Python学习笔记第18天
谏言:穷则独善其身,达则兼善天下
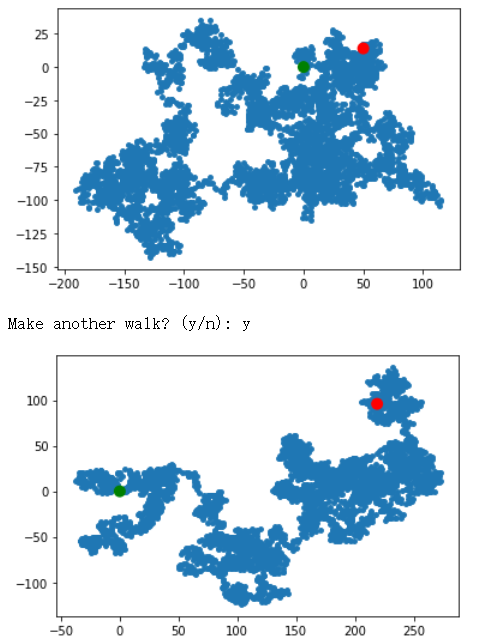
# 创建RandomWalk类 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class RandomWalk(): """一个生成随机漫步数据的表""" def __init__(self,num_points=5000): """初始化随机漫步的属性""" self.num_points=num_points # 所有随机漫步都始于(0,0) self.x_values=[0] self.y_values=[0] def fill_walk(self): """计算随机漫步包含的所有点""" # 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度 while len(self.x_values) <self.num_points: # 决定前进方向以及沿着个方向前进的距离 x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step=x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step=y_direction * y_distance # 拒绝原地踏步 if x_step==0 and y_step==0: continue # 计算下一个点的x和y值 next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) while True: # from random_walk import RandomWalk # 创建一个RandomWalk实例,并将其包含的点都会指出来 rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolors='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1], rw.y_values[-1], c='red', edgecolors='none', s=100) # 隐藏坐标轴 plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
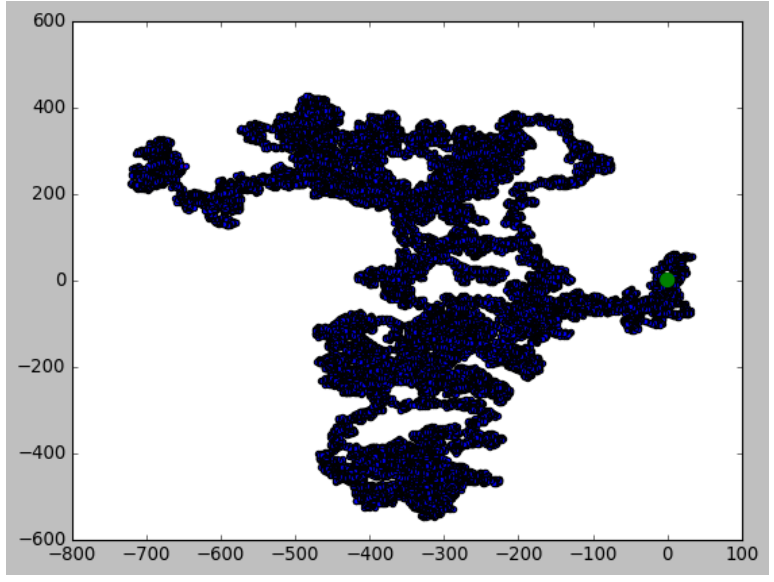
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class RandomWalk(): """一个生成随机漫步数据的表""" def __init__(self,num_points=5000): """初始化随机漫步的属性""" self.num_points=num_points # 所有随机漫步都始于(0,0) self.x_values=[0] self.y_values=[0] def fill_walk(self): """计算随机漫步包含的所有点""" # 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度 while len(self.x_values) <self.num_points: # 决定前进方向以及沿着个方向前进的距离 x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step=x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step=y_direction * y_distance # 拒绝原地踏步 if x_step==0 and y_step==0: continue # 计算下一个点的x和y值 next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) while True: # from