寻找数组中第K大是数
- 解题思路
1. 初始化数组来存放序列
2. 遍历序列元素
3. 将第k大的数据存入结果数组中
4. 调用Arraylist的sort方法从大到小排序
5. 输出
- 代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class sor{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 序列长度
int n = sc.nextInt();
//存放序列
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 存放排序的序列
ArrayList<Integer> lists = new ArrayList<>();
//初始化序列
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++){
list.add(i,sc.nextInt());
}
// 询问个数
int m = sc.nextInt();
// 遍历个数
for (int i = 0;i < m;i++){
// 初始位置第l个数
int l = sc.nextInt();
// 到达位置第r个数
int r = sc.nextInt();
// 询问第K大的数
int K = sc.nextInt();
// 存入数组
for (int j = l - 1;j < r;j++){
lists.add(list.get(j));
}
// 从大到小排序
lists.sort(null);
// 输出询问的答案
System.out.println(lists.get(lists.size() - K));
lists.clear();
}
}
}
- 运行结果
![]()
二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
- 解题思路
1.先序遍历:根在前,从左往右,一棵树的根永远在左子树前面,左子树又永远在右子树前面
2.中序遍历:根在中,从左往右,一棵树的左子树永远在根前面,根永远在右子树前
3.后序遍历:根在后,从左往右,一棵树的左子树永远在右子树前面,右子树永远在根前面
4.层级遍历:就是按层,从上到下,从左到右遍历
- 代码
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Tree{
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
作业要求:叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
自己实现四个方法,main方法中调用,将结果打印到控制台
*/
/* 二叉树的结构
A
/ \
T 6
/
D
/ \
N 5
/ \ /
B 4 1
\
9
*/
Node root = into();
// 先序遍历
System.out.println("\n"+"前序遍历");
A(root);
// 中序遍历
System.out.println("\n"+"中序遍历");
B(root);
// 后续遍历
System.out.println("\n"+"后续遍历");
C(root);
// 层级遍历
System.out.println("\n"+"层级遍历");
D(root);
}
private static void A(Node node) {
// TODO 先序遍历
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
if(node.l != null){
A(node.l);
}
if(node.r != null){
A(node.r);
}
}
private static void B(Node node) {
// TODO 中序遍历
if(node.l != null){
B(node.l);
}
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
if(node.r != null){
B(node.r);
}
}
private static void C(Node node) {
// TODO 后续遍历
if(node.l != null){
C(node.l);
}
if(node.r != null){
C(node.r);
}
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
}
private static void D(Node node) {
// TODO 层级遍历
if(node == null) {
return ;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Node current = null;
queue.offer(node);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
current = queue.poll();
System.out.print(current.data+ "\t");
if(current.l != null) {
queue.offer(current.l);
}
if(current.r != null) {
queue.offer(current.r);
}
}
}
// 构建一颗树,返回根节点
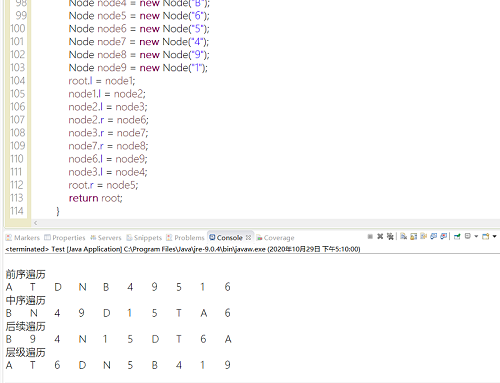
private static Node into(){
Node root = new Node("A");
Node node1 = new Node("T");
Node node2 = new Node("D");
Node node3 = new Node("N");
Node node4 = new Node("B");
Node node5 = new Node("6");
Node node6 = new Node("5");
Node node7 = new Node("4");
Node node8 = new Node("9");
Node node9 = new Node("1");
root.l = node1;
node1.l = node2;
node2.l = node3;
node2.r = node6;
node3.r = node7;
node7.r = node8;
node6.l = node9;
node3.l = node4;
root.r = node5;
return root;
}
// 节点
static class Node{
// 数据
Object data;
// 左孩子
Node l;
// 右孩子
Node r;
public Node(){}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.l = null;
this.r = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node l, Node r) {
this.data = data;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
}
}
- 运行结果
![]()
![]()
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号