matplotlib画图总结--常用功能
0、内容范围
多曲线图、图例、坐标轴、注释文字等。
1、曲线图
多曲线图、图例、网格、坐标轴名称、图标名、坐标轴范围等。
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import numpy as np x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 200, endpoint=True) c, s = np.cos(x), np.sin(x) plt.xlim(-np.pi, np.pi) # p1 = plt.plot(x,c,'r', label = 'cos') # p2 = plt.plot(x,s,'b', label = 'sin') p1 = plt.plot(x,c,'r') p2 = plt.plot(x,s,'b') plt.xlabel('x') plt.ylabel('y') plt.title('cos and sin') plt.legend( ['cos', 'sin']) plt.grid(True) plt.show()
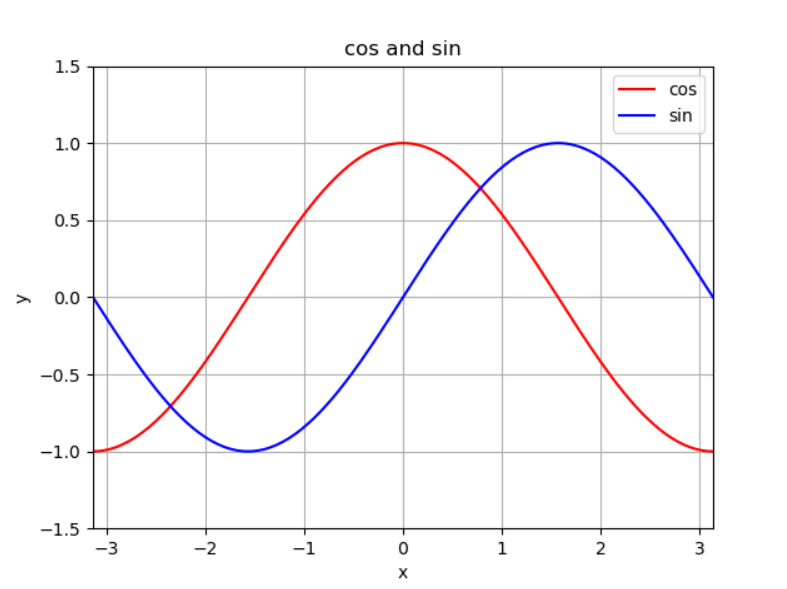
知识点:
1)一个图里绘制条曲线
方法1:
plt.plot(x,c,'r', x,s,'b')
方法2:
p1 = plt.plot(x,c,'r')
p2 = plt.plot(x,s,'b')
2)给图添加图例
方法1:
p1 = plt.plot(x,c,'r', label = 'cos')
p2 = plt.plot(x,s,'b', label = 'sin')
plt.legend()
方法2:
p1 = plt.plot(x,c,'r')
p2 = plt.plot(x,s,'b')
plt.legend( ['cos', 'sin'])
推荐使用方法1,因为方法2必须注意添加曲线的顺序。
2、柱状图
学习柱状图、为图形添加字符坐标轴.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt N = 5 menMeans = (20, 35, 30, 35, 27) womenMeans = (25, 32, 34, 20, 25) menStd = (2, 3, 4, 1, 2) womenStd = (3, 5, 2, 3, 3) ind = np.arange(N) # the x locations for the groups width = 0.35 # the width of the bars: can also be len(x) sequence p1 = plt.bar(ind, menMeans, width, yerr=menStd, label='men') p2 = plt.bar(ind, womenMeans, width, bottom=menMeans, yerr=womenStd, label='women') plt.ylabel('Scores') plt.title('Scores by group and gender') plt.xticks(ind, ('G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5')) plt.yticks(np.arange(0, 81, 10)) plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.show()

为什么会两个图层叠?
