多线程中synchronized的使用细节和遇到的几个问题(代码讲解)(代码注释详情)
不使用同步处理,产生多线程并发问题:
package thread;
/**
* @author 林郁聪
* @create 2022-03-08 12:55
*/
public class threadTest6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Ticket6());
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Ticket6());
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Ticket6());
thread1.setName("小明");
thread2.setName("熊大");
thread3.setName("如花");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class Ticket6 implements Runnable{
public static int tickets = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"抢了一张票,还剩" + String.valueOf(tickets - 1) + "张");
tickets--;
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
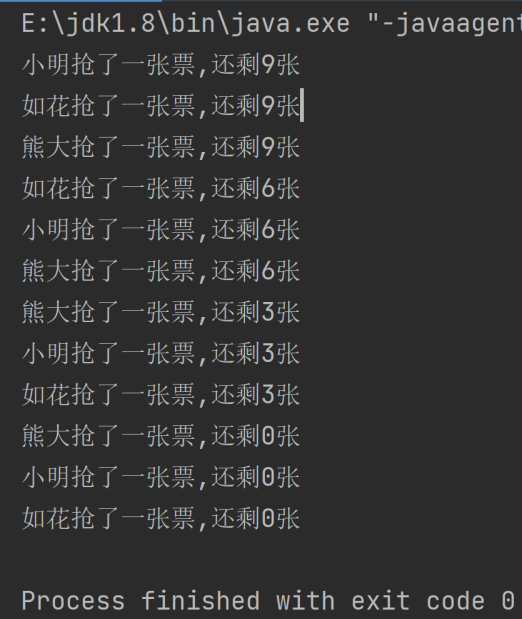
并发结果截图
synchronized 修饰run方法:
package thread;
/**
* @author 林郁聪
* @create 2022-03-08 12:55
*/
public class threadTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Ticket5());
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Ticket5());
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Ticket5());
thread1.setName("小明");
thread2.setName("熊大");
thread3.setName("如花");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class Ticket5 implements Runnable{
public static int tickets = 10;
/**
* synchronized修饰run方法,三个线程在run方法前面排队,也就是start方法,此时
* cpu调度分配锁,某个线程得到锁之后,开始执行整个run方法,需要注意的一点是,
* synchronized修饰非静态方法,所使用的锁是this,也就是调用这个run方法的对象
* 因此锁已经不一样了,同步的前提是锁必须一样,因此整个的同步处理已经没有意义
* 也就是说,这个相当于没有作同步处理
*/
@Override
public synchronized void run() {
while (true) {
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"抢了一张票,还剩" + String.valueOf(tickets - 1) + "张");
tickets--;
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
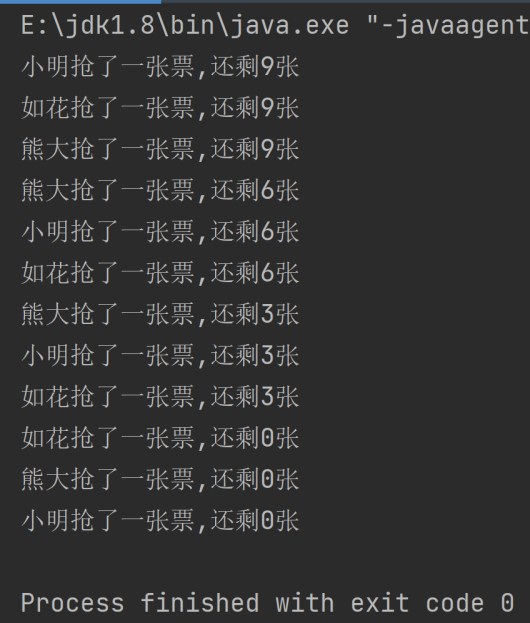
运行结果截图
synchronized 修饰run方法:
package thread;
/**
* @author 林郁聪
* @create 2022-03-08 12:55
*/
public class threadTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Ticket5());
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Ticket5());
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Ticket5());
thread1.setName("小明");
thread2.setName("熊大");
thread3.setName("如花");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class Ticket5 implements Runnable{
public static int tickets = 10;
/**
* synchronized修饰run方法,三个线程在run方法前面排队,也就是start方法,此时
* cpu调度分配锁,某个线程得到锁之后,开始执行整个run方法,需要注意的一点是,
* synchronized修饰非静态方法,所使用的锁是this,也就是调用这个run方法的对象
* 因此锁已经不一样了,同步的前提是锁必须一样,因此整个的同步处理已经没有意义
* 也就是说,这个相当于没有作同步处理
*/
@Override
public synchronized void run() {
while (true) {
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"抢了一张票,还剩" + String.valueOf(tickets - 1) + "张");
tickets--;
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
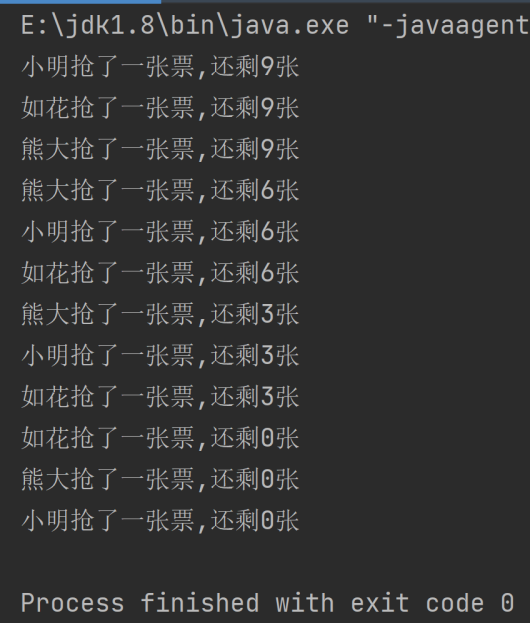
运行结果截图
synchronized代码块放在run方法后面:
package thread;
/**
* @author 林郁聪
* @create 2022-03-08 12:55