random_walk import RandomWalk # 创建一个RandomWalk实例,并将其包含的点都会指出来 rw=RandomWalk(50000) rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolors='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1], rw.y_values[-1], c='red', edgecolors='none', s=1) # 隐藏坐标轴 plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
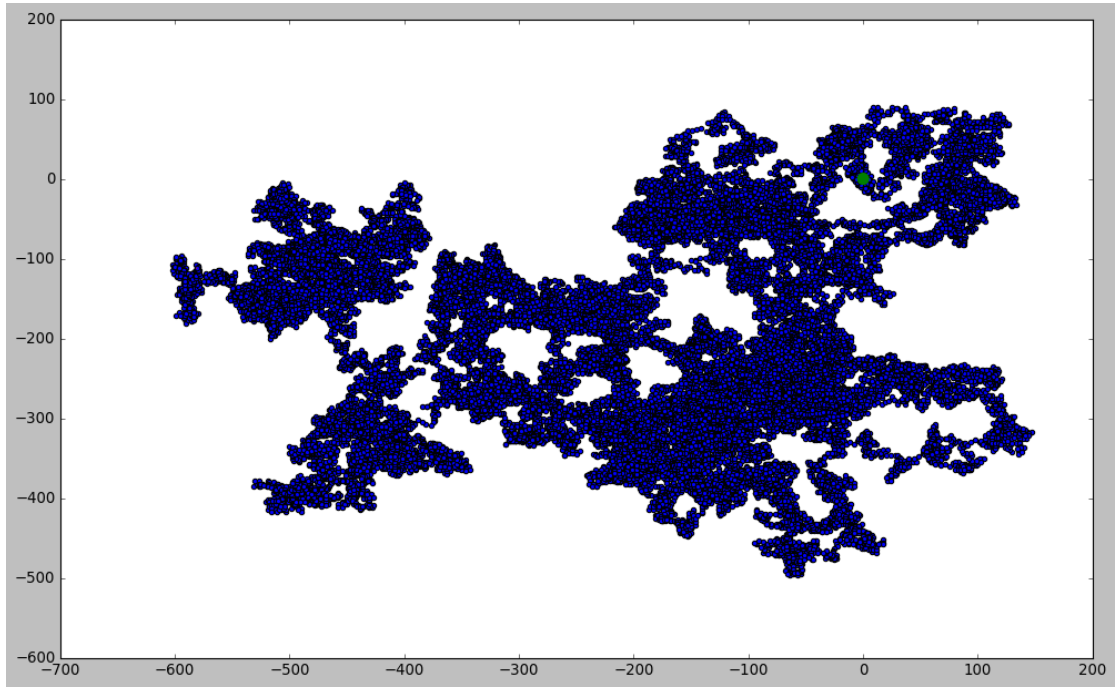
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class RandomWalk(): """一个生成随机漫步数据的表""" def __init__(self,num_points=5000): """初始化随机漫步的属性""" self.num_points=num_points # 所有随机漫步都始于(0,0) self.x_values=[0] self.y_values=[0] def fill_walk(self): """计算随机漫步包含的所有点""" # 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度 while len(self.x_values) <self.num_points: # 决定前进方向以及沿着个方向前进的距离 x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step=x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step=y_direction * y_distance # 拒绝原地踏步 if x_step==0 and y_step==0: continue # 计算下一个点的x和y值 next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) while True: # from random_walk import RandomWalk # 创建一个RandomWalk实例,并将其包含的点都会指出来 rw=RandomWalk(50000) rw.fill_walk() # 设置窗口的尺寸 plt.figure(figsize=(15, 9)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolors='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1], rw.y_values[-1], c='red', edgecolors='none', s=1) # 隐藏坐标轴 plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
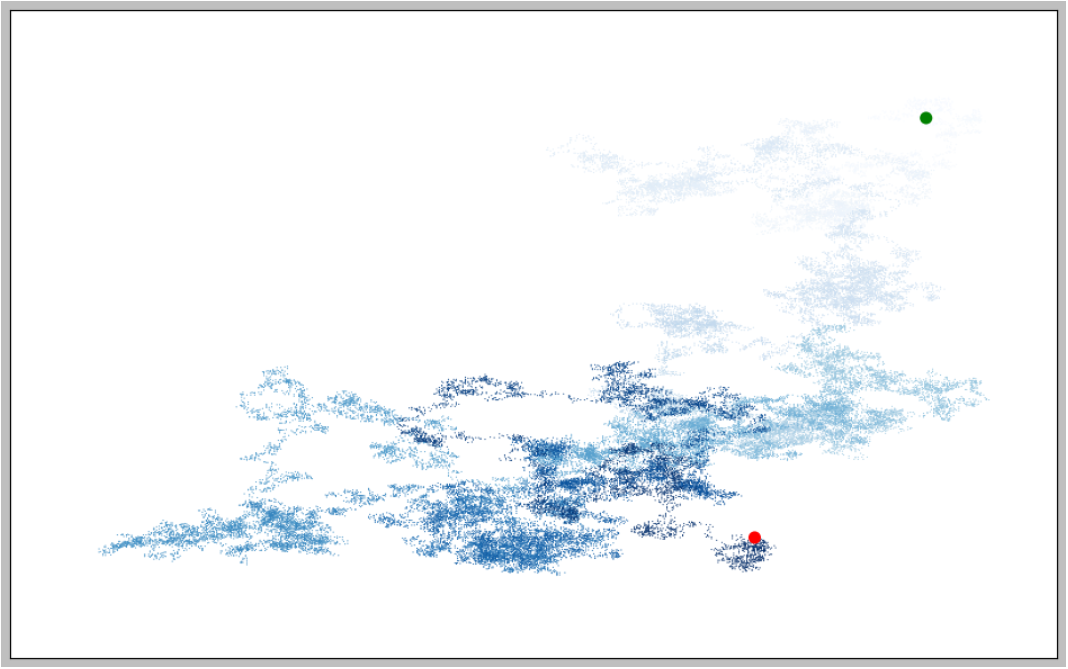
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # from random_walk import RandomWalk # Keep making new walks, as long as the program is active. while True: # Make a random walk. rw = RandomWalk(50000) rw.fill_walk() # Plot the points in the walk. plt.style.use('classic') fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15, 