golang 中 mmap 的使用
-----------------------
https://www.jianshu.com/p/964b887da04c
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"syscall"
)
const maxMapSize = 0x8000000000
const maxMmapStep = 1 << 30 // 1GB
func main() {
file, err := os.OpenFile("my.db", os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE, 0644)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer file.Close()
stat, err := os.Stat("my.db")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
size, err := mmapSize(int(stat.Size()))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println("size:", size)
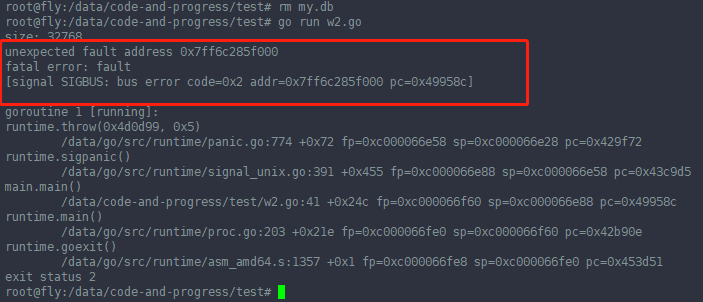
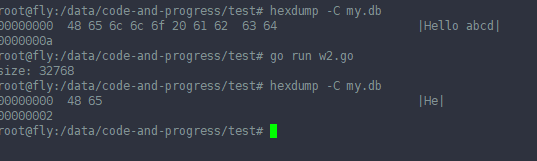
//// 没有下面这句,将会报错
//err = syscall.Ftruncate(int(file.Fd()), 2) //第一种改法, truncate() 这里的2,表示会将参数fd指定的文件大小改为参数length指定的大小
//if err != nil {
// panic(err)
//}
// 第二种改法,对文件执行一下write , 或者WriteAt
file.Write(make([]byte, 10)) // 这里的10, 表示文件大小限定为10了, 后面超多10的写不进(打开文件时,字符e没有)。
b, err := syscall.Mmap(int(file.Fd()), 0, 100, syscall.PROT_WRITE|syscall.PROT_READ, syscall.MAP_SHARED)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
for index, bb := range []byte("Hello abcde") {
b[index] = bb
}
err = syscall.Munmap(b)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
func mmapSize(size int) (int, error) {
// Double the size from 32KB until 1GB.
for i := uint(15); i <= 30; i++ {
if size <= 1<<i {
return 1 << i, nil
}
}
// Verify the requested size is not above the maximum allowed.
if size > maxMapSize {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("mmap too large")
}
// If larger than 1GB then grow by 1GB at a time.
sz := int64(size)
if remainder := sz % int64(maxMmapStep); remainder > 0 {
sz += int64(maxMmapStep) - remainder
}
// Ensure that the mmap size is a multiple of the page size.
// This should always be true since we're incrementing in MBs.
pageSize := int64(os.Getpagesize())
if (sz % pageSize) != 0 {
sz = ((sz / pageSize) + 1) * pageSize
}
// If we've exceeded the max size then only grow up to the max size.
if sz > maxMapSize {
sz = maxMapSize
}
return int(sz), nil
}
另外一个例子:https://gist.github.com/suyash/a19b7f91000b24fde4bc4a015680c611
write.go
package main
import (
"os"
"syscall"
)
func main() {
filename, offset, length := "testgo.out", 10, 20
f, err := os.Create(filename)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
f.Write(make([]byte, length))
fd := int(f.Fd())
b, err := syscall.Mmap(fd, 0, length, syscall.PROT_READ|syscall.PROT_WRITE, syscall.MAP_SHARED)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
b[offset-1] = 'x'
err = syscall.Munmap(b)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
reader.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"syscall"
)
func main() {
filename, offset := "main.c", 10
f, err := os.Open(filename)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fd := int(f.Fd())
stat, err := f.Stat()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
size := int(stat.Size())
b, err := syscall.Mmap(fd, 0, size, syscall.PROT_READ, syscall.MAP_SHARED)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%c\n", b[offset-1])
err = syscall.Munmap(b)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
reader.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
int main () {
const char* filename = "main.c";
int offset = 10;
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
printf("cannot open %s\n", filename);
return -1;
}
struct stat sbuf;
if (stat(filename, &sbuf) == -1) {
printf("cannot stat %s\n", filename);
return -1;
}
int size = sbuf.st_size;
char* data = mmap((caddr_t)0, size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (data == -1) {
printf("cannot mmap %s\n", filename);
return -1;
}
printf("byte at offset %d is %c\n", offset, data[offset - 1]);
int err = munmap(data, size);
if (err == -1) {
printf("cannot munmap %s\n", filename);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
----------------------
最近工作中在研究Hyperledger Fabric区块链开源项目,其中区块链peer节点底层使用了leveldb作为State Database的存储介质,出于好奇,决定对一些常用的KV存储做一些研究。
这一次我主要对2种KV存储的源码做了分析,一个是BoltDB,这是LMDB的Go语言版本,另一个就是goleveldb。
在阅读BoltDB项目源码的过程中,我发现它将持久化文件以只读模式通过mmap映射到内存空间中,然后通过索引找到内存中key对应的value所指向的空间,然后将这段内存返回给用户。之前虽然也听说过内存映射文件技术,但一直没有实际使用过,因此这一次我决定对mmap做一些尝试,以下是这次尝试的过程。
文件写入
内存映射文件(Memory-mapped file)将一段虚拟内存逐字节对应于一个文件或类文件的资源,使得应用程序处理映射部分如同访问主存,用于增加I/O性能。Mmap函数存在于Go's syscall package中,它接收一个文件描述符,需要映射的大小(返回的切片容量)以及需要的内存保护和映射类型。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"syscall"
)
const maxMapSize = 0x8000000000
const maxMmapStep = 1 << 30 // 1GB
func main() {
file, err := os.OpenFile("my.db", os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE, 0644)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer file.Close()
stat, err := os.Stat("my.db")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
size, err := mmapSize(int(stat.Size()))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
b, err := syscall.Mmap(int(file.Fd()), 0, size, syscall.PROT_WRITE|syscall.PROT_READ, syscall.MAP_SHARED)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
for index, bb := range []byte("Hello world") {
b[index] = bb
}
err = syscall.Munmap(b)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
func mmapSize(size int) (int, error) {
// Double the size from 32KB until 1GB.
for i := uint(15); i <= 30; i++ {
if size <= 1<<i {
return 1 << i, nil
}
}
// Verify the requested size is not above the maximum allowed.
if size > maxMapSize {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("mmap too large")
}
// If larger than 1GB then grow by 1GB at a time.
sz := int64(size)
if remainder := sz % int64(maxMmapStep); remainder > 0 {
sz += int64(maxMmapStep) - remainder
}
// Ensure that the mmap size is a multiple of the page size.
// This should always be true since we're incrementing in MBs.
pageSize := int64(os.Getpagesize())
if (sz % pageSize) != 0 {
sz = ((sz / pageSize) + 1) * pageSize
}
// If we've exceeded the max size then only grow up to the max size.
if sz 

