基础算法
1. dfs(深度搜索)和bfs(广度搜索)
1. dfs
深搜的本质就是暴力,分析得出所有的路径,可以解决路径排列等问题,本质是递归实现的。
(1) 例题1

import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Description: dfs
* @Author: YccLin
* @Date: 2024/11/14
*/
public class Main {
static int n;
static int N = 10;
static int[] path = new int[N];
static boolean[] status = new boolean[N];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
dfs(0);
}
private static void dfs(int u) {
if (u == n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(path[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!status[i]) {
path[u] = i;
status[i] = true;
dfs(u + 1);
path[u] = 0;
status[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
(2)例题2


- 解法1(推荐)
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Description: 8皇后_方法1:分析
* @Author: YccLin
* @Date: 2024/10/25
*/
public class Main {
static int n;
static int N = 10;
static char[][] g = new char[N][N];
static boolean[] col = new boolean[N];
static boolean[] dg = new boolean[N];
static boolean[] udg = new boolean[N];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
g[i][j] = '.';
}
}
dfs(0);
}
/**
* 这里的 u -> y(行),i -> x(列)
* @param u
*/
private static void dfs(int u) {
if (u == n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
System.out.print(g[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!col[i] && !dg[u + i] && !udg[n - u + i]) {
g[u][i] = 'Q';
col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = true;
dfs(u + 1);
col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = false;
g[u][i] = '.';
}
}
}
}
- 解法2
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Description: x和y分别是行和列
* @Author: YccLin
* @Date: 2024/10/25
*/
public class Main {
static int n;
static int N = 20;
static char[][] g = new char[N][N];
static boolean[] row = new boolean[N];
static boolean[] col = new boolean[N];
static boolean[] dg = new boolean[N];
static boolean[] udg = new boolean[N];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
g[i][j] = '.';
}
}
dfs(0, 0, 0);
}
private static void dfs(int x, int y, int s) {
if (y == n) {
y = 0;
x++;
}
if (x == n) {
if (s == n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
System.out.print(g[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
return;
}
// 不放皇后
dfs(x, y + 1, s);
// 放皇后
if (!row[x] && !col[y] && !dg[x + y] && !udg[n - x + y]) {
g[x][y] = 'Q';
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[n - x + y] = true;
dfs(x, y + 1, s + 1);
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[n - x + y] = false;
g[x][y] = '.';
}
}
}
2. bfs
这个有一套模版,主要实现核心就是队列,循环判断队列是否为空,每次取出第一个数,然后继续扩展第一个数。
下面是一道迷宫例题:

求走出迷宫的最小步数
import java.util.*;
public class P846 {
// 充当坐标
static class Pair {
int x;
int y;
Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static int[][] map = null; // 地图
static int[][] d = null; // 到起点的距离
static int n;
static int m;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
map = new int[n][m];
d = new int[n][m];
// 初始化地图
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
map[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println(bfs());
}
private static int bfs() {
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// (1, 1) -枚举状态-> 上(-1, 0) 右(0, 1) 下(1, 0) 左(0, -1)
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
queue.offer(new Pair(0, 0));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair pair = queue.poll();
if (pair.x == n - 1 && pair.y == m - 1) {
break;
}
// 遍历四个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = pair.x + dx[i];
int y = pair.y + dy[i];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && map[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == 0) {
queue.offer(new Pair(x, y));
d[x][y] = d[pair.x][pair.y] + 1;
}
}
}
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
}
下面还有一题数字华容道的例题
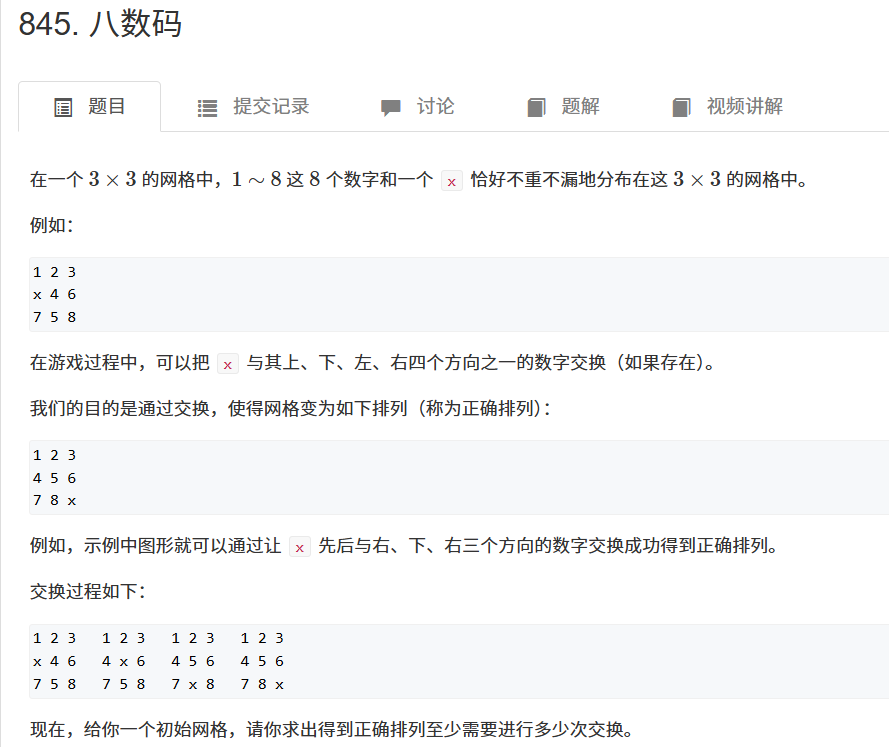

求完成顺序的最小次数
import java.util.*;
public class P845 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String start = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
char c = sc.next().charAt(0);
start += c;
}
System.out.println(bfs(start));
}
private static int bfs(String start) {
String end = "12345678x";
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 到起点的距离
queue.offer(start);
map.put(start, 0);
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String poll = queue.poll();
int distance = map.get(poll);
if (poll.equals(end)) {
return distance;
}
// 状态转移
int k = poll.indexOf('x');
int x = k / 3;
int y = k % 3;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int a = x + dx[i];
int b = y + dy[i];
if (a >= 0 && a < 3 && b >= 0 && b < 3) {
String newState = swap(poll, k, a * 3 + b);
if (!map.containsKey(newState)) {
queue.offer(newState);
map.put(newState, distance + 1);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private static String swap(String c, int c1, int c2) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(c);
char t = sb.charAt(c1);
sb.setCharAt(c1, sb.charAt(c2));
sb.setCharAt(c2, t);
return sb.toString();
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号