基于评论的情绪分析
一、选题背景
由于目前大数据环境,越来越多的数据被可视化,提供给各类对象来分析人们的实践活动,本课题基于对商品的评论的情绪分析,来帮助买家更好的预判客户的喜好,进而达成商品的交易,同时也是对于商品的卖出的反馈的统计,观察商品在生产情况下还有哪些不足,这些不足又该如何改进,通过情绪分析,商家便可以在抛去大量的语料阅读的情况下明显的感受的用户对于商品的感受程度,进一步帮助商家做出选择,尤其是对于目前线上经济快速发展的情况,这更加必要。
二、机器学习案例涉及方案
使用sklearn来进行机器学习,测试集和训练集由网上提供的电商评论。深度学习模型为Embedding + LSTM + Softmax.相关内容后面再修改,先附上代码。
embedding层也称为词向量层或者是词嵌入层,按我的理解来讲,就是把词转成向量来表示,相当于把语义数量化,具体内部实现逻辑没有太研究,看了一下使用方法,我通过句子构建一个词汇表,然后embedding就会利用这个词汇表构造对应的向量表示。
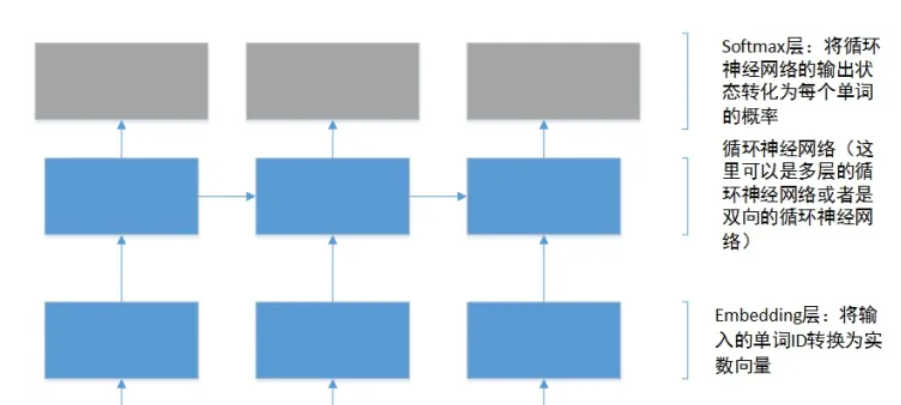
三、机器学习代码
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import font_manager
from itertools import accumulate
# 设置matplotlib绘图时的字体
my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="C:\Windows\Fonts\simsun.ttc")
# 统计句子长度及长度出现的频数
df = pd.read_csv('D:\PyCharm\data_single.csv')
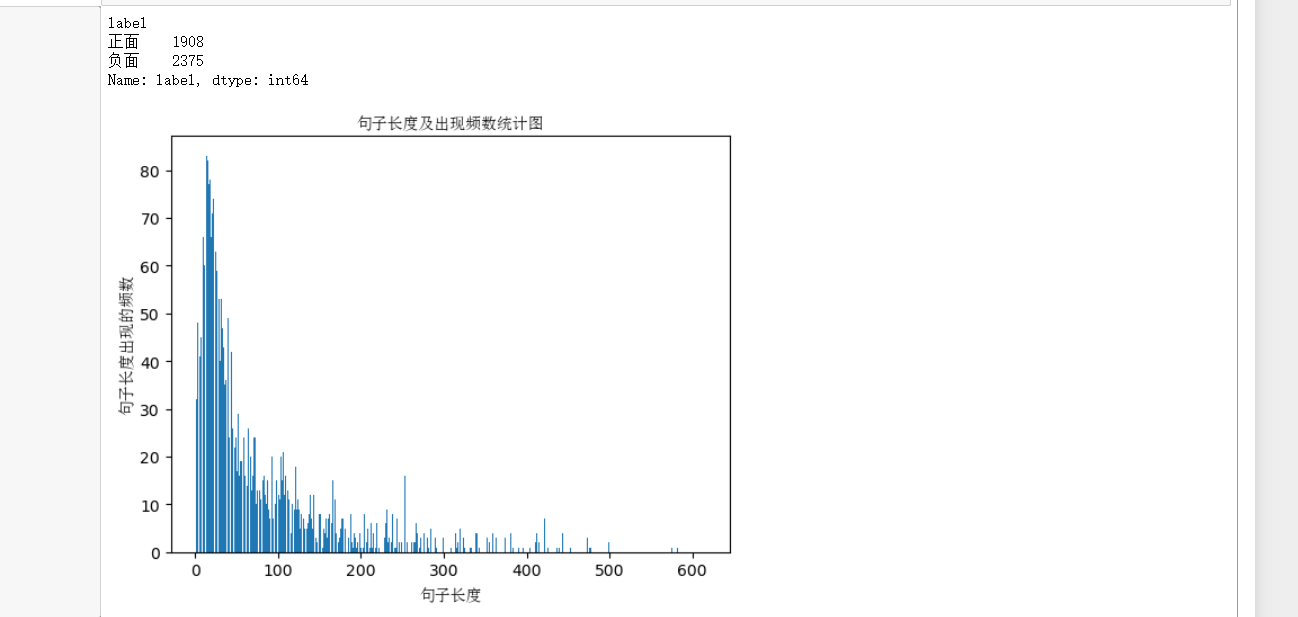
print(df.groupby('label')['label'].count())
df['length'] = df['evaluation'].apply(lambda x: len(x))
len_df = df.groupby('length').count()
sent_length = len_df.index.tolist()
sent_freq = len_df['evaluation'].tolist()
# 绘制句子长度及出现频数统计图
plt.bar(sent_length, sent_freq)
plt.title("句子长度及出现频数统计图", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.xlabel("句子长度", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.ylabel("句子长度出现的频数", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.show()
