Python动态展示遗传算法求解TSP旅行商问题
效果图:
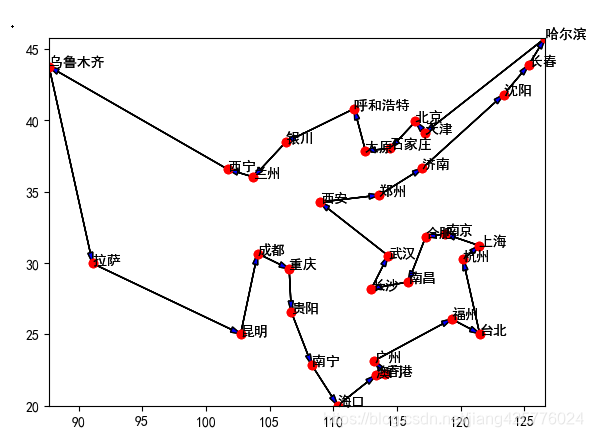
程序会动态的展示迭代过程,40以内城市大概迭代300次能收敛到最优;这里是用中国城市地理坐标直接做欧式距离计算,实际上可以根据问题作出调整。
网址在这:欢迎star啊,我看中这个
Github:https://github.com/425776024/TSP-GA-py
数据:china.csv:
北京 ;116.46;39.92
天津 ;117.2;39.13
上海 ;121.48;31.22
重庆 ;106.54;29.59
拉萨 ;91.11;29.97
乌鲁木齐 ;87.68;43.77
银川 ;106.27;38.47
呼和浩特 ;111.65;40.82
南宁 ;108.33;22.84
哈尔滨 ;126.63;45.75
长春 ;125.35;43.88
沈阳 ;123.38;41.8
石家庄 ;114.48;38.03
太原 ;112.53;37.87
西宁 ;101.74;36.56
济南 ;117;36.65
郑州 ;113.6;34.76
南京;118.78;32.04
合肥;117.27;31.86
杭州;120.19;30.26
福州;119.3;26.08
南昌;115.89;28.68
长沙;113;28.21
武汉;114.31;30.52
广州;113.23;23.16
台北;121.5;25.05
海口;110.35;20.02
兰州;103.73;36.03
西安;108.95;34.27
成都;104.06;30.67
贵阳;106.71;26.57
昆明;102.73;25.04
香港;114.1;22.2
澳门;113.33;22.13
文件:TSP-GA.py
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from DW import *
class TSP(object):
citys = np.array([]) #城市数组
citys_name = np.array([])
pop_size = 50 #种群大小
c_rate = 0.7 #交叉率
m_rate = 0.05 #突变率
pop = np.array([]) #种群数组
fitness = np.array([]) #适应度数组
city_size = -1 #标记城市数目
ga_num = 200 #最大迭代次数
best_dist = -1 #记录目前最优距离
best_gen = [] #记录目前最优旅行方案
dw = Draw() #绘图类
def __init__(self, c_rate, m_rate, pop_size, ga_num):
self.fitness = np.zeros(self.pop_size)
self.c_rate = c_rate
self.m_rate = m_rate
self.pop_size = pop_size
self.ga_num = ga_num
def init(self):
tsp = self
# tsp.load_Citys() #加载城市数据
tsp.load_Citys2() #加载城市数据
tsp.pop = tsp.creat_pop(tsp.pop_size) #创建种群
tsp.fitness = tsp.get_fitness(tsp.pop) #计算初始种群适应度
tsp.dw.bound_x = [np.min(tsp.citys[:, 0]), np.max(tsp.citys[:, 0])] #计算绘图时的X界
tsp.dw.bound_y = [np.min(tsp.citys[:, 1]), np.max(tsp.citys[:, 1])] #计算绘图时的Y界
tsp.dw.set_xybound(tsp.dw.bound_x, tsp.dw.bound_y) #设置边界
def creat_pop(self, size):
pop = []
for i in range(size):
gene = np.arange(self.citys.shape[0]) #问题的解,基因,种群中的个体:[0,...,city_size]
np.random.shuffle(gene) #打乱数组[0,...,city_size]
pop.append(gene) #加入种群
return np.array(pop)
def get_fitness(self, pop):
d = np.array([]) #适应度记录数组
for i in range(pop.shape[0]):
gen = pop[i] # 取其中一条基因(编码解,个体)
dis = self.gen_distance(gen) #计算此基因优劣(距离长短)
dis = self.best_dist / dis #当前最优距离除以当前pop[i](个体)距离;越近适应度越高,最优适应度为1
d = np.append(d, dis) # 保存适应度pop[i]
return d
def get_local_fitness(self, gen, i):
'''
计算地i个城市的邻域
交换基因数组中任意两个值组成的解集:称为邻域。计算领域内所有可能的适应度
:param gen:城市路径
:param i:第i城市
:return:第i城市的局部适应度
'''
di = 0
fi = 0
if i == 0:
di = self.ct_distance(self.citys[gen[0]], self.citys[gen[-1]])
else:
di = self.ct_distance(self.citys[gen[i]], self.citys[gen[i - 1]])
od = []
for j in range(self.city_size):
if i != j:
od.append(self.ct_distance(self.citys[gen[i]], self.citys[gen[i - 1]]))
mind = np.min(od)
fi = di - mind
return fi
def EO(self, gen):
#极值优化,传统遗传算法性能不好,这里混合EO
#其会在整个基因的领域内,寻找一个最佳变换以更新基因
local_fitness = []
for g in range(self.city_size):
f = self.get_local_fitness(gen, g)
local_fitness.append(f)
max_city_i = np.argmax(local_fitness)
maxgen = np.copy(gen)
if 1 < max_city_i < self.city_size - 1:
for j in range(max_city_i):
maxgen = np.copy(gen)
jj = max_city_i
while jj < self.city_size:
gen1 = self.exechange_gen(maxgen, j, jj)
d = self.gen_distance(maxgen)
d1 = self.gen_distance(gen1)
