SpringBoot(一)
SpringBoot(一)
1、简介
Spring是如何简化Java开发的
为了降低Java开发的复杂性,Spring采用了以下4种关键策略:
- 基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程,所有东西都是bean;
- 通过IOC,依赖注入(DI)和面向接口实现松耦合;
- 基于切面(AOP)和惯例进行声明式编程;
- 通过切面和模版减少样式代码,RedisTemplate,xxxTemplate;
什么是SpringBoot
Spring Boot 基于 Spring 开发,Spirng Boot 本身并不提供 Spring 框架的核心特性以及扩展功能,只是用于快速、敏捷地开发新一代基于 Spring 框架的应用程序。也就是说,它并不是用来替代 Spring 的解决方案,而是和 Spring 框架紧密结合用于提升 Spring 开发者体验的工具。Spring Boot 以约定大于配置的核心思想,默认帮我们进行了很多设置,多数 Spring Boot 应用只需要很少的 Spring 配置。同时它集成了大量常用的第三方库配置(例如 Redis、MongoDB、Jpa、RabbitMQ、Quartz 等等),Spring Boot 应用中这些第三方库几乎可以零配置的开箱即用。

什么是微服务架构?
2、第一个SpringBoot程序
创建项目方式一:使用Spring Initializr 的 Web页面创建项目
- 打开 https://start.spring.io/
- 填写项目信息
- 点击”Generate Project“按钮生成项目;下载此项目
- 解压项目包,并用IDEA以Maven项目导入,一路下一步即可,直到项目导入完毕。
- 如果是第一次使用,可能速度会比较慢,包比较多、需要耐心等待一切就绪。
创建项目方式二:使用IDEA直接创建项目
- 创建一个新项目
- 选择spring initalizr , 可以看到默认就是去官网的快速构建工具那里实现
- 填写项目信息
- 选择初始化的组件(初学勾选 Web 即可)
- 填写项目路径
- 等待项目构建成功
pom.xml分析
<!-- 父依赖 -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- web场景启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<!-- 剔除依赖 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 打包插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
编写一个Http接口
-
在主程序的同级目录下,新建一个controller包,一定要在同级目录下,否则识别不到
-
在包中新建一个HelloController类
@RestController public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "Hello World"; } } -
编写完毕后,从主程序启动项目,浏览器发起请求,看页面返回;控制台输出了 Tomcat 访问的端口号!
彩蛋
到项目下的 resources 目录下新建一个banner.txt 即可。
图案可以到:https://www.bootschool.net/ascii 这个网站生成,然后拷贝到文件中即可!

3、运行原理初探
pom.xml
-
父依赖
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent>点进去,发现还有一个父依赖
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version> <relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath> </parent>这里才是真正管理SpringBoot应用里面所有依赖版本的地方,SpringBoot的版本控制中心
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;但是如果导入的包没有在依赖中管理着就需要手动配置版本了
-
启动器 spring-boot-starter
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>springboot-boot-starter-xxx:就是spring-boot的场景启动器
spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter (启动器),只需要在项目中引入这些starter即可,所有相关的依赖都会导入进来 , 我们要用什么功能就导入什么样的场景启动器即可 ;我们未来也可以自己自定义 starter
主启动类
-
默认的主启动类
//@SpringBootApplication : 标注这个类是一个springboot的应用 @SpringBootApplication public class Springboot01HelloworldApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //将springboot应用启动 SpringApplication.run(Springboot01HelloworldApplication.class, args); } } -
@SpringBootApplication
作用:标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类 , SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用
进入这个注解:可以看到上面还有很多其他注解!
@SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan( excludeFilters = {@Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} ), @Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class} )} ) public @interface SpringBootApplication { // ...... } -
@ComponentScan
这个注解在Spring中很重要 ,它对应XML配置中的元素。
作用:自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean , 将这个bean定义加载到IOC容器中
-
@SpringBootConfiguration
作用:SpringBoot的配置类 ,标注在某个类上 , 表示这是一个SpringBoot的配置类;
我们继续进去这个注解查看
// 点进去得到下面的 @Component @Configuration public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {} @Component public @interface Configuration {}这里的 @Configuration,说明这是一个配置类 ,配置类就是对应Spring的xml 配置文件;
里面的 @Component 这就说明,启动类本身也是Spring中的一个组件而已,负责启动应用!
