Java 8 新特性 Stream使用详解
Java 8 Stream
Java 8 API添加了一个新的抽象称为流Stream,可以让你以一种声明[^1]的方式处理数据。
这种风格将要处理的元素集合看作一种流, 流在管道中传输, 并且可以在管道的节点上进行处理, 比如筛选, 排序,聚合等。
元素流在管道中经过中间操作(intermediate operation)的处理,最后由最终操作(terminal operation)得到前面处理的结果。
+--------------------+ +------+ +------+ +---+ +-------+
| stream of elements +-----> |filter+-> |sorted+-> |map+-> |collect|
+--------------------+ +------+ +------+ +---+ +-------+
以上的流程转换为 Java 代码为:
List<Integer> transactionsIds =
widgets.stream()
.filter(b -> b.getColor() == RED)
.sorted((x,y) -> x.getWeight() - y.getWeight())
.mapToInt(Widget::getWeight)
.sum();
[1^] 编程范式:命令式编程(Imperative)、声明式编程(Declarative)和函数式编程(Functional)
概念
Stream(流)是一个来自数据源的元素队列并支持聚合操作
- 元素是特定类型的对象,形成一个队列。 Java中的Stream并不会存储元素,而是按需计算。
- 数据源 流的来源。 可以是集合,数组,I/O channel, 产生器generator 等。
- 聚合操作 类似SQL语句一样的操作, 比如filter, map, reduce, find, match, sorted等。
和以前的Collection操作不同, Stream操作还有两个基础的特征:
- Pipelining: 中间操作都会返回流对象本身。 这样多个操作可以串联成一个管道, 如同流式风格(fluent style)。 这样做可以对操作进行优化, 比如延迟执行(laziness)和短路( short-circuiting)。
- 内部迭代: 以前对集合遍历都是通过Iterator或者For-Each的方式, 显式的在集合外部进行迭代, 这叫做外部迭代。 Stream提供了内部迭代的方式, 通过访问者模式(Visitor)实现。
使用
生成流
- 集合 Collection.stream()
- 静态方法 Stream.of
- 数组 Arrays.stream
//1.集合
Stream<Student> stream = basketballClub.stream();
//2.静态方法
Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of("a", "b", "c");
//3.数组
String[] arr = {"a","b","c"};
Stream<String> stream3 = Arrays.stream(arr);
在 Java 8 中, 集合接口有两个方法来生成流:
- stream() − 为集合创建串行流。
- parallelStream() − 为集合创建并行流。
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
List<String> filtered = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.toList());
常见操作
终止操作
foreach(Consumer c)遍历操作
collect(Collector)将流转化为其他形式
max(Comparator)返回流中最大值
min(Comparator)返回流中最小值
count返回流中元素综述
Collectors 具体方法
- toList List 把流中元素收集到List
- toSet Set 把流中元素收集到Set
- toCollection Coolection 把流中元素收集到Collection中
- groupingBy Map<K,List> 根据K属性对流进行分组
- partitioningBy Map<boolean, List> 根据boolean值进行分组
中间操作
filter(Predicate) 筛选流中某些元素
map(Function f) 接收流中元素,并且将其映射成为新元素,例如从student对象中取name属性
flatMap(Function f) 将所有流中的元素并到一起连接成一个流
peek(Consumer c) 获取流中元素,操作流中元素,与foreach不同的是不会截断流,可继续操作流
distinct() 通过流所生成元素的equals和hashCode去重
limit(long val) 截断流,取流中前val个元素
sorted(Comparator) 产生一个新流,按照比较器规则排序
sorted() 产生一个新流,按照自然顺序排序
匹配
-
booelan allMatch(Predicate) 都符合
-
boolean anyMatch(Predicate) 任一元素符合
-
boolean noneMatch(Predicate) 都不符合
寻找元素
-
findFirst——返回第一个元素
-
findAny——返回当前流中的任意元素
计数和极值
-
count——返回流中元素的总个数
-
max——返回流中最大值
-
min——返回流中最小值
示例
示例一
forEach
Stream 提供了新的方法 'forEach' 来迭代流中的每个数据。以下代码片段使用 forEach 输出了10个随机数:
Random random = new Random();
random.ints().limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
map
map 方法用于映射每个元素到对应的结果,以下代码片段使用 map 输出了元素对应的平方数:
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 2, 2, 3, 7, 3, 5);
