Vuex的安装使用及工作原理
一、Vuex的工作原理
1.什么是vuex
在vue中实现集中式状态(统一数据管理)管理的一个vue插件(不属于任意一个组件),对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(多个组件共同进行读/写操作),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信。
2.vuex的工作原理图
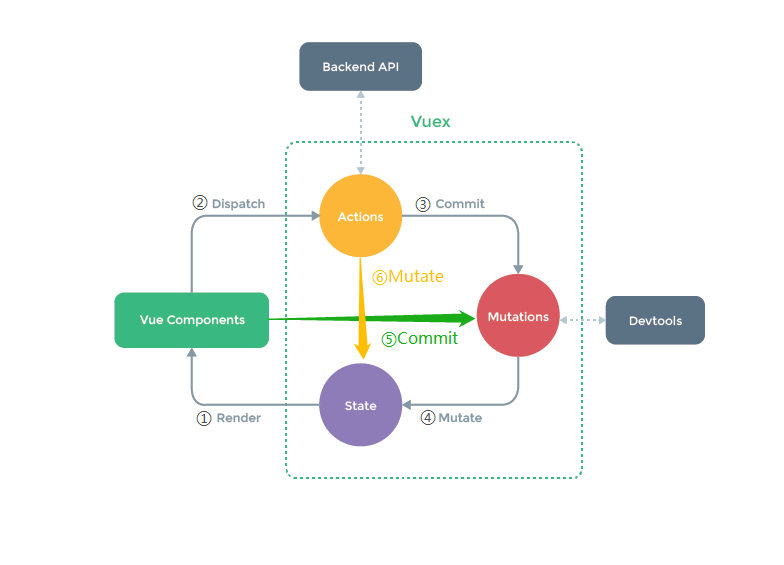
3.vuex是如何工作的
工作对象
state:状态,用于存储对象数据
Actions:行为,用于保存方法的行为,可以包含异步操作
Mutations:转变,用于提交行为的结果,不可以包含异步操作
Getters:类似于在store中的计算属性
Modules:模块,将store分割成不同的模块,每个模块有自己的state、actions、mutations
工作原理
Render:vue组件中可以读取state中的数据(对应工作原理图中的①这一条线)
Dispatch:调用store中的dispatch方法,由vue组件派发给Actions执行,Actions可以继续给自身派发,也可以调用异步方法(Backend API)(对应工作原理图中的②这一条线)
Commit:调用store中的commit方法,由Actions提交给Mutations执行,也可以直接由组件提交(对应工作原理图中的③⑤这两条线)
Mutate:Actions、Mutations中更改state中的数据,不需要手动执行,由api直接调用。一般是Mutations调用,在此处调用,可以被开发者工具(Devtools)直接监控,由Actions调用时,不被监控。(对应工作原理图中的④⑥这两条线)
二、Vuex的安装使用
1.搭建一个vuex
① 下载vuex,执行以下命令,当前vue最新版本为vue3,vuex最新版本为vuex4,如果不加@3则默认安装vuex4,vuex4当前用在vue3中,如果使用的是vue2,则需要下载vuex3版本。
npm i vuex@3
② 新建一个store.js文件或者在store文件夹下新建一个index.js文件
import Vue from 'vue'
// 该文件用于创建Vuex中最为核心的store
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 引入vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
const actions = {
// 准备actions,用于响应组件中的动作
// context:context可调用commit、dispatch方法
// value:接收到的参数
increaseOdd(context, value) {
// actions中一般写业务逻辑
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
// 提交给mutations,执行操作数据的步骤
context.commit('ADDSUM', value)
}
}
}
const mutations = {
// 准备mutations,用于操作数据(state)
// state:state中的数据
// value:接收到的参数
ADDSUM(state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
MINUSSUM(state, value) {
state.sum -= value
},
}
const state = {
// 准备state,用于存储数据
sum: 0,
average: 70
}
const getters = {
// state:state中的数据
// getters:
scores(state, getters) {
// 类似于vue中的计算属性
return state.sum * state.average
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
actions,
mutations,
getters
})
③ 在main.js中引入store
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入store
import store from './store'
import App from './App'
// 阻止 vue 在启动时生成生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#app',
// 在vue中使用store
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
2.在组建中使用vuex
state的使用
第一种:直接通过$store.state获取到vuex中数据
<div>
<h1>学校名是:{{ $store.state.schoolName }}</h1>
</div>
第二种:通过引入mapState
<template>
<div>
<h1>学校名是:{{ schoolName }}</h1>
<h1>学校简述是:{{ schoolDesc }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "School",
computed: {
// 组件中与store中使用的名称一致时可以直接使用数组形式
...mapState(['schoolName','schoolDesc'])
// 组件中与store中使用的名称不一致时只能使用对象形式
//...mapState({schoolName: 'schoolName', schoolDesc: 'storeDesc'})
}
}
</script>
actions的使用
第一种:在methods方法调用中,使用$store.dispatch派发给actions
<template>
<div>
<h1>学生数量:{{ sum }}</h1>
<!-- 点击按钮触发事件 -->
<button @click="increaseOdd">奇数时再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
// 获取store.state下的数据
...mapState(['sum']),
}
methods: {
// 调用方法
increaseOdd(){
// 派发给actions执行业务逻辑
this.$store.dispatch('increaseOdd',this.n)
},
}
}
</script>
第二种:通过引入mapActions
<template>
<div>
<h1>学生数量:{{ sum }}</h1>
<button @click="increaseOdd(n)">奇数时再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入mapState、mapActions
import {mapState, mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['sum'])
},
methods: {
// 使用这种方法,只能通过increaseOdd(n)这样传参,否则在actions中接收到的就是event事件
// 方法名与store中一致时可以直接使用数组形式
...mapActions(['increaseOdd']),
// 方法名与store中不一致时只能使用对象形式
// ...mapActions({increaseOdd: 'increaseOdd'}),
}
}
</script>
mutations的使用
第一种:在methods方法调用中,使用$store.commit提交给mutations
<template>
<div>
<h1>学生数量:{{ sum }}</h1>
<!-- 调用方法增加减少学生数量 -->
<button @click="addSum">+</button>
<button @click="minusSum">-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['sum'])
},
methods: {
addSum() {
// 提交给mutations修改数据
this.$store.commit('ADDSUM', this.n)
},
minusSum() {
this.$store.commit('MINUSSUM', this.n)
},
}
}
</script>
第二种:通过引入mapMutations
<template>
<div>
