(六)STL序列容器(list)
list: 底层实现为双向链表
1、基本用法
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// list:双向链表
void ShowPrint(list<int> d)
{
for (list<int>::iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
list<int>val;
val.push_back(1);
val.push_back(9);
val.push_back(5);
val.sort();
ShowPrint(val);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
访问元素
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
/*
访问:不支持随机访问
未提供[]、at()、data()成员函数
*/
int main()
{
// 可以通过front和back访问
list<int> a{ 1,2,3,4 };
int& first = a.front();
int& last = a.back();
cout << first << " " << last << endl;
first = 90;
last = 80;
cout << first << " " << last << endl;
// 访问其他元素,只能通过迭代器
list<int>b{ 1,2,3,4 };
auto it = b.begin();
cout << *it << endl;
++it;
while (it != b.end()) {
cout << *it << endl;
++it;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
删除元素
#include <iostream> #include <list> using namespace std; void ShowPrint(list<int> a) { for (auto i = a.begin(); i != a.end(); i++) { cout << *i << " "; } cout << endl; } /* erase():根据被删除元素所在的下标位置来进行删除 remove():根据元素的值删除 */ int main() { list<int>val{ 1,22,3,4 }; auto del = val.begin(); ++del; val.erase(del); ShowPrint(val); val.remove(3); ShowPrint(val); system("pause"); return 0; }

2、迭代器失效
list:插入(insert)、接合(splice())都不会造成原有的迭代器失效,甚至进行删除操作,只有指向被删除元素的迭代器失效,其它迭代器不受任何影响;
进行插入后,仍然使用先前创建的迭代器遍历,程序不出错,但是插入的位置不同,可能会遗漏新插入的元素
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// list:双向链表
void ShowPrint(list<int> d)
{
for (list<int>::iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
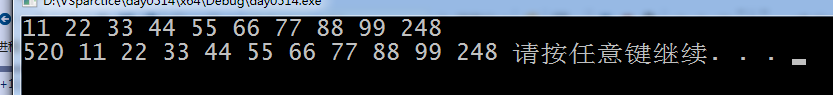
list<int> x {11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99};
// 创建begin和end迭代器
list<int>::iterator begin = x.begin();
list<int>::iterator end = x.end();
// 头部和尾部插入字符w
x.insert(begin, 520); // 漏掉显示
x.insert(end, 248);
while (begin != end) {
cout << *begin<<" ";
++begin;
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator b1 = x.begin();
list<int>::iterator b2 = x.end();
while (b1 != b2) {
cout << *b1 << " ";
++b1;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
做一个优秀的程序媛


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号