p1 = plt.bar(ind, menMeans, width, yerr=menStd, label='men') p2 = plt.bar(ind, womenMeans, width, bottom=menMeans, yerr=womenStd, label='women')
bar函数的x坐标一样,并且y坐标值是bottom=menMeans,所以第二个图会堆叠在第一个图上面。
下面实现2条柱状图。
import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5'] men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27] women_means = [25, 32, 34, 20, 25] x = np.arange(len(labels)) # the label locations width = 0.35 # the width of the bars fig, ax = plt.subplots() rects1 = ax.bar(x - width/2, men_means, width, label='Men') rects2 = ax.bar(x + width/2, women_means, width, label='Women') # Add some text for labels, title and custom x-axis tick labels, etc. ax.set_ylabel('Scores') ax.set_title('Scores by group and gender') ax.set_xticks(x) ax.set_xticklabels(labels) ax.legend() plt.show()
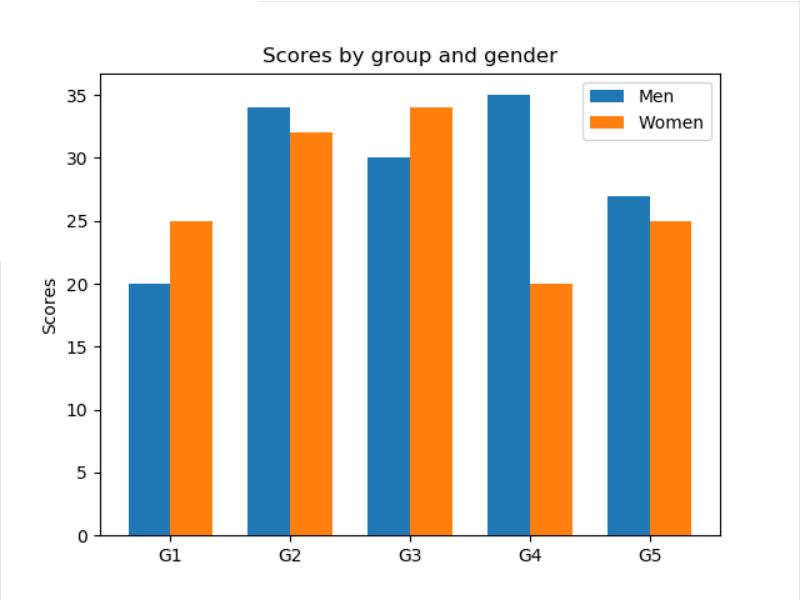
x轴的坐标不是数子,实现方法如下,先设定坐标轴的tick,然后把ticklabel改为字符值。
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
如果需要实现水平柱状图,则使用ax.barh(y_pos, performance, xerr=error, align='center')函数。
3、添加文字、注释、箭头指示、花式文字
