【前三次作业总结】
前言:
对于前三次作业,题量除了第一次多,剩下两次都是三道题,但题目少不代表容易。第一次作业像是大杂烩,题目之间没什么联系,感觉是为后面的两次作业做热身。第二次作业主要考察我们提取输入数据的能力,第三次作业主要考察我们提取输入的能力,同时对我们的高中数学知识点也进行了一次考察。
设计与分析:
一、第一次作业:
第一次作业相对于后两次作业都是比较容易的,一共有9道题,虽然题目有点多但是每道题都不难,题目要求的东西也少,即便如此也不能掉以轻心,经常会出现因为有些情况没有考虑周全而在测试点丢分的情况,个人感觉第一次作业更像是在让我们为后面作业做好准备的热身,主要考察我们对一般情况的考量以及对一些特例的特别关注。
二、第二次作业:
第二次作业虽然只有三道题,但是难度却比第一次作业上了一个台阶。
第一题要求我们写一个程序将输入的英文字母转换为其在字母表中序号输出,我将所有输入的字母都存储在一个String类型的字符串中,先判断输入格式是否正确,然后将每个单词转化为对应的ascII码,再将ascII码与1-26对应最后输出。代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 7 String s = sc.nextLine(); 8 int i = 0; 9 int n = 65; 10 int j = 1; 11 int[] num = new int[100]; 12 for( i = 0; i < s.length(); i ++ ){ 13 if(((int)s.charAt(i) >= 0 && (int)s.charAt(i) < 65) || ((int)s.charAt(i) >= 91 && (int)s.charAt(i) <= 96) || ((int)s.charAt(i) >= 123 && (int)s.charAt(i) <= 127)) { 14 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 15 return; 16 } 17 }for(n = 65 ;n <= 90;n ++) { 18 num[n] = j++; 19 }for(i = 0;i < s.length();i ++) { 20 if((int)s.charAt(i) <= 90) { 21 System.out.print(num[(int)s.charAt(i)]); 22 }else { 23 System.out.print(num[(int)s.charAt(i)-32]); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 }
第二题难度挺大,考察了串口字符解析,要求我们从输入的二进制流中提取出有效信息,题目要求如下:
- 过滤掉空闲、起始、结束以及奇偶校验位之后的数据,数据之前加上序号和英文冒号。
- 如有多个数据,每个数据单独一行显示。
- 若数据不足11位或者输入数据全1没有起始位,则输出"null data",
- 若某个数据的结束符不为1,则输出“validate error”。
- 若某个数据奇偶校验错误,则输出“parity check error”。
- 若数据结束符和奇偶校验均不合格,输出“validate error”。
- 发送方有数据发送时,会在有效数据(5~8位,具体位数由通信双方提前设置)前加上1位起始位“0”,在有效数据之后加上1位可选的奇偶校验位和1位结束位“1”。
光是非法输入的要求就有4种情况,让人很容易弄混,我虽然多次修改代码但还是没能做到全对。我的做法是先将输入的二进制流传入字符串中然后挨个查找是否有符合输出要求的数字,如果有就输出,没有就继续查找,如果有非法输入就输出对应情况的语句。现在重新审视我写的代码,发现我不应该先判断符合情况的输入数字,而应该先判断非法输入,最后留下来的就是合法输入。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 7 String s = sc.nextLine(); 8 int j = 1; 9 int i = 0; 10 int m = 0; 11 for(i = 0; i < s.length(); i ++) { 12 if(s.charAt(i) == '0') { 13 m = 1; 14 break; 15 }} 16 if(s.length() < 11) { 17 System.out.println("null data"); 18 }else{ 19 for(i = 0; i < s.length(); i ++) { 20 if(m != 1) { 21 System.out.println("null data"); 22 return; 23 }else { 24 if(s.charAt(i) == '0') { 25 if(s.charAt(i + 9) == '1' && s.charAt(i + 10) == '1'){ 26 System.out.print(j + ":"); 27 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 1)); 28 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 2)); 29 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 3)); 30 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 4)); 31 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 5)); 32 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 6)); 33 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 7)); 34 System.out.println(s.charAt(i + 8)); 35 j ++; 36 if(s.length() - i < 8) { 37 return; 38 }else { 39 i += 8; 40 } 41 }else if(s.charAt(i + 9) != '1' && j != 1) { 42 System.out.println(j + ":parity check error"); 43 }else if(s.charAt(i + 10) != '1' && j != 1) { 44 System.out.println(j + ":validate error"); 45 }else if(s.charAt(i + 9) != '1' && s.charAt(i + 10) != '1' && j != 1) { 46 System.out.println(j + ":validate error"); 47 }else if(s.charAt(i + 9) != '1' && j == 1) { 48 System.out.println("parity check error"); 49 }else if(s.charAt(i + 10) != '1' && j == 1) { 50 System.out.println("validate error"); 51 }else if(s.charAt(i + 9) != '1' && s.charAt(i + 10) != '1' && j == 1) { 52 System.out.println("validate error"); 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 }
第三题考查String的格式判断与内容提取,要求与第二题类似,要我们从输入的一串数字中提取出两个特定班学生的学号然后输出后四位,都是要我们提取输入的一部分再输出,但第三题比第二题容易一些,要求更容易读懂。我的处理方法和第二题类似,都是将输入存储在字符串中然后判断、输出。但是我的代码没有做到满足所有测试点的要求。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 7 String s = sc.nextLine(); 8 if(s.length() % 8 != 0) { 9 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 10 }else{ 11 for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i ++) { 12 if((int)s.charAt(i) < 48 || (int)s.charAt(i) > 57) { 13 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 14 return; 15 } 16 }for(int i = 0; i < s.length() - 4; i ++){ 17 if(s.charAt(i) == '2' && s.charAt(i + 1) == '0') { 18 if((s.charAt(i + 4) == '1' && s.charAt(i + 5) == '7') || (s.charAt(i + 4) == '6' && s.charAt(i + 5) == '1')) { 19 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 4)); 20 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 5)); 21 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 6)); 22 System.out.print(s.charAt(i + 7)); 23 System.out.print(" "); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 28 } 29 30 } 31 32 }
三、第三次作业:
第三次作业的三道题都是在平面直角坐标系下完成的,考察了我们高中数学素养。
第一题要我们提取输入的点坐标然后计算他们之间的距离,这题在为后两题打基础,也不难。我将输入的数字存入字符串中,先判断是否包含非法输入的情况,判断完后将字符串中逗号和空格用split()方法全部删除后存入一个字符串数组中,用来判断输入数据是否不符合要求,判断完毕再将字符串数组中内容传入double类型数组中进行计算,最后输出结果。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); 5 String sc = scan.nextLine(); 6 for(int i = 0;i < sc.length();i ++) { 7 if(((int)sc.charAt(i) == 43 && (int)sc.charAt(i + 1) == 43) || ((int)sc.charAt(i) == 45 && (int)sc.charAt(i + 1) == 45)) { 8 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 9 return; 10 }else if(((int)sc.charAt(i) < 43 && (int)sc.charAt(i) != 32) || (int)sc.charAt(i) == 47 || (int)sc.charAt(i) > 57) { 11 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 12 return; 13 } 14 } 15 int j = 0; 16 String[] a = sc.split("[, ]"); 17 double[] b = new double[4]; 18 for(int i = 0;i < a.length;i ++) { 19 if(a.length > 5) { 20 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 21 return; 22 }else{ 23 b[j++] = Double.valueOf(a[i]); 24 } 25 } 26 27 double dis = 0; 28 dis = Math.sqrt( ( Math.pow( (b[0] - b[2]) , 2 ) + Math.pow( ( b[1] - b[3] ), 2 ) ) ); 29 System.out.println(dis); 30 31 } 32 }
第二题要求我们通过输入的点坐标求出经过两点的直线方程,然后按照要求进行相关计算。题目要求如下:
1:输入两点坐标,计算斜率,若线条垂直于X轴,输出"Slope does not exist"。
2:输入三个点坐标,输出第一个点与另外两点连线的垂直距离。
3:输入三个点坐标,判断三个点是否在一条线上,输出true或者false。
4:输入四个点坐标,判断前两个点所构成的直线与后两点构成的直线是否平行,输出true或者false.
