lc0331
✅ 538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/
描述
给定一个二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree),把它转换成为累加树(Greater Tree),使得每个节点的值是原来的节点值加上所有大于它的节点值之和。
例如:
输入: 原始二叉搜索树:
5
/ \
2 13
输出: 转换为累加树:
18
/ \
20 13
注意:本题和 1038: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/ 相同
解答
我们要遍历整个二叉树,然后找比较大的吗?
非也,二叉搜索树 BST 有性质:右边的大啊。
RNL的 中序遍历搞一搞。
java
以右->根->左的顺序遍历二叉树,将遍历顺序的前一个结点的累加值记录起来,和当前结点相加,得到当前结点的累加值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int preNum = 0;
//递归写法
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
unPreOrder(root);
return root;
}
public void unPreOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null)
return;
unPreOrder(root.right);
root.val += preNum;
preNum = root.val;
unPreOrder(root.left);
}
//非递归写法 todo 重点观看
/*public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return root;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//stack.add(root);
TreeNode node = root;
while(node != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(node != null){
stack.add(node);
node = node.right;
}
node = stack.pop();
node.val += preNum;
preNum = node.val;
if(node.left != null)
node = node.left;
else
node = null;
}
return root;
}*/
}
py
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
my_sum = 0
def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if root is None:
return
self.convertBST(root.right)
tmp = root.val
root.val += self.my_sum
self.my_sum += tmp
self.convertBST(root.left)
return root
'''
执行用时 :
132 ms
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
16.13%
的用户
内存消耗 :
15.9 MB
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
5.44%
的用户
'''
✅ 1022. 从根到叶的二进制数之和
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-of-root-to-leaf-binary-numbers/
描述
给出一棵二叉树,其上每个结点的值都是 0 或 1 。每一条从根到叶的路径都代表一个从最高有效位开始的二进制数。例如,如果路径为 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1,那么它表示二进制数 01101,也就是 13 。
对树上的每一片叶子,我们都要找出从根到该叶子的路径所表示的数字。
以 10^9 + 7 为模,返回这些数字之和。(tt: aka: 即下面java 里的 1000_000_007 )
示例:
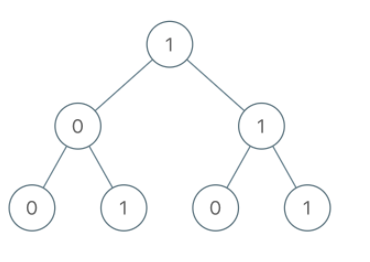
输入:[1,0,1,0,1,0,1]
输出:22
解释:(100) + (101) + (110) + (111) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22
解答
还是遍历问题。DFS 到头了,然后就进行转10进制呗。(c在过程中就边走边计算,不是最后才转10进制)
c
//C 语言描述。
//tt 由此,你可以深刻理解 递归 的实质。
int _sumRootToLeaf(struct TreeNode *root, int num) {
int sum = 0;
//计算 加上 这个节点后的 总值num
num = (num << 1) + root->val;
// 如果已经到了尽头,那么就返回这个 总值num
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) return num;
// 如果还没到 左边 的尽头,那么就把 左边 孩子的总值, 算出来,记得传当前
// 的总值 num 进去。
if (root->left) sum += _sumRootToLeaf(root->left, num);
// 如果还没到 右边 的尽头,那么就把 右边 孩子的总值, 算出来,记得传当前
// 的总值 num 进去。
if (root->right) sum += _sumRootToLeaf(root->right, num);
return sum;
}
int sumRootToLeaf(struct TreeNode *root) {
return root ? _sumRootToLeaf(root, 0) : 0;
}
java
class Solution {
public int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int mod = root.val % 1000_000_007;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return mod;
if (root.left != null) root.left.val += mod << 1;
if (root.right != null) root.right.val += mod << 1;
//tt 这种方式 似乎 就像是 ,把每个 父亲 节点的值,依次下放
// 到每个子节点,然后最后这句,下面这句 return ,就是
// 递归处理每个子节点。
return (sumRootToLeaf(root.left) + sumRootToLeaf(root.right)) % 1000_000_007;
}
}
//牛,实在是牛
class Solution {
int sum =0;
int num = 0;
public int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode root) {
//从根节点开始,记录二进制
if (root==null)return 0;
num = (num<<1) + root.val;//tt1 这样就做到了边走 边转位 10进制
if (root.left==null&&root.right==null){//如果是叶子节点
sum += num;
}
sumRootToLeaf(root.left);
sumRootToLeaf(root.right);
num = (num-root.val)>>1;//tt 这里算是回溯,是tt1 的正好的逆操作
//tt 其实这个回溯 还是 需要 下一次理解 ,todo
return sum;
}
}
py
只是重写了上面的c
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def sumRootToLeaf(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def _sumRootToLeft(root: TreeNode, num: int):
num = (num << 1) + root.val
if (root.left is None) and (root.right is None):
return num
# if not go to the end
sum = 0
if (root.left is not None):
sum += _sumRootToLeft(root.left, num)
if (root.right is not None):
sum += _sumRootToLeft(root.right, num)
return sum
if root is None:
return 0
else:
return _sumRootToLeft(root, 0)
'''
执行用时 :
84 ms
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
5.37%
的用户
内存消耗 :
14.1 MB
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
5.41%
的用户
'''



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号