我们回到 SpringBootApplication 注解中继续看。
-
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能
以前我们需要自己配置的东西,而现在SpringBoot可以自动帮我们配置 ;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能,这样自动配置才能生效
点进注解接续查看
-
@AutoConfigurationPackage :自动配置包
@Import({Registrar.class}) public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage { } -
@import:Spring底层注解@import , 给容器中导入一个组件
Registrar.class 作用:将主启动类的所在包及包下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器 ;
这个分析完了,退到上一步,继续看
-
**@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) :给容器导入组件 **
AutoConfigurationImportSelector :自动配置导入选择器,那么它会导入哪些组件的选择器呢?我们点击去这个类看源码
这个类中有一个这样的方法
// 获得候选的配置 protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { //这里的getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()方法 //返回的就是我们最开始看的启动自动导入配置文件的注解类;EnableAutoConfiguration List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }这个方法又调用了 SpringFactoriesLoader 类的静态方法!我们进入SpringFactoriesLoader类loadFactoryNames() 方法
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); //这里它又调用了 loadSpringFactories 方法 return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList()); }我们继续点击查看 loadSpringFactories 方法
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { //获得classLoader , 我们返回可以看到这里得到的就是EnableAutoConfiguration标注的类本身 MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } else { try { //去获取一个资源 "META-INF/spring.factories" Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); //将读取到的资源遍历,封装成为一个Properties while(urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next(); String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim(); String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()); int