这里我们先对数据集进行可视化,展示目前的句子的长度。同时显示正面和负面的评论数。
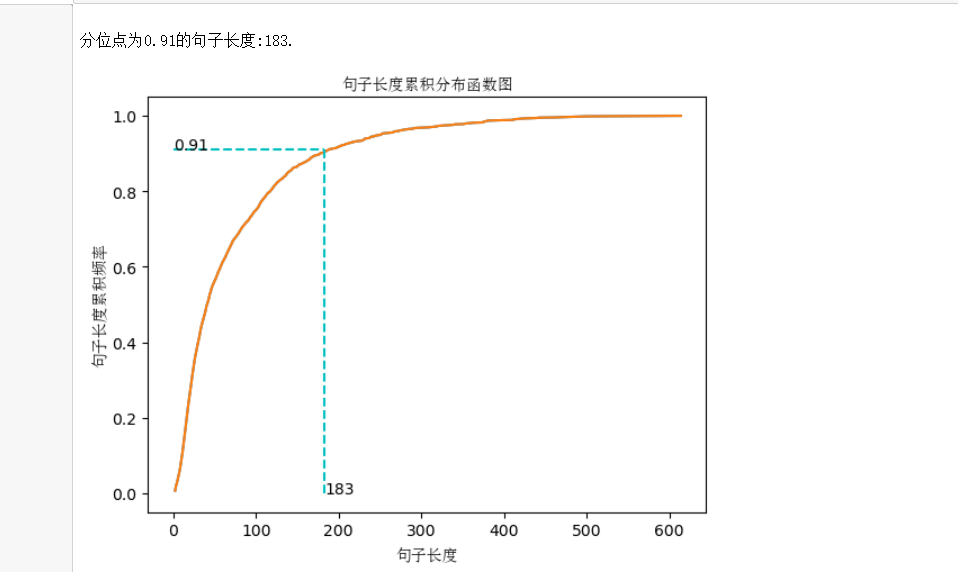
接下来我们可以进一步分析句子长度累积分布函数(CDF),来进一步了解句子的分布情况。
# 绘制句子长度累积分布函数(CDF)
sent_pentage_list = [(count/sum(sent_freq)) for count in accumulate(sent_freq)]
# 绘制CDF
plt.plot(sent_length, sent_pentage_list)
# 寻找分位点为quantile的句子长度
quantile = 0.91
#print(list(sent_pentage_list))
for length, per in zip(sent_length, sent_pentage_list):
if round(per, 2) == quantile:
index = length
break
print("\n分位点为%s的句子长度:%d." % (quantile, index))
# 绘制句子长度累积分布函数图
plt.plot(sent_length, sent_pentage_list)
plt.hlines(quantile, 0, index, colors="c", linestyles="dashed")
plt.vlines(index, 0, quantile, colors="c", linestyles="dashed")
plt.text(0, quantile, str(quantile))
plt.text(index, 0, str(index))
plt.title("句子长度累积分布函数图", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.xlabel("句子长度", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.ylabel("句子长度累积频率", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.show()
在可视化完成后,我们需要先做好文本处理工作
import pickle
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from keras.utils import np_utils, plot_model
from keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Embedding, Dropout
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 导入数据
# 文件的数据中,特征为evaluation, 类别为label.
def load_data(filepath, input_shape=20):
df = pd.read_csv(filepath)
# 标签及词汇表
labels, vocabulary = list(df['label'].unique()), list(df['evaluation'].unique())
# 构造字符级别的特征
string = ''
for word in vocabulary:
string += word
vocabulary = set(string)
# 字典列表
word_dictionary = {word: i+1 for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)}
with open('word_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(word_dictionary, f)
inverse_word_dictionary = {i+1: word for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)}
label_dictionary = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(labels)}
with open('label_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(label_dictionary, f)
output_dictionary = {i: labels for i, labels in enumerate(labels)}
vocab_size = len(word_dictionary.keys()) # 词汇表大小
label_size = len(label_dictionary.keys()) # 标签类别数量
# 序列填充
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent] for sent in df['evaluation']]
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0)
y = [[label_dictionary[sent]] for sent in df['label']]
y = [np_utils.to_categorical(label, num_classes=label_size) for label in y]
y = np.array([list(_[0]) for _ in y])
return x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary
接下来创建深度学习的对象,并保存模型,以提供给后面的测试用例。
# 创建深度学习模型, Embedding + LSTM + Softmax.
def create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath):
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size + 1, output_dim=output_dim,
input_length=input_shape, mask_zero=True))#使模型加入Embedding层,将离散数据转为连续向量,把词句数量化,使得语义相近的词句具有相近的向量
model.add(LSTM(n_units, input_shape=(x.shape[0], x.shape[1])))#加入LSTM层,长短期记忆神经网络
model.add(Dropout(0.2))#Dropout防止数据过拟合
model.add(Dense(label_size, activation='softmax'))#Dense全连接层,使用softmax多分类的激活函数,表示最后的概率
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
plot_model(model, to_file='./model_lstm.png', show_shapes=True)
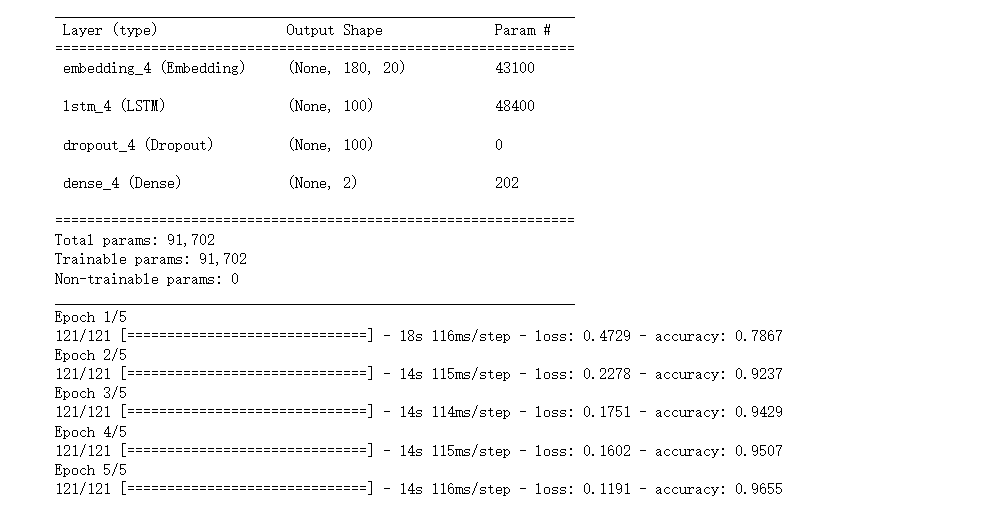
model.summary()
return model
# 模型训练
def model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path):
# 将数据集分为训练集和测试集,占比为9:1
# input_shape = 100
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath, input_shape)