5:输入四个点坐标,计算输出前两个点所构成的直线与后两点构成的直线的交点坐标,x、y坐标之间以英文分隔",",并输出交叉点是否在两条线段之内(不含四个端点)的判断结果(true/false),判断结果与坐标之间以一个英文空格分隔。若两条线平行,没有交叉点,则输出"is parallel lines,have no intersection point"。
因为题目要求有五种情况,所以代码量激增,解题方法与第一题类似,都是将输入数据通过处理后传入一个double类型数组中再调用数组元素进行运算,只不过第二题运算量更大,我使用的是直线方程的一般式解题的,这导致我要算出三个未知系数,一不小心很容易搞错。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); 5 String a = scan.nextLine(); 6 String[] b = a.split("[:, ]"); 7 int op = Integer.parseInt(b[0]); 8 int j = 0; 9 double[] c = new double[b.length - 1]; 10 for(int i = 0;i < a.length();i ++) { 11 if(((int)a.charAt(i) == 43 && (int)a.charAt(i + 1) == 43) || ((int)a.charAt(i) == 45 && (int)a.charAt(i + 1) == 45)) { 12 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 13 return; 14 }else if(((int)a.charAt(i) < 43 && (int)a.charAt(i) != 32) || (int)a.charAt(i) == 47 || (int)a.charAt(i) > 58) { 15 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 16 return; 17 } 18 } 19 switch (op) { 20 case 1: 21 if (b.length > 5) { 22 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 23 break; 24 }else if(b[1].equals(b[3]) && b[2].equals(b[4])) { 25 System.out.println("points coincide"); 26 break; 27 }else { 28 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 29 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 30 } 31 double k = 0; 32 if (c[2] - c[0] == 0) { 33 System.out.println("Slope does not exist"); 34 } else { 35 k = (c[3] - c[1]) / (c[2] - c[0]); 36 System.out.println(k); 37 } 38 break; 39 } 40 case 2: 41 if (b.length > 7) { 42 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 43 break; 44 }else if(b[5].equals(b[3]) && b[6].equals(b[4])) { 45 System.out.println("points coincide"); 46 break; 47 }else { 48 double A = 0; 49 double B = 0; 50 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 51 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 52 } 53 A = c[5] - c[3]; 54 B = c[2] - c[4]; 55 double C = 0; 56 C = c[4] * c[3] - c[2] * c[5]; 57 double dis = Math.abs(A * c[0] + B * c[1] + C) / Math.sqrt(A * A + B * B); 58 System.out.println(dis); 59 } 60 break; 61 case 3: 62 if (b.length > 7) { 63 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 64 break; 65 }else if(b[5].equals(b[3]) && b[6].equals(b[4])) { 66 System.out.println("points coincide"); 67 break; 68 }else { 69 double A = 0; 70 double B = 0; 71 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 72 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 73 } 74 A = c[5] - c[3]; 75 B = c[2] - c[4]; 76 double C = 0; 77 C = 0 - (A * c[2] + B * c[3]); 78 if ((A * c[0] + B * c[1] + C) == 0) { 79 System.out.println(true); 80 } else { 81 System.out.println(false); 82 } 83 } 84 break; 85 case 4: 86 if (b.length > 9) { 87 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 88 break; 89 }else if((b[1].equals(b[3]) && b[2].equals(b[4])) || (b[5].equals(b[7]) && b[6].equals(b[8]))) { 90 System.out.println("points coincide"); 91 break; 92 }else { 93 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 94 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 95 } 96 double k1 = 0; 97 double k2 = 0; 98 k1 = (c[3] - c[1]) / (c[2] - c[0]); 99 k2 = (c[7] - c[5]) / (c[6] - c[4]); 100 if (k1 == k2) { 101 System.out.println(true); 102 } else { 103 System.out.println(false); 104 } 105 } 106 break; 107 case 5: 108 if (b.length > 9) { 109 