JavaScript数据结构与算法总结四——图(深度优先、广度优先、最短路径、最小生成树)
图
图由边的集合及顶点的集合组成。
边由顶点 对 (v1,v2) 定义,v1 和 v2 分别是图中的两个顶点。顶点也有权重,也称为成本。如果一个 图的顶点对是有序的,则可以称之为有向图。在对有向图中的顶点对排序后,便可以在两 个顶点之间绘制一个箭头。有向图表明了顶点的流向。
图的表示
图最常见的实现是邻接矩阵。每个节点都和一个整数相关联,该整数将作为数组的索引。用一个二维数组来表示顶点之间的连接。
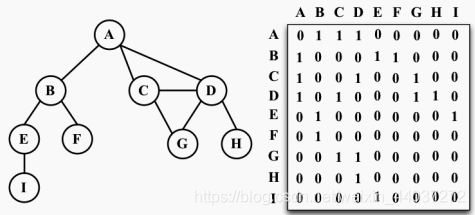
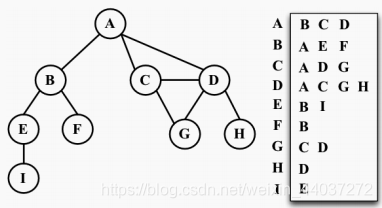
也可以使用一种叫作邻接表的动态数据结构来表示图。邻接表由图中每个顶点的相邻顶点列表所组成。存在好几种方式来表示这种数据结构。我们可以用列表(数组)、链表,甚至是散列表或是字典来表示相邻顶点列表。
//构建图,输入顶点数量
function Graph(v) {
this.vertices = v;
this.edges = 0;
this.adj = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; ++i) {
this.adj[i] = []; this.adj[i].push("");
}
this.addEdge = addEdge;
this.showGraph = showGraph;
}
//添加边
function addEdge(v, w) {
this.adj[v].push(w);
this.adj[w].push(v);
this.edges++;
}
//输出所有顶点及其相邻顶点
function showGraph() {
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; ++i) {
document.write(i ," -> ");
for (var j = 0; j < this.vertices; ++j) {
if (this.adj[i][j] != undefined) {
document.write(this.adj[i][j] ,' ');
}
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
graphA = new Graph(5);
graphA.addEdge(0, 1);
graphA.addEdge(0, 2);
graphA.addEdge(1, 3);
graphA.addEdge(2, 4);
graphA.showGraph();
图的遍历
深度优先搜索
本质是回溯算法
深度优先搜索包括从一条路径的起始顶点开始追溯,直到到达最后一个顶点,然后回溯, 继续追溯下一条路径,直到到达最后的顶点,如此往复,直到没有路径为止。这不是在搜 索特定的路径,而是通过搜索来查看在图中有哪些路径可以选择。
- 遍历所有节点,如果没有被搜索则调用DFS方法
- DFS方法,递归遍历当前节点的下一个节点
广度优先搜索
广度优先搜索算法会从指定的第一个顶点开始遍历图,先访问其所有的邻点(相邻顶点),再访问邻点的邻点。
编码
//无向图
//构建图,输入顶点数量
function Graph(v) {
this.vertices = v;//顶点数
this.edges = 0;//边数
this.adj = [];
//通过 for 循环为数组中的每个元素添加一个子数组来存储所有的相邻顶点,并 将所有元素初始化为空字符串。
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; ++i) {
this.adj[i] = []; this.adj[i].push("");
}
//为 Graph 类添加一个数组,用来存储已访问过的顶点,将它所有元 素的值全部初始化为 false。
this.marked = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; ++i) {
this.marked[i] = false;
}
this.addEdge = addEdge;
this.showGraph = showGraph;
this.DFS = DFS;
this.DFSTraverse = DFSTraverse;
this.BFS = BFS;
this.BFSTraverse = BFSTraverse;
}
//添加边
function addEdge(v, w) {
this.adj[v].push(w);
this.adj[w].push(v);
this.edges++;
}
//输出所有顶点及其相邻顶点
function showGraph() {
for (var i in this.adj) {
document.write(i, " -> ");
for (var j = 0; j < this.vertices; ++j) {
if (this.adj[i][j] != undefined) {
document.write(this.adj[i][j], ' ');
}
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
//深度优先
function DFSTraverse() {
let v = this.vertices;
for (let i = 0; i < v; ++i) {
if (!this.marked[i]) {
this.DFS(i);
}
}
}
function DFS(v) {
this.marked[v] = true;
if (this.adj[v] != undefined) {
document.write("Visited vertex: ", v, "<br>");
}
for (var w in this.adj[v]) {
let k = this.adj[v][w];
if (!this.marked[k]) {
this.DFS(k);
}
}
}
//广度优先
function BFSTraverse() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; ++i) {
if (!this.marked[i]) {
this.BFS(i);
}
}
}
function BFS(v) {
this.marked[v] = true;