*/
public class threadTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Ticket4());
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Ticket4());
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Ticket4());
thread1.setName("小明");
thread2.setName("熊大");
thread3.setName("如花");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class Ticket4 implements Runnable{
public static int tickets = 10;
/**
* synchronized代码块紧接在run方法的后面,三个线程停留在run方法,
* cpu调度分配锁,某个线程拿到锁,进入while方法,一直循环抢票,等到释放锁的时候,
* while循环已经结束,即此时tickets变量为0。另一个线程拿到锁,进入while循环,
* 此时已经没票了。
*/
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Ticket4.class) {
while (true) {
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"抢了一张票,还剩" + String.valueOf(tickets - 1) + "张");
tickets--;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
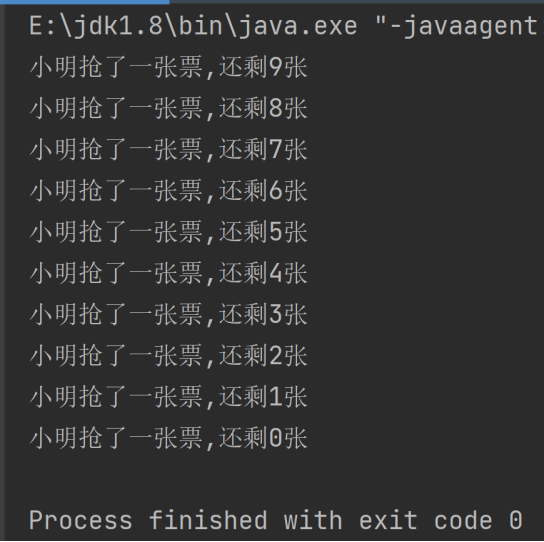
运行代码截图
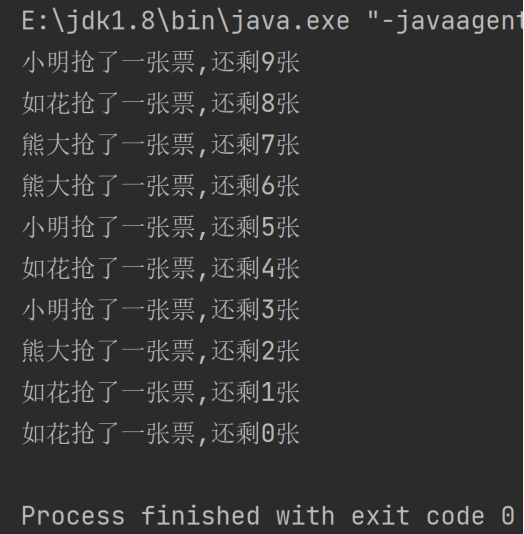
synchronized代码块放在if判断的后面
package thread;
/**
* @author 林郁聪
* @create 2022-03-08 12:55
*/
public class threadTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Ticket3());
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Ticket3());
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Ticket3());
thread1.setName("小明");
thread2.setName("熊大");
thread3.setName("如花");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class Ticket3 implements Runnable{
public static int tickets = 10;
/**
* synchronized代码块放在if判断的后面,三个线程停留在if判断的后面,
* cpu调度分配锁,某个线程拿到锁,直接进行抢票,抢一次票之后释放锁,
* 继续进行排队进行抢票。当tickets==1时,三个线程都在准备进行抢票。
* 由于抢票的校验已经进行完毕,因此会出现票数为负数的现象
*/
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
synchronized (Ticket3.class) {
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"抢了一张票,还剩" + String.valueOf(tickets - 1) + "张");
tickets--;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行结果截图
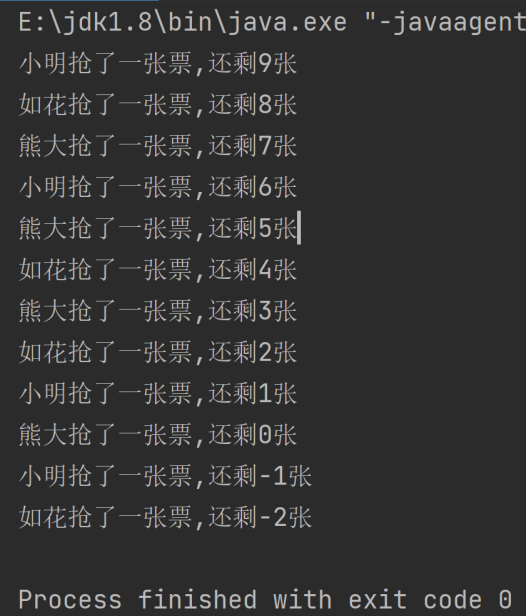
synchronized代码块紧接在while循环的后面:
package thread;
/**
* @author 林郁聪
* @create 2022-03-08 12:55
*/
public class threadTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Ticket2());
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Ticket2());
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Ticket2());
thread1.setName("小明");
thread2.setName("熊大");
thread3.setName("如花");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class Ticket2 implements Runnable{
public static int tickets = 10;
/**
* synchronized代码块紧接在while循环的后面,三个线程停留在while循环里面,
* cpu调度分配锁,某个线程拿到锁,进入if判断,抢票之前先判断一下还有没有票,
* 没有票了就退出while循环,有票的话就抢一张票
*/
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (Ticket2.class) {
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() +
"抢了一张票,还剩" + String.valueOf(tickets - 1) + "张");
tickets--;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行结果截图


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号