// 获取对应的平方数
List<Integer> squaresList = numbers.stream().map( i -> i*i).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
filter
filter 方法用于通过设置的条件过滤出元素。以下代码片段使用 filter 方法过滤出空字符串:
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
// 获取空字符串的数量
long count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();
limit
limit 方法用于获取指定数量的流。 以下代码片段使用 limit 方法打印出 10 条数据:
Random random = new Random();
random.ints().limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
sorted
sorted 方法用于对流进行排序。以下代码片段使用 sorted 方法对输出的 10 个随机数进行排序
Random random = new Random();
random.ints().limit(10).sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
Collectors
Collectors 类实现了很多归约操作,例如将流转换成集合和聚合元素。Collectors 可用于返回列表或字符串:
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
List<String> filtered = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("筛选列表: " + filtered);
String mergedString = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
System.out.println("合并字符串: " + mergedString);
统计
另外,一些产生统计结果的收集器也非常有用。它们主要用于int、double、long等基本类型上,它们可以用来产生类似如下的统计结果。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 2, 2, 3, 7, 3, 5);
IntSummaryStatistics stats = numbers.stream().mapToInt((x) -> x).summaryStatistics();
System.out.println("列表中最大的数 : " + stats.getMax());
System.out.println("列表中最小的数 : " + stats.getMin());
System.out.println("所有数之和 : " + stats.getSum());
System.out.println("平均数 : " + stats.getAverage());
并行(parallel)程序
parallelStream 是流并行处理程序的代替方法。以下实例我们使用 parallelStream 来输出空字符串的数量:
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
// 获取空字符串的数量
long count = strings.parallelStream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();
示例二
准备数据
//计算机俱乐部
private static List<Student> computerClub = Arrays.asList(
new Student("2015134001", "小明", 15, "1501"),
new Student("2015134003", "小王", 14, "1503"),
new Student("2015134006", "小张", 15, "1501"),
new Student("2015134008", "小梁", 17, "1505")
);
//篮球俱乐部
private static List<Student> basketballClub = Arrays.asList(
new Student("2015134012", "小c", 13, "1503"),
new Student("2015134013", "小s", 14, "1503"),
new Student("2015134015", "小d", 15, "1504"),
new Student("2015134018", "小y", 16, "1505")
);
//乒乓球俱乐部
private static List<Student> pingpongClub = Arrays.asList(
new Student("2015134022", "小u", 16, "1502"),
new Student("2015134021", "小i", 14, "1502"),
new Student("2015134026", "小m", 17, "1504"),
new Student("2015134027", "小n", 16, "1504")
);
private static List<List<Student>> allClubStu = new ArrayList<>();
allClubStu.add(computerClub);
allClubStu.add(basketballClub);
allClubStu.add(pingpongClub);
终止操作
//此处只是演示 此类需求直接用List构造器即可
List<Student> collect = computerClub.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
Set<Student> collect1 = pingpongClub.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
