2022/8/15 训练:搜索专栏(包含 Cleaning Robot,Bloxorz I,城市距离)
Cleaning Robot
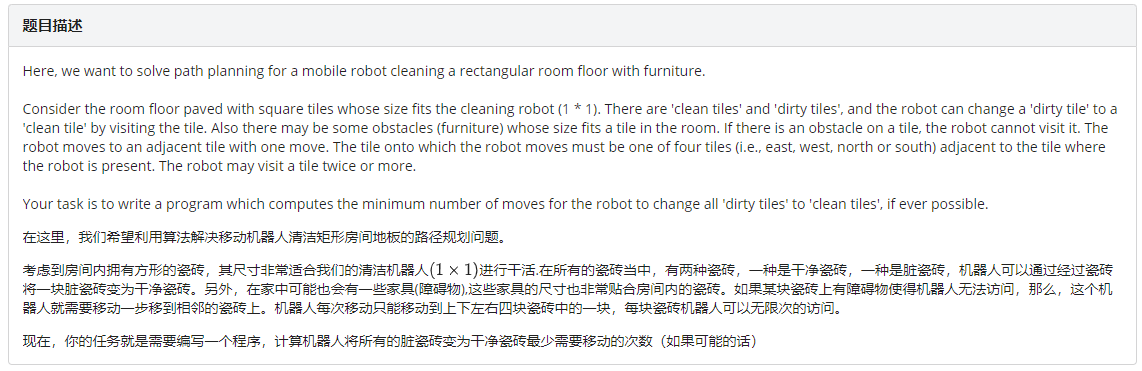
这道题可以先用bfs把任意两个脏点的最小距离算出来,然后利用TSP算出答案。
TSP是什么?详见 百度百科 。
至于这个TSP暴力怎么写,私以为very important。相当于全排列,似乎可以用next_permutation(),再求相邻两个点之间的mp[i-1][i]
模板
void dfs(int t,int sum,int dep) { //当前编号, 当前最小次数 , 已经经过的编号数
if(sum>ans) return;
if(dep==idx+1) {
ans=min(ans,sum);
return;
}
for(int i=1;i<idx;i++) {
if(!f[i]) {
f[i]=1;
dfs(i,sum+mp[t][i],dep+1);//mp是从t到i的最短路径
f[i]=0;
}
}
}
解题步骤:
①:将所有脏地板和起点(置为0号位)存入一个集合
②:跑bfs,计算出集合中两两的最小距离
③:暴力dfs枚举出这个图的所有路径,保存最小值并输出
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int x,y,l;
};
node u,v;
bool f[12];
node P[12];
queue<node> q;
char s[25][25];
int mp[12][12];
int r,c,pk,ans;
int dx[]={1,0,-1,0};
int dy[]={0,1,0,-1};
int fnd(int x,int y)
{
for(int i=0;i<pk;i++)
if(P[i].x==x&&P[i].y==y)
return i;
}
void dfs(int t,int sum,int cur)//当前编号,当前最小次数,已经经过的编号数
{
if(sum>ans) return;
if(cur==pk)
{
if(sum<ans) ans=sum;
return;
}
for(int i=1;i<pk;i++)
if(!f[i])
{
f[i]=1;
dfs(i,sum+mp[t][i],cur+1);
f[i]=0;
}
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d %d",&c,&r)&&c&&r)
{
memset(mp,0x3f,sizeof(mp));
pk=1;
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
{
scanf("%s",s[i]);
for(int j=0;j<c;++j)//将脏地面与起点拉入集合
if(s[i][j]=='o')
P[0].x=i,P[0].y=j,s[i][j]='*';//将起点置为0号位脏地板
else if(s[i][j]=='*')
P[pk].x=i,P[pk++].y=j;
}
for(int i=0;i<pk;i++)//计算以每个脏地板两两之间的距离
{
int f[25][25];
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
u.x=P[i].x,u.y=P[i].y,u.l=0;
q.push(u);
f[u.x][u.y]=1;
int cnt=pk;
while(!q.empty()&&cnt)
{
u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int j=0;j<4&&cnt;++j)
{
int xx,yy;
xx=u.x+dx[j],yy=u.y+dy[j];
if(xx<0||xx>=r||yy<0||yy>=c||s[xx][yy]=='x'||f[xx][yy])
continue;
if(s[xx][yy]=='*')
{
cnt--;
mp[i][fnd(xx,yy)]=u.l+1;//xx,yy在几号位
}
f[xx][yy]=1;
v.x=xx,v.y=yy,v.l=u.l+1;
q.push(v);
}
}
while(!q.empty())
q.pop();
}
ans=0x3f3f3f3f;
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
dfs(0,0,1);
if(ans==0x3f3f3f3f||ans==0)
ans=-1;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
Bloxorz I
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
题目描述
Bloxorz是一个风靡世界的小游戏。Bloxorz的地图是一个N行M列的矩阵,每个位置可能是硬地(用.表示)、易碎地面(用E表示)、禁地(用#表示)、起点(用X表示)或终点(用O表示)。
你的任务是操作一个112的长方体。这个长方体在地面上有两种放置形式,“立”在地面上(11的面接触地面)或者“躺”在地面上(12的面接触地面)。在每一步操作中,可以按上下左右四个键之一。按下之后,长方体向对应的方向沿着棱滚动90度。任意时刻,长方体不能有任何部位接触禁地(否则就会掉下去),并且不能立在易碎地面上(否则会因为压强太大掉下去)。X标识长方体的起始位置,地图上可能有一个X或者两个相邻的X。地图上唯一的一个O标识目标位置。求把长方体移动到目标位置(即立在O上)所需要的最少步数。如果无解,输出Impossible。在移动过程中,X和O标识的位置都可以看作是硬地被利用,3<=N,M<=500。

