机器学习作业(四)神经网络参数的拟合——Matlab实现
题目下载【传送门】
题目简述:识别图片中的数字,训练该模型,求参数θ。
第1步:读取数据文件:
%% Setup the parameters you will use for this exercise
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = 25; % 25 hidden units
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10)
% Load Training Data
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n')
load('ex4data1.mat');
m = size(X, 1);
% Randomly select 100 data points to display
sel = randperm(size(X, 1));
sel = sel(1:100);
displayData(X(sel, :));
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
fprintf('\nLoading Saved Neural Network Parameters ...\n')
% Load the weights into variables Theta1 and Theta2
load('ex4weights.mat');
% Unroll parameters
nn_params = [Theta1(:) ; Theta2(:)];
第2步:初始化参数:
initial_Theta1 = randInitializeWeights(input_layer_size, hidden_layer_size); initial_Theta2 = randInitializeWeights(hidden_layer_size, num_labels); % Unroll parameters initial_nn_params = [initial_Theta1(:) ; initial_Theta2(:)];
其中randInitializeWeights函数实现初始化θ:
function W = randInitializeWeights(L_in, L_out) % You need to return the following variables correctly W = zeros(L_out, 1 + L_in); epsilon_init = 0.12; W = rand(L_out, 1 + L_in) * 2 * epsilon_init - epsilon_init; end
第3步:实现nnCostFunction函数,计算 J 和 D:
function [J grad] = nnCostFunction(nn_params, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, ...
X, y, lambda)
% Reshape nn_params back into the parameters Theta1 and Theta2, the weight matrices
% for our 2 layer neural network
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1));
Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1));
% Setup some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
Theta1_grad = zeros(size(Theta1));
Theta2_grad = zeros(size(Theta2));
% X:5000*400
% Y:5000*10
% a1:5000*401(后5000*400)
% z2:5000*25
% a2:5000*26(后5000*25)
% z3:5000*10
% a3:5000*10
% Theta1:25*401
% Theta2:10*26
% delta3:5000*10
% delta2:5000*25
% bigDelta1:25*401
% bigDelta2:10*26
% Theta1_grad:25*401
% Theta2_grad:10*26
Y = zeros(size(X, 1), num_labels);
for i = 1: size(X, 1),
Y(i, y(i, 1)) = 1;
end
a1 = [ones(m, 1) X];
z2 = a1*Theta1';
a2 = sigmoid(z2);
a2 = [ones(size(a2, 1), 1) a2];
z3 = a2*Theta2';
a3 = sigmoid(z3);
J = 1 / m * sum(sum(-Y .* log(a3) - (1 - Y) .* log(1 - a3)));
Theta1_copy = Theta1(:, 2: end);
Theta2_copy = Theta2(:, 2: end);
J = J + lambda * (sum(sum(Theta1_copy.^2)) + sum(sum(Theta2_copy.^2))) / (2*m);
delta3 = a3 - Y;
delta2 = delta3 * Theta2_copy .* sigmoidGradient(z2);
bigDelta1 = zeros(size(Theta1));
bigDelta2 = zeros(size(Theta2));
bigDelta1 = delta2' * a1;
bigDelta2 = delta3' * a2;
Theta1_grad = bigDelta1 / m + lambda / m * Theta1;
Theta2_grad = bigDelta2 / m + lambda / m * Theta2;
Theta1_grad(:, 1) = bigDelta1(:, 1) / m;
Theta2_grad(:, 1) = bigDelta2(:, 1) / m;
% Unroll gradients
grad = [Theta1_grad(:) ; Theta2_grad(:)];
end
其中sigmoid函数:
function g = sigmoid(z) g = 1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z)); end
其中sigmoidGradient函数:
function g = sigmoidGradient(z) g = zeros(size(z)); g = sigmoid(z) .* (1 - sigmoid(z)) end
第4步:梯度检测:
% Check gradients by running checkNNGradients lambda = 3; checkNNGradients(lambda);
其中checkNNGradients函数实现梯度检测:
function checkNNGradients(lambda)
if ~exist('lambda', 'var') || isempty(lambda)
lambda = 0;
end
input_layer_size = 3;
hidden_layer_size = 5;
num_labels = 3;
m = 5;
% We generate some 'random' test data
Theta1 = debugInitializeWeights(hidden_layer_size, input_layer_size);
Theta2 = debugInitializeWeights(num_labels, hidden_layer_size);
% Reusing debugInitializeWeights to generate X
X = debugInitializeWeights(m, input_layer_size - 1);
y = 1 + mod(1:m, num_labels)';
% Unroll parameters
nn_params = [Theta1(:) ; Theta2(:)];
% Short hand for cost function
costFunc = @(p) nnCostFunction(p, input_layer_size, hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, X, y, lambda);
[cost, grad] = costFunc(nn_params);
numgrad = computeNumericalGradient(costFunc, nn_params);
% Visually examine the two gradient computations. The two columns
% you get should be very similar.