var10 = var9.length; for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) { String factoryName = var9[var11]; result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim()); } } } cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException var13) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13); } } }发现一个多次出现的文件:spring.factories,全局搜索它
spring.factories
我们根据源头打开spring.factories , 看到了很多自动配置的文件;这就是自动配置根源所在!
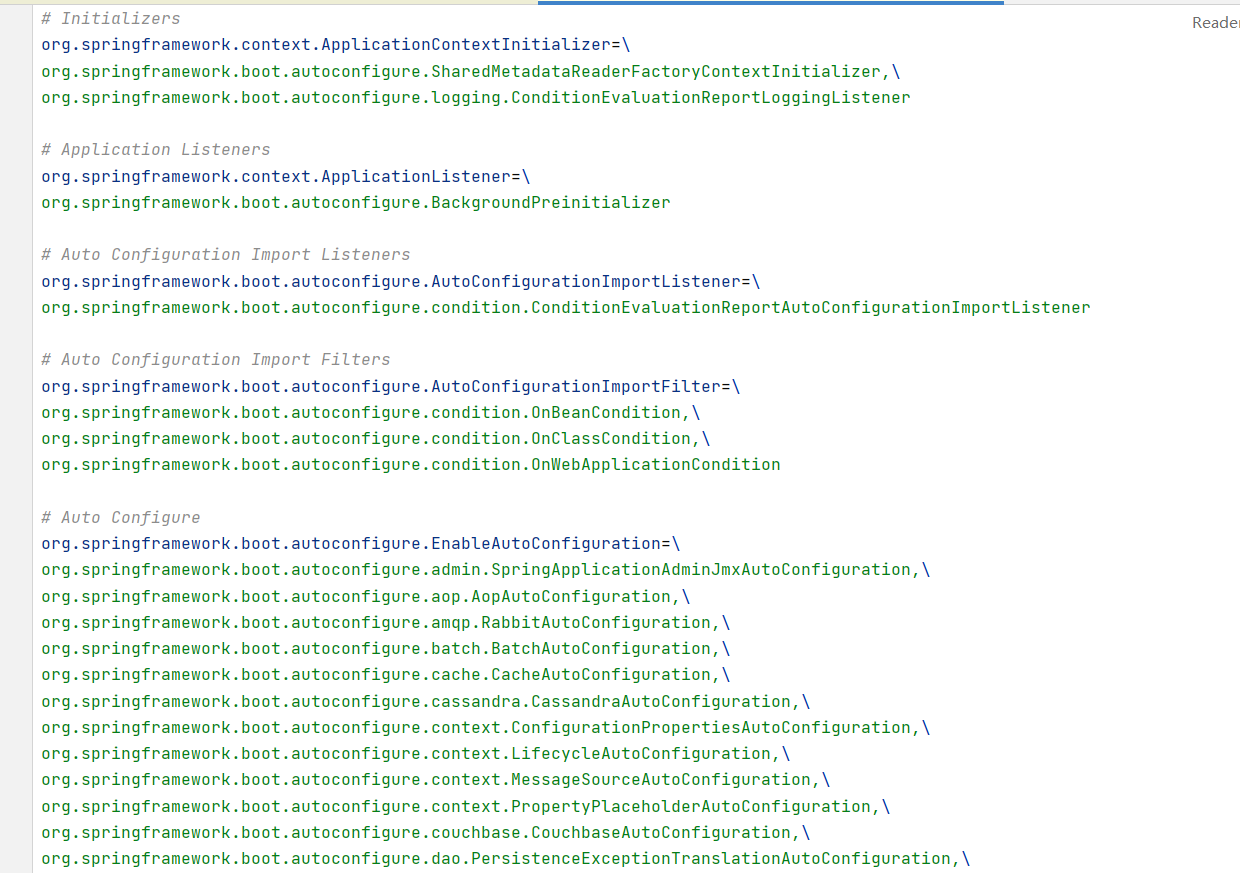
-
WebMvcAutoConfiguration
我们在上面的自动配置类随便找一个打开看看,比如 :WebMvcAutoConfiguration
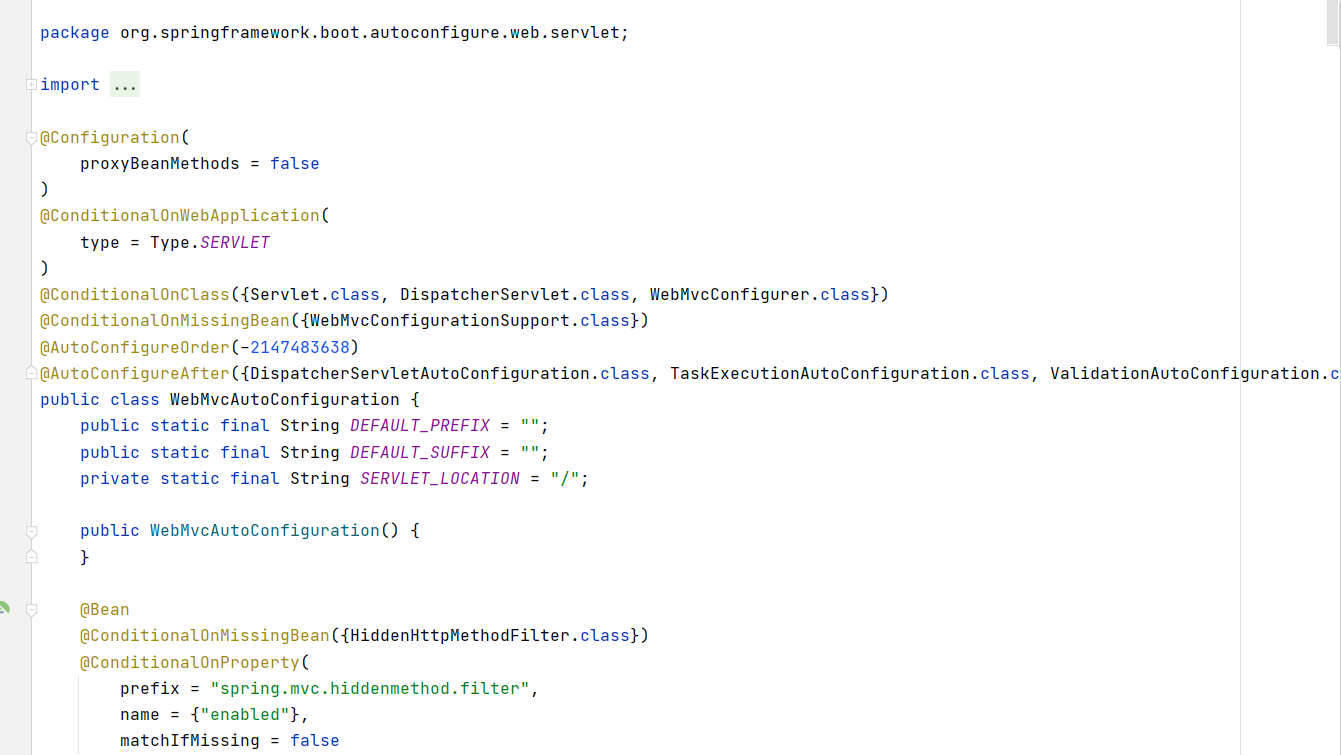
可以看到这些一个个的都是JavaConfig配置类,而且都注入了一些Bean
所以,自动配置真正实现是从classpath中搜寻所有的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件 ,并将其中对应的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure. 包下的配置项,通过反射实例化为对应标注了 @Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IOC容器配置类 , 然后将这些都汇总成为一个实例并加载到IOC容器中。
结论:
- SpringBoot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值
- 将这些值作为自动配置类导入容器 , 自动配置类就生效 , 帮我们进行自动配置工作
- 整个J2EE的整体解决方案和自动配置都在springboot-autoconfigure的jar包中
- 它会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类 (xxxAutoConfiguration), 就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件 , 并配置好这些组件
- 有了自动配置类 , 免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作
SpringApplication
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
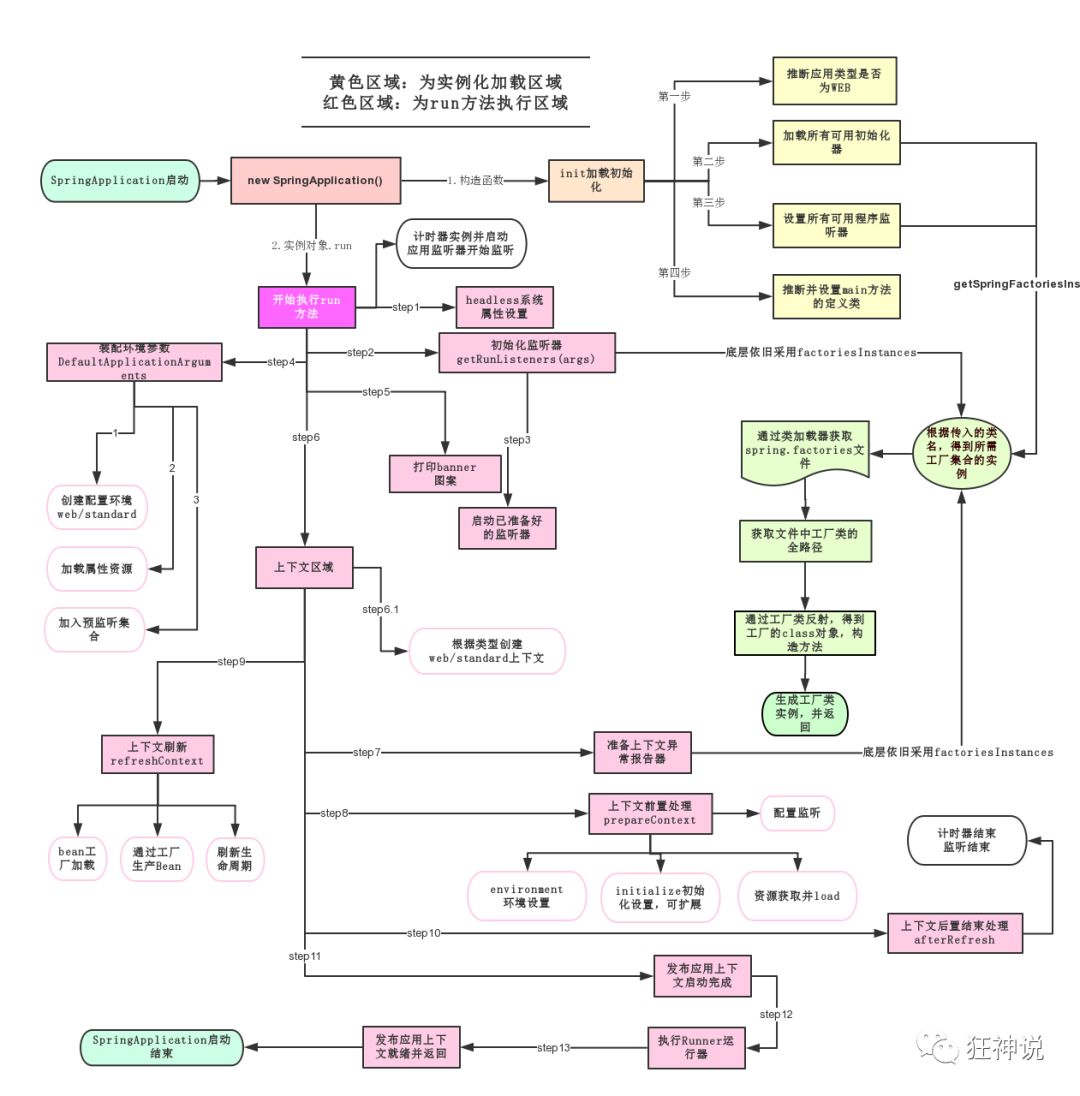
SpringApplication.run分析
分析该方法主要分两部分,一部分是SpringApplication的实例化,二是run方法的执行
这个类主要做了以下四件事情
1、推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
