20191324第十一章读书笔记
第十一章:EXT2文件系统
什么是EXT2文件系统?
The Second Extended File System ( ext2)文件系统是linux系统中的标准文件系统。对于ext2文件系统,磁盘首先被划分为一个个block,每个block大小是相同的,一般为1kByte或4kByte,这些block被聚在一起分成几个大的block group,每个group中的block数量是固定的。

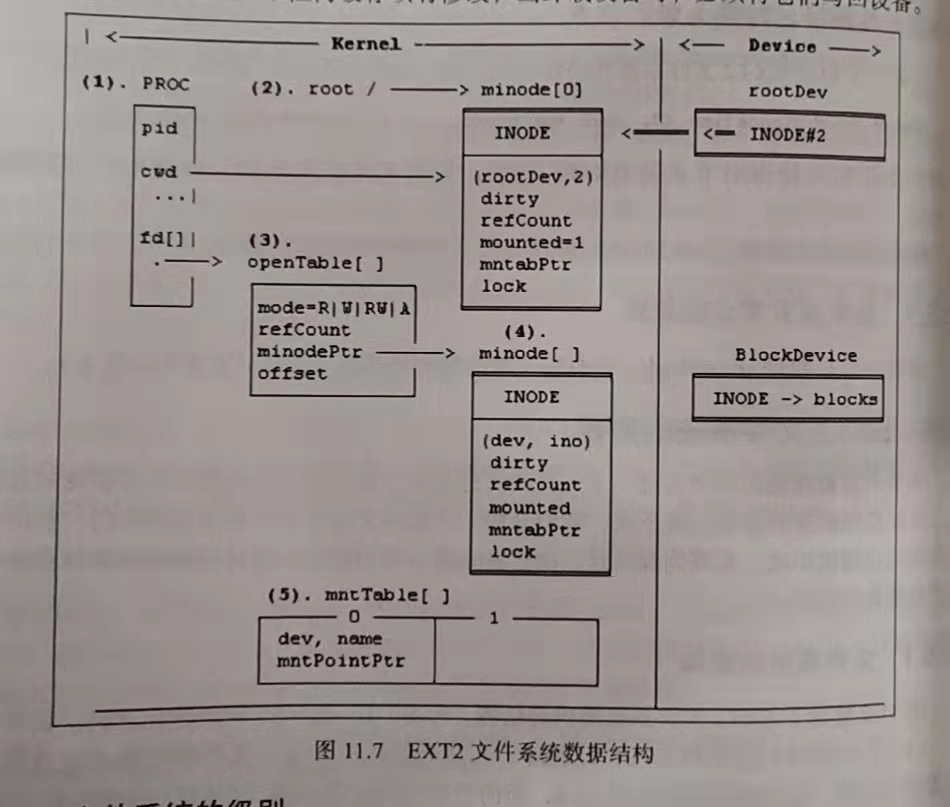
EXT2文件系统数据结构
-
在linux下,通过mkfs创建虚拟磁盘,输入命令:
mke2fs [-b blksize -N ninodes] device nblocks可创建一个带有nblocks个块(每个块大小为blksize个字节)和ninodes个索引节点的EXT2文件系统 -
虚拟磁盘布局:
![]()
-
Block#0:引导块文件系统不会使用它,用来容纳一个引导程序,从磁盘引导操作系统
-
Block#1:超级块,用于容纳整个文件系统的信息。
部分重要字段:
struct ext2_super_block {
u32 s_inodes_count; // Inodes count
u32 s_blocks_count; // Blocks count
u32 s_r_blocks_count; // Reserved blocks count
u32 s_free_blocks_count; // Free blocks count
u32 s_free_inodes_count; // Free inodes count
u32 s_first_data_block; // First Data Block
u32 s_log_block_size; // Block size
u32 s_log_cluster_size; // Allocation cluster size
u32 s_blocks_per_group; // # Blocks per group
u32 s_clusters_per_group; // # Fragments per group
u32 s_inodes_per_group; // # Inodes per group
u32 s_mtime; // Mount time
u32 s_wtime; // Write time
u32 s_mnt_count; // Mount count
u16 s_max_mnt_count; // Maximal mount count
u16 s_magic; // Magic signature
// more non-essential fields
u16 s_inode_size; // size of inode structure
};
- Block#2块组描述符块(EXT2将磁盘块分成几个组。每个组有8192个块(硬盘上的大小为32K)。每组用一个块组描述符结构体描述):
struct ext2_ group_ desc (
u32
bg_ block_ bi tmap; // Bmap block number
u32 bg inode_ bi tmap; //Imap b1ock number
u32 bg inode_ table; // Indes begin block number
u16 bg_ free_ blocks_ count ; // THESE are OBVIOUS
u16 bg_ free_ inodes_ count ;
u16 bg_ used_ dirs_ count;
u16 bg_ pad; //ignore these
u32 bg_ reserved[3] ;
};
- Block#8:块位图(Bmap)(bg_block_bitmap)位图用来表示某种项的位序列,例如,磁盘块或索引节点。位图用于分配和回收项。在位图中,0位表示对应项处于FREE状态,1位表示对应项处于IN_USE状态。一个软盘有1440块。
- Block#9:索引节点位图(Imap)(bg_inode_bitmap)一个索引节点就是用来代表一个文件的数据结构。EXT2文件系统是使用有限数量的索引节点创建的。各索引节点的状态用B9中Imap中的一个位表示。在EXT2 FS中,前10个索引节点是预留的。
- 索引节点Block#10:索引(开始)节点块(bg_inode_table)每个文件都用一个128字节(EXT4中的是256字节)的独特索引节点结构体表示。
struct ext2_ inode {
u16 i_ mode;// 16 bits - ttttlugsIrwxJrwxIrwxl
u16 i_ uid;//owner uid
u32 i_ size;//file size in bytes
u32 i_ atime;//time fields in seconds
u32 i_ ctime;// since 00:00:00,1-1-1970
u32 i_ mtime;
u32 i_ dtime;
u16 i_ gid;// group ID
u16 i_ 1 inks_ count;// hard-link count
u32 i_ blocks;// number of 512-byte sectors
u32 i_ flags;//IGNORE
