强化学习理论-第8课-值函数近似
当state space太大的时候,需要用一个函数来对state value 或action value进行近似,方便处理
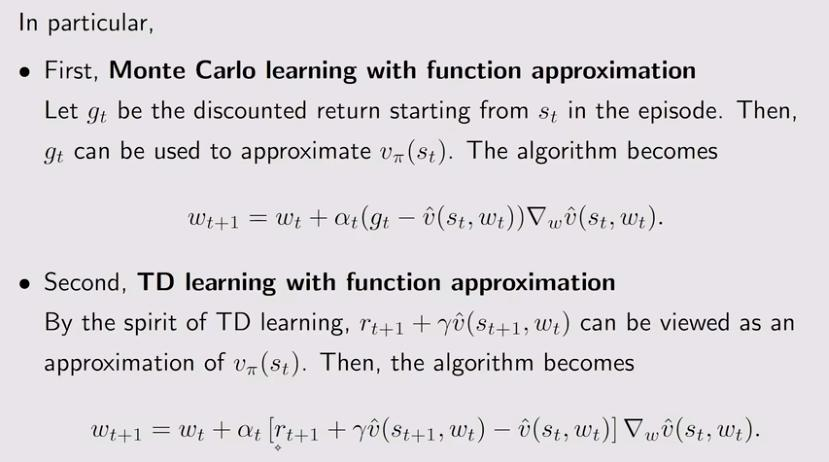
1. Algorithm for state value estimation
1.1 Objective function
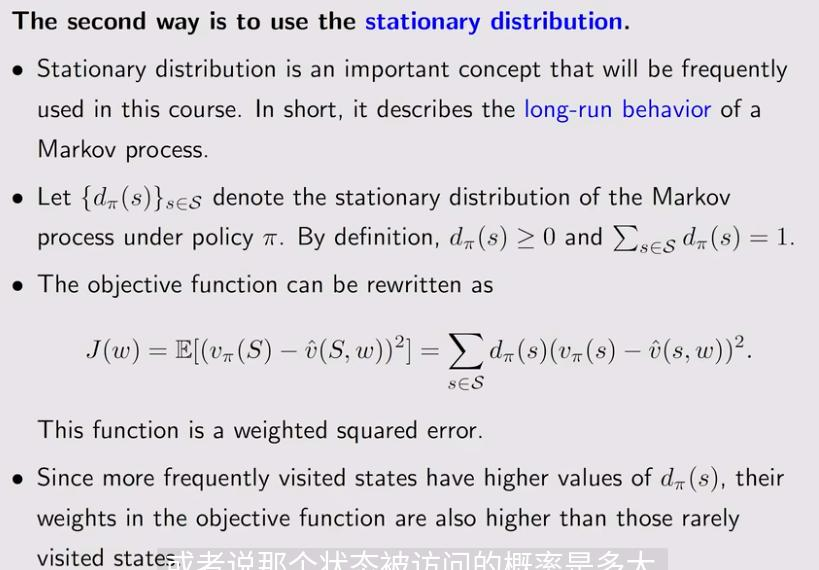
这里\(d_{\pi}\)是权重,可以决定哪个state权重比较大,就让它的误差变得更小
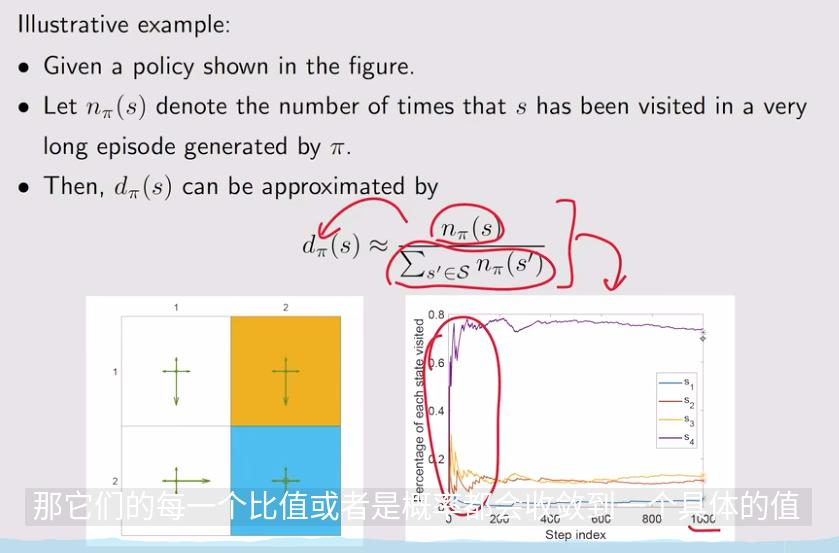
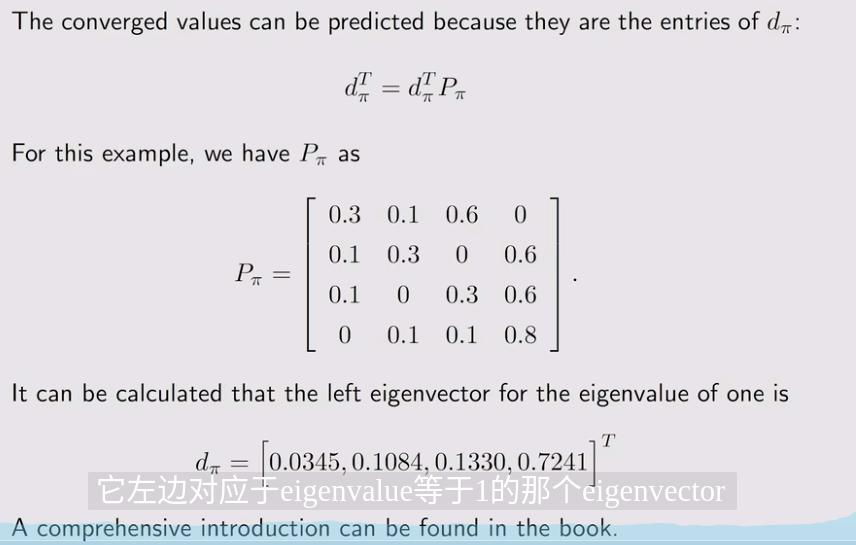
这里的\(P_{\pi}\)和贝尔曼公式里的是一个,里面每个元素代表当前状态到下一个状态的转移的概率
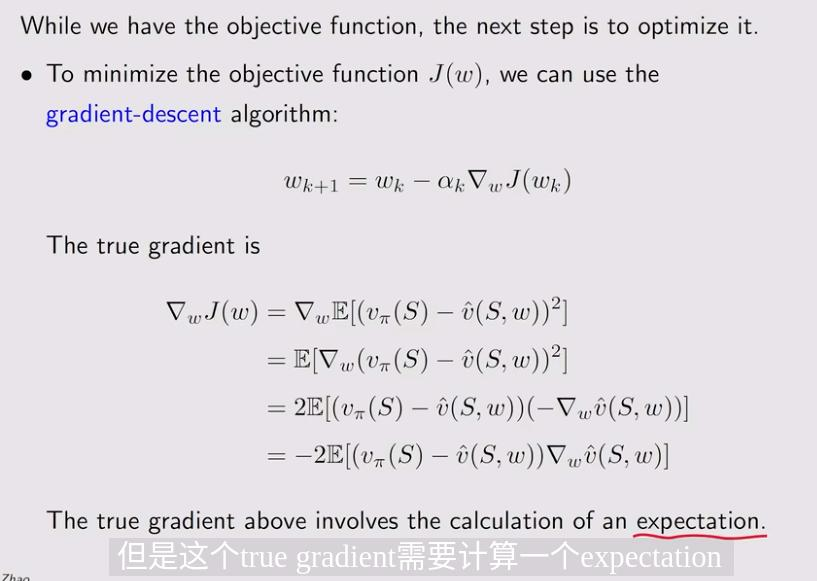
1.2 Optimization algorithms

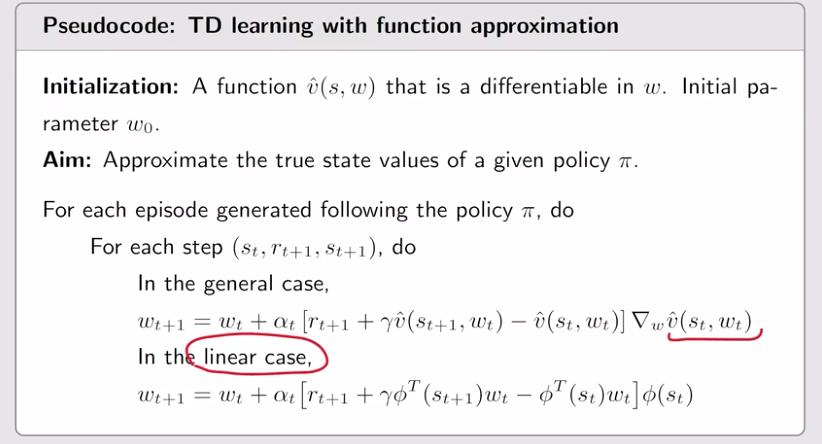
1.3 Selection of function approximators

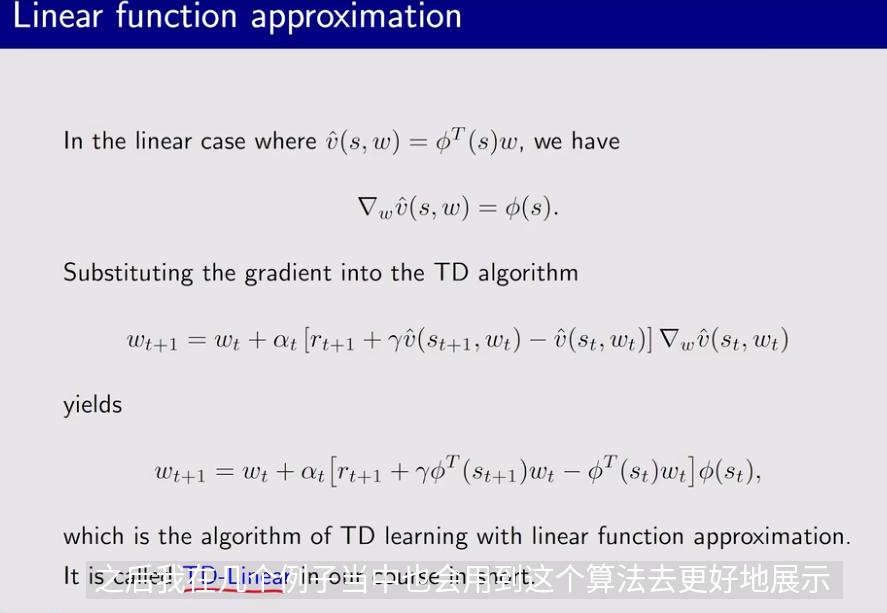
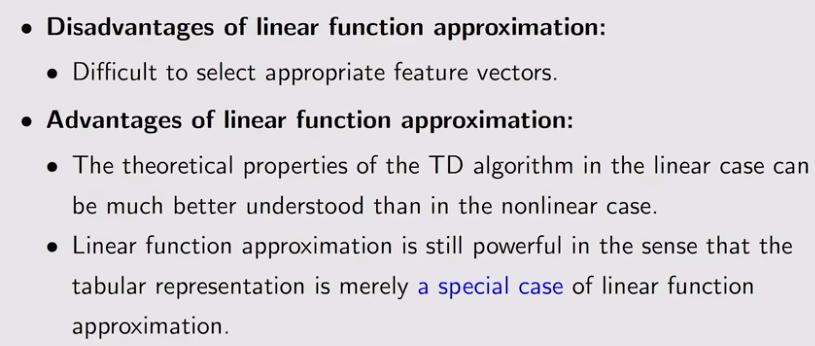
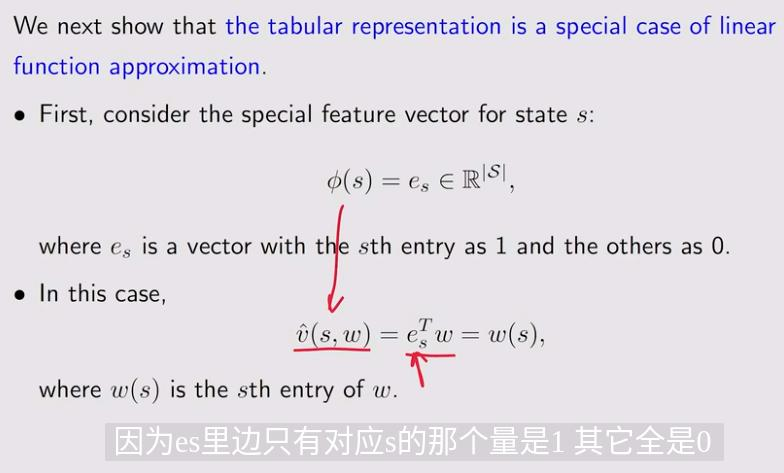

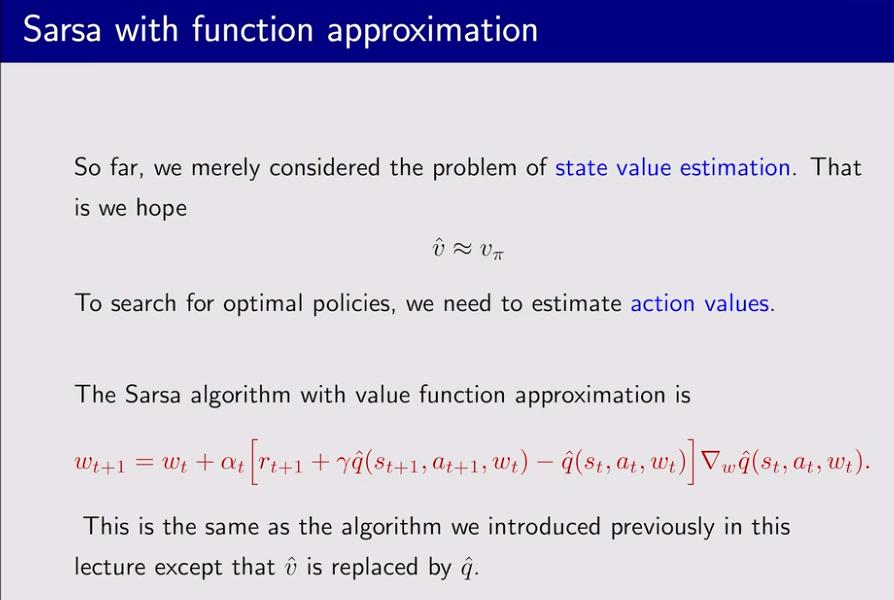
2. Sarsa with function approximation(action value)

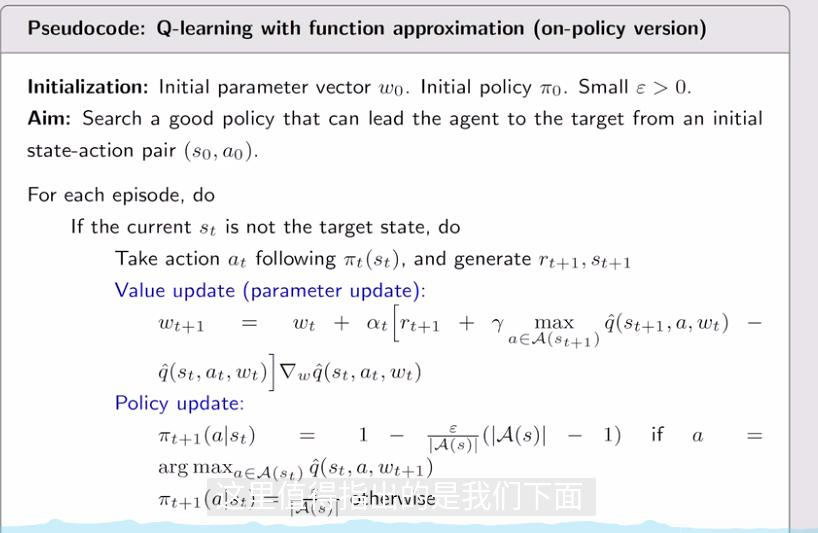
3. Q-learning with function approximation

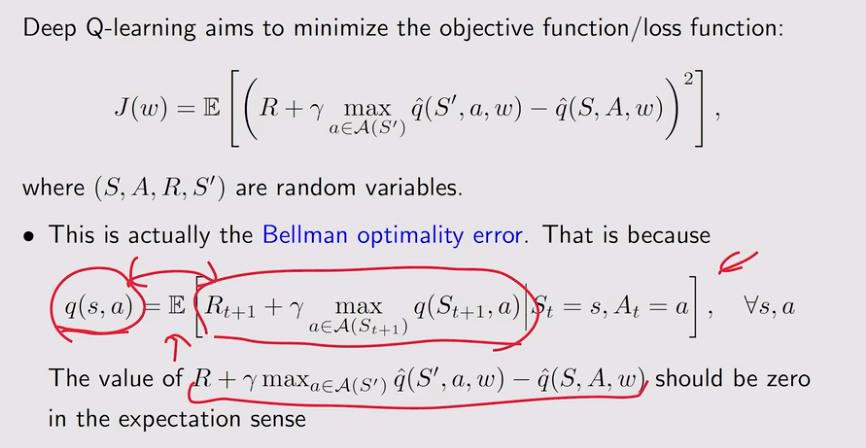
4. Deep Q-learning

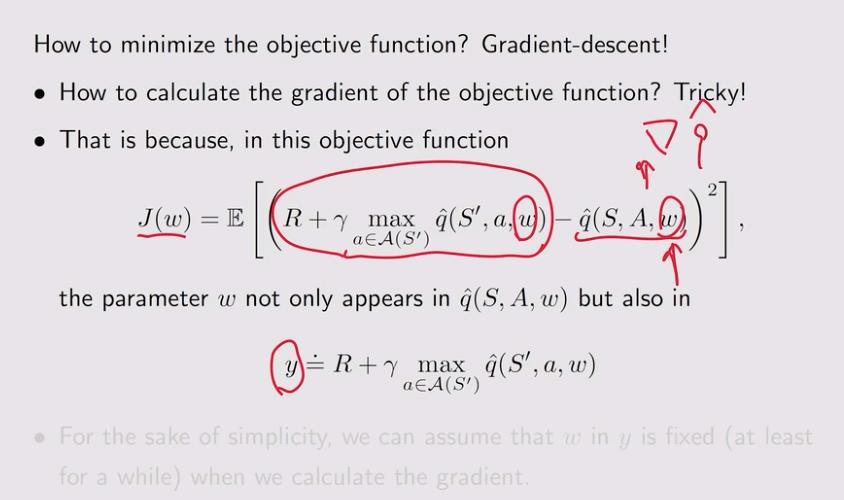
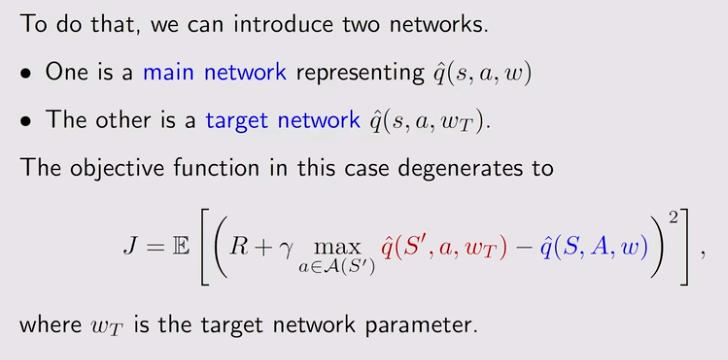
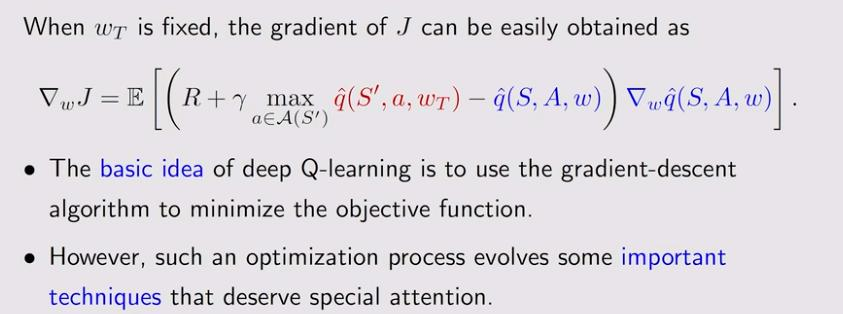

5. Deep Q-learning-Experience replay



6. Deep Q-learning-implementation and example


def gfv(self, fourier: bool, state: int, ord: int) -> np.ndarray:
"""
get_feature_vector
:param fourier: 是否使用傅里叶特征函数
:param state: 状态
:param ord: 特征函数最高阶次数/傅里叶q(对应书)
:return: 代入state后的计算结果
"""
if state < 0 or state >= self.state_space_size:
raise ValueError("Invalid state value")
y, x = self.env.state2pos(state) + (1, 1)
feature_vector = []
if fourier:
# 归一化到 -1 到 1
x_normalized = x / self.env.size
y_normalized = y / self.env.size
for i in range(ord + 1):
for j in range(ord + 1):
feature_vector.append(np.cos(np.pi * (i * x_normalized + j * y_normalized)))
else:
# 归一化到 0 到 1
x_normalized = (x - (self.env.size - 1) * 0.5) / (self.env.size - 1)
y_normalized = (y - (self.env.size - 1) * 0.5) / (self.env.size - 1)
for i in range(ord + 1):
for j in range(i + 1):
feature_vector.append(y_normalized ** (ord - i) * x_normalized ** j)
return np.array(feature_vector)
def gfv_a(self, fourier: bool, state: int, action: int, ord: int) -> np.ndarray:
"""
get_feature_vector_with_action
:param fourier: 是否使用傅里叶特征函数
:param state: 状态
:param ord: 特征函数最高阶次数/傅里叶q(对应书)
:return: 代入state后的计算结果
"""
if state < 0 or state >= self.state_space_size or action < 0 or action >= self.action_space_size:
raise ValueError("Invalid state/action value")