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.1, random_state = 42)
# 模型输入参数
n_units = 100
batch_size = 32
epochs = 5
output_dim = 20
# 模型训练
lstm_model = create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath)
result = lstm_model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=1)
acc = result.history['accuracy']
loss =result.history['loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b', label='loss')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 模型保存
lstm_model.save(model_save_path)
N = test_x.shape[0] # 测试的条数
predict = []
label = []
for start, end in zip(range(0, N, 1), range(1, N+1, 1)):
sentence = [inverse_word_dictionary[i] for i in test_x[start] if i != 0]
y_predict = lstm_model.predict(test_x[start:end])
label_predict = output_dictionary[np.argmax(y_predict[0])]
label_true = output_dictionary[np.argmax(test_y[start:end])]
print(''.join(sentence), label_true, label_predict) # 输出预测结果
predict.append(label_predict)
label.append(label_true)
acc = accuracy_score(predict, label) # 预测准确率
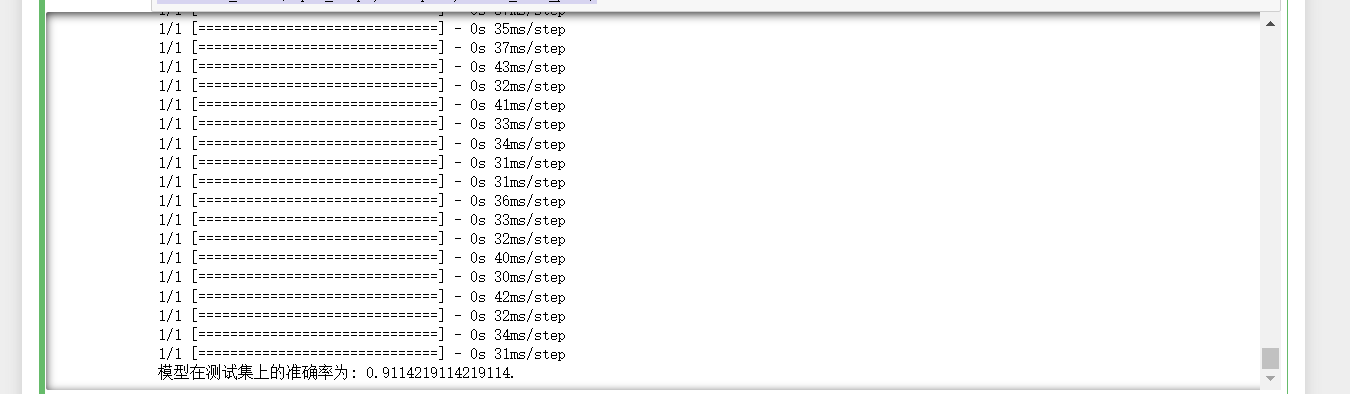
print('模型在测试集上的准确率为: %s.' % acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
filepath = 'D:\PyCharm\data_single.csv'
input_shape = 180
model_save_path = './corpus_model.h5'
model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path)
在此次训练中,我们先训练五次,来看看成功率的分布情况。
同时绘制损失和正确曲线。
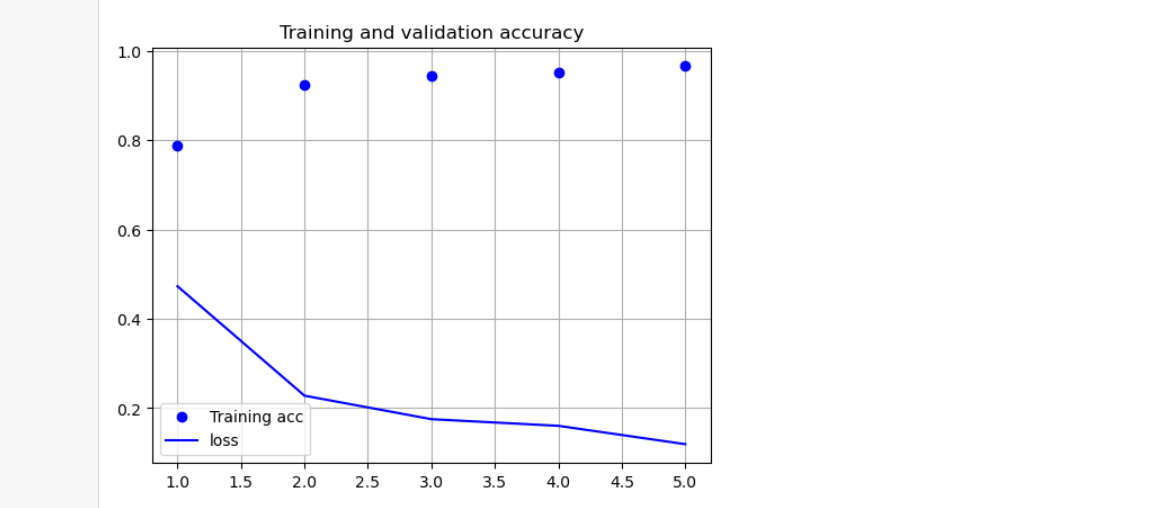
在测试集的测试用例中,精度达到了百分之90以上。

接下来我们评估一下这个模型对单一测试用例的预测情况。
# Import the necessary modules
import pickle
import numpy as np
from keras.models import load_model
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
# 导入字典
with open('word_dict.pk', 'rb') as f:
word_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
with open('label_dict.pk', 'rb') as f:
output_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
try:
# 数据预处理
input_shape = 180
sent = "这个商品怎么回事啊,商家到底有没有良心卖东西啊,真的无语死了"
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent]]
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0)
# 载入模型
model_save_path = 'D:\PyCharm\corpus_model.h5'
lstm_model = load_model(model_save_path)
# 模型预测
y_predict = lstm_model.predict(x)
label_dict = {v:k for k,v in output_dictionary.items()}
print('输入语句: %s' % sent)
print('情感预测结果: %s' % label_dict[np.argmax(y_predict)])
except KeyError as err:
print("有汉字不在词汇表中,请重新输入!")