u32 i_ reserved1 ;//IGNORE
u32 i_ b1ock[15] ;//See details below
u32 i_ pad[7] ;//for inode size = 128 bytes
}
- 直接块:i_block[0]至i_block[11]指向直接磁块盘
- 间接块:i_block[12]指向一个包含256个块编号的磁盘块,每个块编号指向一个磁盘块
- 双重间接块:i_block[13]指向一个指向256个块的块,每个块指向256个磁盘块
- 三重间接块:i_block[14]对于小型EXT2文件可忽略
- 目录条目
EXT2目录条目;目录包含dir_entry_2结构,即:
struct ext2_dir_entry_2 {
u32 inode;
u16 rec_len;
u8 name_len;
u8 file_type;
char name[EXT2_NAME_LEN];
};
遍历EXT2文件系统树
- 遍历算法:1.读取超级块2.读取块组描述符3.读取InodeBegin Block,以获取/的索引节点4.将路径名标记为组件字符串5.从3.中的跟索引节点开始搜索6.使用索引节点号ino来定位相应的索引节点7.重复第5第6步
文件系统结构:
- 共三个级别:第一级别实现基本文件系统树,第二级别实现文件读/写函数,第三级别实现系统的挂载,卸载和文件保护
![]()
基本文件系统
- type.h文件:包含ext2文件系统的数据结构类型
- global.c文件:这类文件包含文件系统的全局变量
- 实用程序函数util.c file:该文件包含文件系统常用的实用程序函数
get_block/put_block 将虚拟磁盘块读/写到内存的缓冲区中
iget(dev,ino) 返回一个指针,指向包含INODE(dev,ino)的内存minode
The put(INODE *mip) 释放一个mip指向用完的minode
getino() 实现文件系统树遍历算法
- mkdir命令:创建一个带目录名的新路径
- rmdir命令:可删除目录
- 2级文件系统由open,close,lseek,read,write,opendir和readdir组成
- 挂载操作命令: mount filesys mount_point 允许文件系统包含其他文件系统作为现有文件系统一部分
实践:
点击查看代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<ext2fs/ext2_fs.h>
#define BLKSIZE 1024
typedef struct ext2_group_desc GD;
typedef struct ext2_super_block SUPER;
typedef struct ext2_inode INODE;
typedef struct ext2_dir_entry_2 DIR;
SUPER *sp;
GD *gp;
INODE *ip;
DIR *dp;
char buf[BLKSIZE];
int fd, firstdata, inodesize, blksize, iblock;
char *dev = "mydisk";
int get_block(int fd, int blk, char *buf)
{
lseek(fd, blk*BLKSIZE, SEEK_SET);
return read(fd, buf, BLKSIZE);
}
int inode(char *dev)
{
int i;
fd = open(dev, O_RDONLY);
if(fd<0)
{
printf("open failed\n");
exit(1);
}
get_block(fd, 2, buf);
gp = (GD *)buf;
printf("bmap_block = %d, imap_block = %d, inodes_table = %d",
gp->bg_block_bitmap,
gp->bg_inode_bitmap,
gp->bg_inode_table);
iblock = gp->bg_inode_table;
printf("---- root inode information ----");
get_block(fd, iblock, buf);
ip = (INODE *)buf;
ip++;
printf("mode = %4x ", ip->i_mode);
printf("uid = %d gid = %d\n",ip->i_uid, ip->i_gid);
printf("size = %d\n", ip->i_size);
printf("ctime = %s",ctime(&ip->i_ctime));
printf("link = %d\n", ip->i_links_count);
for(i = 0; i<15; i++)
{
if(ip->i_block[i])
{
printf("i_block[%d] = %d\n",i, ip->i_block[i]);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc>1) dev=argv[1];
inode(dev);
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号