「Solution」 BZOJ3894 文理分科
Problem
题意:有 \(n*m\) 个同学,每个同学选科目有一个满意值,若 ta 上下左右的同学与 ta 选的科目相同则有额外的满意值,求最大的满意值。
Solution
利用最小割的思路来做,问题转化为 总贡献-最小割。
考虑建模。
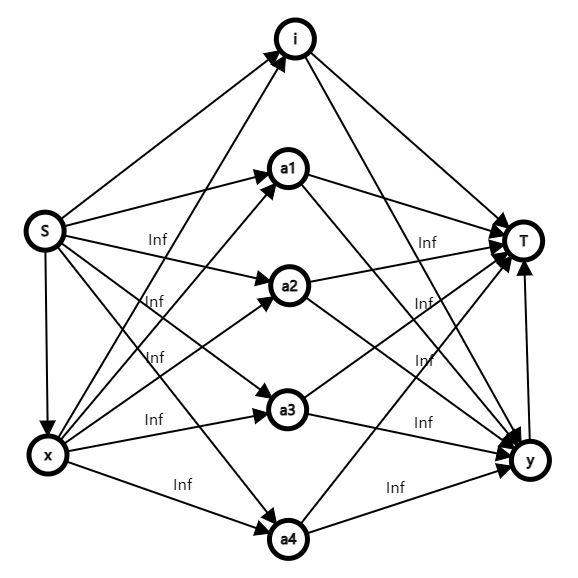
\(s \rightarrow i\) 容量为 \(i\) 选文科的贡献。
\(i \rightarrow t\) 容量为 \(i\) 选理科的贡献。
\(a1,a2,a3,a4\) 同理。
\(s \rightarrow x\) 容量为同选文科的贡献。
\(y \rightarrow t\) 容量为同选理科的贡献。
我们来证明一下,每一个割法下来都是一个合法(符合题目定义)的方案。
一条容量为正无穷的边,则意味这这条边不会被割。
- 当 \(i,a1,a2,a3,a4\) 选理。
则 \(s \rightarrow i\) 被割掉,\(a1,a2,a3,a4\) 同样被割。
最后发现还可以通过 \(s \rightarrow x\) 走向 \(T\) ,则 \(s \rightarrow x\) 也要被割掉。所以割贡献就是 \(i,a1,a2,a3,a4\) 的选文的贡献 + 同文的贡献。最终得到的就是都选理的贡献。(都选文科同理)
- 当 \(i\) 选理,\(a1\) 选文,\(a2-a4\) 随便选。即选科不相同。
这说明已经不能得到同选理科的贡献了。
割掉每个点没选的科目的边后,则直接通过 \(S \rightarrow node \rightarrow T\) 的路径已经没有了。只有通过 \(x,y\) 两点的路了。
不难发现存在 \(S \rightarrow a1 \rightarrow y \rightarrow T\) 的路径,由于 \(S \rightarrow a1\) 不能割,\(a1 \rightarrow x\) 容量为无穷也不能割,所以只能割掉 \(y \rightarrow T\)。\(S \rightarrow x \rightarrow i \rightarrow T\) 同理。
所以既不是全选文科,也不是全选理科的情况一定不会算上同选文和同选理的贡献。
Code
//by Poison
//c++11 Dinic
#include <queue>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define Maxn 500
#define LL long long
#define rep(i, j, k) for(int i = (j); i <= (k); i ++)
#define per(i, j, k) for(int i = (j); i >= (j); i --)
int dx[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
struct Score {
int art, science;
int sart, sscience;
} a[Maxn + 5][Maxn + 5];
struct Flow_Edge {
int v, u;
long long cap, flow = 0;
Flow_Edge (int v, int u, LL cap) : v (v), u (u), cap (cap) {}
} ;
struct Dinic {
const LL Maxn_Flow = 1e18;
int n, m = 0, s, t;
queue < int > q;
vector < int > ptr, level;
vector < Flow_Edge > edge;
vector < vector < int > > adj;
Dinic (int n, int s, int t) : n (n), s (s), t (t) {
adj.resize (n + 1);
ptr.resize (n + 1);
level.resize (n + 1);
}
void Add_Edge (int v, int u, LL c) {
edge.emplace_back (v, u, c);
edge.emplace_back (u, v, 0);
adj[v].push_back (m);
adj[u].push_back (m + 1);
m += 2;
}
bool Bfs () {
while (q.size ()) {
int v = q.front (); q.pop ();
for (int id : adj[v]) {
if (edge[id].cap - edge[id].flow < 1) continue;
if (level[edge[id].u] != -1) continue;
level[edge[id].u] = level[v] + 1;
q.push (edge[id].u);
}
}
return level[t] != -1;
}
LL Dfs (int v, LL pushed) {
if (!pushed) return 0;
if (v == t) return pushed;
for (int& i = ptr[v]; i < (int) adj[v].size (); i ++) {
int id = adj[v][i];
int u = edge[id].u;
if (level[v] + 1 != level[u] || edge[id].cap - edge[id].flow < 1) continue;
LL tr = Dfs (u, min (pushed, edge[id].cap - edge[id].flow));
if (!tr) continue;
edge[id].flow += tr;
edge[id ^ 1].flow -= tr;
return tr;
}
return 0;
}
LL Flow () {
LL f = 0;
while (true) {
fill (level.begin (), level.end (), -1);
level[s] = 0;
q.push (s);
if (!Bfs ()) break;
fill (ptr.begin (), ptr.end (), 0);
while (LL pushed = Dfs (s, Maxn_Flow)) f += pushed;
}
return f;
}
} ;
int main () {
int n, m;
scanf ("%d %d", &n, &m);
int tot = 0;
rep (i, 1, n)
rep (j, 1, m) {
scanf ("%d", &a[i][j].art);
tot += a[i][j].art;
}
rep (i, 1, n)
rep (j, 1, m) {
scanf ("%d", &a[i][j].science);
tot += a[i][j].science;
}
rep (i, 1, n)
rep (j, 1, m) {
scanf ("%d", &a[i][j].sart);
tot += a[i][j].sart;
}
rep (i, 1, n)
rep (j, 1, m) {
scanf ("%d", &a[i][j].sscience);
tot += a[i][j].sscience;
}
Dinic T (n * m * 3 + 1, 0, n * m * 3 + 1);
int s = 0, t = n * m * 3 + 1;
rep (i, 1, n) {
rep (j, 1, m) {
T.Add_Edge (s, (i - 1) * m + j, a[i][j].art);
T.Add_Edge ((i - 1) * m + j, t, a[i][j].science);
T.Add_Edge (s, n * m + (i - 1) * m + j, a[i][j].sart);
T.Add_Edge (n * m * 2 + (i - 1) * m + j, t, a[i][j].sscience);
T.Add_Edge (n * m + (i - 1) * m + j, (i - 1) * m + j, 1e18);
T.Add_Edge ((i - 1) * m + j, n * m * 2 + (i - 1) * m + j, 1e18);
rep (k, 0, 3) {
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
if (x < 1 || y < 1 || x > n || y > m) continue;
T.Add_Edge (n * m + (i - 1) * m + j, (x - 1) * m + y, 1e18);
T.Add_Edge ((x - 1) * m + y, n * m * 2 + (i - 1) * m + j, 1e18);
}
}
}
printf ("%lld", tot - T.Flow ());
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号