Python学习Day07
DAY07
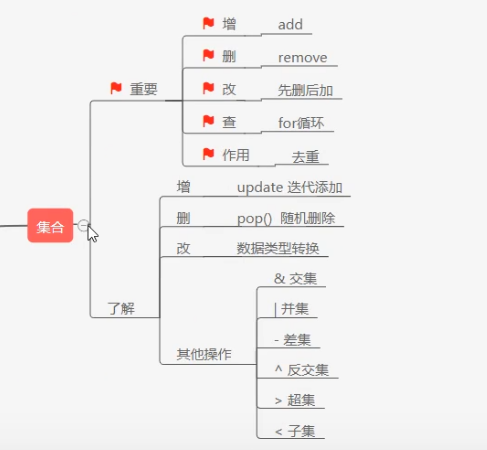
集合
-
作用
# 集合 -- set --无序 --可变的 # 集合 -- 作用 (天然)去重!!! # 集合就是一个没有值的字典 # 集合中可变数据类型不能当作元素 s0 = {"key1", "key2"} print(type(s0)) print(s0) -
增
s0.add(7) print(s0) s0.update("niu") print(s0) -
删
s0.remove("key2") print(s0) s0.pop() # 随机删除 print(s0) -
改
# 先删后加 # 数据类型转换 a_list = list(s0) a_list[-1] = "key3" print(a_list) print(set(a_list)) -
查
for i in s0: print(i) -
其他操作
s3 = {6, 5, 456, 12, 84} s4 = {13, 856, 16, 8, 5} print(s3 & s4) # 交集 print(s4 - s3) # 求谁没有的谁当前者,差集 print(s3 | s4 | s0) # 并集 print(s3 ^ s4) # 补集,类似于算交集相反 print(s3 > s4) # s4是否是s3的子集 # 字典怎么合并 dic1 = {1: 2} dic2 = {2: 1} dic1.update(dic2) print(dic1) s = frozenset({"niuda", "niuer", "niusan"}) dic3 = {s: 123} # 就可以正常使用 print(dic3) -
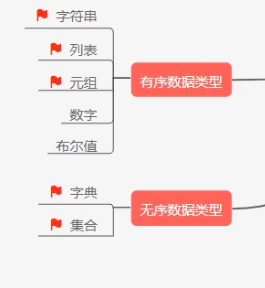
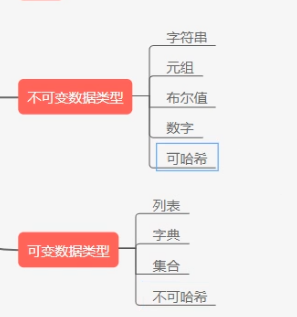
数据类型总结
![]()
深浅拷贝
-
is和==的区别
# is 是;is not 不是;== 判断两边的值是否一至 a = 10 b = 10 print(a is b) # 判断a和b的内存地址是否相同 print(id(a), id(b)) # 驻留机制:节省内存开销,提高效率 # 小数据池 在这个区域值相同就是相同的地址空间 # 数字 -5~256 pycharm大于256后会设计到代码块,因此还会返回true,终端中会是false # 字符串 自己定义的内容一致 -
浅拷贝
# 浅拷贝:只拷贝第一层元素的内存地址 low_list = [1, 2, 3, []] print(low_list.copy(), id(low_list.copy())) print(low_list, id(low_list)) print(low_list.copy()[-1], id(low_list.copy()[-1])) print(low_list[-1], id(low_list[-1])) low_list[-1].append(5) print(low_list) # copy会随着原有列表已有的元素变化而变化,看的是id -
深拷贝
# 深拷贝:不管嵌套多少层,不可变数据类型共用,可用数据类型开辟新空间 import copy deep_list = [1, 2, 3, [2, 3]] deep_list_dc=copy.deepcopy(deep_list) print(deep_list) print(deep_list_dc) deep_list.append(5) print(deep_list) print(deep_list_dc) deep_list[-2].append(10) print(deep_list) print(deep_list_dc) -
总结
赋值:多个变量名指向同一个内存地址
浅拷贝:只拷贝第一层元素,不可变数据类型不会有影响,可变数据类型会有联动效果
深拷贝:不管嵌套多少层,不可变数据类型共用,可变数据类型开辟新空间
二次编码
-
编码
# 文件存储和网络传输使用的都是字节 # 编码:上锁 str01="你好" print(type(str01.encode("utf-8"))) print(str01.encode("utf-8")) -
解码
# 解码:开锁 str02=str01.encode("utf-8") str03=str02.decode("utf-8") print(str03) str04=str02.decode("gbk") print(str04) # 转换utf-8为gbk可正常读取 str05=str03.encode("gbk") print(str05.decode("gbk"))




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号