数据结构 - 数组
数据结构 - 数组
1 数组
1.1 自定义动态数组
public class Array<E> {
//内部维护一个泛型数组,该数组的长度代表容量,少维护一个变量
private E[] data;
//size用来表示数组中元素的实际数量
private int size;
//无参构造自动创建一个长度为10的数组,构造函数之间的相互调用通过this
public Array() {
this(10);
}
//初始化size和data
public Array(int size) {
this.size = 0;
this.data = (E[]) new Object[size];
}
// 添加数据到指定索引的位置
public void add(int index, E element) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index out of bounds");
for (int i = size; i > index; i--) {
data[i] = data[i-1];
}
data[index] = element;
size++;
//数组元素实际数里达到容量的0.85时扩容两倍
if (size >= data.length * 0.85)
resize(data.length << 1);
}
//尾插
public void addLast(E element){
add(size,element);
}
//头插
public void addFirst(E element){
add(0,element);
}
//删除指定索引的数据
public E remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index out of bounds");
E e = data[index];
for (int i = index; i < size-1; i++) {
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
size--;
data[size] = null;
// 当数组参数实际数量达到容量的1/4时,缩容为原来的1/2,采用lazy的策略防止复杂度震荡
// 复杂度震荡即如果size<容量的1/2缩容,而size>容量又扩容,则重复以上操作时间复杂度会很高
if (size <= data.length>>2 && data.length>>2 != 0)
resize(data.length>>1);
return e;
}
//删除第一个
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
//删除最后一个
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size-1);
}
//获取指定下标的元素
public E get(int index){
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index out of bounds");
return data[index];
}
//修改指定下标位置的元素
public void set(int index, E element){
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index out of bounds");
data[index] = element;
}
//判断是否为数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
//判断数组是否包含元素
public boolean contains(E element){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i].equals(element))
return true;
}
return false;
}
//根据元素查找下标
public int find(E element) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i].equals(element))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
//动态数组,这里为了复用同时实现扩容和缩容
public void resize(int capacity) {
E[] arr = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = data[i];
}
data = arr;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Capacity = "+data.length+", Size = "+size+ "\n"+ "[");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
builder.append(data[i]);
if (i != size-1)
builder.append(", ");
}
builder.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
// 均摊时间复杂度
// - 假设capacity=n,执行n+1次addLast操作,触发resize,n+1次add进行n+1次操作,resize进行n次操作,总共2n+1次操作,平均每次add进行2次操作
1.2 二维数组
- 数组一般采用顺序存储结构,当需要存储多维数组时,Java是按行存储,先存第一行,再存第二行 ...
// 二维数组下标从0 开始
// 按行存储,找aij的存储位置,假设每行n个元素,前面一共存储了i*n+j 个元素
// 每个元素占L个字节,基地址LOC(a00),也就是元素中第一个元素的地址
LOC(aij) = LOC(a00) + (i*n+j)*L
// 按列存储,找aij的存储位置,假设每列m个元素,前面一共存储了j*m+i 个元素
// 每个元素栈L个字节,基地址LOC(a00)
LOC(aij) = LOC(a00) + (j*m+i)*L
// 二维数组下标从1 开始
// 按行存储,找aij的存储位置,假设每行n个元素,前面一共存储了(i-1)*n+j-1 个元素
// 每个元素占L个字节,基地址LOC(a11),也就是元素中第一个元素的地址
LOC(aij) = LOC(a11) + ((i-1)*n+j-1)*L
// 按列存储,找aij的存储位置,假设每列m个元素,前面一共存储了(j-1)*m+i-1 个元素
// 每个元素栈L个字节,基地址LOC(a11)
LOC(aij) = LOC(a11) + ((j-1)*m+i-1)*L
1.3 特殊矩阵压缩
- 什么是压缩矩阵?
把多个相同的元素分配一个存储空间,元素为0的不分配空间
- 什么样的矩阵能够压缩?
特殊矩阵,如对称矩阵,对角矩阵,三角矩阵,稀疏矩阵等
- 什么是稀疏矩阵?