<h1>学生数量:{{ sum }}</h1>
<button @click="ADDSUM(n)">+</button>
<button @click="MINUSSUM(n)">-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState, mapMutations} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['sum'])
},
methods: {
// 方法名与store中一致时可以直接使用数组形式
...mapMutations(['ADDSUM','MINUSSUM']),
// 方法名与store中不一致时只能使用对象形式
// ...mapMutations({
// addSum: 'ADDSUM',
// minusSum: 'MINUSSUM'
// })
}
}
</script>
getter的使用
第一种:直接通过$store.getters获取
<template>
<div>
<h1>学生数量:{{ sum }}</h1>
<h1>学生平均成绩:{{ average }}</h1>
<h2>学生总成绩:{{ scores }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState, mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
//
...mapState(['sum', 'average']),
scores(){
// 获取store中的getters数据
return this.$store.getters.scores
}
}
}
</script>
第二种:引用mapGetters
<template>
<div>
<h1>学生数量:{{ sum }}</h1>
<h1>学生平均成绩:{{ average }}</h1>
<!-- store中的getters数据 -->
<h2>学生总成绩:{{ scores }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState, mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['sum', 'average']),
...mapGetters(['scores'])
},
}
</script>
3.vuex的模块化
①封装一个对象,此处以school作为案例
export default {
// 指定命名空间,如果需要以mapState...的方式获取数据
namespaced: true,
state: {
// 此处封装数据
schoolName: '第一中心小学',
schoolDesc: '自信自强',
studentList: [{id: '001', studentName: '张三'}]
},
getters: {
// 此处写计算属性
// 计算第一个学生名
firstStudent(state) {
return state.studentList[0].studentName
},
// 计算学生数量
studentCount(state) {
return state.studentList.length
}
},
actions: {
// 此处写业务逻辑方法
// 添加一个姓李的学生
addLi(context, value) {
if (value.studentName.indexOf('李') == 0) {
context.commit('ADD_STUDENT', value)
} else {
alert('学生必须姓李')
}
},
// 检查学生姓名是否正确
checkName(context, value) {
if (!value) {
alert('学生名为空')
} else {
const filterList = context.state.studentList.filter(m => {
return m.studentName === value
})
if (filterList.length > 0) {
alert('学校中已有该学生名')
} else {
alert('校验通过')
}
}
}
},
mutations: {
// 此处写操作数据方法
// 添加一个学生
ADD_STUDENT(state, value) {
state.studentList.unshift(value)
}
}
}
②在store下的index.js中引入school
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import student from './student'
import school from './school'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
student,
school
}
})
③在组件中使用
<template>
<div>
<!-- 从school模块中的state中获取数据 -->
<h1>学校名是:{{ schoolName }}</h1>
<h2>学校简述是:{{ schoolDesc }}</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(index,key) in studentList" :key="key">
{{ index.studentName }}
</li>
</ul>
<!-- 从school模块中的getters中获取数据 -->
<h2>第一个学生名是:{{ firstStudent }}</h2>
<h2>学生总数为:{{ studentCount }}</h2>
<!-- input输入框 -->
<input v-model="name"></input>
<!-- 调用school模块中的actions方法 -->
<button @click="checkName(name)">校验该名称是否可用</button>
<button @click="add">添加一个学生</button>
<!-- 调用school模块中的mutations方法 -->
<button @click="addLi">添加一个姓李的学生</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState, mapActions, mapMutations, mapGetters} from 'vuex'
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name: "School",
data() {
return {
name: ''
}
},
computed: {
// 通过引入mapState获取school模块下的state数据
...mapState('school', ['schoolName', 'studentList']),
schoolDesc() {
// 直接通过$store.state.school获取数据
return this.$store.state.school.schoolDesc
},
// 通过引入mapGetters获取school模块下的getters数据
...mapGetters('school', ['studentCount']),
firstStudent() {
// 直接通过$store.getters获取数据,getters下的数据是以路径形式存放,所以可通过一下写法获取
return this.$store.getters['school/firstStudent']
}
},
methods: {
// 引入mapActions和mapMutations与mapState类似
...mapActions('school', ['checkName']),
// 调用school中的actions方法
addLi() {
const student = {id: nanoid(), studentName: this.name}
this.$store.dispatch('school/addLi', student)
this.name = ''
},
// 调用school中的mutations方法
add() {
const student = {id: nanoid(), studentName: this.name}
this.$store.commit('school/ADD_STUDENT', student)
this.name = ''
},
}
}
</script>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号