//注意key必须是唯一的 如果不是唯一的会报错而不是像普通map那样覆盖
Map<String, String> collect2 = pingpongClub.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getIdNum, Student::getName));
//分组 类似于数据库中的group by
Map<String, List<Student>> collect3 = pingpongClub.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getClassNum));
//字符串拼接 第一个参数是分隔符 第二个参数是前缀 第三个参数是后缀
String collect4 = pingpongClub.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(",", "【", "】"));
//【小u,小i,小m,小n】
//三个俱乐部符合年龄要求的按照班级分组
Map<String, List<Student>> collect5 = Stream.of(basketballClub, pingpongClub, computerClub)
.flatMap(e -> e.stream().filter(s -> s.getAge() < 17))
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getClassNum));
//按照是否年龄>16进行分组 key为true和false
ConcurrentMap<Boolean, List<Student>> collect6 = Stream.of(basketballClub, pingpongClub, computerClub)
.flatMap(Collection::stream)
.collect(Collectors.groupingByConcurrent(s -> s.getAge() > 16));
中间操作
filter(Predicate) 筛选流中某些元素
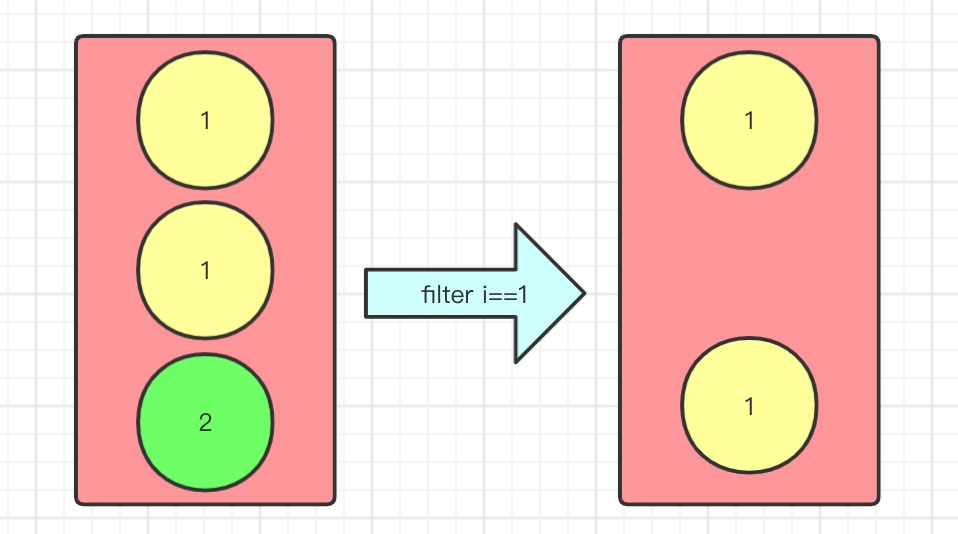
//筛选1501班的学生
computerClub.stream().filter(e -> e.getClassNum().equals("1501")).forEach(System.out::println);
//筛选年龄大于15的学生
List<Student> collect = computerClub.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge() > 15).collect(Collectors.toList());
map(Function f) 接收流中元素,并且将其映射成为新元素,例如从student对象中取name属性
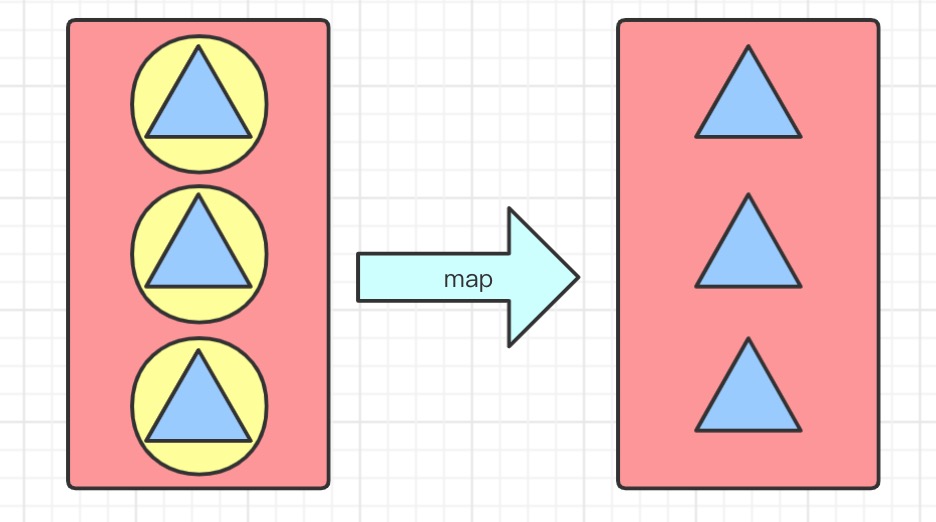
//篮球俱乐部所有成员名 + 暂时住上商标^_^,并且获取所有队员名
List<String> collect1 = basketballClub.stream()
.map(e -> e.getName() + "^_^")
.collect(Collectors.toList());
collect1.forEach(System.out::println);
//小c^_^^_^
//小s^_^^_^
//小d^_^^_^
//小y^_^^_^
flatMap(Function f) 将所有流中的元素并到一起连接成一个流
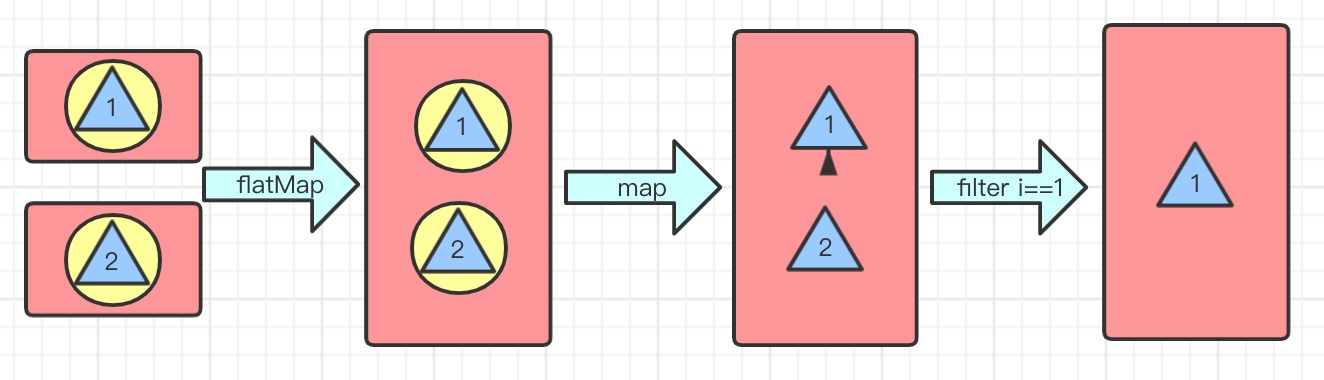
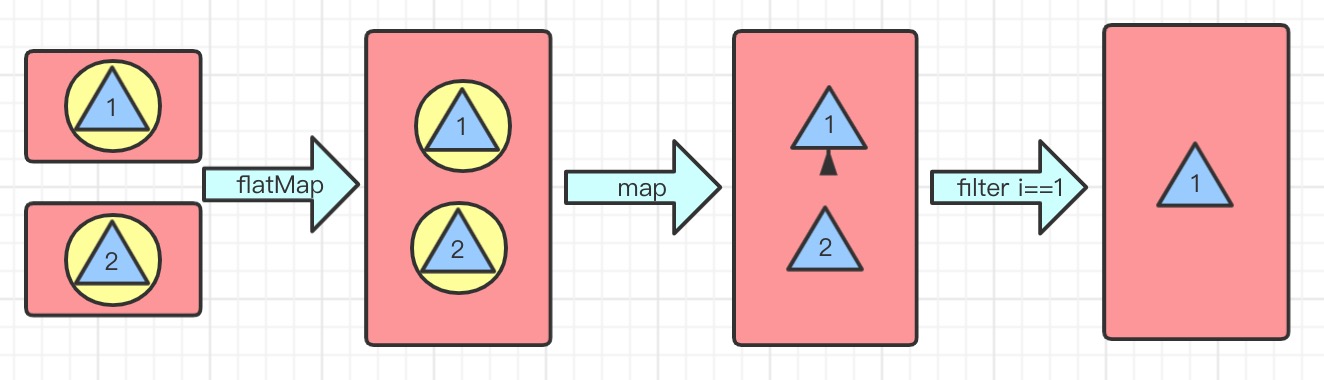
//获取年龄大于15的所有俱乐部成员
List<Student> collect2 = Stream.of(basketballClub, computerClub, pingpongClub)
.flatMap(e -> e.stream().filter(s -> s.getAge() > 15))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
collect2.forEach(System.out::println);
//用双层list获取所有年龄大于15的俱乐部成员
List<Student> collect3 = allClubStu.stream()
.flatMap(e -> e.stream().filter(s -> s.getAge() > 15))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
collect3.forEach(System.out::println);
peek(Consumer c) 获取流中元素,操作流中元素,与foreach不同的是不会截断流,可继续操作流
//篮球俱乐部所有成员名 + 赞助商商标^_^,并且获取所有队员详细内容
List<Student> collect = basketballClub.stream()
.peek(e -> e.setName(e.getName() + "^_^"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
collect.forEach(System.out::println);
//Student{idNum='2015134012', name='小c^_^', age=13, classNum='1503'}
//Student{idNum='2015134013', name='小s^_^', age=14, classNum='1503'}
//Student{idNum='2015134015', name='小d^_^', age=15, classNum='1504'}
//Student{idNum='2015134018', name='小y^_^', age=16, classNum='1505'}
distinct() 通过流所生成元素的equals和hashCode去重
limit(long val) 截断流,取流中前val个元素
sorted(Comparator) 产生一个新流,按照比较器规则排序