2、查找并加载所有可用初始化器 , 设置到initializers属性中
3、找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
4、推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
查看构造器:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
// ......
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances();
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
run方法流程分析
4、yaml配置
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件 , 配置文件名称是固定的
- application.properties
- 语法结构 :key=value
- application.yml
- 语法结构 :key:空格 value
配置文件的作用 :修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值,因为SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好了
比如我们可以在配置文件中修改Tomcat 默认启动的端口号!测试一下!
server.port=8081
1. yaml概述
这种语言以数据作为中心,而不是以标记语言为重点!
以前的配置文件,大多数都是使用xml来配置;比如一个简单的端口配置,我们来对比下yaml和xml
传统xml配置:
<server>
<port>8081<port>
</server>
yaml配置:
server:
prot: 8080
2. yaml基础语法
说明:语法要求严格!
- 空格不能省略
- 以缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的。
- 属性和值的大小写都是十分敏感的。
字面量:普通的值 [ 数字,布尔值,字符串 ]
字面量直接写在后面就可以 , 字符串默认不用加上双引号或者单引号
注意
-
“ ” 双引号,不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符 , 特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
比如 :name: "kuang \n shen" 输出 :kuang 换行 shen
-
'' 单引号,会转义特殊字符 , 特殊字符最终会变成和普通字符一样输出
比如 :name: ‘kuang \n shen’ 输出 :kuang \n shen
对象、Map(键值对)
#对象、Map格式
k:
v1:
v2:
在下一行来写对象的属性和值得关系,注意缩进;比如:
student:
name: qinjiang
age: 3
行内写法
student: {name: qinjiang,age: 3}
数组( List、set )
用 - 值表示数组中的一个元素,比如:
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
修改SpringBoot的默认端口号
配置文件中添加,端口号的参数,就可以切换端口;
server:
port: 8082
3. yaml注入配置文件
yaml文件更强大的地方在于,他可以给我们的实体类直接注入匹配值!
