarked','pclass'], axis=1)
print(titanic_data.columns )
titanic_data.to_excel(r"C:\Users\86133\Desktop\data_survived.xlsx")
#分离样本和标签
labels = titanic_data["survived"].to_numpy()
data_features = titanic_data.drop(['survived'], axis=1)
data = data_features.to_numpy()
#样本的属性名称
feature_names = list(titanic_data.columns)
#将样本分为训练和测试两部分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_features,test_features,train_labels,test_labels = train_test_split(data,labels,test_size=0.3,random_state=10)
class Mish(nn.Module):#Mish激活函数
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
print("Mish activation loaded...")
def forward(self,x):
x = x * (torch.tanh(F.softplus(x)))
return x
torch.manual_seed(0) #设置随机种子
#构建一个三层网络12-8-2
class ThreelinearModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(12, 5)
self.mish1 = Mish()
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(5, 9)
self.mish2 = Mish()
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(9, 7)
self.mish3 = Mish()
self.linear4 = nn.Linear(7, 12)
self.mish4 = Mish()
self.linear5 = nn.Linear(12, 8)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
self.criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() #定义交叉熵函数
def forward(self, x): #定义一个全连接网络
lin1_out = self.linear1(x)
out1 = self.mish1(lin1_out)
out2 = self.mish2(self.linear2(out1))
return self.softmax(self.linear3(out2))
def getloss(self,x,y): #实现LogicNet类的损失值计算接口
y_pred = self.forward(x)
loss = self.criterion(y_pred,y)#计算损失值得交叉熵
return loss
net = ThreelinearModel()#模型实例化
num_epochs = 200 #迭代数次
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.04) #优化器选择Adam,只有一个参数学习率
#把特征和标签值转成torch张量形式
input_tensor = torch.from_numpy(train_features).type(torch.FloatTensor)
label_tensor = torch.from_numpy(train_labels)
losses = []#定义列表,用于接收每一步的损失值
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
loss = net.getloss(input_tensor,label_tensor)
losses.append(loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad()#清空之前的梯度。
loss.backward()#反向传播损失值
optimizer.step()#更新参数
if epoch % 20 == 0:
print ('Epoch {}/{} => Loss: {:.2f}'.format(epoch+1, num_epochs, loss.item()))
#.item()方法 是得到一个元素张量里面的元素值
os.makedirs('models', exist_ok=True)
#os.makedirs自动创建一个文件夹models
#如果exist_ok为True,则在目标目录已存在的情况下不会触发FileExistsError异常。
torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'models/titanic_model.pht') #保存模型

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def moving_average(a, w=10):#定义函数计算移动平均损失值 if len(a) < w: return a[:] return [val if idx < w else sum(a[(idx-w):idx])/w for idx, val in enumerate(a)] #enumerate() 函数用于将一个可遍历的数据对象(如列表、元组或字符串)组合为一个索引序列,同时列出数据和数据下标,一般用在 for 循环当中。 def plot_losses(losses): avgloss= moving_average(losses) #获得损失值的移动平均值 print(len(avgloss)) plt.figure(1) plt.subplot(211) plt.plot(range(len(avgloss)), avgloss, 'b--') plt.xlabel('step number') plt.ylabel('Training loss') plt.title('step number vs. Training loss') plt.show() #输出训练结果 out_probs = net(input_tensor).detach().numpy() out_classes = np.argmax(out_probs, axis=1) print("Train Accuracy:", sum(out_classes == train_labels) / len(train_labels)) #测试模型 test_input_tensor = torch.from_numpy(test_features).type(torch.FloatTensor) out_probs = net(test_input_tensor).detach().numpy() out_classes = np.argmax(out_probs, axis=1) print("Test Accuracy:", sum(out_classes == test_labels) / len(test_labels))




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号