回溯问题
目录
参考资料:回溯算法套路
一、子集型回溯
17.电话号码的字母组合
class Solution {
public:
string mp[10] = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
vector<string> ans;
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
int n = digits.size();
if (n == 0) return {};
string p(n, 0);
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int u) {//当前枚举到第u位
if (u == n) {//枚举到最后一位的后一位,说明选择字符结束,将
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
for (auto c : mp[digits[u] - '0']) {
p[u] = c;//直接覆盖
dfs(u + 1);//枚举下一位
}
};
dfs(0);//从第0位开始枚举
return ans;
}
};
78.子集
思考角度一、考虑每个数选或不选,这样枚举到 \(i\) = \(n\) 时说明所有情况考虑完毕,退出 \(\rm dfs\)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (n == 0) return {};
vector<int> p;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {//枚举第i个数选或不选
if (i == n) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
dfs(i + 1);//不选这个数,直接跳过,枚举下一个数
p.push_back(nums[i]);//选这个数
dfs(i + 1);
p.pop_back();//恢复现场
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
思考角度二、
从答案的角度考虑:枚举第 \(i\) 个位置应该选原数组中的哪个数。(\(i\) 表示枚举的起点)

class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> p;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
ans.push_back(p);
if (i == n) return;//由于i = n时不进入循环,这行可以省略
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
p.push_back(nums[j]);
dfs(j + 1);
p.pop_back();
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
131.分割回文串
思考角度一、假设每对相邻字符之间有个逗号,那么就看每个逗号是选还是不选。
class Solution {
public:
bool is(string a, int l, int r) {
while (l < r) {
if (a[l++] != a[r--]) return false;
}
return true;
}
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
vector<vector<string>> ans;
vector<string> p;
int n = s.size();
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int u) {//i表示起始位置,u表示当前枚举到的位置
if (u == n) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
if (u != n - 1) dfs(i, u + 1);
if (is(s, i, u)) {
p.push_back(s.substr(i, u - i + 1));
dfs(u + 1, u + 1);
p.pop_back();
}
};
dfs(0, 0);
return ans;
}
};
思考角度二、依次枚举每个字串结束(逗号)的具体位置
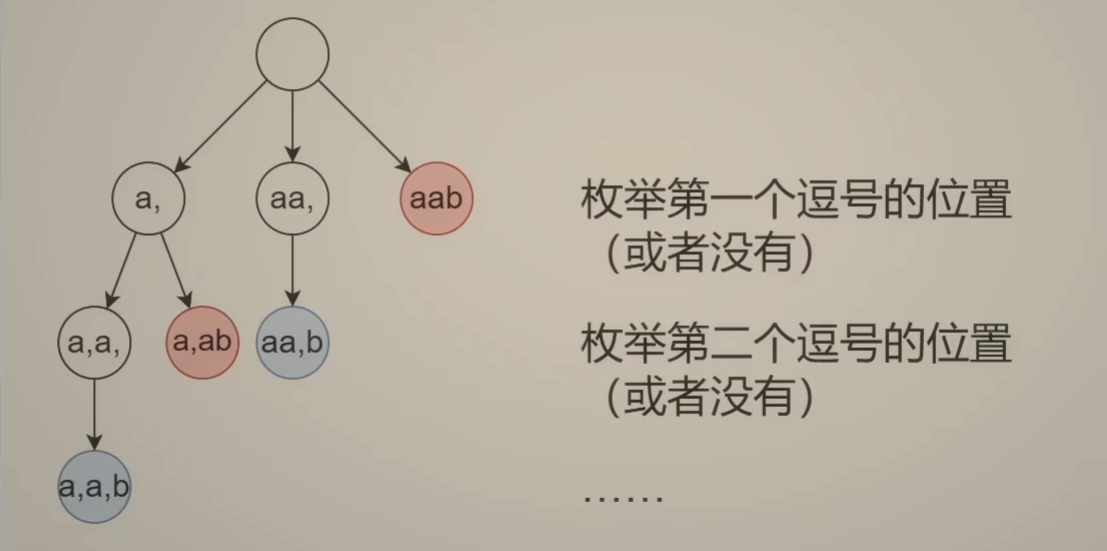
class Solution {
public:
bool is(string a, int l, int r) {
while (l < r) {
if (a[l++] != a[r--]) return false;
}
return true;
}
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
int n = s.size();
vector<vector<string>> ans;
vector<string> p;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (i == n) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
if (is(s, i, j)) {
p.push_back(s.substr(i, j - i + 1));
dfs(j + 1);
p.pop_back();
}
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
257.二叉树的所有路径
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> ans;
void dfs(TreeNode* t, string s) {
if (!t) return;
s += to_string(t->val);
if (t->left == nullptr && t->right == nullptr) {
ans.push_back(s);
return;
}
s += "->";
dfs(t->left, s);
dfs(t->right, s);
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return ans;
dfs(root, "");
return ans;
}
};
784.字母大小写全排列
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> letterCasePermutation(string s) {
int n = s.size();
string p(n, '0');
vector<string> ans;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (i == n) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
p[i] = s[i];
dfs(i + 1);
if (isalpha(s[i])) {
p[i] = s[i] ^ ' ';
dfs(i + 1);
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
LCP 51.烹饪料理
思考角度一、枚举第 \(i\) 个料理选或不选
class Solution {
public:
bool check(vector<vector<int>>& cookbooks, vector<int>& materials, vector<vector<int>>& attribute, int i) {
for (int j = 0; j < materials.size(); j++) {
if (materials[j] < cookbooks[i][j]) return false;
}
return true;
}
int perfectMenu(vector<int>& materials, vector<vector<int>>& cookbooks, vector<vector<int>>& attribute, int limit) {
int n = materials.size();//n = 5,食材种数
int m = cookbooks.size();//料理种数
int ans = -1, feel = 0, taste = 0;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (i == m) {
if (feel >= limit) {
ans = max(ans, taste);
}
return;
}
dfs(i + 1);//不选第i种
if (check(cookbooks, materials, attribute, i)) {//选择第i种
for (int j = 0; j < materials.size(); j++) {
materials[j] -= cookbooks[i][j];
}
feel += attribute[i][1];
taste += attribute[i][0];
dfs(i + 1);
for (int j = 0; j < materials.size(); j++) {
materials[j] += cookbooks[i][j];
}
feel -= attribute[i][1];
taste -= attribute[i][0];
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
思考角度二、从答案的角度,枚举选哪个
class Solution {
public:
bool check(vector<vector<int>>& cookbooks, vector<int>& materials, vector<vector<int>>& attribute, int i) {
for (int j = 0; j < materials.size(); j++) {
if (materials[j] < cookbooks[i][j]) return false;