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 110 break; 111 }else if((b[1].equals(b[3]) && b[2].equals(b[4])) || (b[5].equals(b[7]) && b[6].equals(b[8]))) { 112 System.out.println("points coincide"); 113 break; 114 }else { 115 double x = 0; 116 double y = 0; 117 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 118 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 119 } 120 double k1 = 0; 121 double k2 = 0; 122 k1 = (c[3] - c[1]) / (c[2] - c[0]); 123 k2 = (c[7] - c[5]) / (c[6] - c[4]); 124 if (k1 == k2) { 125 System.out.println("is parallel lines,have no intersection point"); 126 } else { 127 double A = 0; 128 double B = 0; 129 double A1 = 0; 130 double B1 = 0; 131 A = c[3] - c[1]; 132 B = c[0] - c[2]; 133 A1 = c[7] - c[5]; 134 B1 = c[4] - c[6]; 135 double C = 0; 136 double C1 = 0; 137 C = 0 - (A * c[2] + B * c[3]); 138 C1 = 0 - (A1 * c[4] + B1 * c[5]); 139 y = (A1 * C - A * C1) / (A * B1 - A1 * B); 140 x = -(B * y + C) / A; 141 System.out.print(x + "," + y); 142 double x1 = Math.max(c[0], c[2]); 143 double x3 = Math.max(c[4], c[6]); 144 double x2 = Math.min(c[0], c[2]); 145 double x4 = Math.min(c[4], c[6]); 146 if ((x > x2 || x > x4) && (x < x3 || x < x1)) { 147 System.out.println(" " + true); 148 } else { 149 System.out.println(" " + false); 150 } 151 } 152 } 153 break; 154 default: 155 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 156 break; 157 } 158 } 159 }
第三题最为复杂,在前两题的基础上又有了新的要求,这次是对输入的点处理成三角形,进行三角形有关的计算。题目要求如下:
1:输入三个点坐标,判断是否是等腰三角形、等边三角形,判断结果输出true/false,两个结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入三个点坐标,输出周长、面积、重心坐标,三个参数之间以一个英文空格分隔,坐标之间以英文","分隔。
3:输入三个点坐标,输出是钝角、直角还是锐角三角形,依次输出三个判断结果(true/false),以一个英文空格分隔,
4:输入五个点坐标,输出前两个点所在的直线与三个点所构成的三角形相交的交点数量,如果交点有两个,则按面积大小依次输出三角形被直线分割成两部分的面积。若直线与三角形一条线重合,输出"The point is on the edge of the triangle"
5:输入四个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后三个点所构成的三角形的内部(输出in the triangle/outof triangle)。
必须使用射线法,原理:由第一个点往任一方向做一射线,射线与三角形的边的交点(不含点本身)数量如果为1,则在三角形内部。如果交点有两个或0个,则在三角形之外。若点在三角形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle"
前三个要求还好,但是第四个开始就不简单了,交点数量一共分为三种情况,要么没有交点;要么一个交点;要么两个交点,而两个交点又有两种情况,要么一个交点在三角形顶点;另一个在三角形的某条边上,要么两个交点都在三角形的边上,这两种情况决定了计算被分割的面积的方法。至于第五个要求,射线法我闻所未闻,当场学了一下也不会用只能遗憾放弃。这道题算是我花了比较多的心思,还写了一个装满函数的类来方便计算。(但是并没有方便到哪里去)
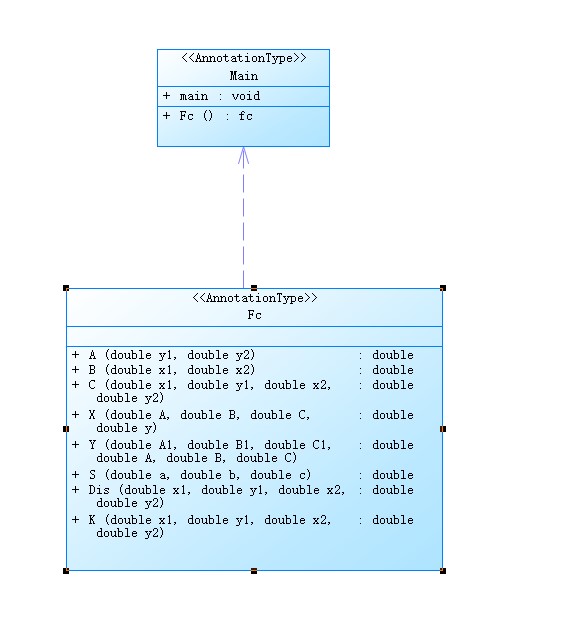
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); 5 String a = scan.nextLine(); 6 String[] b = a.split("[:, ]"); 7 int op = Integer.parseInt(b[0]); 8 int j = 0; 9 double[] c = new double[b.length - 1]; 10 switch (op) { 11 case 1: 12 if (b.length > 7) { 13 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 14 break; 15 }else if(b[1].equals(b[3]) && b[2].equals(b[4])) { 16 System.out.println("data error"); 17 break; 18 }else { 19 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 20 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 21 } 22 double d = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[0] - c[2], 2) + Math.pow(c[1] - c[3],2)); 23 double e = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[0] - c[4], 2) + Math.pow(c[1] - c[5],2)); 24 double f = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[2] - c[4], 2) + Math.pow(c[5] - c[3],2)); 25 if(d + e <= f) { 26 System.out.println("data error"); 27 }else { 28 if((d > e && e == f) || (e > d && d == f) || (f > e && e == d) || (d < e && e == f) || (e < d && d == f) || (f < e && e == d)) { 29 System.out.print(true); 30 }else { 31 System.out.println(false + " " + false); 32 break; 33 } 34 if(d == e && e == f) { 35 System.out.println(" " + true); 36 }else{ 37 System.out.println(" " + false); 38 } 39 } 40 break; 41 } 42 case 2: 43 if (b.length > 7) { 44 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 45 break; 46 }else if(b[5].equals(b[3]) && b[6].equals(b[4])) { 47 System.out.println("data error"); 48 break; 49 }else { 50 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 51 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 52 } 53 double d = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[0] - c[2], 2) + Math.pow(c[1] - c[3],2)); 54 double e = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[0] - c[4], 2) + Math.pow(c[1] - c[5],2)); 55 double f = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[2] - c[4], 2) + Math.pow(c[5] - c[3],2)); 56 double zc = d + e + f; 57 double p = zc / 2; 58 double s = Math.sqrt(p * (p - d) * (p - e) * (p - f)); 59 double zx = (c[0] + c[2] + c[4]) / 3; 60 double zy = (c[1] + c[3] + c[5]) / 3; 61 zc = ( ( int )( zc * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 62 s = ( ( int )( s * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 63 zx = ( ( int )( zx * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 64 zy = ( ( int )( zy * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 65 System.out.println(zc + " " + s + " " + zx + "," + zy); 66 } 67 break; 68 case 3: 69 if (b.length > 7) { 70 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 71 break; 72 }else if(b[5].equals(b[3]) && b[6].equals(b[4])) { 73 System.out.println("data error"); 74 break; 75 }else { 76 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 77 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 78 } 79 double d = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[0] - c[2], 2) + Math.pow(c[1] - c[3],2)); 80 double e = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[0] - c[4], 2) + Math.pow(c[1] - c[5],2)); 81 double f = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(c[2] - c[4], 2) + Math.pow(c[5] - c[3],2)); 82 if((e * e + d * d - f * f) / (2 * e * d) < 0 || (e * e + f * f - d * d) / (2 * e * f) < 0 || (f * f + d * d - e * e) / (2 * f * d) < 0) { 83 System.out.print(true); 84 }else { 85 System.out.print(false); 86 }if((e * e + d * d - f * f) / (2 * e * d) == 0 || (e * e + f * f - d * d) / (2 * e * f) == 0 || (f * f + d * d - e * e) / (2 * f * d) == 0) { 87 System.out.print(" " + true); 88 }else { 89 System.out.print(" " + false); 90 }if((e * e + d * d - f * f) / (2 * e * d) > 0 && (e * e + f * f - d * d) / (2 * e * f) > 0 && (f * f + d * d - e * e) / (2 * f * d) > 0) { 91 System.out.print(" " + true); 92 }else { 93 System.out.print(" " + false); 94 } 95 } 96 break; 97 case 4://4:输入五个点坐标,输出前两个点所在的直线与三个点所构成的三角形相交的交点数量,如果交点有两个, 98 //则按面积大小依次输出三角形被直线分割成两部分的面积。