feature_vector = []
y, x = self.env.state2pos(state) + (1, 1)
if fourier:
# 归一化到 -1 到 1
x_normalized = x / self.env.size
y_normalized = y / self.env.size
action_normalized = action / self.action_space_size
for i in range(ord + 1):
for j in range(ord + 1):
for k in range(ord + 1):
feature_vector.append(
np.cos(np.pi * (i * x_normalized + j * action_normalized + k * y_normalized)))
else:
# 归一化到 0 到 1
state_normalized = (state - (self.state_space_size - 1) * 0.5) / (self.state_space_size - 1)
action_normalized = (action - (self.action_space_size - 1) * 0.5) / (self.action_space_size - 1)
for i in range(ord + 1):
for j in range(i + 1):
feature_vector.append(state_normalized ** (ord - i) * action_normalized ** j)
return np.array(feature_vector)
def td_value_approximation(self, learning_rate=0.0005, epochs=100000, fourier=True, ord=5):
self.state_value=self.policy_evaluation(self.policy)
if not isinstance(learning_rate, float) or not isinstance(epochs, int) or not isinstance(
fourier, bool) or not isinstance(ord, int):
raise TypeError("Invalid input type")
if learning_rate <= 0 or epochs <= 0 or ord <= 0:
raise ValueError("Invalid input value")
episode_length = epochs
start_state = np.random.randint(self.state_space_size)
start_action = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.action_space_size),
p=self.mean_policy[start_state])
episode = self.obtain_episode(self.mean_policy, start_state, start_action, length=episode_length)
dim = (ord + 1) ** 2 if fourier else np.arange(ord + 2).sum()
w = np.random.default_rng().normal(size=dim)
rmse = []
value_approximation = np.zeros(self.state_space_size)
for epoch in range(epochs):
reward = episode[epoch]['reward']
state = episode[epoch]['state']
next_state = episode[epoch]['next_state']
target = reward + self.gama * np.dot(self.gfv(fourier, next_state, ord), w)
error = target - np.dot(self.gfv(fourier, state, ord), w)
gradient = self.gfv(fourier, state, ord)
w = w + learning_rate * error * gradient
for state in range(self.state_space_size):
value_approximation[state] = np.dot(self.gfv(fourier, state, ord), w)
rmse.append(np.sqrt(np.mean((value_approximation - self.state_value) ** 2)))
print(epoch)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(1, 6), np.arange(1, 6))
Z = self.state_value.reshape(5, 5)
Z1 = value_approximation.reshape(5, 5)