这个盒子放在一个单元上

盒子水平放置在两个相邻的单元上

The box lies on two neighbouring cells, vertically
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
图片来自:@ WA_自动机

#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct State
{
int x,y,lie;
};
const int N = 510;
int n,m;
char g[N][N];
int dist[N][N][3];
bool check(int x,int y)
{
if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m) return false;
return g[x][y]!='#';
}
int bfs(State start,State end)
{
int d[3][4][3]={ //看着很唬人
{{-2, 0, 2}, {0, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 2}, {0, -2, 1}},
{{-1, 0, 1}, {0, 2, 0}, {1, 0, 1}, {0, -1, 0}},
{{-1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 2}, {2, 0, 0}, {0, -1, 2}}
};
queue<State> q;
q.push(start);
memset(dist,-1,sizeof dist);
dist[start.x][start.y][start.lie]=0;
while(q.size())
{
State t=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
//t.lie为当前状态。如果t.lie==0,那么就枚举d数组的第一排
State next={t.x+d[t.lie][i][0],t.y+d[t.lie][i][1],d[t.lie][i][2]};//那一排,那一坨中的哪一个
int x=next.x, y=next.y;
if(!check(x,y)) continue;
if(next.lie==0 && g[x][y]=='E') continue;//立着不能立在易碎地面上
if(next.lie==1 && !check(x,y+1)) continue;//横着的下一个是否满足
if(next.lie==2 && !check(x+1,y)) continue;//竖着的下一个是否满足
if(dist[next.x][next.y][next.lie]==-1)//相当于一个bool数组,看这个点是否搜过
{
dist[next.x][next.y][next.lie]=dist[t.x][t.y][t.lie]+1;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
return dist[end.x][end.y][end.lie];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%s",g[i]);
State start={-1,0,0},end;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
if(g[i][j]=='X'&&start.x==-1)
{
//初始的状态
if(g[i+1][j]=='X') start={i,j,2};
else if(g[i][j+1]=='X') start={i,j,1};
else start={i,j,0};
}
else if(g[i][j]=='O') end={i,j,0};
int res=bfs(start,end);
if(res==-1) puts("Impossible");
else printf("%d\n",res);
return 0;
}
城市距离
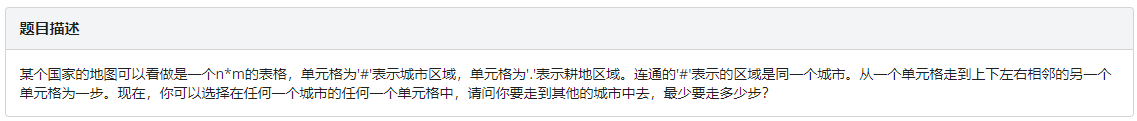
我们可以把联通的一个城市看作同一个起点。整个过程相当于是确定起点,寻找终点的过程。
解题步骤:
①:遍历整个地图,用dfs找到一个连通块里的所有城市
②:当作起点压入队列,进行bfs,当第一次搜到'#',停止,比较答案
③:继续找下一个城市
Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int Maxn = 5e2 + 5;
const int zx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, zy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n, m, ans = 1e6;
char c[Maxn][Maxn];
bool vis[Maxn][Maxn];
struct node {
int x, y, step;
};
queue<node> q;
void dfs(int x, int y) {
c[x][y] = 'A';
q.push((node){x, y, 0});
for(int i = 0;i < 4; ++i) {
int dx = x + zx[i], dy = y + zy[i];
if(dx >= 1 and dy >= 1 and dx <= n and dy <= m and c[dx][dy] == '#') dfs(dx, dy);
}
}
void bfs() {
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
while(!q.empty()) {
node p = q.front();
q.pop();
if(c[p.x][p.y] == '#') {
ans = min(ans, p.step);
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
return ;
}
for(int i = 0;i < 4; ++i) {
int dx = p.x + zx[i], dy = p.y + zy[i];
if(dx >= 1 and dy >= 1 and dx <= n and dy <= m and !vis[dx][dy] and c[dx][dy] != 'A') {
vis[dx][dy] = 1;
q.push((node){dx, dy, p.step + 1});
}
}
}
}
int main() {
freopen("city.in","r",stdin);
freopen("city.out","w",stdout);
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++i) scanf("%s", c[i] + 1);
for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++i)
for(int j = 1;j <= m; ++j) {
if(c[i][j] == '#') {
dfs(i, j);
bfs();
}
}
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
本文来自博客园,作者:Doria_tt,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/pangtuan666/p/16587472.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号