若直线与三角形一条线重合,输出"The point is on the edge of the triangle" 99 if (b.length > 11) { 100 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 101 break; 102 }else if(b[1].equals(b[3]) && b[2].equals(b[4])) { 103 System.out.println("points coincide"); 104 break; 105 }else { 106 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 107 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 108 } 109 Fc t = new Fc(); 110 if ((t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[4],c[5],c[6],c[7]) && t.A(c[7],c[5]) * c[0] + t.B(c[4],c[6]) * c[1] + t.C(c[4],c[5],c[6],c[7]) == 0) || (t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[4],c[5],c[8],c[9]) && t.A(c[5],c[9]) * c[0] + t.B(c[4],c[8]) * c[1] + t.C(c[4],c[5],c[8],c[9]) == 0) || (t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[8],c[9],c[6],c[7]) && t.A(c[9],c[7]) * c[0] + t.B(c[8],c[6]) * c[1] + t.C(c[8],c[9],c[6],c[7]) == 0)) { 111 System.out.println("The point is on the edge of the triangle"); 112 }else if((t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[4] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[5] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0 && t.A(c[9],c[7]) * c[0] + t.B(c[8],c[6]) * c[1] + t.C(c[8],c[9],c[6],c[7]) != 0 ) || (t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[6] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[7] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0 && t.A(c[5],c[9]) * c[0] + t.B(c[4],c[8]) * c[1] + t.C(c[4],c[5],c[8],c[9]) != 0)|| (t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[8] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[9] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0 && t.A(c[7],c[5]) * c[0] + t.B(c[4],c[5]) * c[1] + t.C(c[4],c[5],c[6],c[7]) != 0)) { 113 System.out.println(1); 114 }else if (t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[4],c[5],c[6],c[7]) || t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[4],c[5],c[8],c[9]) || t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[8],c[9],c[6],c[7])){ 115 System.out.println(0); 116 }else { 117 System.out.print(2 + " "); 118 if(t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[4] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[5] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0){ 119 double y1 = t.Y(t.A(c[9],c[7]),t.B(c[8],c[6]),t.C(c[8],c[9],c[6],c[7]),t.A(c[1],c[3]),t.B(c[0],c[2]),t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3])); 120 double x1 = t.X(t.A(c[1],c[3]),t.B(c[0],c[2]),t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]),y1); 121 double m = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[4], c[5]); 122 double n = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[6], c[7]); 123 double p = t.Dis(c[4], c[5], c[6], c[7]); 124 double n1 = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[8], c[9]); 125 double p1 = t.Dis(c[4], c[5], c[8], c[9]); 126 double s = ( ( int )( t.S(m,n,p) * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 127 double s1 = ( ( int )( t.S(m,n1,p1) * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 128 System.out.print(Math.min(s, s1) + " "); 129 System.out.println(Math.max(s1, s)); 130 }else if(t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[6] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[7] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0) { 131 double y1 = t.Y(t.A(c[5],c[9]),t.B(c[4],c[8]),t.C(c[4],c[5],c[8],c[9]),t.A(c[1],c[3]),t.B(c[0],c[2]),t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3])); 132 double x1 = t.X(t.A(c[1],c[3]),t.B(c[0],c[2]),t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]),y1); 133 double m = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[6], c[7]); 134 double n = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[4], c[5]); 135 double p = t.Dis(c[4], c[5], c[6], c[7]); 136 double n1 = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[8], c[9]); 137 double p1 = t.Dis(c[6], c[7], c[8], c[9]); 138 double s = ( ( int )( t.S(m,n,p) * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 139 double s1 = ( ( int )( t.S(m,n1,p1) * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 140 System.out.print(Math.min(s, s1) + " "); 141 System.out.println(Math.max(s1, s)); 142 }else if(t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[8] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[9] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0) { 143 double y1 = t.Y(t.A(c[7],c[5]),t.B(c[4],c[6]),t.C(c[4],c[5],c[6],c[7]),t.A(c[1],c[3]),t.B(c[0],c[2]),t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3])); 144 double x1 = t.X(t.A(c[1],c[3]),t.B(c[0],c[2]),t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]),y1); 145 double m = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[8], c[9]); 146 double n = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[4], c[5]); 147 double p = t.Dis(c[4], c[5], c[8], c[9]); 148 double n1 = t.Dis(x1, y1, c[6], c[7]); 149 double p1 = t.Dis(c[6], c[7], c[8], c[9]); 150 double s = ( ( int )( t.S(m,n,p) * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 151 double s1 = ( ( int )( t.S(m,n1,p1) * 1000000 + 0.5 ) ) / 1000000.0; 152 System.out.print(Math.min(s, s1) + " "); 153 System.out.println(Math.max(s1, s)); 154 }else { 155 156 } 157 } 158 } 159 break; 160 case 5: 161 if (b.length > 9) { 162 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 163 break; 164 }else if((b[1].equals(b[3]) && b[2].equals(b[4])) || (b[5].equals(b[7]) && b[6].equals(b[8]))) { 165 System.out.println("data error"); 166 break; 167 }else { 168 double x = 0; 169 double y = 0; 170 for (int i = 1; i < b.length; i++) { 171 c[j++] = Double.valueOf(b[i]); 172 } 173 double k1 = 0; 174 double k2 = 0; 175 k1 = (c[3] - c[1]) / (c[2] - c[0]); 176 k2 = (c[7] - c[5]) / (c[6] - c[4]); 177 if (k1 == k2) { 178 System.out.println("is parallel lines,have no intersection point"); 179 } else { 180 double A = 0; 181 double B = 0; 182 double A1 = 0; 183 double B1 = 0; 184 A = c[3] - c[1]; 185 B = c[0] - c[2]; 186 A1 = c[7] - c[5]; 187 B1 = c[4] - c[6]; 188 double C = 0; 189 double C1 = 0; 190 C = 0 - (A * c[2] + B * c[3]); 191 C1 = 0 - (A1 * c[4] + B1 * c[5]); 192 y = (A1 * C - A * C1) / (A * B1 - A1 * B); 193 x = -(B * y + C) / A; 194 System.out.print(x + "," + y); 195 double x1 = Math.max(c[0], c[2]); 196 double x3 = Math.max(c[4], c[6]); 197 double x2 = Math.min(c[0], c[2]); 198 double x4 = Math.min(c[4], c[6]); 199 if ((x > x2 || x > x4) && (x < x3 || x < x1)) { 200 System.out.println(" " + true); 201 } else { 202 System.out.println(" " + false); 203 } 204 } 205 } 206 break; 207 default: 208 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 209 break; 210 } 211 } 212 } 213 class Fc{ 214 public double A(double y1,double y2) { 215 double a1 = y2 - y1; 216 return a1; 217 } 218 public double B(double x1,double x2) { 219 double b1 = x1 - x2; 220 return b1; 221 } 222 public double C(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2) { 223 double c1 = x2 * y1 - x1 * y2; 224 return c1; 225 } 226 public double K(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2) { 227 if(x1 == x2) { 228 return -365; 229 } 230 double m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1); 231 return m; 232 } 233 public double X(double A,double B,double C,double y) { 234 double x = -(B * y + C) / A; 235 return x; 236 } 237 public double Y(double A1,double B1,double C1,double A,double B,double C) { 238 double y = (A1 * C - A * C1) / (A * B1 - A1 * B); 239 return y; 240 } 241 public double Dis(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2) { 242 double dis = Math.sqrt( ( Math.pow((x1 - x2) , 2 ) + ( Math.pow( ( y1 - y2 ), 2 ) ) ) ); 243 return dis; 244 } 245 public double S(double a,double b,double c) { 246 double z = (a + b + c) / 2; 247 double mianji = Math.sqrt(z * (z - a) * (z - b) * (z - c)); 248 return mianji; 249 } 250 }
踩坑心得:
第二次作业第二题我因为没读懂题目写了半天非法输入都搞不懂到底哪种情况才算非法输入,最后还是靠同学的帮助才勉强理解,下次在写代码之前要多读几遍题目,有必要的话可以在草稿纸上写写思路什么的,有助于理解。第三次作业第三题真的很折磨人,我以为我把计算直线方程写到方法里面去能减少我的代码行数,但事实并非如此,我要多次将元素传入方法,而且传入的元素数量不少,导致我经常看花眼将传入元素的顺序弄错,而且我也没有想到很好的办法判断直线与三角形的关系,只是在那里硬算直线和三角形有无交点,是否平行,以此作为判断位置关系的依据,虽然暴力解题不用动脑,但是要写的代码真的多了很多(如下),而且还会有考虑不到的情况,比如我如果硬算很难判断直线与三角形没有交点的情况,然后就写不出来。写完一搜才发现有更简单的方法来判断直线与三角形的位置关系。所以说,要多百度,不要闭门造车。
1 if ((t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[4],c[5],c[6],c[7]) && t.A(c[7],c[5]) * c[0] + t.B(c[4],c[6]) * c[1] + t.C(c[4],c[5],c[6],c[7]) == 0) || (t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[4],c[5],c[8],c[9]) && t.A(c[5],c[9]) * c[0] + t.B(c[4],c[8]) * c[1] + t.C(c[4],c[5],c[8],c[9]) == 0) || (t.K(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == t.K(c[8],c[9],c[6],c[7]) && t.A(c[9],c[7]) * c[0] + t.B(c[8],c[6]) * c[1] + t.C(c[8],c[9],c[6],c[7]) == 0)) {
2 System.out.println("The point is on the edge of the triangle");
3 }else if((t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[4] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[5] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0 && t.A(c[9],c[7]) * c[0] + t.B(c[8],c[6]) * c[1] + t.C(c[8],c[9],c[6],c[7]) != 0 ) || (t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[6] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[7] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0 && t.A(c[5],c[9]) * c[0] + t.B(c[4],c[8]) * c[1] + t.C(c[4],c[5],c[8],c[9]) != 0)|| (t.A(c[1],c[3]) * c[8] + t.B(c[0],c[2]) * c[9] + t.C(c[0],c[1],c[2],c[3]) == 0 && t.A(c[7],c[5]) * c[0] + t.B(c[4],c[5]) * c[1] + t.C(c[4],c[5],c[6],c[7]) != 0)) {
4 System.out.println(1);
改进建议:
我觉得我第三次作业的第三题可以把自己写的方法去掉,说不定看起来更美观。对于老师布置的作业,首先,我认为pta上的题目最好能告诉我们测试点的具体内容,要不然在改代码的时候根本无从下手,都不知道自己哪里错了,有时候改半天代码放进去一跑,错的还是错,对的有时候都变成错的了;其次,我觉得在pta的作业截止以后最好能给我们一份正确的代码,让我们学习一下解题思路和解题技巧,也能让我们发现自己的不足,否则pta的作业对我们而言,写完了就是写完了,不会再去深入思考题目考察的知识点,也无法通过学习答案优化代码,久而久之就会开始敷衍了事,现在pta的作业就像高中时没有正确答案,老师也不讲的题目,让人觉得没有写的必要。
总结:
通过这三次作业,我获益良多,首先是要细心,要考虑到输入的各种情况然后写好对应的输出,其次就是在写题之前要把题目弄懂,在心中有个大致的框架,比如要写哪些函数,我要怎么做才能满足这个要求,这么做会不会太麻烦了,有没有什么更好的解决方法等等,万万不可想到哪写到哪,我更进一步的掌握了书写类及方法的格式,在写题过程中查阅了许多资料,掌握了split()方法的使用并且对数组有了更进一步的认识。我还学会了基本数据类型,String类型和包装类之间的转换,也初次接触了power designer这个功能强大的软件并第一次用它做出了一张UML类图,我也将在接下来的学习过程中不断充实自己的知识体系,争取下次作业能够全对。但是也能从之前的代码中发现,我对于类和方法的运用仍旧不熟练,大部分程序都是一main到底,没有调用任何方法,导致我对于方法和类的书写仍旧不熟练,我也会在今后的作业中争取多写几个方法来锻炼自己。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号