矩阵中非零元素的个数少(一般认为非零元素个数少于5%的矩阵)
三元组 i j k 以及矩阵行列m*n 存储
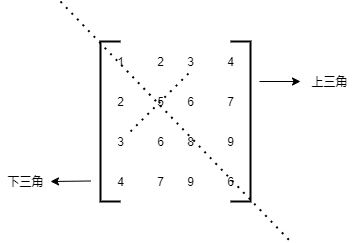
1.3.1 对称矩阵
/*
基本概念
- 数据沿着对角线对称
- 根据其对称性,只存储上三角或下三角即可
*/
// 按行序存储下三角,确定aij的位置
// 前面i-1 行一共 (i-1)*i / 2 个元素,第一行1个元素,第二行2个元素 ... 第i-1 行 i-1个元素,等差数列求和
// 第i行有 j-1 个元素
LOC(aij) = LOC(a11) + ((i-1)*i / 2 + j-1)*L
// 上三角 i<j
// 下三角 i>=j
// 当要在下三角中寻找存储在上三角中的元素时,可以根据对称性 aij = aji
// n*n 对称矩阵A,下三角按行存放在一维数组B中,A[0][0]存放在B[0]中,求A[i][i]在B数组中的下标
(i * i+1) / 2 + i
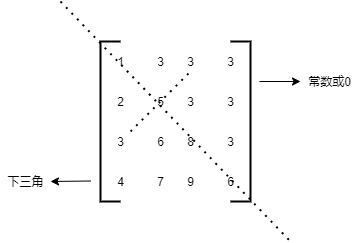
1.3.2 三角矩阵
/*
基本概念
- 分为下三角矩阵和上三角矩阵
- 下三角矩阵指矩阵的下三角有数据,其余部分都是常数C或0(常数c在数组中只占一个位置,0不存储)
*/
// 按行存储下三角,从a11开始存入数组中,其中aij的下表为
(i - 1)*i / 2 + j - 1 (i >= j)
n * (n+1) / 2 (i < j)
// 等差数列求和公式:a1 .... 1n
(a1 + an)*n / 2
// 上三角矩阵按行存储,每行最多n个元素 从a11开始,求aij 的下标位置,第一行n个元素,第二行n-1个 ... 第i-1 行 n-i+2 个
(n + n-i+2)(i-1) / 2 + j-i (i <= j)
n*(n+1) / 2 (i > j)
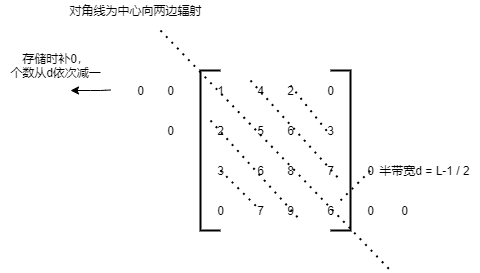
1.3.3 对角矩阵
// 概念
// 又称带状矩阵,在n*n的矩阵中,非零元素集中在主对角线及其两侧,共L(奇数)条对角线的带状区域内,成为L对角矩阵
//存储时节省空间,第一行前面和最后一行后面的d个0可不存储,掐头去尾,需要L*n - 2d
//求aij前元素个数k,第一个元素为a11,L条对角线
// - d 是掐头,去掉第一排的0,+ d 是对角线左边的元素个数为d个
k = (i-1)*L - d + j - i + d = (i-1)*L + j - i (|i-j|<=d)在带状区域内
3 数组相关例题
/*
现有n个正整数,n≤10000,
* 要求出这nn个正整数中的第k个最小整数(相同大小的整数只计算一次),
* k≤1000,正整数均小于30000
*/
// 解题思路:先排序再去重
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String line = scanner.nextLine();
String[] s = line.split(" ");
int[] arr = new int[Integer.parseInt(s[0])];
int k = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
line = scanner.nextLine();
s = line.split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < s.length; j++) {
arr[j] = Integer.parseInt(s[j]);
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
int c = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < s.length; j++) {
if (j != s.length-1 && arr[j] == arr[j+1])
continue;
if (++c == k) {
System.out.println(arr[j]);
break;
}
}
if (c < k)
System.out.println("NO RESULT");
/*
此题简化后意为需要统计输入的n组数组中和目标数组中相同的元素个数(不考虑顺序),最后在用一个数组来显示结果
解题思路:
将固定长度[1-33]声明一个数组,将目标数组中元素和其对应相同的下标加一,再查看n个数组中对应下标的元素是否为0
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P2550 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String line = null;
int[] res = new int[7];
int[] com = new int[33];
int count = 0;
int end = 0;
while (true){
line = scanner.nextLine();
int g = 0;
if (count < 1) {
end = Integer.parseInt(line);
count++;
continue;
}
if (count == 1) {
String[] s = line.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
com[Integer.parseInt(s[i])]++;
}
count++;
continue;
}
if (count++ > 1) {
String[] s = line.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if (com[Integer.parseInt(s[i])] != 0)
g++;
}
if (g > 0)
res[7-g]++;
if (count >= end+2)
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
System.out.print(res[i]);
if (i != res.length-1)
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
/*
输入:
0001000
0001000
0001111
0001000
0001000
0001000
1111111
输出:
7 3 1 6 1 6 4 3 1 6 1 6 1 3 7
解题思路:
首先将字符串拼接,将N行字符串拼接为一个连续的字符串s
java 中可以直接使用+ 拼接
遍历字符串,先单独判断第一个字符串是否为1,为一拼接为" 0"
声明计数变量index,初始值为1,cs用来记录当前字符串为0还是1,遍历字符串,判断下一个值和cs是否相等
如果相等则index++,继续
如果不相等,结果拼接" index",index置1,
最后循环结束后,结果再拼接一次index
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P1320 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String line = null;
String s = "";
String res = "";
int count = 0;
int end = 0;
while (true) {
line = scanner.nextLine();