if d > d1:
maxgen = gen1[:]
jj += 1
gen = maxgen
return gen
def select_pop(self, pop):
#选择种群,优胜劣汰,策略1:低于平均的要替换改变
best_f_index = np.argmax(self.fitness)
av = np.median(self.fitness, axis=0)
for i in range(self.pop_size):
if i != best_f_index and self.fitness[i] < av:
pi = self.cross(pop[best_f_index], pop[i])
pi = self.mutate(pi)
# d1 = self.distance(pi)
# d2 = self.distance(pop[i])
# if d1 < d2:
pop[i, :] = pi[:]
return pop
def select_pop2(self, pop):
#选择种群,优胜劣汰,策略2:轮盘赌,适应度低的替换的概率大
probility = self.fitness / self.fitness.sum()
idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.pop_size), size=self.pop_size, replace=True, p=probility)
n_pop = pop[idx, :]
return n_pop
def cross(self, parent1, parent2):
"""交叉p1,p2的部分基因片段"""
if np.random.rand() > self.c_rate:
return parent1
index1 = np.random.randint(0, self.city_size - 1)
index2 = np.random.randint(index1, self.city_size - 1)
tempGene = parent2[index1:index2] # 交叉的基因片段
newGene = []
p1len = 0
for g in parent1:
if p1len == index1:
newGene.extend(tempGene) # 插入基因片段
if g not in tempGene:
newGene.append(g)
p1len += 1
newGene = np.array(newGene)
if newGene.shape[0] != self.city_size:
print('c error')
return self.creat_pop(1)
# return parent1
return newGene
def mutate(self, gene):
"""突变"""
if np.random.rand() > self.m_rate:
return gene
index1 = np.random.randint(0, self.city_size - 1)
index2 = np.random.randint(index1, self.city_size - 1)
newGene = self.reverse_gen(gene, index1, index2)
if newGene.shape[0] != self.city_size:
print('m error')
return self.creat_pop(1)
return newGene
def reverse_gen(self, gen, i, j):
#函数:翻转基因中i到j之间的基因片段
if i >= j:
return gen
if j > self.city_size - 1:
return gen
parent1 = np.copy(gen)
tempGene = parent1[i:j]
newGene = []
p1len = 0
for g in parent1:
if p1len == i:
newGene.extend(tempGene[::-1]) # 插入基因片段
if g not in tempGene:
newGene.append(g)
p1len += 1
return np.array(newGene)
def exechange_gen(self, gen, i, j):
#函数:交换基因中i,j值
c = gen[j]
gen[j] = gen[i]
gen[i] = c
return gen
def evolution(self):
#主程序:迭代进化种群
tsp = self
for i in range(self.ga_num):
best_f_index = np.argmax(tsp.fitness)
worst_f_index = np.argmin(tsp.fitness)
local_best_gen = tsp.pop[best_f_index]
local_best_dist = tsp.gen_distance(local_best_gen)
if i == 0:
tsp.best_gen = local_best_gen
tsp.best_dist = tsp.gen_distance(local_best_gen)
if local_best_dist < tsp.best_dist:
tsp.best_dist = local_best_dist #记录最优值
tsp.best_gen = local_best_gen #记录最个体基因
#绘图
tsp.dw.ax.cla()
tsp.re_draw()
tsp.dw.plt.pause(0.001)
else:
tsp.pop[worst_f_index] = self.best_gen
print('gen:%d evo,best dist :%s' % (i, self.best_dist))
tsp.pop = tsp.select_pop(tsp.pop) #选择淘汰种群
tsp.fitness = tsp.get_fitness(tsp.pop) #计算种群适应度
for j in range(self.pop_size):
r = np.random.randint(0, self.pop_size - 1)
if j != r:
tsp.pop[j] = tsp.cross(tsp.pop[j], tsp.pop[r]) #交叉种群中第j,r个体的基因
tsp.pop[j] = tsp.mutate(tsp.pop[j]) #突变种群中第j个体的基因
#self.best_gen = self.EO(self.best_gen) #极值优化,防止收敛局部最优
tsp.best_dist = tsp.gen_distance(self.best_gen) #记录最优值
def load_Citys(self, file='china_main_citys.csv', delm=','):
# 中国34城市经纬度
data = pd.read_csv(file, delimiter=delm, header=None).values
