SQL逻辑
RDB (Relational Database)
关系型数据库源于relational model.
Relational model?
Relational model的内在逻辑是first-order (predicate) logic. (所有data表示为tuples, grouped into relations.)
First-order logic?
First-order Logic :Constants, Variables, Predicates, Functions, Quantifiers...
Example:
Only one student failed in Mathematics.
In this question, the predicate is "failed(x, y),"...
∃(x) [ student(x) → failed (x, Mathematics) ∧∀ (y) [¬(x==y) ∧ student(y) → ¬failed (x, Mathematics)].
SQL作为声明式语言(Declarative language)
Declarative language... WHAT.
你要query的系统已经实现了具体怎么取 (query optimizer),声明式语言只须关注what results to get。
还有哪些常见的Declarative langages?
- XML, XPath, XQuery
- Regex
- Prolog, Datalog...
看起来声明式语言抽象层次更高(先有what再有how),所以学习这类语言,关键是准确理解具体query本身对应什么(what)功能、执行顺序如何。
SQL的运算
Relational algebra基本操作:Union, Difference, Certesian Product, Projection, Selection, natural join.
Query: The query evaluation problem, the query equivalence problem, the query containment problem.
SQL的执行顺序
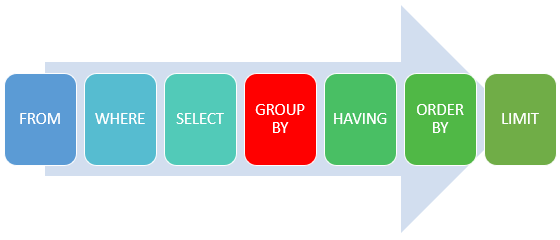
FROM (JOIN)
- Joins: Inner Join? Left Join? Right Join? Natural Join? Self Join? ... etc.
- 笛卡尔积
- 超过两个表?
WHERE
GROUP BY
- 常和SELECT Aggregation一起用
- 相同值的到同一行上
HAVING
- 限定group by的结果
SELECT
ORDER BY
- Multi-columns?
- Using FIELD(col, value1, value2...)
LIMIT
SQL Query优化
- 多数情况下,join faster than subqueries.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号