c++继承
继承
继承是面向对象三大特性之一
有些类与类之间存在特殊关系如动物 包含了狗和猫,狗又分哈奇士,京巴,猫又分为加菲猫,狸花猫等
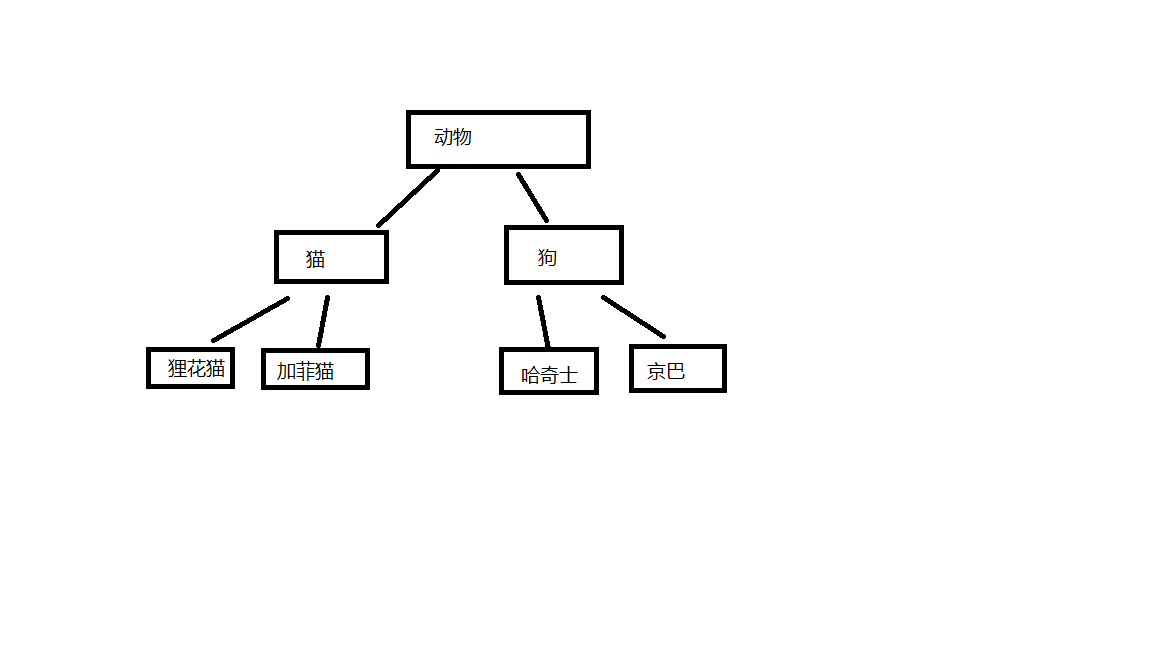
像这样一个类下面还分为很多类,下级别的类成员除了拥有上级别的共性,还有自己的特性,只是可以考虑用继承减少重复代码
格式
class 子类:继承方式 父类
子类又叫派生类
父类又叫基类
1 calss A:public B 2 { 3 4 }
继承方式
。公共继承 pubilic ------------->父类中的public和protected 到子类中不变
。保护继承 protected----------->赴俄历中的public和protected到子类中全变为protected
。私有继承private--------------->父类中的private 子类不可访问

继承中的对象模型
父类中所有非静态成员都会被子类继承
父类中的private 成员被子类继承,是被编译器隐藏了,但确实被子类继承了。
继承中的构造和析构顺序
子类继承父类,当创建子类对象,也会调用父类的构造函数
先构造父类,再构造子类,析构顺序与构造相反
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string > 3 using namespace std; 4 class Father 5 { 6 public: 7 Father() 8 { 9 cout << "fater()构造函数" << endl; 10 } 11 ~Father() 12 { 13 cout << "~fater()分析造函数" << endl; 14 } 15 }; 16 class Son1 : public Father 17 { 18 public: 19 Son1() 20 { 21 cout << "Son1构造函数" << endl; 22 } 23 24 ~Son1() 25 { 26 cout << "Son1析构函数" << endl; 27 } 28 }; 29 30 31 32 int main() 33 { 34 35 36 Son1 p;//子类继承父类,当创建子类对象,也会调用父类的构造函数
//先构造父类,再构造子类,析构顺序与构造相反 37 38 return 0; 39 }
输出
1 fater()构造函数 2 Son1构造函数 3 Son1析构函数 4 ~fater()分析造函数
继承同名成员处理方式
。访问子类同名成员直接访问即可
。访问父类同名成员,需加作用域即 son1.Father::m_A
如果子类中的出现和父类中同名成员函数,子类的同名成员
会隐藏掉父类中所有同名的成员函数包括重载函数。加作用域可以访问到父类中同名函数
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include <string > 3 using namespace std; 4 5 6 7 class Father 8 { 9 public: 10 void Print() 11 { 12 cout << "Father::Print()" << endl; 13 } 14 void Print(int a) 15 { 16 cout << "Father::Print(int a)" << endl; 17 } 18 19 }; 20 21 22 class Son1 : public Father 23 { 24 public: 25 void Print(int a) 26 { 27 cout << "Son1::Print(int a)" << endl; 28 } 29 }; 30 31 32 int main() 33 { 34 Son1 p1; 35 p1.Print(10);//直接调用子类中的Print(int a) 36 p1.Father::Print(10);//加作用域调用Father类中的Print(int a)成员函数 37 38 39 return 0; 40 }
输出
1 Son1::Print(int a) 2 Father::Print(int a)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号