可以看到模型正确的评估了测试的情况。
接下来我们提高一些训练的次数,来看一下模型的情况,是否会有所改善。
# 导入数据
# 文件的数据中,特征为evaluation, 类别为label.
def load_data(filepath, input_shape=20):
df = pd.read_csv(filepath)
# 标签及词汇表
labels, vocabulary = list(df['label'].unique()), list(df['evaluation'].unique())
# 构造字符级别的特征
string = ''
for word in vocabulary:
string += word
vocabulary = set(string)
# 字典列表
word_dictionary = {word: i+1 for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)}
with open('word_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(word_dictionary, f)
inverse_word_dictionary = {i+1: word for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)}
label_dictionary = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(labels)}
with open('label_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(label_dictionary, f)
output_dictionary = {i: labels for i, labels in enumerate(labels)}
vocab_size = len(word_dictionary.keys()) # 词汇表大小
label_size = len(label_dictionary.keys()) # 标签类别数量
# 序列填充
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent] for sent in df['evaluation']]
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0)
y = [[label_dictionary[sent]] for sent in df['label']]
y = [np_utils.to_categorical(label, num_classes=label_size) for label in y]
y = np.array([list(_[0]) for _ in y])
return x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary
# 创建深度学习模型, Embedding + LSTM + Softmax.
def create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath):
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size + 1, output_dim=output_dim,
input_length=input_shape, mask_zero=True))
model.add(LSTM(n_units, input_shape=(x.shape[0], x.shape[1])))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(label_size, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
plot_model(model, to_file='./model_lstm.png', show_shapes=True)
model.summary()
return model
# 模型训练
def model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path):
# 将数据集分为训练集和测试集,占比为9:1
# input_shape = 100
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath, input_shape)
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.1, random_state = 42)
