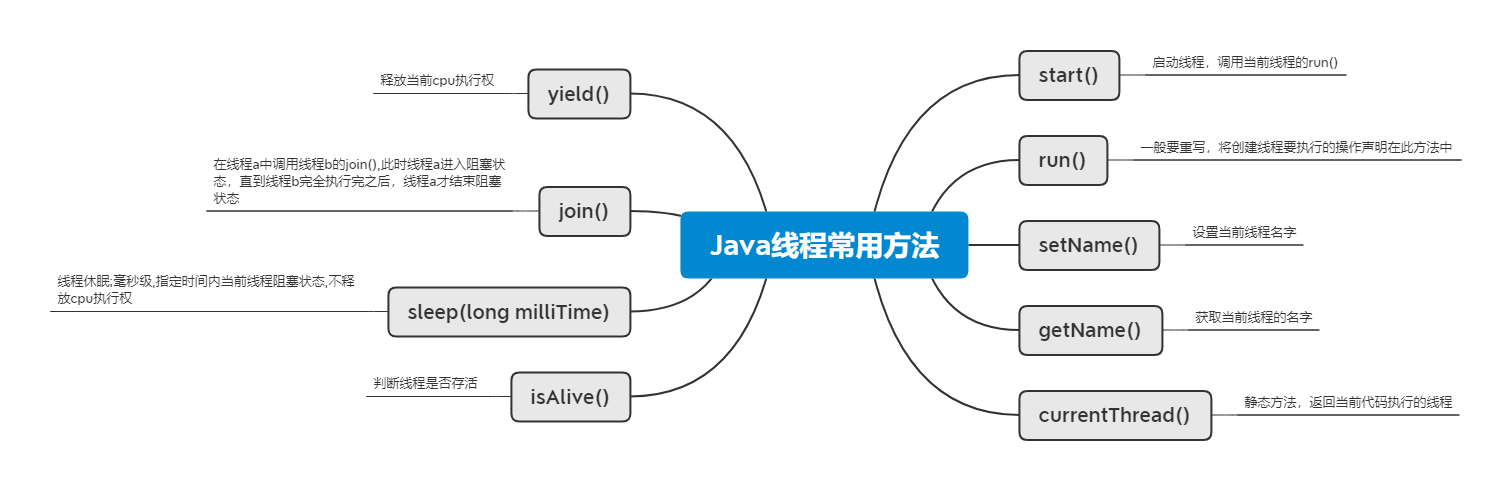
Thread中常用方法:start()、run()、sleep(long milliTime)、yield()、setName()、getName()、currentThread()、join()、isAlive()
Thread中常用方法
* 1.start();启动线程,调用当前线程的run();
* 2.run();一般要重写,将创建线程要执行的操作声明在此方法中
* 3.currentThread();静态方法,返回当前代码执行的线程
* 4.getName();获取当前线程的名字
* 5.setName();设置当前线程名字
* 6.yield();释放当前cpu执行权,
* 7.join();在线程a中调用线程b的join(),此时线程a进入阻塞状态,直到线程b完全执行完之后,线程a才结束阻塞状态
* 8.stop();强制结束线程;已过时
* 9.sleep(long milliTime);线程休眠;毫秒级,指定时间内当前线程阻塞状态
* 10.isAlive();判断线程是否存活
*
*线程优先级
* 1.MAX_PRIORITY:10
* MIN_PRIORITY:1
* NORM_PRIORITY:5
* 2.如何获取或设置当前线程优先级:
* getPriority();//获取
* setPriority(int p);//设置
*
* 说明:高优先级要抢占低优先级线程cpu的执行权,但是只是从概率上讲,高优先级高概率的情况下被执行,
* 并不意味只有在高优先级的线程执行完以后,低优先级的线程才执行
import static java.lang.Thread.sleep;
/**
* @author orz
* @create 2020-08-11 14:57
*/
public class Method1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3.
Thread1 th1=new Thread1();
//4.
Thread t1=new Thread(th1);
//setName();设置当前线程名字
t1.setName("线程一");
//5.
//start();启动线程,调用当前线程的run();
t1.start();
}
}
//1.
class Thread1 implements Runnable
{
//2.
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <=100; i++) {
try {
//sleep(long milliTime);线程休眠;毫秒级,指定时间内当前线程阻塞状态
//需要处理异常
sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i%2==0)
{
//currentThread();静态方法,返回当前代码执行的线程
//getName();获取当前线程的名字
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
}
}
import static java.lang.Thread.yield;
/**
* @author orz
* @create 2020-08-11 15:06
*/
public class Method2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread2 th2=new Thread2();
Thread t2=new Thread(th2);
t2.setName("线程一");
t2.start();
Thread.currentThread().setName("主线程");
for (int i = 0; i <=100 ; i++) {
if(i%2!=0)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
//yield();释放当前cpu执行权
yield();
}
}
}
}
//1.
class Thread2 implements Runnable
{
//2.
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <=100; i++) {
if(i%2==0)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
//yield();释放当前cpu执行权
yield();
}
}
}
}
import static java.lang.Thread.sleep;
/**
* @author orz
* @create 2020-08-11 15:13
*/
public class Method3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread3 th3=new Thread3();
Thread t3=new Thread(th3);
t3.setName("线程一");
t3.start();
Thread.currentThread().setName("主线程");
for (int i = 0; i <=100 ; i++) {
if(i%2!=0)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
if(i==20)
{
try {
//join();在线程a中调用线程b的join(),此时线程a进入阻塞状态,直到线程b完全执行完之后,线程a才结束阻塞状态
t3.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
class Thread3 implements Runnable
{
//2.
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <=100; i++) {
try {
sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i%2==0)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
}
}
import static java.lang.Thread.MAX_PRIORITY;
import static java.lang.Thread.sleep;
/**
* @author orz
* @create 2020-08-11 15:20
*/
public class Method4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread4 th4=new Thread4();
Thread5 th5=new Thread5();
Thread t4=new Thread(th4);
Thread t5=new Thread(th5);
t4.setName("奇数");
t5.setName("偶数");
/**
* 线程优先级
* * 1.MAX_PRIORITY:10
* * MIN_PRIORITY:1
* * NORM_PRIORITY:5
* * 2.如何获取或设置当前线程优先级:
* * getPriority();//获取
* * setPriority(int p);//设置
* *
* * 说明:高优先级要抢占低优先级线程cpu的执行权,但是只是从概率上讲,高优先级高概率的情况下被执行,
* * 并不意味只有在高优先级的线程执行完以后,低优先级的线程才执行
*/
t4.setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);
t5.setPriority(8);
System.out.println("t4.getPriority():"+t4.getPriority());
System.out.println("t5.getPriority():"+t5.getPriority());
t5.start();
t4.start();
//isAlive();判断线程是否存活
System.out.println("t5.isAlive():"+t5.isAlive());
}
}
class Thread5 implements Runnable
{
//2.
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <=100; i++) {
try {
sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i%2==0)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
}
}
class Thread4 implements Runnable
{
//2.
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <=100; i++) {
try {
sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i%2!=0)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号