if (this.adj[v] != undefined) {
document.write("Visited vertex: ", v, "<br>");
}
for (let w in this.adj[v]) {
let k = this.adj[v][w];
if (!this.marked[k]) {
this.marked[k] = true;
if (this.adj[k] != undefined) {
document.write("Visited vertex: ", k, "<br>");
}
}
}
}
graphA = new Graph(5);
graphA.addEdge(0, 1);
graphA.addEdge(0, 2);
graphA.addEdge(1, 3);
graphA.addEdge(2, 4);
document.write("Show all vertices and their neighbors:<br>");
graphA.showGraph();
// document.write("Depth first traversal:<br>");
// graphA.DFSTraverse();
document.write("Breadth first traversal:<br>");
graphA.BFSTraverse();
最短路径
Dijkstra 算法
Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的单源最短路径算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。Dijkstra算法是很有代表性的最短路径算法,在很多专业课程中都作为基本内容有详细的介绍,如数据结构,图论,运筹学等等。注意该算法要求图中不存在负权边。
Dijkstra 算法是一种计算从单个源到所有其他源的最短路径的贪心算法
//Dijkstra算法
//构建图,输入顶点数量
function Graph(v) {
this.vertices = v;//顶点数
this.edges = 0;//边数
this.adj = [];
//通过 for 循环为矩阵的每一个元素赋值0。
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.adj[i] = [];
for (let j = 0; j < this.vertices; j++)
this.adj[i][j] = 10000;
}
//为 Graph 类添加一个数组,用来存储已访问过的顶点,将它所有元 素的值全部初始化为 false。
this.marked = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.marked[i] = false;
}
//添加一个数组用于存储路径长度
this.dist = [];
this.dist[0]=0;
for (var i = 1; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.dist[i] = 10000;//取正无穷大
}
//用于存储路径
// this.path = [];
// for (var i = 1; i < this.vertices; i++) {
// this.path[i] = [];
// }
this.addEdge = addEdge;
this.showGraph = showGraph;
this.Dijkstra = Dijkstra;
this.djtPath = djtPath;
this.showDijkstra = showDijkstra;
}
//添加边
function addEdge(v, w, k) {
this.adj[v][w] = k;
this.edges++;
}
//输出所有顶点及其指向的顶点
function showGraph() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
document.write(i, " -> ");
for (let j = 0; j < this.vertices; j++) {
if (this.adj[i][j]) {
document.write(j, ' ');
}
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
//最短路径
function Dijkstra() {
for (let i=0;i<this.vertices;i++) {
this.djtPath(i);
}
}
function djtPath(v) {
let t = this.dist[v];
for(let w in this.adj[v]){
let k = t+this.adj[v][w];
if(this.dist[w]>k){
this.dist[w]=k;
}
}
}
function showDijkstra() {
for(let i =1 ;i<this.vertices;i++){
document.write("0->",i,":",this.dist[i],"<br>");
}
}
graphA = new Graph(6);
graphA.addEdge(0, 1, 2);
graphA.addEdge(0, 2, 4);
graphA.addEdge(1, 2, 2);
graphA.addEdge(1, 3, 4);
graphA.addEdge(1, 4, 2);
graphA.addEdge(2, 4, 3);
graphA.addEdge(3, 5, 2);
graphA.addEdge(4, 3, 3);
graphA.addEdge(4, 5, 2);
document.write("Show all vertices and their neighbors:<br>");
graphA.showGraph();
graphA.Dijkstra();
document.write("The shortest distance is:<br>");
graphA.showDijkstra()
为了方便,我直接遍历,而且没有记录路径,实际上可以缩小时间复杂度,并在path 数组中存储。
Floyd-Warshall 算法
Floyd-Warshall 算法是一种计算图中所有最短路径的动态规划算法。通过该算法,我们可以找出从所有源到所有顶点的最短路径。