-
在springboot项目中的resources目录下新建一个文件 application.yml
-
编写一个实体类 Dog
package com.meng.pojo; @Component //注册bean到容器中 public class Dog { private String name; private Integer age; //有参无参构造、get、set方法、toString()方法 } -
思考,我们原来是如何给bean注入属性值的!@Value,给狗狗类测试一下
@Component //注册bean public class Dog { @Value("阿黄") private String name; @Value("18") private Integer age; } -
在SpringBoot的测试类下注入狗狗输出一下
@SpringBootTest class DemoApplicationTests { @Autowired //将狗狗自动注入进来 Dog dog; @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(dog); //打印看下狗狗对象 } } -
我们在编写一个复杂一点的实体类:Person 类
@Component //注册bean到容器中 public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; private Boolean happy; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog; //有参无参构造、get、set方法、toString()方法 } -
我们来使用yaml配置的方式进行注入,大家写的时候注意区别和优势,我们编写一个yaml配置
person: name: qinjiang age: 3 happy: false birth: 2000/01/01 maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2} lists: - code - girl - music dog: name: 旺财 age: 1 -
我们刚才已经把person这个对象的所有值都写好了,我们现在来注入到我们的类中!
/* @ConfigurationProperties作用: 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中; 告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定 参数 prefix = “person” : 将配置文件中的person下面的所有属性一一对应 */ @Component //注册bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; private Boolean happy; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog; } -
IDEA 提示,springboot配置注解处理器没有找到,让我们看文档,我们可以查看文档,找到一个依赖!
<!-- 导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示,需要重启 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> -
确认以上配置都OK之后,我们去测试类中测试一下
@SpringBootTest class DemoApplicationTests { @Autowired Person person; //将person自动注入进来 @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(person); //打印person信息 } }
4. 加载指定的配置文件
@PropertySource :加载指定的配置文件
@configurationProperties:默认从全局配置文件中获取值
-
我们去在resources目录下新建一个person.properties文件
name=kuangshen -
然后在我们的代码中指定加载person.properties文件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:person.properties") @Component //注册bean public class Person { @Value("${name}") private String name; ...... } -
再次输出测试一下:指定配置文件绑定成功!
5. 配置文件占位符
配置文件还可以编写占位符生成随机数
person:
name: qinjiang${random.uuid} # 随机uuid
age: ${random.int} # 随机int
happy: false
birth: 2000/01/01
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- code
- girl
- music
dog:
name: ${person.hello:other}_旺财
age: 1
6. 回顾Properties配置
【注意】properties配置文件在写中文的时候,会有乱码 , 我们需要去IDEA中设置编码格式为UTF-8
settings-->FileEncodings 中配置
-
新建一个实体类User
@Component //注册bean public class User { private String name; private int age; private String sex; } -
编辑配置文件 user.properties
user1.name=kuangshen user1.age=18 user1.sex=男 -
我们在User类上使用@Value来进行注入!
@Component //注册bean @PropertySource(value = "classpath:user.properties") public class User { //直接使用@value @Value("${user.name}") //从配置文件中取值 private String name; @Value("#{9*2}") // #{SPEL} Spring表达式 private int age; @Value("男") // 字面量 private String sex; } -
Springboot测试
@SpringBootTest class DemoApplicationTests { @Autowired User user; @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(user); } }
7. 对比小结
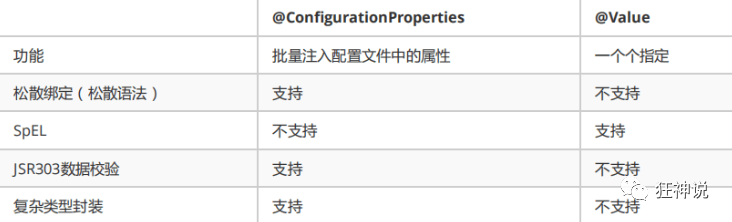
- @ConfigurationProperties只需要写一次即可 , @Value则需要每个字段都添加
- 松散绑定:这个什么意思呢? 比如我的yml中写的last-name,这个和lastName是一样的, - 后面跟着的字母默认是大写的。这就是松散绑定。可以测试一下
- JSR303数据校验 , 这个就是我们可以在字段是增加一层过滤器验证 , 可以保证数据的合法性
- 复杂类型封装,yml中可以封装对象 , 使用value就不支持
结论
配置yml和配置properties都可以获取到值 , 强烈推荐 yml
如果我们在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用一下 @value
如果说,我们专门编写了一个JavaBean来和配置文件进行一一映射,就直接@configurationProperties,不要犹豫
5、JSR303数据校验及多环境切换
JSR303数据校验
Springboot中可以用@validated来校验数据,如果数据异常则会统一抛出异常,方便异常中心统一处理。
我们这里来写个注解让我们的name只能支持Email格式
@Component //注册bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated //数据校验
public class Person {
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误") //name必须是邮箱格式
private String name;
}
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
运行结果
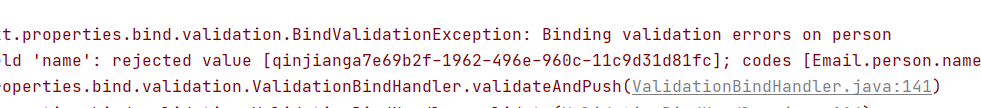
常见参数
@NotNull(message="名字不能为空")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120,message="年龄最大不能查过120")
private int age;
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误")
private String email;
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) string is between min and max included.