# 绘制 3D 曲面图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
ax = fig.add_subplot(121, projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('State Value')
z_min = -5
z_max = -2
ax.set_zlim(z_min, z_max)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection='3d')
ax1.plot_surface(X, Y, Z1)
ax1.set_xlabel('X')
ax1.set_ylabel('Y')
ax1.set_zlabel('Value Approximation')
ax1.set_zlim(z_min, z_max)
fig_rmse = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
ax_rmse = fig_rmse.add_subplot(111)
# 绘制 rmse 图像
ax_rmse.plot(rmse)
ax_rmse.set_title('RMSE')
ax_rmse.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax_rmse.set_ylabel('RMSE')
plt.show()
return value_approximation
def sarsa_function_approximation(self, learning_rate=0.0005, epsilon=0.1, num_episodes=100000, fourier=True, ord=5):
#BUG
dim = (ord + 1) ** 2 if fourier else np.arange(ord + 2).sum()
w = np.random.default_rng().normal(size=dim)
qvalue_approximation = np.zeros((self.state_space_size, self.action_space_size))
reward_list = []
length_list = []
rmse = []
policy_rmse = []
policy = self.mean_policy.copy()
next_state = 0
episode = self.obtain_episode(self.mean_policy, 0, 0, length=num_episodes)
for episode in range(num_episodes):
# epsilon = (epsilon - 1 / num_episodes) if epsilon > 0 else 0
done = False
self.env.reset()
total_rewards = 0
episode_length = 0
while not done:
state = next_state
action = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.action_space_size),
p=policy[state])
_, reward, done, _, _ = self.env.step(action)
episode_length += 1
total_rewards += reward
next_state = self.env.pos2state(self.env.agent_location)
next_action = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.action_space_size),
p=policy[next_state])
target = reward + self.gama * np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, next_state, next_action, ord), w)
error = target - np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, state, action, ord), w)
gradient = self.gfv_a(fourier, state, action, ord)
w = w + learning_rate * error * gradient
# for state in range(self.state_space_size):
# for action in range(self.action_space_size):
qvalue_approximation[state, action] = np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, state, action, ord), w)
qvalue_star = qvalue_approximation[state].max()
action_star = qvalue_approximation[state].tolist().index(qvalue_star)