//Floyd算法
//使用邻接矩阵构建图,输入顶点数量
function Graph(v) {
this.vertices = v;//顶点数
this.edges = 0;//边数
this.adj = [];
//通过 for 循环为矩阵的每一个元素赋值0。
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.adj[i] = [];
for (let j = 0; j < this.vertices; j++)
this.adj[i][j] = Infinity;
}
//添加一个数组用于存储路径长度
this.dist = [];
this.addEdge = addEdge;
this.showGraph = showGraph;
this.floyd=floyd;
this.showFloyf=showFloyf;
}
//添加边
function addEdge(v, w, k) {
this.adj[v][w] = k;
this.edges++;
}
//输出所有顶点及其指向的顶点
function showGraph() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
document.write(i, " -> ");
for (let j = 0; j < this.vertices; j++) {
if (isFinite(this.adj[i][j])) {
document.write(j, ' ');
}
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
function floyd(){
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.dist[i] = [];
for(let j=0;j<this.vertices;j++){
if(i===j){
this.dist[i][j]=0;
}else if(!isFinite(this.adj[i][j])){
this.dist[i][j]=10000;
}else{
this.dist[i][j] = this.adj[i][j];
}
}
}
for(let k = 0;k<this.vertices;k++){
for(let i=0;i<this.vertices;i++){
for(let j=0;j<this.vertices;j++){
if((this.dist[i][k]+this.dist[k][j])<this.dist[i][j]){
this.dist[i][j]=this.dist[i][k]+this.dist[k][j];
}
}
}
}
}
function showFloyf(){
for(let i=0;i<this.vertices;i++){
for(let j=0;j<this.vertices;j++){
if(this.dist[i][j]<10000){
document.write(this.dist[i][j]," ");
}else{
document.write("INF ");
}
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
//最短路径
graphA = new Graph(6);
graphA.addEdge(0, 1, 2);
graphA.addEdge(0, 2, 4);
graphA.addEdge(1, 2, 2);
graphA.addEdge(1, 3, 4);
graphA.addEdge(1, 4, 2);
graphA.addEdge(2, 4, 3);
graphA.addEdge(3, 5, 2);
graphA.addEdge(4, 3, 3);
graphA.addEdge(4, 5, 2);
document.write("Show all vertices and their neighbors:<br>");
graphA.showGraph();
graphA.floyd();
document.write("The shortest distance is:<br>");
graphA.showFloyf();
最小生成树
Prim 算法
Prim 算法是一种求解加权无向连通图的 MST 问题的贪心算法。它能找出一个边的子集,使得其构成的树包含图中所有顶点,且边的权值之和最小。
//Prim算法
//构建图,输入顶点数量
function Graph(v) {
this.vertices = v;//顶点数
this.edges = 0;//边数
this.adj = [];
//通过 for 循环为矩阵的每一个元素赋值0。
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.adj[i] = [];
for (let j = 0; j < this.vertices; j++)
this.adj[i][j] = 10000;
}
//为 Graph 类添加一个数组,用来存储已访问过的顶点,将它所有元 素的值全部初始化为 false。
this.marked = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.marked[i] = false;
}
//添加一个数组用于存储路径长度
this.dist = [];
this.dist[0] = 0;
for (var i = 1; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.dist[i] = 10000;//取正无穷大
}
//用于存储路径
this.path = [];
for (var i = 1; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.path[i] = [];
}
this.addEdge = addEdge;
this.showGraph = showGraph;
this.Prim = Prim;
this.djtPath = djtPath;
this.showPrim = showPrim;
}
//添加边
function addEdge(v, w, k) {
this.adj[v][w] = k;//存储正向边
this.adj[w][v] = k;//存储反向边,若是有向图则删去