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
.......等等
除此以外,我们还可以自定义一些数据校验规则
配置文件加载位置
外部加载配置文件的方式十分多,我们选择最常用的即可,在开发的资源文件中进行配置!
springboot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件
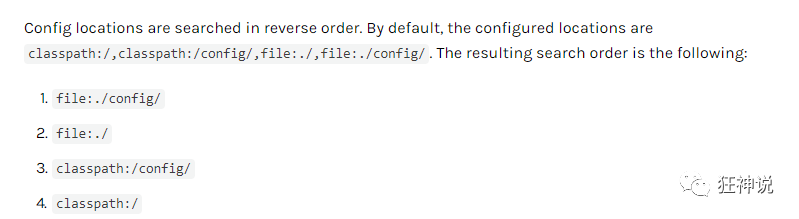
优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置
多环境切换
多配置文件
application-test.properties
server.port=8081
application-dev.properties
server.port=8082
application.properties
# springboot的多环境配置:可以选择激活哪一个配置文件
spring.profiles.active=dev
多文档模块
application.yml
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: test
6、自动配置原理
分析自动配置原理
我们以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理
//表示这是一个配置类,和以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件;
@Configuration
//启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;
//进入这个HttpProperties查看,将配置文件中对应的值和HttpProperties绑定起来;
//并把HttpProperties加入到ioc容器中
@EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class})
//Spring底层@Conditional注解
//根据不同的条件判断,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效;
//这里的意思就是判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
//判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
@ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class})
//判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置:spring.http.encoding.enabled;
//如果不存在,判断也是成立的
//即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "spring.http.encoding",
value = {"enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
//他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了
private final Encoding properties;
//只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties.getEncoding();
}
//给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean //判断容器没有这个组件?
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}
//。。。。。。。
}
一句话总结 :根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效!
- 一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件
- 这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的
- 所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装着
- 配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
//从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http")
public class HttpProperties {
// .....
}
精髓
1、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2、我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
3、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
4、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
@Conditional
@Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用)
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
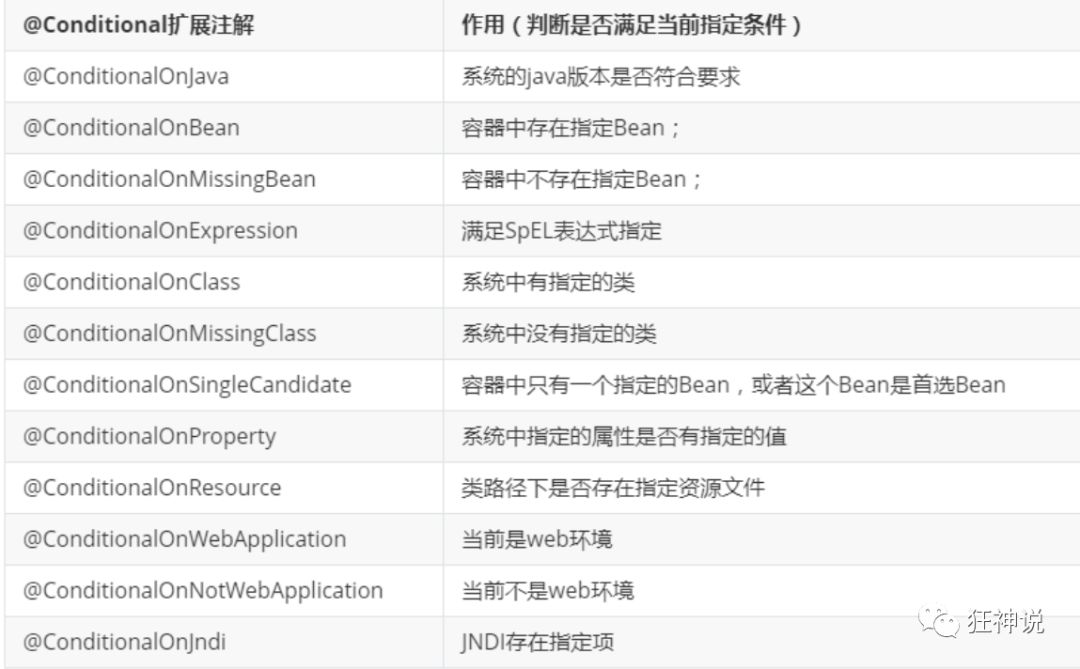
那么多的自动配置类,必须在一定的条件下才能生效;也就是说,我们加载了这么多的配置类,但不是所有的都生效了。
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效?