for a in range(self.action_space_size):
if a == action_star:
policy[state, a] = 1 - (
self.action_space_size - 1) / self.action_space_size * epsilon
else:
policy[state, a] = 1 / self.action_space_size * epsilon
rmse.append(np.sqrt(np.mean((qvalue_approximation - self.qvalue) ** 2)))
# policy_rmse.append(np.sqrt(np.mean((policy - self.policy) ** 2)))
reward_list.append(total_rewards)
length_list.append(episode_length)
print("episode={},length={},reward={}".format(episode, episode_length, total_rewards))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(211)
ax.plot(reward_list)
ax.set_ylabel('total_reward')
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(212)
ax1.plot(length_list)
ax1.set_xlabel('episode index')
ax1.set_ylabel('episode length')
fig_rmse = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
ax_rmse = fig_rmse.add_subplot(111)
ax_rmse.plot(rmse, label='qvalue')
# ax_rmse.plot(policy_rmse,label='policy')
ax_rmse.set_title('RMSE')
ax_rmse.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax_rmse.set_ylabel('RMSE')
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, self.action_space_size), np.arange(0, self.state_space_size))
Z = self.qvalue
Z1 = qvalue_approximation
print(Z.shape, Z1.shape, X.shape)
# 绘制 3D 曲面图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
ax = fig.add_subplot(121, projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('q Value')
# z_min = -5
# z_max = -2
# ax.set_zlim(z_min, z_max)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection='3d')
ax1.plot_surface(X, Y, Z1)
ax1.set_xlabel('X')
ax1.set_ylabel('Y')
ax1.set_zlabel('qValue Approximation')
fig_rmse = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
ax_rmse = fig_rmse.add_subplot(111)
plt.show()
return qvalue_approximation
def qlearning_function_approximation(self, learning_rate=0.0005, epsilon=0.1, num_episodes=100000, fourier=True,
ord=15):
#BUG
dim = (ord + 1) ** 2 if fourier else np.arange(ord + 2).sum()
w = np.random.default_rng().normal(size=dim)
qvalue_approximation = np.zeros((self.state_space_size, self.action_space_size))
reward_list = []
length_list = []
rmse = []
policy = self.mean_policy.copy()
next_state = 0
episode = self.obtain_episode(self.mean_policy, 0, 0, length=num_episodes)
for episode in range(num_episodes):
# epsilon = (epsilon - 1 / num_episodes) if epsilon > 0 else 0
done = False