this.edges++;
}
//输出所有顶点及其指向的顶点
function showGraph() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
document.write(i, " -> ");
for (let j = 0; j < this.vertices; j++) {
if (this.adj[i][j]<10000) {
document.write(j, ' ');
}
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
//最短路径
function Prim() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
if (!this.marked[i]) {
this.djtPath(i);
}
}
}
function djtPath(v) {
this.marked[v]=true;
let t = this.dist[v];
for (let w in this.adj[v]) {
let k = t + this.adj[v][w];//原点到当前节点的距离加当前节点到下一节点的距离
if (this.dist[w] > k) {
this.dist[w] = k;
this.path[w]=[v,w];//记录相应的节点
}
}
}
function showPrim() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.vertices; i++) {
document.write(this.path[i][0],"->",this.path[i][1], ":", this.dist[i],"<br>");
}
}
graphA = new Graph(6);
graphA.addEdge(0, 1, 2);
graphA.addEdge(0, 2, 4);
graphA.addEdge(1, 2, 2);
graphA.addEdge(1, 3, 4);
graphA.addEdge(1, 4, 2);
graphA.addEdge(2, 4, 3);
graphA.addEdge(3, 5, 2);
graphA.addEdge(4, 3, 3);
graphA.addEdge(4, 5, 2);
document.write("Show all vertices and their neighbors:<br>");
graphA.showGraph();
graphA.Prim();
document.write("The shortest distance is:<br>");
graphA.showPrim()
Kruskal 算法
//Kruskal算法
//构建图,输入顶点数量
function Graph(v) {
this.vertices = v;//顶点数
this.edges = 0;//边数
this.adj = [];//边集
this.path = [];//用于存储路径
this.addEdge = addEdge;
this.showGraph = showGraph;
this.Kruskal = Kruskal;
this.find = find;
this.showKruskal = showKruskal;
}
//添加边
function addEdge(v, w, k) {
this.adj.push([v, w, k]);
this.edges++;
}
//输出所有顶点及其指向的顶点
function showGraph() {
for(let i in this.adj){
document.write(this.adj[i][0],"-",this.adj[i][1],":",this.adj[i][2],"<br>")
}
}
//最短路径
function Kruskal() {
let cost = this.adj;
while (this.path.length < this.vertices-1) {//遍历边,得到的最小生成树的边数为顶点数-1
let min = 10000, index = 0;
for (let j in cost) {//找到当前最小边
if (cost[j][2] < min) {
index = j;
min = cost[j][2];
}
}
if (this.find(index, cost)) {
this.path.push(cost[index]);
}
cost.splice(index, 1);//删除找到的最小节点
}
}
function find(v, cost) {
for (let i in this.path) {//遍历存储的节点
if (cost[v][1] === this.path[i][0]) {
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
function showKruskal() {
for(let i in this.path){
document.write(this.path[i],"<br>");
}
}
graphA = new Graph(6);
graphA.addEdge(0, 1, 2);
graphA.addEdge(0, 2, 4);
graphA.addEdge(1, 2, 2);
graphA.addEdge(1, 3, 4);
graphA.addEdge(1, 4, 2);
graphA.addEdge(2, 4, 3);
graphA.addEdge(3, 5, 2);
graphA.addEdge(4, 3, 3);
graphA.addEdge(4, 5, 2);
document.write("Show the map:<br>");
graphA.showGraph();
graphA.Kruskal();
document.write("The minimum spanning tree:<br>");
graphA.showKruskal()
本文来自博客园,作者:Patrick-Rex,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/patrickrex/p/18028821

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号