我们可以通过启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置类生效;
#开启springboot的调试类
debug=true
- Positive matches:(自动配置类启用的:正匹配)
- Negative matches:(没有启动,没有匹配成功的自动配置类:负匹配)
- Unconditional classes: (没有条件的类)
7、SpringBoot Web开发
静态资源导入探究(读源码)
-
在springboot,我们可以使用以下方式处理静态资源
- webjars localhost:8080/webjars/
- public,static,/**,resources localhost:8080/
-
优先级:resources>static(默认)>public
-
主动配置,会导致原来的路径失效
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/hello/,classpath:/kuang/
首页和图标定制
ResourceProperties
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = {"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/","classpath:/static/","classpath:/public/"};
index.html
favicon.ico
#关闭默认图标
spring.mvc.favicon.enabled=false
Thymeleaf模板引擎
-
导入Thymeleaf依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8time</artifactId> </dependency> -
ThymeleafProperties
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = StandardCharsets.UTF-8; public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/"; public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; -
IndexController
@Controller public class IndexController { @RequestMapping("/test") public String test(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","hello,springboot") return "test"; } } -
Thymeleaf使用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <!--所有的html元素都可以被themeleaf替换接管 th:元素名--> <div th:text="${msg}"></div> </body> </html>
Themeleaf语法
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","<h1>hello,springboot</h1>");
model.addAttribute("users",Arrays.asList("qinjiang","kuangshen"))
return "test";
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--所有的html元素都可以被themeleaf替换接管 th:元素名-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
<!--不被转义,可以识别出来-->
<div th:utext="${msg}"></div>
<hr>
<!--遍历-->
<h3 th:each="user:${users}" th:text="${user}"></h3>
<h3 th:each="user:${users}">[[ ${user} ]]</h3>
</body>
</html>


MVC自动配置原理
官方文档
Spring MVC Auto-configuration
// Spring Boot为Spring MVC提供了自动配置,它可以很好地与大多数应用程序一起工作。
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
// 自动配置在Spring默认设置的基础上添加了以下功能:
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
// 包含视图解析器
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
// 支持静态资源文件夹的路径,以及webjars
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars
// 自动注册了Converter:
// 转换器,这就是我们网页提交数据到后台自动封装成为对象的东西,比如把"1"字符串自动转换为int类型
// Formatter:【格式化器,比如页面给我们了一个2019-8-10,它会给我们自动格式化为Date对象】
Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans.
// HttpMessageConverters
// SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的的,比如我们要把一个User对象转换为JSON字符串,可以去看官网文档解释;
Support for HttpMessageConverters (covered later in this document).
// 定义错误代码生成规则的
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (covered later in this document).
// 首页定制
Static index.html support.
// 图标定制
Custom Favicon support (covered later in this document).
// 初始化数据绑定器:帮我们把请求数据绑定到JavaBean中!
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (covered later in this document).
/*
如果您希望保留Spring Boot MVC功能,并且希望添加其他MVC配置(拦截器、格式化程序、视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己
的@configuration类,类型为webmvcconfiguer,但不添加@EnableWebMvc。如果希望提供
RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的自定义
实例,则可以声明WebMVCregistrationAdapter实例来提供此类组件。
*/
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration
(interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own
@Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide
custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
// 如果您想完全控制Spring MVC,可以添加自己的@Configuration,并用@EnableWebMvc进行注释。
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 内容协商视图解析器
自动配置了ViewResolver,就是我们之前学习的SpringMVC的视图解析器
即根据方法的返回值取得视图对象(View),然后由视图对象决定如何渲染(转发,重定向)
我们去看看这里的源码:我们找到 WebMvcAutoConfiguration , 然后搜索ContentNegotiatingViewResolver。找到如下方法!
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(ViewResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "viewResolver", value = ContentNegotiatingViewResolver.class)
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver();
resolver.setContentNegotiationManager(beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class));
// ContentNegotiatingViewResolver使用所有其他视图解析器来定位视图,因此它应该具有较高的优先级
resolver.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return resolver;
}
我们可以点进这类看看!找到对应的解析视图的代码
@Nullable // 注解说明:@Nullable 即参数可为null
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
RequestAttributes attrs = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
Assert.state(attrs instanceof ServletRequestAttributes, "No current ServletRequestAttributes");
List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes = this.getMediaTypes(((ServletRequestAttributes)attrs).getRequest());
if (requestedMediaTypes != null) {
// 获取候选的视图对象
List<View> candidateViews = this.getCandidateViews(viewName, locale, requestedMediaTypes);
// 选择一个最适合的视图对象,然后把这个对象返回
View bestView = this.getBestView(candidateViews, requestedMediaTypes, attrs);
if (bestView != null) {
return bestView;
}
}
// .....
}
我们继续点进去看,他是怎么获得候选的视图的呢?
getCandidateViews中看到他是把所有的视图解析器拿来,进行while循环,挨个解析
Iterator var5 = this.viewResolvers.iterator();
所以得出结论:ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 这个视图解析器就是用来组合所有的视图解析器的
我们再去研究下他的组合逻辑,看到有个属性viewResolvers,看看它是在哪里进行赋值的!
protected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 这里它是从beanFactory工具中获取容器中的所有视图解析器
// ViewRescolver.class 把所有的视图解析器来组合的
Collection<ViewResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(this.obtainApplicationContext(), ViewResolver.class).values();
ViewResolver viewResolver;
if (this.viewResolvers == null) {
this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList(matchingBeans.size());
}
// ...............
}
既然它是在容器中去找视图解析器,我们是否可以猜想,我们就可以去实现一个视图解析器了呢?
