最近处理的一些函数
一、文本预处理
句子分割text_to_word_sequence,将一个句子拆分成单词构成的列表。注意这个函数对中文的分割无效。
from tensorflow import keras text='你去哪里了?我找不到你,快回电话,where are you,mary?can you call me back?' words=keras.preprocessing.text.text_to_word_sequence(text, filters='!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~\t\n', lower=True, split=" ")

参数:
-
text:字符串,待处理的文本
-
filters:需要滤除的字符的列表或连接形成的字符串,例如标点符号。默认值为 '!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[]^_`{|}~\t\n',包含标点符号,制表符和换行符等
-
lower:布尔值,是否将序列设为小写形式
-
split:字符串,单词的分隔符,如空格
返回值:字符串列表
one-hot编码
n=13 words=keras.preprocessing.text.one_hot(text, n, filters='!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~\t\n', lower=True, split=" ") print(words)
![]()
数将一段文本编码为one-hot形式的码,即仅记录词在词典中的下标。
【Tips】 从定义上,当字典长为n时,每个单词应形成一个长为n的向量,其中仅有单词本身在字典中下标的位置为1,其余均为0,这称为one-hot。
为了方便起见,函数在这里仅把“1”的位置,即字典中词的下标记录下来。
参数
- n:整数,字典长度
返回值
整数列表,每个整数是[1,n]之间的值,代表一个单词(不保证唯一性,即如果词典长度不够,不同的单词可能会被编为同一个码)。
分词器Tokenizer(类)
keras.preprocessing.text.Tokenizer(num_words=None, filters='!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~\t\n', lower=True, split=" ", char_level=False)
Tokenizer是一个用于向量化文本,或将文本转换为序列(即单词在字典中的下标构成的列表,从1算起)的类。
构造参数
-
与
text_to_word_sequence同名参数含义相同 -
num_words:None或整数,处理的最大单词数量。若被设置为整数,则分词器将被限制为待处理数据集中最常见的
num_words个单词 -
char_level: 如果为 True, 每个字符将被视为一个标记
类方法
-
fit_on_texts(texts)
- texts:要用以训练的文本列表
-
texts_to_sequences(texts)
-
texts:待转为序列的文本列表
-
返回值:序列的列表,列表中每个序列对应于一段输入文本
-
-
texts_to_sequences_generator(texts)
-
本函数是
texts_to_sequences的生成器函数版 -
texts:待转为序列的文本列表
-
返回值:每次调用返回对应于一段输入文本的序列
-
-
texts_to_matrix(texts, mode):
-
texts:待向量化的文本列表
-
mode:‘binary’,‘count’,‘tfidf’,‘freq’之一,默认为‘binary’
-
返回值:形如
(len(texts), nb_words)的numpy array
-
-
fit_on_sequences(sequences):
- sequences:要用以训练的序列列表
-
sequences_to_matrix(sequences):
-
sequences:待向量化的序列列表
-
mode:‘binary’,‘count’,‘tfidf’,‘freq’之一,默认为‘binary’
-
返回值:形如
(len(sequences), nb_words)的numpy array
-
属性
- word_counts:字典,将单词(字符串)映射为它们在训练期间出现的次数。仅在调用fit_on_texts之后设置。
- word_docs: 字典,将单词(字符串)映射为它们在训练期间所出现的文档或文本的数量。仅在调用fit_on_texts之后设置。
- word_index: 字典,将单词(字符串)映射为它们的排名或者索引。仅在调用fit_on_texts之后设置。
- document_count: 整数。分词器被训练的文档(文本或者序列)数量。仅在调用fit_on_texts或fit_on_sequences之后设置。
text=['你去哪里了?我找不到你,快回电话,Where are you,mary?can you call me back?',\ 'Ming and Hong are playing game in the yard.Hey,what are you doing,赵薇?'] vocab_size =10 # This is a hyperparameter, experiment with different values for your dataset tokenize = keras.preprocessing.text.Tokenizer(num_words=vocab_size, char_level=False) tokenize.fit_on_texts(text) # only fit on train #print(tokenize.word_counts) #print(tokenize.word_docs) #print(tokenize.word_index) #print(tokenize.document_count) #注意看tokenize分词的结果 #sparse bag of words (bow) vocab_size vector description_bow_text = tokenize.texts_to_matrix(text) # #texts_to_matrix(texts, mode): #texts:待向量化的文本列表 #mode:‘binary’,‘count’,‘tfidf’,‘freq’之一,默认为‘binary’ #返回值:形如(len(texts), nb_words)的numpy array print("分词结果:\n",tokenize.word_counts,"\n") print("description_bow_text.shape:\n",description_bow_text.shape,"\n") print("description_bow_text:\n",description_bow_text,"\n")

二、keras.utils
to_categorical
to_categorical(y, num_classes=None)
将类别向量(从0到nb_classes的整数向量)映射为二值类别矩阵, 用于应用到以categorical_crossentropy为目标函数的模型中.
参数
- y: 类别向量
- num_classes:总类别数
应用对属性数据的特征作处理:
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder import numpy as np country=['US','US','UK','UK','UK','China','China','Korea'] to_number=LabelEncoder() to_number.fit(country) country=to_number.transform(country) country_num=np.max(country)+1 print(country_num) print(country)
![]()
from tensorflow import keras country=keras.utils.to_categorical(country, num_classes=country_num) print(country)
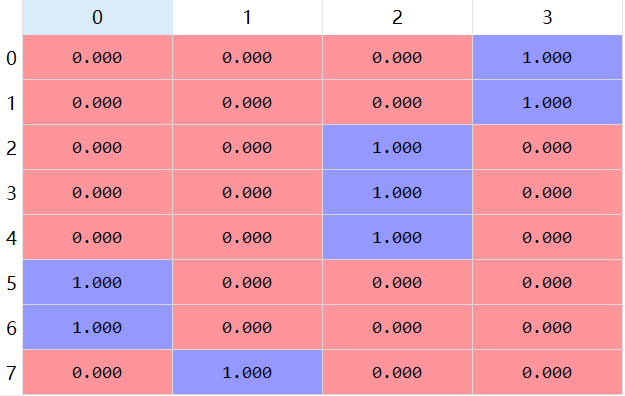
三、




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号