if (count < 1) {
end = line.length();
s+=line;
res+=end;
count++;
continue;
}
count++;
s+=line;
if (count>= end)
break;
}
int cs = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(0,1));
if (cs == 1)
res+=" "+0;
int index = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
int parseInt = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(i, i + 1));
if (cs == parseInt) {
index++;
} else {
cs = parseInt;
res+=" "+index;
index = 1;
}
}
res+=" "+index;
System.out.println(res);
}
}
/*
输入:
10 10 2 3
1 1 5 5
5 5 10 10
3 2
5 5
7 1
输出:
Y 1 1
Y 2 2
N
解题思路:
首先创建多维数组arr[n][4]
再分别判断输入的坐标x和y是否处于轰炸范围内
*/
public class P1830 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int count = 0;
int end = 1;
int a = 0;
int p = 0;
String line = null;
/*int[] attack = null;*/
int[][] attack1 = null;
outer: while (true) {
if (count < 1) {
line = scanner.nextLine();
String[] s = line.split(" ");
a = Integer.parseInt(s[2]);
p = Integer.parseInt(s[3]);
end += a+p;
/*attack = new int[a*4];*/
attack1 = new int[a][4];
count++;
if (p == 0)
break outer;
continue;
}
if (count < a+1){
line = scanner.nextLine();
String[] s = line.split(" ");
/*for (int i = count*4-4; i < count*4; i++) {
attack[i] = Integer.parseInt(s[index]);
index++;
}*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
attack1[count-1][i] = Integer.parseInt(s[i]);
}
count++;
}
int y1;
int y2;
if (count >= a+1) {
y1 = 0;
y2 = 0;
line = scanner.nextLine();
String[] s = line.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < attack1.length; i++) {
if ((Integer.parseInt(s[0]) >= attack1[i][0] && Integer.parseInt(s[0]) <= attack1[i][2]) && Integer.parseInt(s[1]) >= attack1[i][1] && Integer.parseInt(s[1]) <= attack1[i][3]) {
y1++;
y2 = i+1;
}
}
if (y1 > 0)
System.out.println("Y "+y1+" "+y2);
else
System.out.println("N");
count++;
if (count >= end)
break outer;
}
}
}
}
/*
解题思路:
声明n*n的多维数组,并初始化为0
对应萤石和火把,可以声明一个共用函数light,萤石将输入坐标的上下左右2个距离的位置置1,火把将输入坐标的上下左右1个距离的位置置1
判断该点是否再数组内
并判断火把的坐标位置上下左右2个距离的位置置1
最后遍历数组每个元素并输出0的个数
*/
public class P1789 {
static int n = 0;
static int m = 0;
static int k = 0;
static int[][] arr = null;
static void light(int x, int y, int z) {
for (int i = x-z; i <= x+z; i++) {
for (int j = y-z; j <= y+z; j++) {
if (i < 0 || i > n-1 || j < 0 || j > n-1)
continue;
else
arr[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int count = 1;
int end = 1;
String line = null;
outer: while (true) {
if (count < 2) {
line = scanner.nextLine();
String[] s = line.split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
arr = new int[n][n];
m = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
k = Integer.parseInt(s[2]);
end += m+k;
count++;
continue;
}
if (count < m+2) {
line = scanner.nextLine();
String[] s = line.split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(s[0])-1;
int y = Integer.parseInt(s[1])-1;
light(x,y,1);
if (x - 2 >= 0)
arr[x-2][y] = 1;
if (x + 2 <= n-1)
arr[x+2][y] = 1;
if (y - 2 >= 0)
arr[x][y-2] = 1;
if (y + 2 <= n-1)
arr[x][y+2] = 1;
count++;
if (k == 0 && count >= m+2)
break outer;
}
if (count >= m+2) {
line = scanner.nextLine();
String[] s = line.split(" ");
light(Integer.parseInt(s[0])-1,Integer.parseInt(s[1])-1,2);
count++;
if (count > end)
break outer;
}
}
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] == 0)
num++;
}
}
System.out.println(num);
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号