(四)STL序列容器(vector)
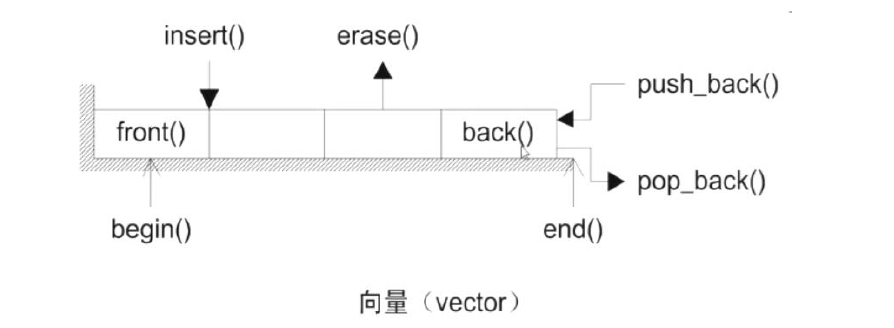
array:静态数组,容量固定的数组
vector:动态数组,可以进行插入和删除(向量容器)
初始化
(1) vector<double> val;
容器内没有元素,当添加第一个元素时,vector会自动分配内存
(2) vector<int> val{2,23,21,26,8};
在创建的同时指定初始值
(3) vector<int> val(10);
在创建的同时指定元素个数
(4) vecror<int> val(10, 3);
不想用0为默认值,可以指定默认值
{}和()的区别,()表示个数,{}表示元素
总结使用
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <vector> using namespace std; void ShowPrint(vector<int> v1) { cout<<"显示: "; for(int i=0; i<v1.size(); i++) { cout<<v1[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } int main() { vector<int> v1; // 尾部添加元素 v1.push_back(1); v1.push_back(2); v1.push_back(3); ShowPrint(v1); // 任意位置插入元素 v1.insert(v1.begin(), 0); // 头部插入 v1.insert(v1.begin(), -1); // 头部插入 v1.insert(v1.end(), 4); // 尾部插入 v1.insert(v1.end()-1, 666); // 倒数第二个位置插入 ShowPrint(v1); // 删除尾部元素 v1.pop_back(); ShowPrint(v1); // 删除任意元素 v1.erase(v1.begin()); ShowPrint(v1); // 全部删除 v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 相当于v1.clear() ShowPrint(v1); return 0; }
基本用法
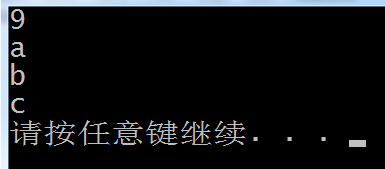
1.基本用法
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<char> v1;
v1.push_back('a');
v1.push_back('b');
v1.push_back('c');
v1.insert(v1.begin(), '9');
for (auto i = v1.begin(); i < v1.end(); i++) {
cout << *i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 1;
}
2.遍历成员
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 初始化
vector<int> v{ 11,22,33,44,55 };
auto first = v.begin();
auto end = v.end();
while (first != end) {
cout << *first << endl;
++first;
}
system("pause");
return 1;
}

3.访问元素
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 初始化
vector<int> v{ 11,22,33,44,55 };
auto first = v.begin();
auto end = v.end();
cout << "v的首个元素的地址:" << v.data() << endl;
// 增加v的容量之后,首个元素的存储地址发生了改变
// 为保险起见,对之前的迭代器重新初始化一遍
v.reserve(20);
cout << "v的首个元素的地址:" << v.data() << endl;
first = v.begin();
end = v.end();
while (first != end) {
cout << *first << endl;
++first;
}
cout << "-------------------------访问单个元素---------" << endl;
cout << "front: " << v.front() << endl;
cout << "back: " << v.back() << endl;
cout << "v[]: " << v[3] << endl;
cout << "data(): " << *(v.data() + 1) << endl;
cout << "\n改值:\n\n";
v.front() = 99;
v.back() = 88;
v[3] = 77;
*(v.data() + 1) = 66;
cout << "front: " << v.front() << endl;
cout << "back: " << v.back() << endl;
cout << "v[]: " << v[3] << endl;
cout << "data(): " << *(v.data() + 1) << endl;
cout << "-------------------------访问多个元素---------" << endl;
// 四种遍历方式
vector<int> v1{ 11,21,31,41,51,61 };
cout << "size 遍历:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) {
cout << v1[i] << endl;
}
cout << "auto& 遍历:\n";
for (auto& a : v1) {
cout << a << endl;
}
cout << "auto&& 遍历:\n";
for (auto&& a : v1) {
cout << a << endl;
}
cout << "begin/end 遍历:\n";
for (auto a = v1.begin(); a < v1.end(); a++) {
cout << *a << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 1;
}

4.容器大小
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
/*
(1)capacity:
在不分配更多内存的情况下,容器可以保存的最多元素个数
(2)size:
实际所包含的元素个数
*/
int main()
{
vector<int> a{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };
cout << a.capacity() << endl;
cout << a.size() << endl;
a.reserve(20);
cout << a.capacity() << endl;
cout << a.size() << endl;
system("pause");
return 1;
}

#include <iostream>#include <stdio.h>#include <vector>using namespace std;
void ShowPrint(vector<int> v1){ cout<<"显示: "; for(int i=0; i<v1.size(); i++) { cout<<v1[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl;}
int main(){ vector<int> v1;
// 尾部添加元素 v1.push_back(1); v1.push_back(2); v1.push_back(3); ShowPrint(v1);
// 任意位置插入元素 v1.insert(v1.begin(), 0); // 头部插入 v1.insert(v1.begin(), -1); // 头部插入 v1.insert(v1.end(), 4); // 尾部插入 v1.insert(v1.end()-1, 666); // 倒数第二个位置插入 ShowPrint(v1);
// 删除尾部元素 v1.pop_back(); ShowPrint(v1);
// 删除任意元素 v1.erase(v1.begin()); ShowPrint(v1);
// 全部删除 v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 相当于v1.clear() ShowPrint(v1); return 0;}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号