9)) point_numbers = range(rw.num_points) ax.scatter(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, c=point_numbers, cmap=plt.cm.Blues, edgecolors='none', s=1) # Emphasize the first and last points. ax.scatter(0, 0, c='green', edgecolors='none', s=100) ax.scatter(rw.x_values[-1], rw.y_values[-1], c='red', edgecolors='none', s=100) # Remove the axes. ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
# 使用Pygal模拟骰子 # die.py from random import randint class Die(): """表示一个骰子的类""" def __init__(self,num_sides=6): self.num_sides=num_sides def roll(self): """返回一个位于1和骰子面数之间的随机值""" return randint(1,self.num_sides) # die_visual.py # from die import Die die=Die() # 掷几次骰子,并将结果存储在一个列表中 results=[] for roll_num in range(100): result =die.roll() results.append(result) print(results)
[5, 3, 3, 4, 2, 5, 2, 1, 4, 4, 1, 4, 2, 3, 2, 6, 4, 3, 4, 1, 1, 5, 4, 5, 6, 5, 1, 3, 6, 5,
3, 3, 5, 3, 2, 4, 2, 2, 1, 1, 3, 2, 4, 3, 6, 4, 3, 1, 6, 6, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 6, 4, 4, 6,
6, 4, 6, 4, 1, 3, 3, 4, 3, 2, 6, 6, 5, 5, 1, 4, 1, 5, 3, 1, 6, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 6, 5, 4,
1, 3, 4, 5, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6, 6, 1]
# die.py from random import randint class Die(): """表示一个骰子的类""" def __init__(self,num_sides=6): self.num_sides=num_sides def roll(self): """返回一个位于1和骰子面数之间的随机值""" return randint(1,self.num_sides) # die_visual.py # from die import Die die=Die() # 掷几次骰子,并将结果存储在一个列表中 results=[] for roll_num in range(1000): result =die.roll() results.append(result) frequencies=[] for value in range(1,die.num_sides+1): frequency= results.count(value) frequencies.append(frequency) print(frequencies)
[180, 169, 156, 151, 177, 167]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号