#china_main_citys.csv数据太大,只计算部分如:湖南省关键字的
self.citys = data[data[:, 0] == '湖南省', 4:]
self.citys_name = data[data[:, 0] == '湖南省', 2]
self.city_size = self.citys.shape[0]
def load_Citys2(self, file='china.csv', delm=';'):
# 中国34城市经纬度
data = pd.read_csv(file, delimiter=delm, header=None).values
self.citys = data[:, 1:]
self.citys_name = data[:, 0]
self.city_size = data.shape[0]
def gen_distance(self, gen):
#计算基因所代表的总旅行距离
distance = 0.0
for i in range(-1, len(self.citys) - 1):
index1, index2 = gen[i], gen[i + 1]
city1, city2 = self.citys[index1], self.citys[index2]
distance += np.sqrt((city1[0] - city2[0]) ** 2 + (city1[1] - city2[1]) ** 2)
return distance
def ct_distance(self, city1, city2):
#计算2城市之间的欧氏距离
d = np.sqrt((city1[0] - city2[0]) ** 2 + (city1[1] - city2[1]) ** 2)
return d
def draw_citys_way(self, gen):
'''
根据一条基因gen绘制一条旅行路线
:param gen:
:return:
'''
tsp = self
dw = self.dw
m = gen.shape[0]
tsp.dw.set_xybound(tsp.dw.bound_x, tsp.dw.bound_y)
for i in range(m):
if i < m - 1:
best_i = tsp.best_gen[i]
next_best_i = tsp.best_gen[i + 1]
best_icity = tsp.citys[best_i]
next_best_icity = tsp.citys[next_best_i]
dw.draw_line(best_icity, next_best_icity)
start = tsp.citys[tsp.best_gen[0]]
end = tsp.citys[tsp.best_gen[-1]]
dw.draw_line(end, start)
def draw_citys_name(self, gen, size=5):
'''
根据一条基因gen绘制对应城市名称
:param gen:
:param size: text size
:return:
'''
tsp = self
m = gen.shape[0]
tsp.dw.set_xybound(tsp.dw.bound_x, tsp.dw.bound_y)
for i in range(m):
c = gen[i]
best_icity = tsp.citys[c]
tsp.dw.draw_text(best_icity[0], best_icity[1], tsp.citys_name[c], 10)
def re_draw(self):
#重绘图;每次迭代后绘制一次,动态展示。
tsp = self
tsp.dw.draw_points(tsp.citys[:, 0], tsp.citys[:, 1])
tsp.draw_citys_name(tsp.pop[0], 8)
tsp.draw_citys_way(self.best_gen)
def main():
tsp = TSP(0.5, 0.1, 100, 500)
tsp.init()
tsp.evolution()
tsp.re_draw()
tsp.dw.plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
绘图文件:DW.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
import matplotlib.animation as animation
class Draw(object):
bound_x = []
bound_y = []
def __init__(self):
self.fig, self.ax = plt.subplots()
self.plt = plt
self.set_font()
def draw_line(self, p_from, p_to):
line1 = [(p_from[0], p_from[1]), (p_to[0], p_to[1])]
(line1_xs, line1_ys) = zip(*line1)
self.ax.add_line(Line2D(line1_xs, line1_ys, linewidth=1, color='blue'))
# def draw_arrow(self, p_from, p_to):
# if p_from.shape[0] != 2 and p_to.shape[0] != 2:
# print('error,', p_from, p_to)
# return
# p_from = list(p_from)
# p_to = list(p_to)
# self.ax.arrow(p_from[0], p_from[1], p_to[0] - p_from[0], p_to[1] - p_from[1],
# length_includes_head=True,
# head_width=(self.bound_x[1] - self.bound_x[0]) / 100,
# head_length=(self.bound_x[1] - self.bound_x[0]) / 50,
# fc='blue', ec='black')
def draw_points(self, pointx, pointy):
self.ax.plot(pointx, pointy, 'ro')
def set_xybound(self, x_bd, y_bd):
self.ax.axis([x_bd[0], x_bd[1], y_bd[0], y_bd[1]])
def draw_text(self, x, y, text, size=8):
self.ax.text(x, y, text, fontsize=size)
def set_font(self, ft_style='SimHei'):
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [ft_style] # 用来正常显示中文标签


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号