}
return true;
}
int perfectMenu(vector<int>& materials, vector<vector<int>>& cookbooks, vector<vector<int>>& attribute, int limit) {
int n = materials.size();//n = 5,食材种数
int m = cookbooks.size();//料理种数
int ans = -1, feel = 0, taste = 0;
//枚举未考虑过的每一种料理
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (feel >= limit) {
ans = max(ans, taste);
}
if (i == m) return;//可以省去
for (int k = i; k < m; k++) {
if (check(cookbooks, materials, attribute, k)) {
for (int j = 0; j < materials.size(); j++) {
materials[j] -= cookbooks[k][j];
}
feel += attribute[k][1];
taste += attribute[k][0];
dfs(k + 1);
for (int j = 0; j < materials.size(); j++) {
materials[j] += cookbooks[k][j];
}
feel -= attribute[k][1];
taste -= attribute[k][0];
}
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
二、组合型回溯
77.组合
法一:枚举下一个数选哪个
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> p;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
int d = k - p.size(); //还需要选d个数
if (d == 0) { //选好了
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
if (i < d) return;//也可以去掉这行,直接把循环条件写成j >= d;
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j--) {
p.push_back(j);
dfs(j - 1);
p.pop_back();
}
};
dfs(n);
return ans;
}
};
法二:从选和不选的角度
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> p;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) { // [1, n]
int d = k - p.size();
if (i < d) return;
if (d == 0) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
dfs(i - 1);//不选
p.push_back(i);//选
dfs(i - 1);
p.pop_back();
};
dfs(n);
return ans;
}
};
216.组合总和Ⅲ

法一、从选或不选的角度:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> p;
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int t) {
int d = k - p.size();
if (i < d || t < 0 || t > (i * 2 - d + 1) * d / 2) // 剪枝
return;
if (d == 0) { //当d = 0时,且能走到这说明不满足剪枝条件t < 0 || t > 0,则 t = 0,满足条件。所以无需单独判断t = 0;
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
dfs(i - 1, t);//不选
p.push_back(i);
dfs(i - 1, t - i);//选
p.pop_back();
};
dfs(9, n);
return ans;
}
};
法二、枚举选哪个数
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> p;
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int t) {
int d = k - p.size();
if (i < d || t < 0 || t > (i * 2 - d + 1) * d / 2) // 剪枝
return;
if (d == 0) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j--) {
p.push_back(j);
dfs(j - 1, t - j);
p.pop_back();
}
};
dfs(9, n);
return ans;
}
};
22.括号生成
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {
vector<string> ans;
string p(n * 2, '0');
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int left) -> void {
if (i == n * 2) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
if (left < n) {//可以填左括号
p[i] = '(';
dfs(i + 1, left + 1);//左括号个数+1
}
if (i - left < left) {//i - left为当前右括号个数,当前右括号个数小于左括号个数为合法
p[i] = ')';
dfs(i + 1, left);//左括号个数不变
}
};
dfs(0, 0);
return ans;
}
};
39.组合总和
法一、从选和不选的视角
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> p;
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int t) {
if (t == 0) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
if (i == candidates.size() || t < 0) return;
dfs(i + 1, t);//不选;
p.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(i, t - candidates[i]);//选;i表示当前元素还可以再次选中
p.pop_back();
};
dfs(0, target);
return ans;
}
};
注意:
可以将数组先排序然后剪枝,如果递归中发现 \(\rm left<candidates[i]\),由于后面的数字只会更大,所以无法把 \(\rm left\) 减小到 \(0\),可以直接返回。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> p;
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int t) {
if (t == 0) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
if (i == candidates.size() || t < candidates[i]) return;
dfs(i + 1, t);//不选;
p.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(i, t - candidates[i]);//选;i表示当前元素还可以再次选中
p.pop_back();
};
dfs(0, target);
return ans;
}
};
法二、从枚举答案选哪个的视角
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> p;
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int t) {
if (t == 0) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
if (i == candidates.size() || t < candidates[i]) return;
for (int j = i; j < candidates.size(); j++) {
p.push_back(candidates[j]);
dfs(j, t - candidates[j]);
p.pop_back();
}
};
dfs(0, target);
return ans;
}
};
三、排列型回溯
46.全排列
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> p(n), st(n);
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {//当前枚举到 p 的第几位
if (i == n) {
ans.push_back(p);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {//枚举原数组哪一位使用了
if (!st[j]) {
p[i] = nums[j];
st[j] = true;//j 位的数字被使用了
dfs(i + 1);
st[j] = false;//恢复现场
}
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号