self.env.reset()
total_rewards = 0
episode_length = 0
while not done:
state = next_state
action = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.action_space_size),
p=policy[state])
_, reward, done, _, _ = self.env.step(action)
episode_length += 1
total_rewards += reward
next_state = self.env.pos2state(self.env.agent_location)
q_list = []
for a in range(self.action_space_size):
q_list.append(np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, next_state, a, ord), w))
target = reward + self.gama * np.array(q_list).max()
error = target - np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, state, action, ord), w)
gradient = self.gfv_a(fourier, state, action, ord)
w = w + learning_rate * error * gradient
for s in range(self.state_space_size):
for a in range(self.action_space_size):
qvalue_approximation[s, a] = np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, s, a, ord), w)
qvalue_star = qvalue_approximation[state].max()
action_star = qvalue_approximation[state].tolist().index(qvalue_star)
for a in range(self.action_space_size):
if a == action_star:
policy[state, a] = 1 - (
self.action_space_size - 1) / self.action_space_size * epsilon
else:
policy[state, a] = 1 / self.action_space_size * epsilon
self.writer.add_scalar('rmse', np.sqrt(np.mean((qvalue_approximation - self.qvalue) ** 2)), episode)
self.writer.add_scalar('episode_length', episode_length, episode)
self.writer.add_scalar('total_reward', total_rewards, episode)
# policy_rmse.append(np.sqrt(np.mean((policy - self.policy) ** 2)))
# reward_list.append(total_rewards)
# length_list.append(episode_length)
print("episode={},length={},reward={}".format(episode, episode_length, total_rewards))
# fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
# ax = fig.add_subplot(211)
# ax.plot(reward_list)
# ax.set_ylabel('total_reward')
# ax1 = fig.add_subplot(212)
# ax1.plot(length_list)
# ax1.set_xlabel('episode index')
# ax1.set_ylabel('episode length')
# fig_rmse = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
# ax_rmse = fig_rmse.add_subplot(111)
# ax_rmse.plot(rmse, label='qvalue')
# # ax_rmse.plot(policy_rmse,label='policy')
#
# ax_rmse.set_title('RMSE')
# ax_rmse.set_xlabel('Epoch')
# ax_rmse.set_ylabel('RMSE')
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, self.action_space_size), np.arange(0, self.state_space_size))