其中,text 函数可以做文本注释,且支持 LaTeX 格式,可以在图例中写公式。
text(x,y,string,fontsize=15,verticalalignment="top",horizontalalignment="right")
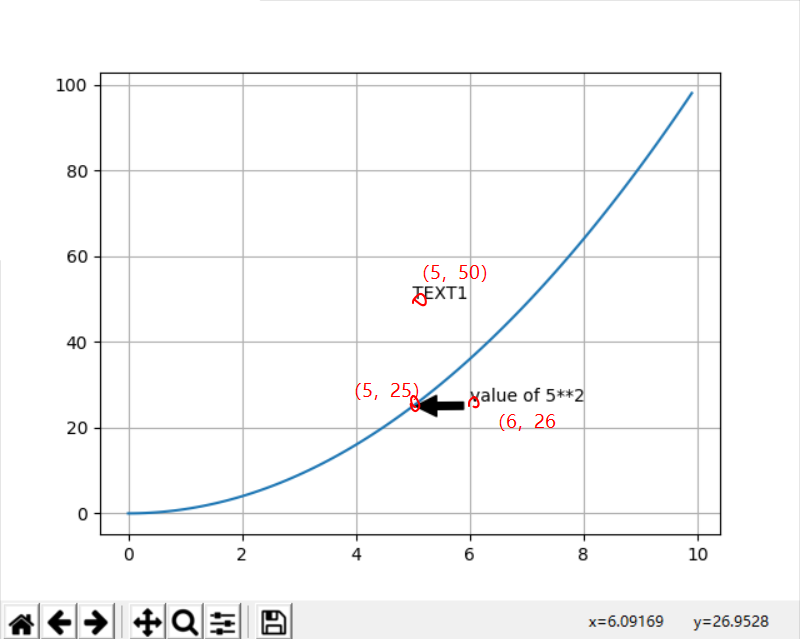
x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1) plt.plot(x, x**2) plt.grid(True) # 设置网格线 plt.text(5,50, "TEXT1") plt.show()
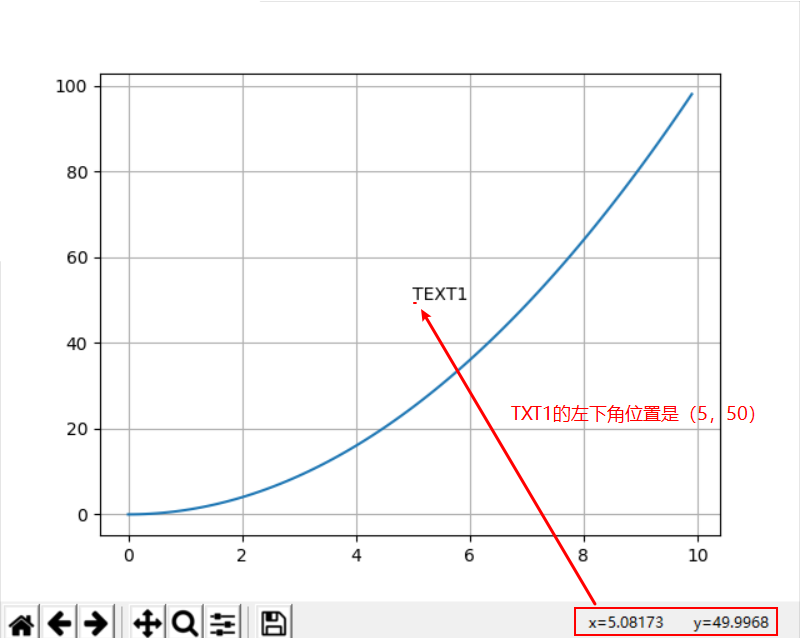
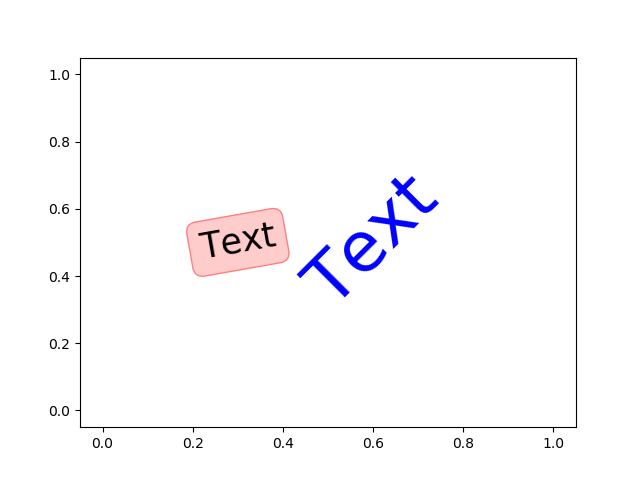
花式文本:
You can put a rectangular box around the text instance (e.g., to set a background color) by using the keyword bbox. bbox is a dictionary of Rectangle properties. For example:
>>> text(x, y, s, bbox=dict(facecolor='red', alpha=0.5))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np plt.text(0.6, 0.5, "Text", size=50, rotation=45, ha="center", va="center", color='b') plt.text(0.3, 0.5, "Text", size=25, rotation=10, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round",ec=(1, 0.5, 0.5),fc=(1., 0.8, 0.8),)) #颜色ec、fc plt.plot() plt.show()
添加箭头和说明信息
plt.annotate('value of 5**2', xy=(5, 25), xytext=(6, 26), arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号