我们可以自己给容器中去添加一个视图解析器;这个类就会帮我们自动的将它组合进来;我们去实现一下
-
我们在我们的主程序中去写一个视图解析器来试试
@Bean //放到bean中 public ViewResolver myViewResolver(){ return new MyViewResolver(); } //我们写一个静态内部类,视图解析器就需要实现ViewResolver接口 private static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{ @Override public View resolveViewName(String s, Locale locale) throws Exception { return null; } } -
怎么看我们自己写的视图解析器有没有起作用呢?
我们给 DispatcherServlet 中的 doDispatch方法 加个断点进行调试一下,因为所有的请求都会走到这个方法中

- 我们启动我们的项目,然后随便访问一个页面,看一下Debug信息
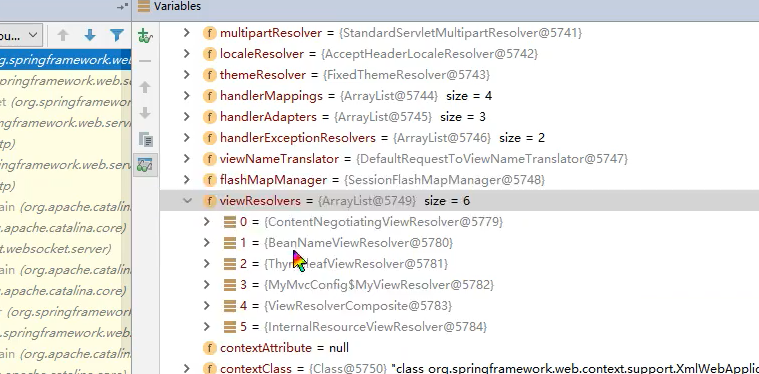
所以说,我们如果想要使用自己定制化的东西,我们只需要给容器中添加这个组件就好了!剩下的事情SpringBoot就会帮我们做了
转换器和格式化器
找到格式化转换器:
WebMvcAutoConfiguration
@Bean
@Override
public FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() {
// 拿到配置文件中的格式化规则
WebConversionService conversionService =
new WebConversionService(this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat());
addFormatters(conversionService);
return conversionService;
}
点进去mvcProperties:
public String getDateFormat() {
return this.dateFormat;
}
/**
* Date format to use. For instance, `dd/MM/yyyy`. 默认的
*/
private String dateFormat;
可以看到在我们的Properties文件中,我们可以进行自动配置它!
如果配置了自己的格式化方式,就会注册到Bean中生效,我们可以在配置文件中配置日期格式化的规则:
spring.mvc.date-format=
修改SpringBoot的默认配置
这么多的自动配置,原理都是一样的,通过这个WebMVC的自动配置原理分析,我们要学会一种学习方式,通过源码探究,得出结论;这个结论一定是属于自己的,而且一通百通。
SpringBoot的底层,大量用到了这些设计细节思想,所以,没事需要多阅读源码!得出结论;
SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(如果用户自己配置@bean),如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有就用自动配置的;
如果有些组件可以存在多个,比如我们的视图解析器,就将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来!
扩展使用SpringMVC
我们要做的就是编写一个@Configuration注解类,并且类型要为WebMvcConfigurer,还不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解;我们去自己写一个;我们新建一个包叫config,写一个类MyMvcConfig;
//应为类型要求为WebMvcConfigurer,所以我们实现其接口
//可以使用自定义类扩展MVC的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// 浏览器发送/test , 就会跳转到test页面;
registry.addViewController("/test").setViewName("test");
}
}
我们去浏览器访问一下:
确实也跳转过来了!所以说,我们要扩展SpringMVC,官方就推荐我们这么去使用,既保SpringBoot留所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置!
我们可以去分析一下原理:
1、WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是 SpringMVC的自动配置类,里面有一个类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
2、这个类上有一个注解,在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
3、我们点进EnableWebMvcConfiguration这个类看一下,它继承了一个父类:DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
这个父类中有这样一段代码:
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
// 从容器中获取所有的webmvcConfigurer
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
}
4、我们可以在这个类中去寻找一个我们刚才设置的viewController当做参考,发现它调用了一个
protected void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addViewControllers(registry);
}
5、我们点进去看一下
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
Iterator var2 = this.delegates.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
// 将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置来一起调用!包括我们自己配置的和Spring给我们配置的
WebMvcConfigurer delegate = (WebMvcConfigurer)var2.next();
delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
}
}
所以得出结论:所有的WebMvcConfiguration都会被作用,不止Spring自己的配置类,我们自己的配置类当然也会被调用
全面接管SpringMVC
全面接管即:SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己去配置!
只需在我们的配置类中要加一个@EnableWebMvc
如果我们全面接管了SpringMVC了,我们之前SpringBoot给我们配置的静态资源映射一定会无效
为什么加了一个注解,自动配置就失效了!我们看下源码:
1、这里发现它是导入了一个类,我们可以继续进去看
@Import({DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class})
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}
2、它继承了一个父类 WebMvcConfigurationSupport
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
// ......
}
3、我们来回顾一下Webmvc自动配置类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
// 这个注解的意思就是:容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
}
总结一句话:@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来了


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号