# 模型输入参数,需要自己根据需要调整
n_units = 100
batch_size = 32
epochs = 10
output_dim = 20
# 模型训练
lstm_model = create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath)
result = lstm_model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=1)
acc = result.history['accuracy']
loss =result.history['loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b', label='loss')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 模型保存
lstm_model.save(model_save_path)
N = test_x.shape[0] # 测试的条数
predict = []
label = []
for start, end in zip(range(0, N, 1), range(1, N+1, 1)):
sentence = [inverse_word_dictionary[i] for i in test_x[start] if i != 0]
y_predict = lstm_model.predict(test_x[start:end])
label_predict = output_dictionary[np.argmax(y_predict[0])]
label_true = output_dictionary[np.argmax(test_y[start:end])]
predict.append(label_predict)
label.append(label_true)
acc = accuracy_score(predict, label) # 预测准确率
print('模型在测试集上的准确率为: %s.' % acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
filepath = 'D:\PyCharm\data_single.csv'
input_shape = 180
model_save_path = './corpus_model2.h5'
model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path)
在这里我们把训练次数改为10次。
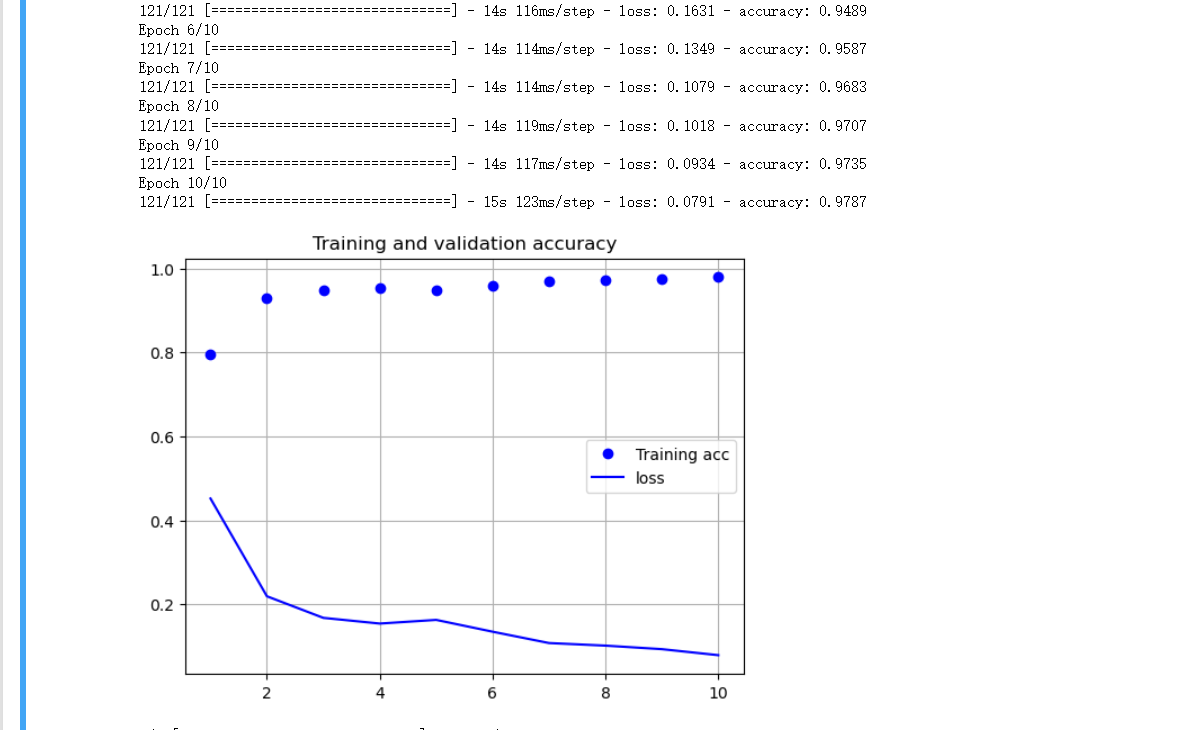
我们可以观察到测试集的正确率反而下降了,这说明是数据过拟合造成的。
我们再重新用新的模型验证一下测试用例。
# Import the necessary modules
import pickle
import numpy as np
from keras.models import load_model
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
# 导入字典
with open('word_dict.pk', 'rb') as f:
word_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
with open('label_dict.pk', 'rb') as f:
output_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
try:
# 数据预处理
input_shape = 180
sent = "商品总体来说其实并没有那么不堪入目,但是我们应当注意的是,是否应该更加提高产品的质量,而不是套牢买家"
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent]]
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0)
# 载入模型
model_save_path = 'D:\PyCharm\corpus_model2.h5'
lstm_model = load_model(model_save_path)
# 模型预测
y_predict = lstm_model.predict(x)
label_dict = {v:k for k,v in output_dictionary.items()}
print('输入语句: %s' % sent)
print('情感预测结果: %s' % label_dict[np.argmax(y_predict)])
except KeyError as err:
print("您输入的句子有汉字不在词汇表中,请重新输入!")