Z = self.qvalue
Z1 = qvalue_approximation
print(Z.shape, Z1.shape, X.shape)
# 绘制 3D 曲面图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
ax = fig.add_subplot(121, projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('q Value')
z_min = -6
z_max = 0
ax.set_zlim(z_min, z_max)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection='3d')
ax1.plot_surface(X, Y, Z1)
ax1.set_xlabel('X')
ax1.set_ylabel('Y')
ax1.set_zlabel('qValue Approximation')
ax1.set_zlim(z_min, z_max)
# fig_rmse = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
# ax_rmse = fig_rmse.add_subplot(111)
self.writer.close()
plt.show()
return qvalue_approximation
def qvalue_function_approximation(self, learning_rate=0.00008, epsilon=0.1, num_episodes=1000000,
fourier=True,
ord=5):
#BUG
dim = (ord + 1) ** 3 if fourier else np.arange(ord + 2).sum()
w = np.random.default_rng().normal(size=dim)
qvalue_approximation = np.zeros(shape=(self.state_space_size, self.action_space_size))
episode = self.obtain_episode(self.mean_policy, 0, 0, length=100000)
for epoch in range(num_episodes):
# epsilon = (epsilon - 1 / num_episodes) if epsilon > 0 else 0
step = int(np.random.randint(low=0, high=99999, size=1))
reward = episode[step]['reward']
state = episode[step]['state']
action = episode[step]['action']
next_action = episode[step]['next_action']
next_state = episode[step]['next_state']
target = reward + self.gama * np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, next_state, next_action, ord), w)
error = target - np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, state, action, ord), w)
gradient = self.gfv_a(fourier, state, action, ord)
w = w + learning_rate * error * gradient
for a in range(self.action_space_size):
qvalue_approximation[state, a] = np.dot(self.gfv_a(fourier, state, a, ord), w)
self.writer.add_scalar('rmse', np.sqrt(np.mean((qvalue_approximation - self.qvalue) ** 2)), epoch)
if epoch % 1000 == 0:
print(epoch, np.sqrt(np.mean((qvalue_approximation - self.qvalue) ** 2)))
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, self.action_space_size), np.arange(0, self.state_space_size))
Z = self.qvalue
Z1 = qvalue_approximation
print(Z.shape, Z1.shape, X.shape)
# 绘制 3D 曲面图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
ax = fig.add_subplot(121, projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('q Value')