sorted() 产生一个新流,按照自然顺序排序
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("b","b","c","a");
list.forEach(System.out::print); //bbca
List<String> collect = list.stream().distinct().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
collect.forEach(System.out::print);//abc
//获取list中排序后的top2 即截断取前两个
List<String> collect1 = list.stream().distinct().sorted().limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
collect1.forEach(System.out::print);//ab
匹配
booelan allMatch(Predicate)都符合boolean anyMatch(Predicate)任一元素符合boolean noneMatch(Predicate)都不符合
boolean b = basketballClub.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge() < 20);
boolean b1 = basketballClub.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getAge() < 20);
boolean b2 = basketballClub.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.getAge() < 20);
寻找元素
findFirst——返回第一个元素findAny——返回当前流中的任意元素
Optional<Student> first = basketballClub.stream().findFirst();
if (first.isPresent()) {
Student student = first.get();
System.out.println(student);
}
Optional<Student> any = basketballClub.stream().findAny();
if (any.isPresent()) {
Student student2 = any.get();
System.out.println(student2);
}
Optional<Student> any1 = basketballClub.stream().parallel().findAny();
System.out.println(any1);
计数和极值
count——返回流中元素的总个数max——返回流中最大值min——返回流中最小值
long count = basketballClub.stream().count();
Optional<Student> max = basketballClub.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge));
if (max.isPresent()) {
Student student = max.get();
}
Optional<Student> min = basketballClub.stream().min(Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getAge));
if (min.isPresent()) {
Student student = min.get();
}
更多方法
Method Summary
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
boolean |
allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)Returns whether all elements of this stream match the provided predicate. |
boolean |
anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)Returns whether any elements of this stream match the provided predicate. |
static <T> Stream.Builder<T> |
builder()Returns a builder for a Stream. |
<R,A> R |
collect(Collector<? super T,A,R> collector)Performs a mutable reduction operation on the elements of this stream using a Collector. |
<R> R |
collect(Supplier<R> supplier, BiConsumer<R,? super T> accumulator, BiConsumer<R,R> combiner)Performs a mutable reduction operation on the elements of this stream. |
static <T> Stream<T> |
concat(Stream<? extends T> a, Stream<? extends T> b)Creates a lazily concatenated stream whose elements are all the elements of the first stream followed by all the elements of the second stream. |
long |
count()Returns the count of elements in this stream. |
Stream<T> |