模型正确评估了测试用句。
四、总结
本来是想做推特评论的情绪分析,但是由于国内的原因,nlp自然语言处理的一些包一直没办法搞清楚,由于最近时间又紧,后面有时间会重新上载推特的评论分析,自然语言处理是一个非常有意思的方向,语言毕竟是思想的载体,如果能够通过机器学习来正确的分割语言文本,理解语义,将对人们的生活有巨大的改善。通过本次实验基础性的了解了一下简单的语言分割方案,和情绪分析,就正面和负面两个方面来分析评论情感,也了解了一些基本的深度学习模型。
全部代码:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import font_manager
from itertools import accumulate
# 设置matplotlib绘图时的字体
my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="C:\Windows\Fonts\simsun.ttc")
# 统计句子长度及长度出现的频数
df = pd.read_csv('D:\PyCharm\data_single.csv')
print(df.groupby('label')['label'].count())
df['length'] = df['evaluation'].apply(lambda x: len(x))
len_df = df.groupby('length').count()
sent_length = len_df.index.tolist()
sent_freq = len_df['evaluation'].tolist()
# 绘制句子长度及出现频数统计图
plt.bar(sent_length, sent_freq)
plt.title("句子长度及出现频数统计图", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.xlabel("句子长度", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.ylabel("句子长度出现的频数", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.show()
# 绘制句子长度累积分布函数(CDF)
sent_pentage_list = [(count/sum(sent_freq)) for count in accumulate(sent_freq)]
# 绘制CDF
plt.plot(sent_length, sent_pentage_list)
# 寻找分位点为quantile的句子长度
quantile = 0.91
#print(list(sent_pentage_list))
for length, per in zip(sent_length, sent_pentage_list):
if round(per, 2) == quantile:
index = length
break
print("\n分位点为%s的句子长度:%d." % (quantile, index))
# 绘制句子长度累积分布函数图
plt.plot(sent_length, sent_pentage_list)
plt.hlines(quantile, 0, index, colors="c", linestyles="dashed")
plt.vlines(index, 0, quantile, colors="c", linestyles="dashed")
plt.text(0, quantile, str(quantile))
plt.text(index, 0, str(index))
plt.title("句子长度累积分布函数图", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.xlabel("句子长度", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.ylabel("句子长度累积频率", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.show()
import pickle
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from keras.utils import np_utils, plot_model
from keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Embedding, Dropout
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# 导入数据
# 文件的数据中,特征为evaluation, 类别为label.
def load_data(filepath, input_shape=20):
df = pd.read_csv(filepath)
# 标签及词汇表
labels, vocabulary = list(df['label'].unique()), list(df['evaluation'].unique())
# 构造字符级别的特征
string = ''
for word in vocabulary:
string += word
vocabulary = set(string)
# 字典列表
word_dictionary = {word: i+1 for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)}
with open('word_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(word_dictionary, f)
inverse_word_dictionary = {i+1: word for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)}
label_dictionary = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(labels)}
with open('label_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(label_dictionary, f)
output_dictionary = {i: labels for i, labels in enumerate(labels)}
vocab_size = len(word_dictionary.keys()) # 词汇表大小
label_size = len(label_dictionary.keys()) # 标签类别数量
# 序列填充
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent] for sent in df['evaluation']]
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0)
y = [[label_dictionary[sent]] for sent in df['label']]
y = [np_utils.to_categorical(label, num_classes=label_size) for label in y]
y = np.array([list(_[0]) for _ in y])
return x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary
# 创建深度学习模型, Embedding + LSTM + Softmax.
def create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath):
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size + 1, output_dim=output_dim,
input_length=input_shape, mask_zero=True))
model.add(LSTM(n_units, input_shape=(x.shape[0], x.shape[1])))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(label_size, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
plot_model(model, to_file='./model_lstm.png', show_shapes=True)
model.summary()
return model
# 模型训练
def model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path):
# 将数据集分为训练集和测试集,占比为9:1
# input_shape = 100
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath, input_shape)
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.1, random_state = 42)
# 模型输入参数,需要自己根据需要调整
n_units = 100
batch_size = 32
epochs = 5
output_dim = 20
# 模型训练
lstm_model = create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath)
result = lstm_model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=1)
acc = result.history['accuracy']
loss =result.history['loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b', label='loss')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 模型保存
lstm_model.save(model_save_path)
N = test_x.shape[0] # 测试的条数
predict = []
label = []
for start, end in zip(range(0, N, 1), range(1, N+1, 1)):
sentence = [inverse_word_dictionary[i] for i in test_x[start] if i != 0]
y_predict = lstm_model.predict(test_x[start:end])
label_predict = output_dictionary[np.argmax(y_predict[0])]
label_true = output_dictionary[np.argmax(test_y[start:end])]
print(''.join(sentence), label_true, label_predict) # 输出预测结果
predict.append(label_predict)
label.append(label_true)
acc = accuracy_score(predict, label) # 预测准确率
print('模型在测试集上的准确率为: %s.' % acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
filepath = 'D:\PyCharm\data_single.csv'
input_shape = 180
model_save_path = './corpus_model.h5'
model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path)
# Import the necessary modules
import pickle
import numpy as np
from keras.models import load_model
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
# 导入字典
with open('word_dict.pk', 'rb') as f:
word_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
with open('label_dict.pk', 'rb') as f:
output_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
try:
# 数据预处理
input_shape = 180
sent = "这个商品怎么回事啊,商家到底有没有良心卖东西啊,真的无语死了"
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent]]
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0)
# 载入模型
model_save_path = 'D:\PyCharm\corpus_model.h5'
lstm_model = load_model(model_save_path)
# 模型预测
y_predict = lstm_model.predict(x)
label_dict = {v:k for k,v in output_dictionary.items()}
print('输入语句: %s' % sent)
print('情感预测结果: %s' % label_dict[np.argmax(y_predict)])
except KeyError as err:
print("您输入的句子有汉字不在词汇表中,请重新输入!")