z_min = -6
z_max = 0
ax.set_zlim(z_min, z_max)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection='3d')
ax1.plot_surface(X, Y, Z1)
ax1.set_xlabel('X')
ax1.set_ylabel('Y')
ax1.set_zlabel('qValue Approximation')
ax1.set_zlim(z_min, z_max)
for i in range(self.state_space_size):
for j in range(self.action_space_size):
print("qvalue:{},approximation:{}".format(self.qvalue[i, j], qvalue_approximation[i, j]))
self.writer.close()
plt.show()
return qvalue_approximation
def get_data_iter(self, episode, batch_size=64, is_train=True):
"""构造一个PyTorch数据迭代器"""
reward = []
state_action = []
next_state = []
for i in range(len(episode)):
reward.append(episode[i]['reward'])
action = episode[i]['action']
y, x = self.env.state2pos(episode[i]['state'])
state_action.append((y, x, action))
y, x = self.env.state2pos(episode[i]['next_state'])
next_state.append((y, x))
reward = torch.tensor(reward).reshape(-1, 1)
state_action = torch.tensor(state_action)
next_state = torch.tensor(next_state)
data_arrays = (state_action, reward, next_state)
dataset = data.TensorDataset(*data_arrays)
return data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=is_train, drop_last=False)
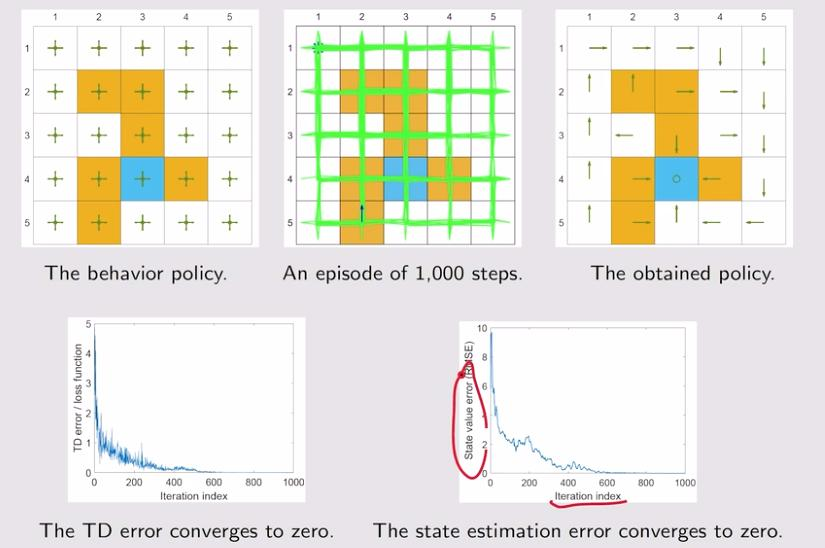
def dqn(self, learning_rate=0.0015, episode_length=5000, epochs=600, batch_size=100, update_step=10):
q_net = QNET()
policy = self.policy.copy()
state_value = self.state_value.copy()
q_target_net = QNET()
q_target_net.load_state_dict(q_net.state_dict())
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(q_net.parameters(),
lr=learning_rate)
episode = self.obtain_episode(self.mean_policy, 0, 0, length=episode_length)
date_iter = self.get_data_iter(episode, batch_size)
loss = torch.nn.MSELoss()
approximation_q_value = np.zeros(shape=(self.state_space_size, self.action_space_size))
i = 0
rmse_list=[]
loss_list=[]
for epoch in range(epochs):
for state_action, reward, next_state in date_iter:
i += 1
q_value = q_net(state_action)
q_value_target = torch.empty((batch_size, 0)) # 定义空的张量
for action in range(self.action_space_size):
s_a = torch.cat((next_state, torch.full((batch_size, 1), action)), dim=1)
q_value_target = torch.cat((q_value_target, q_target_net(s_a)), dim=1)
q_star = torch.max(q_value_target, dim=1, keepdim=True)[0]
y_target_value = reward + self.gama * q_star
l = loss(q_value, y_target_value)