distinct()Returns a stream consisting of the distinct elements (according to Object.equals(Object)) of this stream. |
static <T> Stream<T> |
empty()Returns an empty sequential Stream. |
Stream<T> |
filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate)Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream that match the given predicate. |
Optional<T> |
findAny()Returns an Optional describing some element of the stream, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty. |
Optional<T> |
findFirst()Returns an Optional describing the first element of this stream, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty. |
<R> Stream<R> |
flatMap(Function<? super T,? extends Stream<? extends R>> mapper)Returns a stream consisting of the results of replacing each element of this stream with the contents of a mapped stream produced by applying the provided mapping function to each element. |
DoubleStream |
flatMapToDouble(Function<? super T,? extends DoubleStream> mapper)Returns an DoubleStream consisting of the results of replacing each element of this stream with the contents of a mapped stream produced by applying the provided mapping function to each element. |
IntStream |
flatMapToInt(Function<? super T,? extends IntStream> mapper)Returns an IntStream consisting of the results of replacing each element of this stream with the contents of a mapped stream produced by applying the provided mapping function to each element. |
LongStream |
flatMapToLong(Function<? super T,? extends LongStream> mapper)Returns an LongStream consisting of the results of replacing each element of this stream with the contents of a mapped stream produced by applying the provided mapping function to each element. |
void |
forEach(Consumer<? super T> action)Performs an action for each element of this stream. |
void |
forEachOrdered(Consumer<? super T> action)Performs an action for each element of this stream, in the encounter order of the stream if the stream has a defined encounter order. |
static <T> Stream<T> |
generate(Supplier<T> s)Returns an infinite sequential unordered stream where each element is generated by the provided Supplier. |
static <T> Stream<T> |
iterate(T seed, UnaryOperator<T> f)Returns an infinite sequential ordered Stream produced by iterative application of a function f to an initial element seed, producing a Stream consisting of seed, f(seed), f(f(seed)), etc. |
Stream<T> |
limit(long maxSize)Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, truncated to be no longer than maxSize in length. |
<R> Stream<R> |
map(Function<? super T,? extends R> mapper)Returns a stream consisting of the results of applying the given function to the elements of this stream. |
DoubleStream |
mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T> mapper)Returns a DoubleStream consisting of the results of applying the given function to the elements of this stream. |