disp([numgrad grad]);
fprintf(['The above two columns you get should be very similar.\n' ...
'(Left-Your Numerical Gradient, Right-Analytical Gradient)\n\n']);
% Evaluate the norm of the difference between two solutions.
% If you have a correct implementation, and assuming you used EPSILON = 0.0001
% in computeNumericalGradient.m, then diff below should be less than 1e-9
diff = norm(numgrad-grad)/norm(numgrad+grad);
fprintf(['If your backpropagation implementation is correct, then \n' ...
'the relative difference will be small (less than 1e-9). \n' ...
'\nRelative Difference: %g\n'], diff);
end
其中数值方法计算函数computeNumericalGradient实现:
function numgrad = computeNumericalGradient(J, theta)
numgrad = zeros(size(theta));
perturb = zeros(size(theta));
e = 1e-4;
for p = 1:numel(theta)
% Set perturbation vector
perturb(p) = e;
loss1 = J(theta - perturb);
loss2 = J(theta + perturb);
% Compute Numerical Gradient
numgrad(p) = (loss2 - loss1) / (2*e);
perturb(p) = 0;
end
end
其中测试数据初始化函数debugInitializeWeights函数:
function W = debugInitializeWeights(fan_out, fan_in) % Set W to zeros W = zeros(fan_out, 1 + fan_in); % Initialize W using "sin", this ensures that W is always of the same % values and will be useful for debugging W = reshape(sin(1:numel(W)), size(W)) / 10; end
第5步:训练模型,计算最优解:
% After you have completed the assignment, change the MaxIter to a larger
% value to see how more training helps.
options = optimset('MaxIter', 50);
% You should also try different values of lambda
lambda = 1;
% Create "short hand" for the cost function to be minimized
costFunction = @(p) nnCostFunction(p, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, X, y, lambda);
% Now, costFunction is a function that takes in only one argument (the
% neural network parameters)
[nn_params, cost] = fmincg(costFunction, initial_nn_params, options);
% Obtain Theta1 and Theta2 back from nn_params
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1));
Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1));
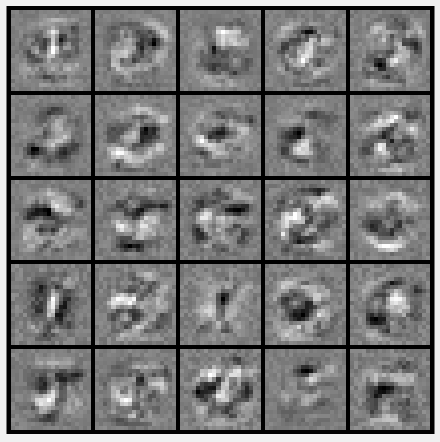
第6步:可视化隐藏层:
displayData(Theta1(:, 2:end));
运行结果:
第7步:计算准确率:
pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100);
其中predict函数:
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X) % Useful values m = size(X, 1); num_labels = size(Theta2, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); h1 = sigmoid([ones(m, 1) X] * Theta1'); h2 = sigmoid([ones(m, 1) h1] * Theta2'); [dummy, p] = max(h2, [], 2); end
运行结果:
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号