optimizer.zero_grad() # PyTorch中默认梯度会累积,这里需要显式将梯度置为0S
l.backward() # 反向传播更新参数
optimizer.step()
if i % update_step == 0 and i != 0:
q_target_net.load_state_dict(
q_net.state_dict()) # 更新目标网络
# policy = np.zeros(shape=(self.state_space_size, self.action_space_size))
loss_list.append(float(l))
print("loss:{},epoch:{}".format(l, epoch))
self.policy = np.zeros(shape=(self.state_space_size, self.action_space_size))
self.state_value = np.zeros(shape=self.state_space_size)
for s in range(self.state_space_size):
y, x = self.env.state2pos(s)
for a in range(self.action_space_size):
approximation_q_value[s, a] = float(q_net(torch.tensor((y, x, a)).reshape(-1, 3)))
q_star_index = approximation_q_value[s].argmax()
self.policy[s, q_star_index] = 1
self.state_value[s] = approximation_q_value[s, q_star_index]
rmse_list.append(np.sqrt(np.mean((state_value - self.state_value) ** 2)))
# policy_rmse = np.sqrt(np.mean((policy - self.policy) ** 2))
fig_rmse = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 12)) # 设置图形的尺寸,宽度为8,高度为6
ax_rmse = fig_rmse.add_subplot(211)
# 绘制 rmse 图像
ax_rmse.plot(rmse_list)
ax_rmse.set_title('RMSE')
ax_rmse.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax_rmse.set_ylabel('RMSE')
self.writer.close()
ax_loss = fig_rmse.add_subplot(212)
ax_loss.plot(loss_list)
ax_loss.set_title('loss')
ax_loss.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax_loss.set_ylabel('Loss')
plt.show()
def obtain_episode_p(self, policy_net, start_state, start_action):
f"""
:param policy_net: 由指定策略产生episode
:param start_state: 起始state
:param start_action: 起始action
:return: 一个 state,action,reward,next_state,next_action 序列
"""
self.env.agent_location = self.env.state2pos(start_state)
episode = []
next_action = start_action
next_state = start_state
done = False
while not done:
state = next_state
action = next_action
_, reward, done, _, _ = self.env.step(action)
next_state = self.env.pos2state(self.env.agent_location)
y, x = self.env.state2pos(next_state) / self.env.size
prb = policy_net(torch.tensor((y, x)).reshape(-1, 2))[0]
next_action = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.action_space_size),
p=prb.detach().numpy())
episode.append({"state": state, "action": action, "reward": reward, "next_state": next_state,
"next_action": next_action})
return episode



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号