IntStream |
mapToInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> mapper)Returns an IntStream consisting of the results of applying the given function to the elements of this stream. |
LongStream |
mapToLong(ToLongFunction<? super T> mapper)Returns a LongStream consisting of the results of applying the given function to the elements of this stream. |
Optional<T> |
max(Comparator<? super T> comparator)Returns the maximum element of this stream according to the provided Comparator. |
Optional<T> |
min(Comparator<? super T> comparator)Returns the minimum element of this stream according to the provided Comparator. |
boolean |
noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)Returns whether no elements of this stream match the provided predicate. |
static <T> Stream<T> |
of(T... values)Returns a sequential ordered stream whose elements are the specified values. |
static <T> Stream<T> |
of(T t)Returns a sequential Stream containing a single element. |
Stream<T> |
peek(Consumer<? super T> action)Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, additionally performing the provided action on each element as elements are consumed from the resulting stream. |
Optional<T> |
reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator)Performs a reduction on the elements of this stream, using an associative accumulation function, and returns an Optional describing the reduced value, if any. |
T |
reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator)Performs a reduction on the elements of this stream, using the provided identity value and an associative accumulation function, and returns the reduced value. |
<U> U |
reduce(U identity, BiFunction<U,? super T,U> accumulator, BinaryOperator<U> combiner)Performs a reduction on the elements of this stream, using the provided identity, accumulation and combining functions. |
Stream<T> |
skip(long n)Returns a stream consisting of the remaining elements of this stream after discarding the first n elements of the stream. |
Stream<T> |
sorted()Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, sorted according to natural order. |
Stream<T> |
sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator)Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, sorted according to the provided Comparator. |
Object[] |
toArray()Returns an array containing the elements of this stream. |
<A> A[] |
toArray(IntFunction<A[]> generator)Returns an array containing the elements of this stream, using the provided generator function to allocate the returned array, as well as any additional arrays that might be required for a partitioned execution or for resizing. |



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号