# 导入数据
# 文件的数据中,特征为evaluation, 类别为label.
def load_data(filepath, input_shape=20):
df = pd.read_csv(filepath)
# 标签及词汇表
labels, vocabulary = list(df['label'].unique()), list(df['evaluation'].unique())
# 构造字符级别的特征
string = ''
for word in vocabulary:
string += word
vocabulary = set(string)
# 字典列表
word_dictionary = {word: i+1 for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)}
with open('word_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(word_dictionary, f)
inverse_word_dictionary = {i+1: word for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)}
label_dictionary = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(labels)}
with open('label_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(label_dictionary, f)
output_dictionary = {i: labels for i, labels in enumerate(labels)}
vocab_size = len(word_dictionary.keys()) # 词汇表大小
label_size = len(label_dictionary.keys()) # 标签类别数量
# 序列填充
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent] for sent in df['evaluation']]
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0)
y = [[label_dictionary[sent]] for sent in df['label']]
y = [np_utils.to_categorical(label, num_classes=label_size) for label in y]
y = np.array([list(_[0]) for _ in y])
return x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary
# 创建深度学习模型, Embedding + LSTM + Softmax.
def create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath):
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size + 1, output_dim=output_dim,
input_length=input_shape, mask_zero=True))
model.add(LSTM(n_units, input_shape=(x.shape[0], x.shape[1])))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(label_size, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
plot_model(model, to_file='./model_lstm.png', show_shapes=True)
model.summary()
return model
# 模型训练
def model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path):
# 将数据集分为训练集和测试集,占比为9:1
# input_shape = 100
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath, input_shape)
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.1, random_state = 42)
# 模型输入参数,需要自己根据需要调整
n_units = 100
batch_size = 32
epochs = 10
output_dim = 20
# 模型训练
lstm_model = create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath)
result = lstm_model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=1)
acc = result.history['accuracy']
loss =result.history['loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b', label='loss')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 模型保存
lstm_model.save(model_save_path)
N = test_x.shape[0] # 测试的条数
predict = []
label = []
for start, end in zip(range(0, N, 1), range(1, N+1, 1)):
sentence = [inverse_word_dictionary[i] for i in test_x[start] if i != 0]
y_predict = lstm_model.predict(test_x[start:end])
label_predict = output_dictionary[np.argmax(y_predict[0])]
label_true = output_dictionary[np.argmax(test_y[start:end])]
predict.append(label_predict)
label.append(label_true)
acc = accuracy_score(predict, label) # 预测准确率
print('模型在测试集上的准确率为: %s.' % acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
filepath = 'D:\PyCharm\data_single.csv'
input_shape = 180
model_save_path = './corpus_model2.h5'
model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path)
# Import the necessary modules
import pickle
import numpy as np
from keras.models import load_model
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
# 导入字典
with open('word_dict.pk', 'rb') as f:
word_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
with open('label_dict.pk', 'rb') as f:
output_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
try:
# 数据预处理
input_shape = 180
sent = "商品总体来说其实并没有那么不堪入目,但是我们应当注意的是,是否应该更加提高产品的质量,而不是套牢买家"
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent]]
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0)
# 载入模型
model_save_path = 'D:\PyCharm\corpus_model2.h5'
lstm_model = load_model(model_save_path)
# 模型预测
y_predict = lstm_model.predict(x)
label_dict = {v:k for k,v in output_dictionary.items()}
print('输入语句: %s' % sent)
print('情感预测结果: %s' % label_dict[np.argmax(y_predict)])
except KeyError as err:
print("您输入的句子有汉字不在词汇表中,请重新输入!")


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号